1026
15 incredible cloud formations (20 photos)
Steep celestial phenomena.
1. lenticular (lens-shaped) clouds
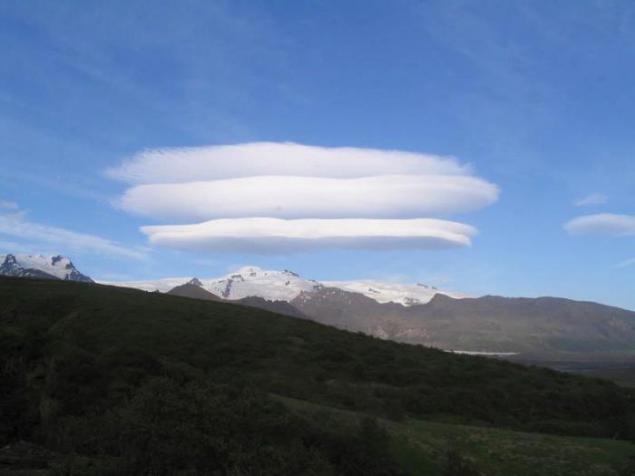

Lenticular (lens-shaped) clouds - a term that refers to a rare natural phenomenon. Lenticular clouds are formed on the crests of waves or air between two layers of air. A characteristic feature of these clouds is that they do not move, no matter how strong the wind. The flow of air above the surface zipping flows around obstacles, and thus forms an air wave. Clouds are usually stuck in the lee of mountain ranges and ridges of the individual peaks at a height of two to fifteen kilometers.
2. The wave flows is a continuous process of condensation of water vapor when the height of the dew point and evaporation during the downward movement of air. Therefore, lenticular clouds do not change their position in space, and are in the sky, like glued.
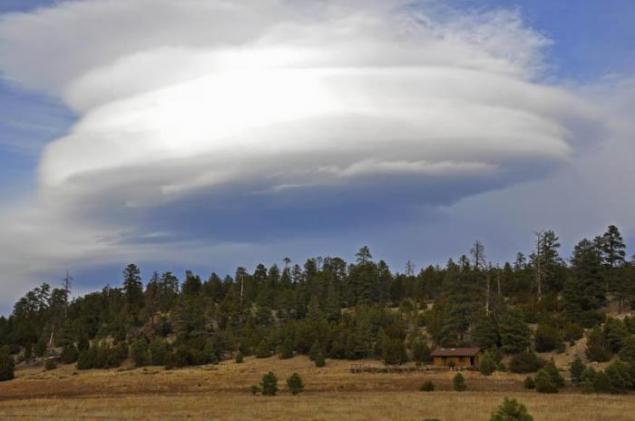

The emergence of lenticular clouds indicates that the atmosphere - strong horizontal currents of air, forming waves over the mountain barriers that the air is sufficiently high moisture content. It is usually associated with the approach of the front or rear with an energetic transfer of air from remote areas.
3. Clouds Asperatus
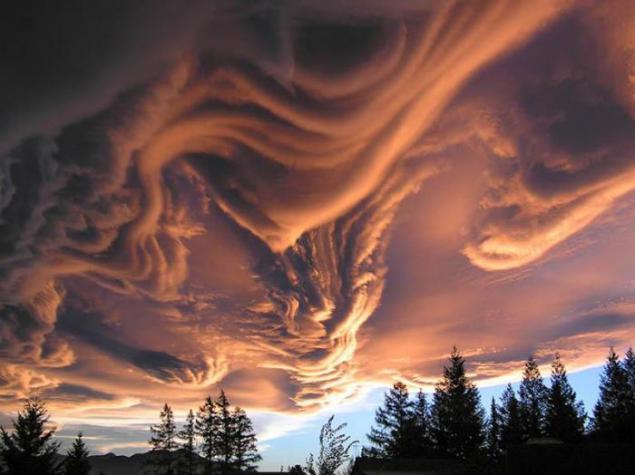

