601
6 main causes of disease of fruit trees
The garden is the pride and joy of the cottager. What could be better than the moment when it comes to your tree, pluck an Apple, and habitual gesture of wiping it on his Trouser leg (or skirt), bitten with a juicy crunch, brazowski juice fruit...

But the garden is also a responsibility. Before the trees, which we give life in our garden. They, like members of the family, we must love, feed, water, protect and heal... Trees, like people, get sick. And the many reasons. Today we will look at 6 main
Cause 1: mechanical damageMechanical damage is a physical violation of the integrity of the plant. Most often it is the failure of the branches, cuts the bark, breaks the leaves. Cause them to different causes: atmospheric phenomena, animals and man himself.
The main causes of mechanical damage:

Any damage to trunks, branches, leaves, flowers and fruits become the gate through which penetrate infection and harmful microorganisms.
In the following video we will learn why and how wrong sawn off branch of a fruit tree can lead to serious diseases and the formation of the hollow
Reason 2: thermal damagethermal damage is damage that occurs as a result of low or high temperatures.
Frost Low temperatures cause damage to bark, cambium and wood of branches. With a sharp drop in temperature in early winter, when there is good snow cover, it may affect even the root system. The most difficult for fruit tree — the freezing wood of the trunk and skeletal branches that forever disturbs the relationship "root system — leaves".
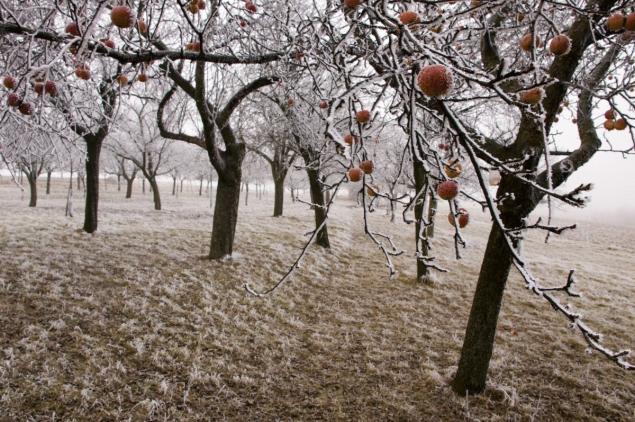

Sun+cold In the Sunny winter days, the bark heats up in the sun, which causes the awakening of the cambium and the beginning of SAP flow. And at night the temperature dropped sharply, and awakened the cells die. With cracks the bark and exposed wood. In the same way and damaged flower buds.
Spring frosts are Very common reason. An abrupt temperature drop after warm days, when fruit trees have bloomed, causing damage to flowers, ovaries and even the young leaves. At a temperature of -2...-4°C damaged buds and flowers, and lowering the temperature to -1°C causes the death of the ovaries.
Affected buds and flowers usually die and fall off, and if they continue to rise, the fruits turn out ugly and of poor quality.
Summer overheating In the southern regions during the summer months, the surface of the trunks, branches and leaves of fruit trees is heated during the day to +50, and +60 degrees. Not surprisingly, that the crust formed burns.
Reason 3: lack of or excess water is Known that the tissue of fruit crops by 70-80% water, and fruits its content is even higher. So the water is almost the most important condition of life in our garden.
The main source of water for fruit trees is soil moisture. It is known that the optimum soil moisture for garden plants 65-80 %. If this figure were reduced, and no watering, trees experience moisture deficit.
The lack of water in the summer heat leads to premature aging of leaves and the whole tree, drastically reducing the productive period of his life. For this reason, the trees fruit irregularly, go into the winter unprepared and often damaged by frost.
But excess soil moisture is also not useful garden plants. Due to waterlogged oxygen in the soil is displaced, and carbon dioxide accumulates. In the end, the root system is inhibited and may die. In addition, the plant becomes resistant to scab, mildew, kokkomikoza and other fungal diseases.
The plants need constantly moist, but nizamiyya soil, and therefore aren't suitable for them located in the lowlands areas with constant danger of flooding.
The groundwater level must not be above a certain mark (if it is above normal, this leads to waterlogging):
Reason 4: infestation Is one of the most frequent causes of diseases of the garden. Parasites enter the body of a tree or Bush through the damaged tissue or weaknesses — "stomata".
Diseases of trees cause, basically, 3 groups of parasites:
Pathogens slow the growth and development of the tree, oppress the vital functions, and disturb the work of its organs, inhibit the metabolism and the processes of formation of organic substances. The result is greatly reduced productivity.
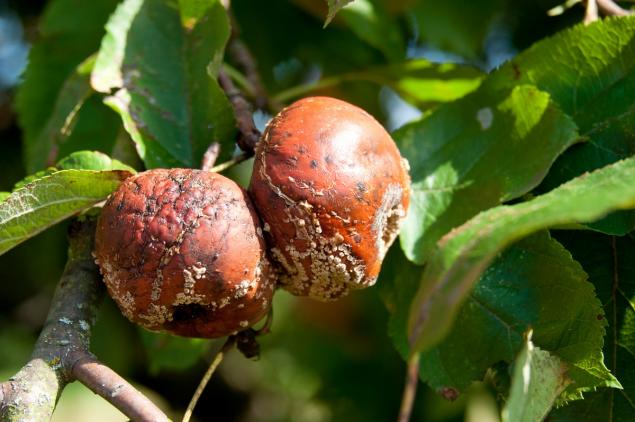

