514
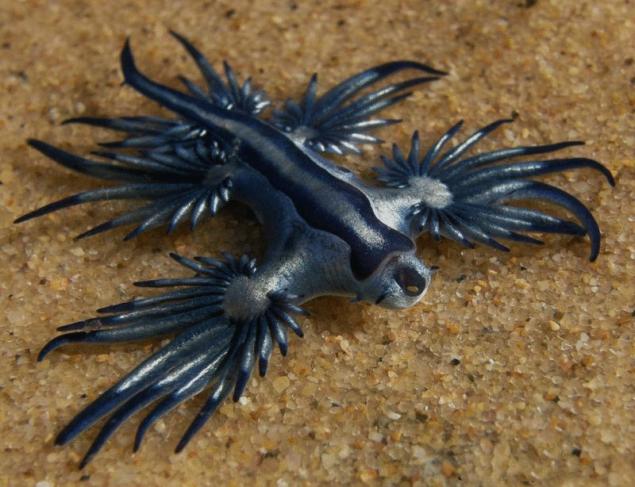
A masterpiece of nature—the blue mollusk

Glaucus Atlanticus – the common name of sea swallows, they are the same blue Glaucus, sea missiles or bullets. The blue Glaucus (Glaucus atlanticus) is a species golosemennyh, marine gastropods of the family Glaucidae. This one of a kind look. Normal size adult usually reaches up to 3 cm Molluscum is very beautiful: he is all silver-gray top and dark blue bottom. In addition, it is shaded dark blue stripes on the edges of the tentacles. Body, narrowed and flattened at the sides, and has six appendages which branch out rays and tentacles. It has no protective shell, but it is not required, such coloration serves as a warning to predators that it is poisonous.

Shellfish is really similar to the fantastic blue birds. These golosemennye slugs are widespread throughout the world's oceans, mainly in temperate and tropical waters. The regions where they live, and include the East coast of South Africa. Can meet somewhere in European waters, and on the East coast of Australia and Mozambique. This kind of shellfish is swimming upside down and kept at the surface of the water. Help him to be there special gas bags located in the stomach. Scientists are still arguing, moves whether the Central Board on its own initiative or depending on wind direction and currents.

Glaucus prefers to prey on other, larger pelagic organisms, even, especially of poisonous and dangerous to humans, such as the Portuguese ships and velella, the blue button, Agria Agria, and violet snail. Sometimes individuals become cannibals if they are given the opportunity. Due to its resistance to the poisonous nematocysts of the Portuguese ship, the mollusk completely it digests and stores the strongest poisons for your own use. The poison accumulates it in specialized sacs (cnidosacs), on the ends of tentacles, thin feathery "fingers". As Domes accumulate the poison, they can produce stronger and more deadly stings, compared to the Portuguese ships, on which they feed.
The Glaucus is a hermaphrodite, i.e. contain male and female reproductive organs, although unlike most nudibranchs, sea swallows mate with ventral sides. After mating, they lay eggs, but since they can't leave them somewhere at the bottom of, or attached to something solid, because they spend all their life attach to the surface of the water, we had to invent a way of rearing. The thread of the concatenated eggs cupola is enclosed in a thin tube of slime, and like that those drifting in the ocean until the release of larvae.
source
Source: /users/1077
How to easily update the interior – repaint furniture
Plant Chicago's vertical farm and food waste treatment