Since 1953, meteorologists say that appears a new type of cloud. These clouds look like whether on a stormy sea, whether on the earth's surface. They are dark, bizarre "dented". Of these, stick swirling "horns." View - frightening, sinister. Pictures of clouds coming from around the world.
4. "Judging by the color, the structure contains a lot of moisture, - says Professor Paul Hardaker, executive director of the British Royal Meteorological Society. - We need a lot of energy and heat to form such a cloud. "Some associate the appearance of clouds Asperatus alleged apocalyptic events of 2012.
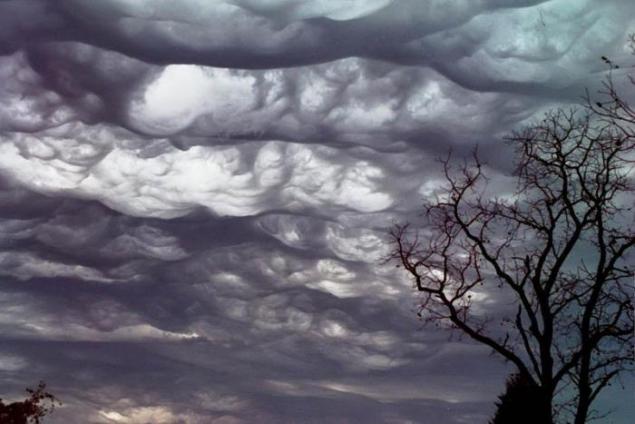

5. Silver (night, mesospheric) clouds
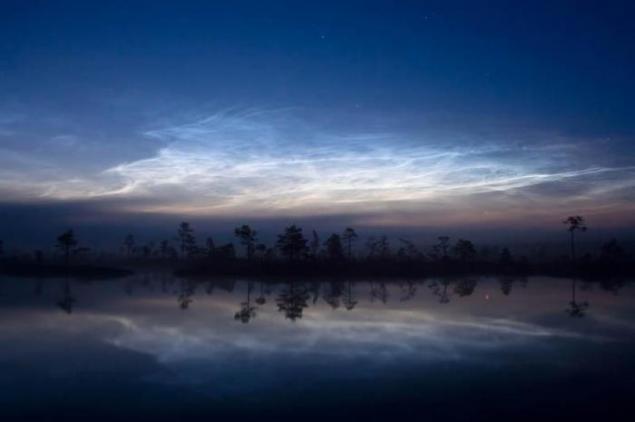

Noctilucent clouds - a rare atmospheric phenomenon. Such clouds are visible in the twilight. These are the highest clouds in the Earth's atmosphere; formed in the mesosphere at an altitude of about 85 km, and are visible only when illuminated by the sun over the horizon, while the lower layers of the atmosphere are in the Earth's shadow; they are not visible during the day. Moreover, their optical density is so insignificant that they are often lurking through the stars.
6. Clouds with a hole or dyrokolnoe cloud
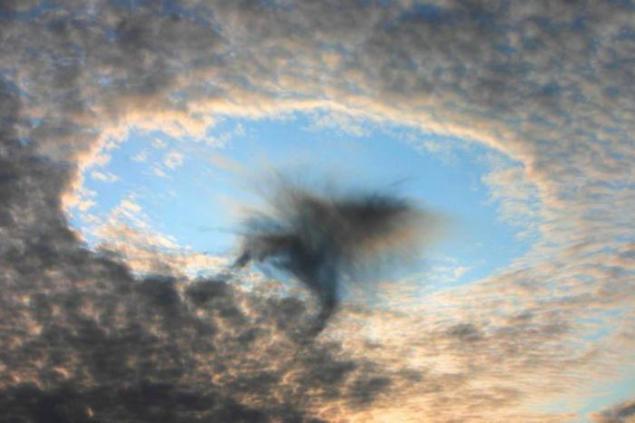

These unusual clouds similar to the "gates to paradise", amazing and strange hole in the sky. The most common hypothesis argues that the hole in the clouds caused by falling ice crystals. The ice crystals may form in the higher clouds or exhaust overflying aircraft. If the air has a suitable temperature and humidity, the falling crystals will absorb water from the air and grow. In order for this to happen, the water must be so cold that freezing it needs only a suitable surface. The loss of moisture in the air increases the rate of evaporation of water droplets in the cloud, and they are scattered, forming a hole. Become heavier ice crystals continue to fall and form a sparse, ragged, like clouds of rain, which can be seen inside and under the hole. Water and ice in these sediments evaporates before reaching the ground.
7. Vymyaobraznye or tubular cloud
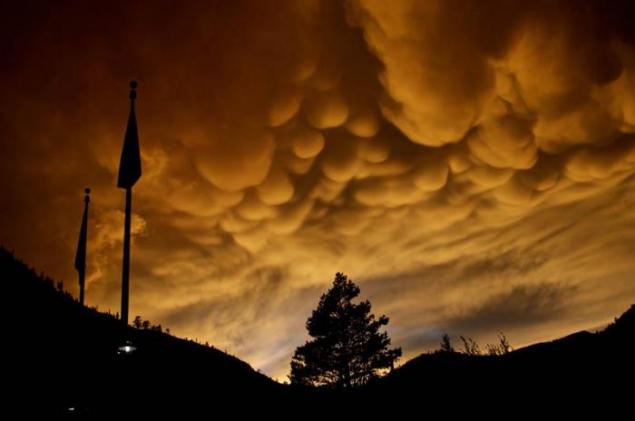

