Technology development in the new decade: from the cloud to the disappearance of computers and the heyday of robots

Summary: make short-term predictions about investing in technology is relatively simple - to try to understand how to develop the IT industry in the future ten years is much more difficult. I>
For the industry, which, at least at first glance, control logic and cold calculation, the technology industry is surprisingly easy to hype and enjoys regular «новинками, that will change our future ».
Perhaps this happens because, unlike, say, the scope of sales or HR, where innovation is determined by the new management strategies, technological investments are "the product". Buying a new hardware or software often entails the potential for "subversive" leap forward to achieve higher productivity, or any other critical business metrics. Technology providers, thus rightly interested in the best possible active promotion of its products: the level of marketing costs and attract users of some fast-growing technology firms can make many consumer brands green with envy.
As a result, CIO lure weight constantly changing set of "buzz words» ( cloud services , wearable gadgets, internet of things - known for their representatives) that CIO has to sift to find as a result of the concepts that will be really useful to their organizations and will be comparable to the company's budget, acceptable and adequate time to the organization's level of risk. Short-term solutions in this regard may be relatively clear, but the farther you look into the future, the more difficult it becomes to predict who will be the winner of the competition.
Technological innovation in the long term from one year to three years h4> Despite the possible fluctuations, the technology that many CIO planning to implement in the near future, are relatively risk-free - they are quite safe. According to a study TechRepublic, the main priorities for investment CIO in the coming years will be issues of improving safety, mobility, the use of big data and cloud services for business. Fashion trends such as 3D-printing or portable gadgets will be at the end of the list.
Other исследование from the Deloitte confirms these data: many technologies that CIO is now run as a pilot project and plan to implement in the near future, there are already quite a long time - it is, for example, business analytics, mobile applications, social media and tools to work with big data. Augmented reality and gamification techniques are considered a lower priority.
This estimate reflects the preferences of the majority of CIO, which tend to focus on reliability as opposed to "disruptive" innovations: a study TechRepublic states that "protection / network security and data" for technical managers, who do not want to risk once again turn out to be more important than " changing business requirements ».
Another important factor in this issue - money. Few CIO have a big budget to spend on potentially unprofitable innovative projects, even if they want them to (and many will surely remember the excesses of the dot-com era, and really do not want to repeat past mistakes).
According to a study Deloitte, technological innovation is allocated less than 10% of the budget (CIO, spending more in this direction, work in smaller, less conservative companies). There is another reason why the CIO is increasingly no longer control the budget allocated to innovation - this task перенаправляется other business units (for example, the marketing department), which is believed to have a better understanding of the entrepreneurial approach to technology.

CIO tend to blame his superiors in the conservative attitude to risk - according to them, this is the biggest limitation that does not allow them to make more risky IT investments with the aim of higher growth and development of innovations. Although the CIO say they are willing to assume the risks of IT investments, such an attitude does not correspond to the current portfolio of IT initiatives of most companies.
Another problem is that it is very difficult to estimate the return on investment in certain technologies. Managers are always measured the benefits of such investments, using the standard formula ROI, which includes only the most obvious costs: for example, the amount of payments based on the number of employees or the cost of new equipment. But the definition of return on investment in a project related to social media and the Internet of Things - a much more difficult task.
Investing in technology in the medium term h4> If the CIO investment plans in the short term remain conservative and tied to a limited budget, it is necessary to look a little further to understand where could come the new technological revolution.
One of the resources that can be used - perhaps the most famous set of forecasts about the future of IT: maturity cycle technologies from Gartner, which reflects an attempt to assess the potential of new technologies, taking into account the expectations of society.
Schedule divides technology not only about how great their acceptance by the majority, but also in terms of expectations from them - so it shows what analysts call a fundamental truth: that we can not help but be fascinated by new technologies on the one hand, and on the other - rather quickly loses interest in him when he realized that to successfully implement them is extremely difficult. During the peak of excessive expectations inevitably follows Getting rid of illusions, then the technology finally included in the zone to overcome the disadvantages and fall on the plateau of productivity.
"This pattern of behavior we see in virtually all technology - a movement up and down the expectations to get rid of illusions and the resulting increased productivity" - says Jack Finn, vice president and analyst at Gartner, who worked on the project since the first cycle of mature technologies which was first published 20 years ago. This cycle is considered an example of human response to any new product.