Some of the disease quickly lead to plant death. Diseases that are caused by fungi, bacteria and viruses:
Damage from pests is noticeable not only in the year in which happened their attack. As a rule, the crop of the subsequent year for the weakened tree is also under threat. Pests significantly reduce the winter hardiness of fruit trees and berry plants, their resistance to various diseases.
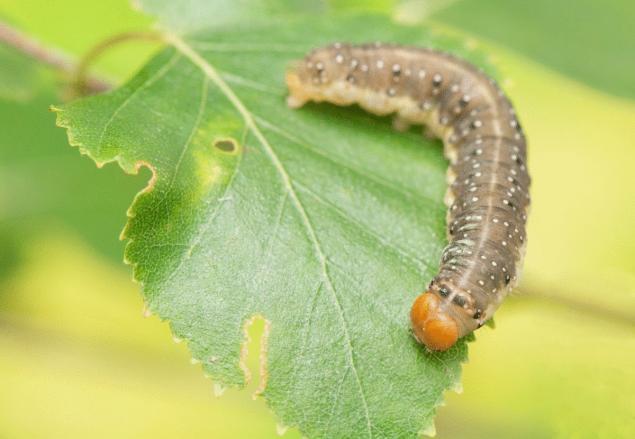

Pests of fruit trees:
Deficiency of minerals May be the result
1. The plant is delayed in growth
2. Leaves are pale green and develop smaller than the other trees.
The lack of phosphorus
1. Have seed the leaves become narrow
2. The petioles and veins on the lower side noticeable blush
3. Young shoots have red-brown color
4. The leaves of the berry bushes are shrinking, become reddish-purple
A lack of potassium
1.Noticeable mild chlorosis between the leaf veins
2. Pome at first pale leaves, then their edges formed a yellow-brown band, similar to a burn
3. Acute potassium deficiency in Apple leaves become brown, and pear — black
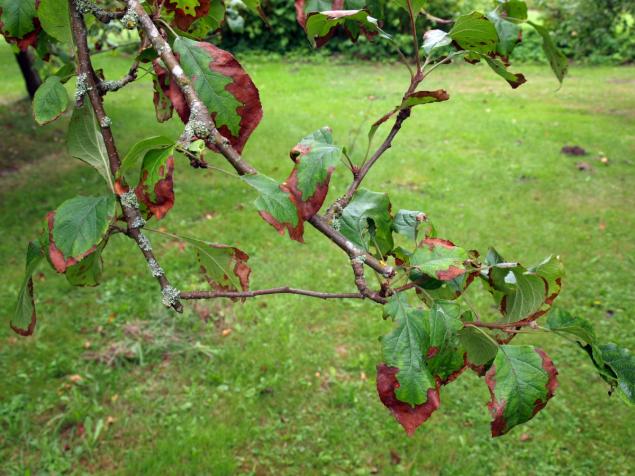