Rare, mainly in the tropics and are associated with the formation of tropical cyclones. The cells typically have a size of about half a kilometer, all chaschё sharply delineated, but there are also with soft edges. Their color is usually gray-blue, as in the main cloud, but because of the direct rays of the sun hit or illumination from other clouds may appear golden or reddish. In meteorology "vymyaobraznye" clouds are called Mammatus (or Mammatocumulus), then there are a type of cumulus (Cumulus) clouds, with a honeycomb structure and is usually located under the "parent" a cluster of cumulus or cumulonimbus clouds.
8. from the elements. However, the low altitude of the Sun above the horizon (eg at sunset) mammatusy can acquire blue-gray, gray-pink, gold, and even reddish color. Mammatusy always associated with lightning storms and, therefore, with cumulonimbus clouds.
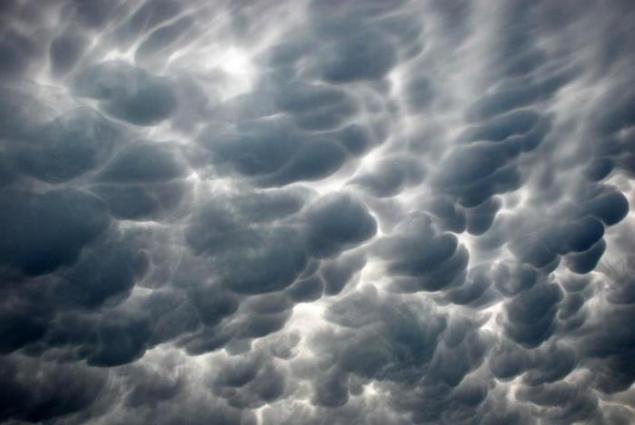

However, these clouds can defend lightning focus at a distance of up to several tens of kilometers. Mammatus saved in the sky from several minutes to several hours, gradually disappearing with the dying lightning storm. Persistence Mammatus depends on the size of droplets (or ice crystals), circulating within the cloud band, because the larger the size of droplets or ice crystals, the more energy must be expended on their evaporation. Consisting of fine droplets or ice crystals mammatusy seen in the sky a few minutes and quickly disappear.
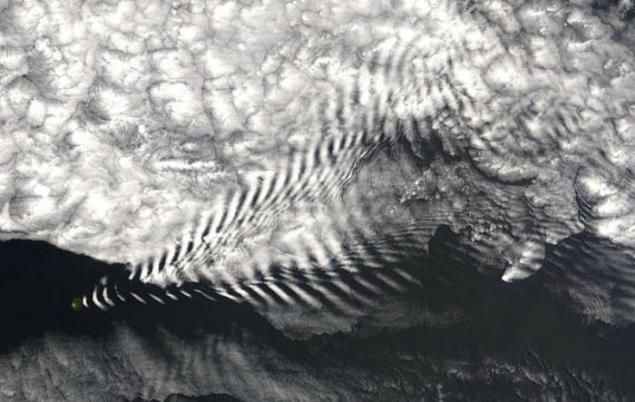
9. Wavy clouds

10. This - clouds in the occurrence of which involve wave processes in the atmosphere, as opposed to stratiform clouds associated with an upward sliding, and cumuliform associated with convection.