"It's not just about the technology itself - as we respond to every innovation. This approach is retained in relation to the new trends in management and work on projects. People have told me that this is true in your personal life - the initial wave of enthusiasm, knowing that everything is much more complicated than it seemed, and the resulting understanding of what it takes to everything eventually worked as it should ».
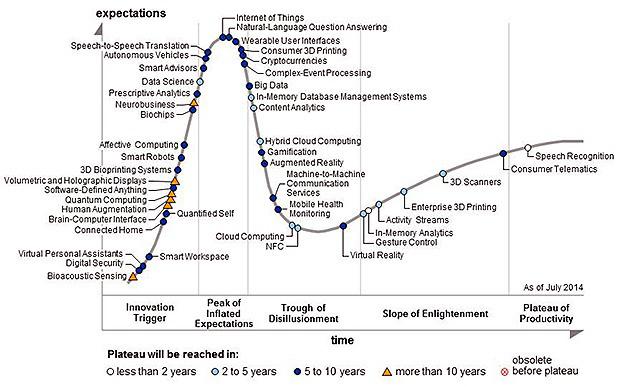
The cycle of mature technologies from Gartner for 2014 i>
According to Gartner for 2014, the direction of which in the next two years will reach plateau production (where they are widely applicable) - it is, in particular, speech recognition technology and in-memory computing.
Within the next 5-10 years, forecasts include virtual reality, Cryptocurrency and wearable user interfaces.
The hardest thing to understand when the technology will be successfully used as a mass product, and that is why so CIO need perfect timing to invest. Some of the technologies Gartner marked on their first maturity curve in 1995 - such as speech recognition and virtual reality - are still on the curve 2014-year, and did not become mainstream.
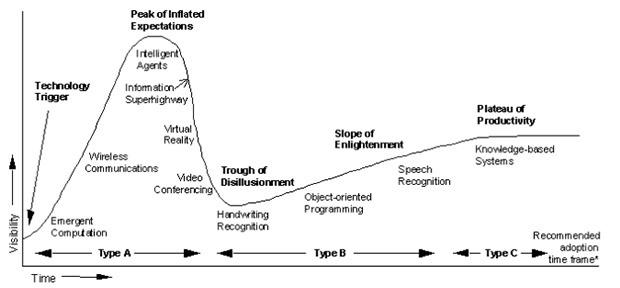
The cycle of mature technologies from Gartner for 1995 i>
These types of user interface technologies needed time to "grow up," says Finn. For example, voice recognition originally appeared in a highly structured applications for call centers, but in its latest incarnation - Siri - the technology has advanced significantly, "although it has not yet become universally applicable interface type" - she adds.
Almost all technologies go through these "roller coaster" because our attitude towards new concepts does not change, says Finn. "It's an innate psychological reaction - we excited when we see something new. What attracts us, partly due to the structure of our brain: we are interested in the first part of the cycle in which new technologies seem curious and fascinating; but with the onset of the second part of the hard work begins, which we like a lot less ».
But despite the fact that the break out of this cycle is impossible, CIO can use the concept like this to manage their own aspirations: if the investment company's strategy assumes that the firm consistently starts with new technologies at the peak of expectations from them (remember a few years ago Each CEO had a blog?), maybe it's time to revise the strategy, even if the pressure on the CIO colleagues complicates this process.
Finn: "This pressure - the feeling that if you do not, you get nothing - really exists. Rate at which point a new technology adds value to your business, and if this does not happen, then it is normal to enter the late majority and allow others to fill the cones, if you do this direction is not particularly critical ». Blockquote> Going further, it is worth noted that technology, which, according to Gartner, will become mainstream, not earlier than 10 years are more likely to science fiction: it is, for example, holographic displays, quantum computing, and human augmetika (mechanical body modification). Analysis of this curve - an entertaining process of learning technologies of the near future, from the relatively well-known to absolutely exotic. "Employers need to weigh the" pros and cons "augmetiki compared with growing opportunities working robots, including because the use of robots is without prejudice to the ethical and legal aspects of the issue, unlike augmetiki" - said Gartner.