Trace elements from fruit trees often lack of boron, zinc, copper and manganese.
Boron deficiency
1. The worse tie Apple fruit tissue during growth probkovejut
2. Leaves develop small, thickened
3. Shoots are often bushes.
Copper deficiency
1. The leaves develop brown spots
2. The leaves at the tips of shoots turn brown at the edges, deformed and often fall off
Zinc deficiency
1. Small, narrow, hard leaves from the rosettes at the tips of annual shoots
The lack of manganese
1. The leaves become variegated
2. Between the veins is observed chlorosis
The excess of mineral fertilizers Cause excess minerals is covered generally in "the human factor": the problem arises in making excessively high doses of nutrients.
The surplus of nitrogen
1. The growth of the highly active branches, leaves large, dark green, with flowering and fruiting is weak and fruits fall early
2. Deteriorating the quality of the fruit: they significantly reduced the content of dry substances and sugars, they are poorly stored
3. Trees more susceptible to disease and less resistant to parasites defeat
4. May develop chlorosis (or reinforced if it already exists)
5. The young trees slows the growth of shoots
An excess of phosphorus
Iron and zinc in the soil pass into the plants indigestible to the state. The result:
1. Triggered chlorosis (iron deficiency)
2. Enhanced Apple rosette (zinc deficiency).
Caring for your garden is difficult, but very interesting work. Vacationers need to be not just an agronomist and a good host, but also patient and caring doctor Doolittle for their Pets. The time taken preventive measures and a love of Nature will definitely help to grow a healthy, pleasing to the eye and soul of the garden.published by P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: www.7dach.ru

But the garden is also a responsibility. Before the trees, which we give life in our garden. They, like members of the family, we must love, feed, water, protect and heal... Trees, like people, get sick. And the many reasons. Today we will look at 6 main
Cause 1: mechanical damageMechanical damage is a physical violation of the integrity of the plant. Most often it is the failure of the branches, cuts the bark, breaks the leaves. Cause them to different causes: atmospheric phenomena, animals and man himself.
The main causes of mechanical damage:
- Heavy snowfall and ice, that break the branches
- Hares and rodents that gnaw bark
- Pests-insects that damage the leaves, flowers and fruits
- Strong wind on the leaves (due to contact with branches) appear fading
- Hail, which causes laceration of the leaves and leaves indentations on the fruit
- Sloppy manual treatment, in which damaged trunks and branches
- Negligence at harvest when damaged bark and broken branches

Any damage to trunks, branches, leaves, flowers and fruits become the gate through which penetrate infection and harmful microorganisms.
In the following video we will learn why and how wrong sawn off branch of a fruit tree can lead to serious diseases and the formation of the hollow
Reason 2: thermal damagethermal damage is damage that occurs as a result of low or high temperatures.
Frost Low temperatures cause damage to bark, cambium and wood of branches. With a sharp drop in temperature in early winter, when there is good snow cover, it may affect even the root system. The most difficult for fruit tree — the freezing wood of the trunk and skeletal branches that forever disturbs the relationship "root system — leaves".

Sun+cold In the Sunny winter days, the bark heats up in the sun, which causes the awakening of the cambium and the beginning of SAP flow. And at night the temperature dropped sharply, and awakened the cells die. With cracks the bark and exposed wood. In the same way and damaged flower buds.
Spring frosts are Very common reason. An abrupt temperature drop after warm days, when fruit trees have bloomed, causing damage to flowers, ovaries and even the young leaves. At a temperature of -2...-4°C damaged buds and flowers, and lowering the temperature to -1°C causes the death of the ovaries.
Affected buds and flowers usually die and fall off, and if they continue to rise, the fruits turn out ugly and of poor quality.
Summer overheating In the southern regions during the summer months, the surface of the trunks, branches and leaves of fruit trees is heated during the day to +50, and +60 degrees. Not surprisingly, that the crust formed burns.
Reason 3: lack of or excess water is Known that the tissue of fruit crops by 70-80% water, and fruits its content is even higher. So the water is almost the most important condition of life in our garden.
The main source of water for fruit trees is soil moisture. It is known that the optimum soil moisture for garden plants 65-80 %. If this figure were reduced, and no watering, trees experience moisture deficit.
The lack of water in the summer heat leads to premature aging of leaves and the whole tree, drastically reducing the productive period of his life. For this reason, the trees fruit irregularly, go into the winter unprepared and often damaged by frost.
But excess soil moisture is also not useful garden plants. Due to waterlogged oxygen in the soil is displaced, and carbon dioxide accumulates. In the end, the root system is inhibited and may die. In addition, the plant becomes resistant to scab, mildew, kokkomikoza and other fungal diseases.
The plants need constantly moist, but nizamiyya soil, and therefore aren't suitable for them located in the lowlands areas with constant danger of flooding.
The groundwater level must not be above a certain mark (if it is above normal, this leads to waterlogging):
- for Apple — 150 cm
- for pear — 180-200 cm
- for the cherries — 200-210 cm
- for plum — 100-120 cm
- for berry bushes — 100cm
Reason 4: infestation Is one of the most frequent causes of diseases of the garden. Parasites enter the body of a tree or Bush through the damaged tissue or weaknesses — "stomata".
Diseases of trees cause, basically, 3 groups of parasites:
- Phytopathogenic fungi
- Bacteria
- Viruses
Pathogens slow the growth and development of the tree, oppress the vital functions, and disturb the work of its organs, inhibit the metabolism and the processes of formation of organic substances. The result is greatly reduced productivity.