11. Iridescent Cloud
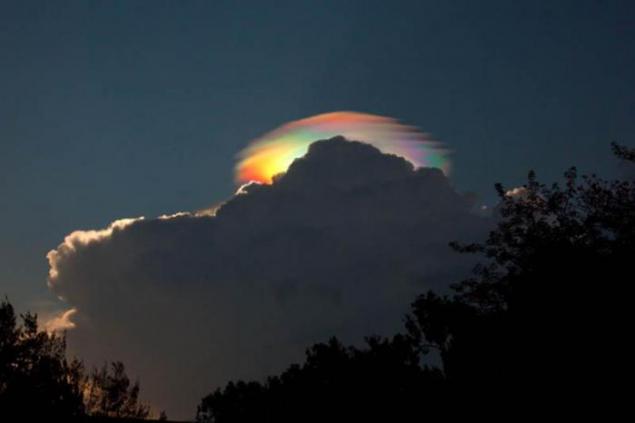

The so-called iridescent clouds - a relatively rare phenomenon. These clouds can be painted in all colors of the spectrum. They consist of small water droplets of almost identical size. Iridescent clouds appear when the Sun occupies a certain position in the sky and thus almost completely hidden behind a dense clouds. As a result, nearly coherent diffraction sunlight thin clouds are painted in different colors, since the light beams of different wavelengths are deflected in different ways. Therefore, light of different wavelengths arrives to the observer from several different directions. It often happens that the clouds, first painted in rainbow colors, become too dense and heterogeneous, also removed from the sun at a great distance.
12. Shkvalovy gate
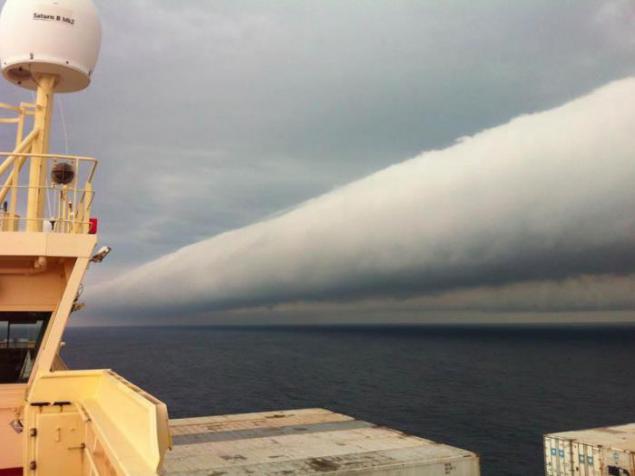

Formed in wet conditions as a consequence of the interaction of air flows of different temperatures.
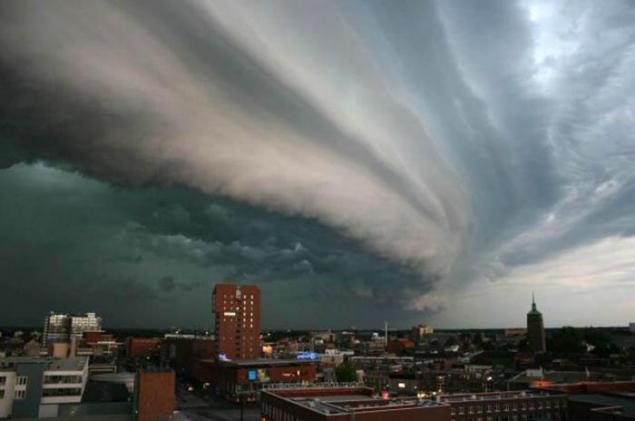
13. Rolling or gross clouds

They are usually formed during thunderstorms and before advancing cold front. It looks like a dark cloud bands, or projections of "shelves" under "shelter" storm clouds. The lower edges ragged, sometimes like a bud boiling. Beneath them is almost always observed squall winds, just behind such a shaft - typically a rain. Nothing good comes from them do not wait. In the deserts of such shafts bring dust storms.