Plenty of room for futurists h4> Beyond the 10-year horizon, you find yourself in an area in which work mainly futurists who study the development of technology.
Steve Brown, a futurist at Intel, said that within 10 years, the future of computing will be determined by three mega-trend. "They are very simple - it is decreasing, increasing and naturalness," - he said.
"Reduction" - a consequence of Moore's Law, this trend will determine the development of small devices with low power consumption and significantly increase the likelihood of the spread of portable gadgets and the Internet of Things. "Increase" refers to the continued growth of computing power, and "naturalness" - a condition in which the objects of everyday life are endowed with some computing power.
"Calculations were our final point: [before] you had to go somewhere, to implement them - for example, in a room with a huge humming computers that you had to wait - to get there, you had to be lucky. And then came the era in which the calculation is made possible to produce on the fly ", - says Brown.
«In the next era will be integrated in the calculation of the world around us - as soon as you can to achieve it, you will eventually do all the things around you able to perform calculations - you can all turn to the computer. And once that happens, will be very interesting things "- continues to Brown. Blockquote> At this point, a new computing power will cause a number of problems for the management of the business, said Brown. CIO and complexity for enterprise-architects will consist in the fact that by making everything capable of computing, they need to address the question of how to use it. "In the future we will be faced with the philosophical questions that you should answer before deploying a new technology," - says Brown.

He foresees the emergence of ubiquitous computing power of the world in which robots will be able to observe and understand all the processes around.
"Stand-alone machines изменят all », - he said. "Enterprises face difficulties when people have to work side by side with the machines - both physical machines and algorithms. Businesses will not be easy to find the most efficient solution of a problem, which will consist of works carried out, and the process that one way or another can be optimized through the use of algorithms ».
Accelerated pace of technological development: where the decisions we took decades, now processes occur faster and faster, says Brown. And all this means that we need to make more informed decisions about how to use new technologies, and have to deal with ever more complex issues related to information security.
"If we use this or that technology will improve if it ourselves? We all have to decide in advance what to use to get better. At the enterprise level, we need to define what we achieve and how we want to work ».
It's not just about the programs and the "iron» h4> For many organizations, an obstacle to this beautiful future is your own staff and your company's ways of working. Determine where to invest, can be much easier than persuading staff and the entire organization to change the usual format of activity.
"We need to define the essence of the relationship between people and technology, because now the vast majority of people perceive technology is incorrect", - says Dave Coplin, Head of Forecasting Microsoft (he says that it is quite ironic name for his position).
Koplin observes that many of us tend to use new technologies to carry out the tasks usual way, as they have been made over the years, while the essence of the new technology is to force us to fundamentally change the approach to the tasks. A classic example - the concept of productivity: "We had to reconsider its attitude towards productivity. Unfortunately, many believe that productivity - this process: the better I perform the process, so I'm more productive. This shifts the focus of our attention, because in reality productivity related solely to the increase in performance. " Three-quarters of employees believe that a productive day at the office is to review and respond to all the accumulated letters, he said.
Develop a more literate relationship with technology is necessary because of the major changes coming, says Coplin: "What happens when technology goes by the wayside, what happens when every surface it is possible to derive contextual information based on what's going on and that who looks at her? This is the world to which we are moving - a world where data naked many ethical questions. If we do not prepare people for these changes, we will never be able to carry out most of them ».
Nicolas Millyar, futurologist from giant telecom industry, the company BT, echoed these ideas, stating that the CIO will have to take into account not only technological change, but also how they affect people: extension of seniority will require the creation of technologies that fit and the young staff, and people over 70. This entails rethinking the concept of workplace employee "Openspeys without partitions can distract employees from work," - he says - "But is it possible to generate innovations in gray cubbyhole? Employees who use tablets, may prefer to work without using the traditional tables, and to those who will use the devices that respond to gestures, you may need more space. Even the manager's role may change - it will be less about giving orders and monitoring their implementation, and to a greater extent will be similar to the duties of "party host": manager will look for employees with the most appropriate combination of skills to perform a specific job ».
In the longer term fundamentally change not only the technology itself: employees and managers will also have to create a new way of thinking.
Source: habrahabr.ru/company/1cloud/blog/244801/