Some of the disease quickly lead to plant death. Diseases that are caused by fungi, bacteria and viruses:
- Necrosis (rot)
- Hyperplasia (cancer)
- Wilt (vascular mycosis)
- Powdery mildew
- Rust
- Anthracnose
- Mummification
- Scab
- Spotting
- Infectious strain
- Infectious chlorosis
- Mosaic
Damage from pests is noticeable not only in the year in which happened their attack. As a rule, the crop of the subsequent year for the weakened tree is also under threat. Pests significantly reduce the winter hardiness of fruit trees and berry plants, their resistance to various diseases.

Pests of fruit trees:
- Mites
- Aphids
- Baryshnikova, Codling and fruit moths
- The aporia Crataegi
- Apple pollen beetle
- The Oriental fruit moth
- Pear trubkovich
- Zabolonnye
- West unpaired bark beetle
- Goose
- Ringed, oakleaf and Gypsy moth
- Pokorova leaf rollers
Deficiency of minerals May be the result
- abnormal movements of nutrients in plants due to damage to the tissues of the trunk and branches
- limited absorption of nutrients due to the genetic characteristics of plants
- lack or, on the contrary, excess water in the soil
- partial freezing of the root system
- damage to the root system of the tree rodents
- too low or too high temperature, as soil and air
- the lack of necessary nutrient
- low or high pH
1. The plant is delayed in growth
2. Leaves are pale green and develop smaller than the other trees.
The lack of phosphorus
1. Have seed the leaves become narrow
2. The petioles and veins on the lower side noticeable blush
3. Young shoots have red-brown color
4. The leaves of the berry bushes are shrinking, become reddish-purple
A lack of potassium
1.Noticeable mild chlorosis between the leaf veins
2. Pome at first pale leaves, then their edges formed a yellow-brown band, similar to a burn
3. Acute potassium deficiency in Apple leaves become brown, and pear — black

Trace elements from fruit trees often lack of boron, zinc, copper and manganese.
Boron deficiency
1. The worse tie Apple fruit tissue during growth probkovejut
2. Leaves develop small, thickened
3. Shoots are often bushes.
Copper deficiency
1. The leaves develop brown spots
2. The leaves at the tips of shoots turn brown at the edges, deformed and often fall off
Zinc deficiency
1. Small, narrow, hard leaves from the rosettes at the tips of annual shoots
The lack of manganese
1. The leaves become variegated
2. Between the veins is observed chlorosis
The excess of mineral fertilizers Cause excess minerals is covered generally in "the human factor": the problem arises in making excessively high doses of nutrients.
The surplus of nitrogen
1. The growth of the highly active branches, leaves large, dark green, with flowering and fruiting is weak and fruits fall early
2. Deteriorating the quality of the fruit: they significantly reduced the content of dry substances and sugars, they are poorly stored
3. Trees more susceptible to disease and less resistant to parasites defeat
4. May develop chlorosis (or reinforced if it already exists)
5. The young trees slows the growth of shoots
An excess of phosphorus
Iron and zinc in the soil pass into the plants indigestible to the state. The result:
1. Triggered chlorosis (iron deficiency)
2. Enhanced Apple rosette (zinc deficiency).
Caring for your garden is difficult, but very interesting work. Vacationers need to be not just an agronomist and a good host, but also patient and caring doctor Doolittle for their Pets. The time taken preventive measures and a love of Nature will definitely help to grow a healthy, pleasing to the eye and soul of the garden.published by P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: www.7dach.ru