Pyrocumulus cloud or pirokumulyus
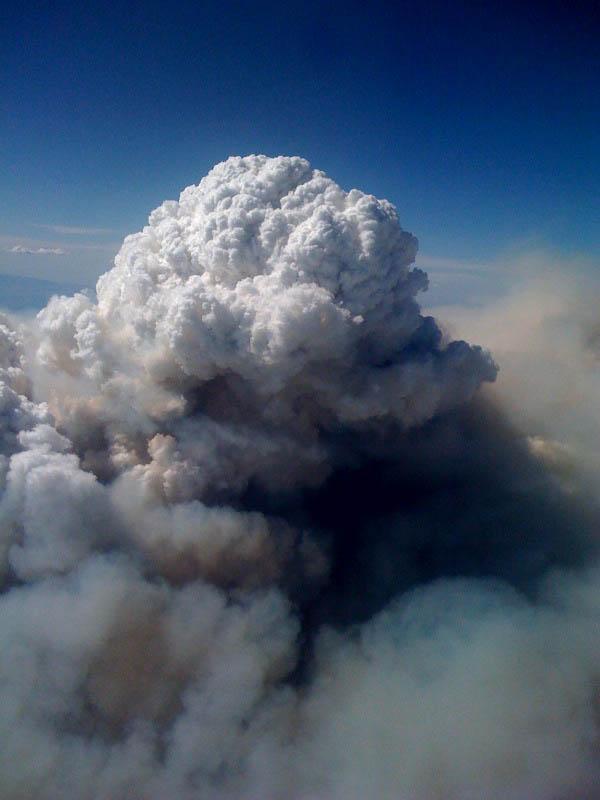

Literally, "the fiery cloud" - convective (cumulus or cumulonimbus) clouds caused by fire or volcanic activity. These clouds got their name because fire creates convective updrafts that at least when the lifting condensation level leading to the formation of clouds - cumulus, first, and under favorable conditions - and cumulonimbus. In this case, possible thunderstorms; lightning from the cloud then cause new fires. Often the rain falling from the clouds, under a cloud of fire limiting or may even extinguish it.
Pirokumulyusy can be seen everywhere, where there are larger duration of the fire, for example, in California, the French Riviera, in the south-eastern Australia. Pyrocumulus cloud have a high percentage of positive lightning "cloud-to-earth," in contrast to "normal" cumulus clouds.
During forest fires in Russia in late July and early August 2010, according to data from NASA "Terra" (spectrometer MISR) and "Aqua" pirokumulyusy were recorded in the stratosphere - their peaks reach a height of 12 km, which shows, according to NASA employees, the high-intensity fires.
16. The window in the clouds

