633
6 facts about holography, which you might not know
If a two-dimensional picture is worth a thousand words, then three-dimensional is worth a million. Using holography it is possible to reconstruct the three-dimensional image using a hologram, and this process has nothing to do with the technology of traditional displays. Despite the fact that holography was invented more than 70 years ago, it remains the best candidate for the true 3D displays.
Before you six important facts about holography, you might not know.
Celebrity — not a hologram
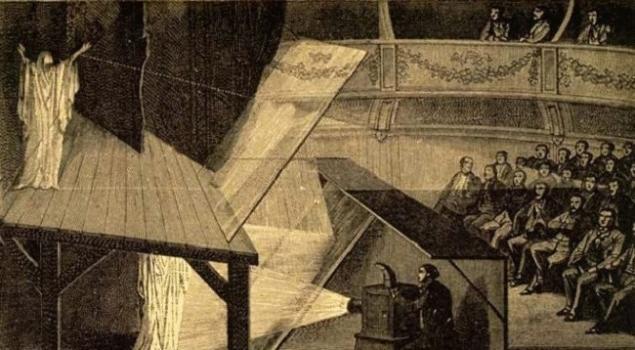
When you see Tupac, Michael Jackson, or anyone else, a three-dimensional image which appears at a concert or somewhere else, it's not a hologram. It's a trick, and at its core, the hologram does not have anything to do with him. It was first demonstrated in 1800 years John pepper to surprise unsuspecting viewers with the Ghost, who appeared alongside the actor's scene. In reality it was a clever illusion, because between the stage and the audience was placed the glass at an angle. The stage used to reflect light from the actor to the audience, but so that she could see the stage. Since the glass is effectively transparent, the people felt that the scene appeared a Ghost. Most of the "holograms" that show on TV, just a variation of the trick of pepper's Ghost.
Only the hologram is a hologram: it is easily distinguished from other

Let's say you just took a picture. You took the camera, pointed, clicked and took some information. From the point of view of the optics you maintain a certain amplitude of the light field, time-averaged emanating from the stage using some form of sensor. The result is a large amount of information in this field of light was thrown away. You just filmed a small part of the information that managed to catch. Hologram (invented in 1847 by Dennis Gabor) holography, in its basic sense means the entry, and then reconstruction of the entire light field, which hit the lens, and so that the observer could not distinguish it from the original scene, since the hologram "gives" the observer all initial information.
Of course, you ask: how do we do that? Well, if you take the object you want to display, and illuminate it with a laser and interferonbeta this scattered light with another laser, recording of this pattern will create a hologram. It captures the amplitude, phase, and wavelength information of the object. Now, if we look at the pattern under a microscope, we would see interference fringes that are interested. However, if we light from one source, the light is scattered from all bands simultaneously and interferes with itself to reconstruct the original light field of the object.
The beauty of this method is that it is the only way to truly reconstruct the three-dimensional information and to obtain true 3D displays. However, this technique, invented almost 70 years ago, allows you to create only static holograms. Why can't we dynamically change the holograms and effectively to create a holographic display?
Holographic displays in homes will not be soon
The problem of creating three-dimensional holographic displays that the amount of information in a conventional hologram is enormous; the light contains a lot of information. For example, you want a million-trillion pixels to collect three-dimensional holographic display, and at normal level, 30 frames per second, for example, the amount of data is enormous. In addition, we need technology that can record (in real time) all comprehensive information of the light field, the technologies that will be able to transfer these huge amounts of data, and a computer that will all of this handle. Given that we just enter into the era of 4K TVs (which can be of the order of 10 million pixels), the era of holography will come soon.
A hologram can be created and displayed using computers

As we have seen, we are dealing with a large volume of information. Modern methods of image dynamic holograms are called spatial light modulators (SLM). It's a little similar to the TV device display holograms using reflection of laser light.
As we expect a hologram? Ideally, we could record all the information about the light field of the scene, but yet we have no commercial technology that can. We could do a full simulation of electromagnetic waves simulated scene to find that fading light in a field looks like a point in space, and then write this information to form a hologram. However, the present technology is a computing nightmare. Perhaps the best way will be deeply mathematical approach to this phenomenon.
In fact, we do the approximation. It turns out that when light is diffracted, if you are far enough away from point of diffraction pattern that you see is associated with the Fourier transform of the mathematical representation of diffraction. This means that, since our computers can do the Fourier transform rather quickly, we can quickly generate holograms on the fly. Then, displayed on the SLM, we can use the diffraction of light for the formation of arbitrary images at will. This area is called the generated or computer holography. And now that computers are becoming faster, this field of research is becoming increasingly popular.
The best holographic television was established ten years ago and cost a fortune
Qinetiq has developed a prototype holographic display based on spatial light modulation, 12 years ago. She used an active system with two different SLM to ensure that the full depth of the signal, necessary for the production of three-dimensional images. This undertaking was extremely expensive and was closed almost immediately, but the highest quality holographic display at least has been demonstrated.
Holography is necessary not only for television
Although we believe that holography more interesting possibilities for 3D displays, in General, it has possibility of application in many areas. Here are some examples:
- Electronic survey: observing the phase shift of the interference of electrons when they pass through thin film materials, it is possible to determine the composition of materials.
- Data storage: conventional optical discs store information on the surface. With the help of holography to record information in the volume of material at different angles — hence, you can store more information than traditional methods allow data storage.
- Holographic optical tweezers: optical tweezers use the force of light to move small particles (mainly in biology) and create the optical trap. Using generated on computers holograms, scientists can manipulate large arrays of particles at small distances.
- Security: holograms are already used on banknotes and credit cards. Used mostly due to the fact that the technology to create them is quite complex.published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: hi-news.ru