Photo: Dhaluza
17. Radiant clouds
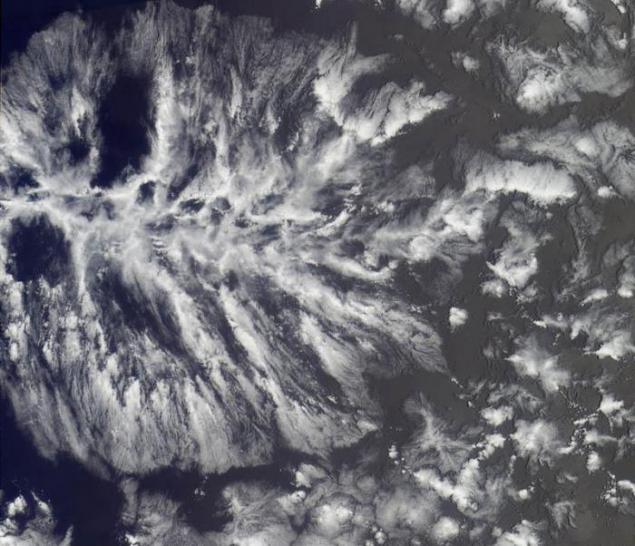

Photo: NASA
18. Pearl clouds
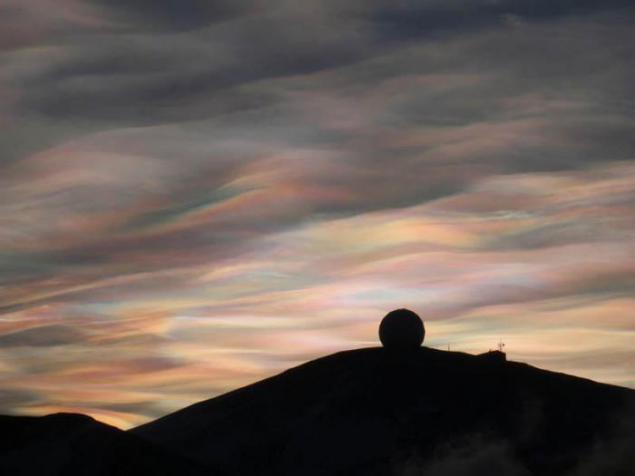

Cloud formed in the air at high altitudes (20-30 km) and consisting, presumably, of the ice crystals or supercooled water droplets. It is thin, translucent clouds. They occur relatively rarely, usually at latitudes 55-60 °, directly after sunset or before sunrise. Happy on a background of bright ambient light, they become invisible.
19. Cloud Cap
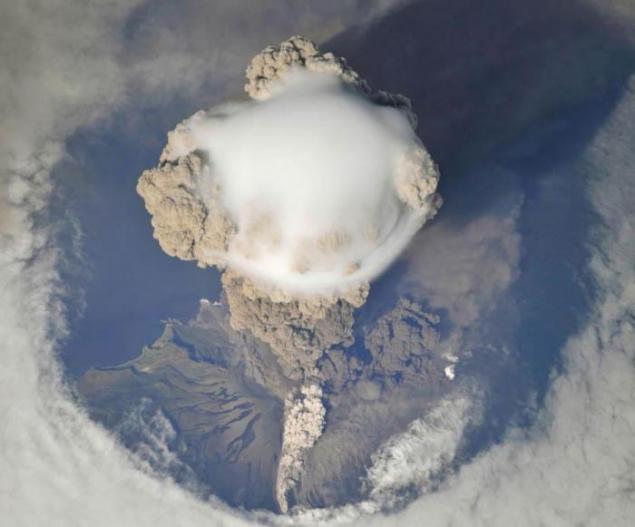

Photo: NASA
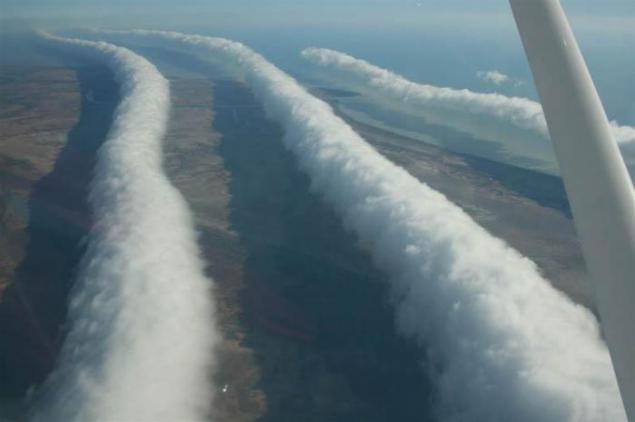
20. Morning Glory

1. lenticular (lens-shaped) clouds

Lenticular (lens-shaped) clouds - a term that refers to a rare natural phenomenon. Lenticular clouds are formed on the crests of waves or air between two layers of air. A characteristic feature of these clouds is that they do not move, no matter how strong the wind. The flow of air above the surface zipping flows around obstacles, and thus forms an air wave. Clouds are usually stuck in the lee of mountain ranges and ridges of the individual peaks at a height of two to fifteen kilometers.
2. The wave flows is a continuous process of condensation of water vapor when the height of the dew point and evaporation during the downward movement of air. Therefore, lenticular clouds do not change their position in space, and are in the sky, like glued.

The emergence of lenticular clouds indicates that the atmosphere - strong horizontal currents of air, forming waves over the mountain barriers that the air is sufficiently high moisture content. It is usually associated with the approach of the front or rear with an energetic transfer of air from remote areas.
3. Clouds Asperatus

Since 1953, meteorologists say that appears a new type of cloud. These clouds look like whether on a stormy sea, whether on the earth's surface. They are dark, bizarre "dented". Of these, stick swirling "horns." View - frightening, sinister. Pictures of clouds coming from around the world.
4. "Judging by the color, the structure contains a lot of moisture, - says Professor Paul Hardaker, executive director of the British Royal Meteorological Society. - We need a lot of energy and heat to form such a cloud. "Some associate the appearance of clouds Asperatus alleged apocalyptic events of 2012.

5. Silver (night, mesospheric) clouds

Noctilucent clouds - a rare atmospheric phenomenon. Such clouds are visible in the twilight. These are the highest clouds in the Earth's atmosphere; formed in the mesosphere at an altitude of about 85 km, and are visible only when illuminated by the sun over the horizon, while the lower layers of the atmosphere are in the Earth's shadow; they are not visible during the day. Moreover, their optical density is so insignificant that they are often lurking through the stars.
6. Clouds with a hole or dyrokolnoe cloud

These unusual clouds similar to the "gates to paradise", amazing and strange hole in the sky. The most common hypothesis argues that the hole in the clouds caused by falling ice crystals. The ice crystals may form in the higher clouds or exhaust overflying aircraft. If the air has a suitable temperature and humidity, the falling crystals will absorb water from the air and grow. In order for this to happen, the water must be so cold that freezing it needs only a suitable surface. The loss of moisture in the air increases the rate of evaporation of water droplets in the cloud, and they are scattered, forming a hole. Become heavier ice crystals continue to fall and form a sparse, ragged, like clouds of rain, which can be seen inside and under the hole. Water and ice in these sediments evaporates before reaching the ground.
7. Vymyaobraznye or tubular cloud

Rare, mainly in the tropics and are associated with the formation of tropical cyclones. The cells typically have a size of about half a kilometer, all chaschё sharply delineated, but there are also with soft edges. Their color is usually gray-blue, as in the main cloud, but because of the direct rays of the sun hit or illumination from other clouds may appear golden or reddish. In meteorology "vymyaobraznye" clouds are called Mammatus (or Mammatocumulus), then there are a type of cumulus (Cumulus) clouds, with a honeycomb structure and is usually located under the "parent" a cluster of cumulus or cumulonimbus clouds.
8. from the elements. However, the low altitude of the Sun above the horizon (eg at sunset) mammatusy can acquire blue-gray, gray-pink, gold, and even reddish color. Mammatusy always associated with lightning storms and, therefore, with cumulonimbus clouds.

However, these clouds can defend lightning focus at a distance of up to several tens of kilometers. Mammatus saved in the sky from several minutes to several hours, gradually disappearing with the dying lightning storm. Persistence Mammatus depends on the size of droplets (or ice crystals), circulating within the cloud band, because the larger the size of droplets or ice crystals, the more energy must be expended on their evaporation. Consisting of fine droplets or ice crystals mammatusy seen in the sky a few minutes and quickly disappear.
9. Wavy clouds

10. This - clouds in the occurrence of which involve wave processes in the atmosphere, as opposed to stratiform clouds associated with an upward sliding, and cumuliform associated with convection.

11. Iridescent Cloud

The so-called iridescent clouds - a relatively rare phenomenon. These clouds can be painted in all colors of the spectrum. They consist of small water droplets of almost identical size. Iridescent clouds appear when the Sun occupies a certain position in the sky and thus almost completely hidden behind a dense clouds. As a result, nearly coherent diffraction sunlight thin clouds are painted in different colors, since the light beams of different wavelengths are deflected in different ways. Therefore, light of different wavelengths arrives to the observer from several different directions. It often happens that the clouds, first painted in rainbow colors, become too dense and heterogeneous, also removed from the sun at a great distance.
12. Shkvalovy gate

Formed in wet conditions as a consequence of the interaction of air flows of different temperatures.
13. Rolling or gross clouds

They are usually formed during thunderstorms and before advancing cold front. It looks like a dark cloud bands, or projections of "shelves" under "shelter" storm clouds. The lower edges ragged, sometimes like a bud boiling. Beneath them is almost always observed squall winds, just behind such a shaft - typically a rain. Nothing good comes from them do not wait. In the deserts of such shafts bring dust storms.

Pyrocumulus cloud or pirokumulyus

Literally, "the fiery cloud" - convective (cumulus or cumulonimbus) clouds caused by fire or volcanic activity. These clouds got their name because fire creates convective updrafts that at least when the lifting condensation level leading to the formation of clouds - cumulus, first, and under favorable conditions - and cumulonimbus. In this case, possible thunderstorms; lightning from the cloud then cause new fires. Often the rain falling from the clouds, under a cloud of fire limiting or may even extinguish it.
Pirokumulyusy can be seen everywhere, where there are larger duration of the fire, for example, in California, the French Riviera, in the south-eastern Australia. Pyrocumulus cloud have a high percentage of positive lightning "cloud-to-earth," in contrast to "normal" cumulus clouds.
During forest fires in Russia in late July and early August 2010, according to data from NASA "Terra" (spectrometer MISR) and "Aqua" pirokumulyusy were recorded in the stratosphere - their peaks reach a height of 12 km, which shows, according to NASA employees, the high-intensity fires.
16. The window in the clouds

Photo: Dhaluza
17. Radiant clouds

Photo: NASA
18. Pearl clouds

Cloud formed in the air at high altitudes (20-30 km) and consisting, presumably, of the ice crystals or supercooled water droplets. It is thin, translucent clouds. They occur relatively rarely, usually at latitudes 55-60 °, directly after sunset or before sunrise. Happy on a background of bright ambient light, they become invisible.
19. Cloud Cap

Photo: NASA
20. Morning Glory