623
How to build an eco-house? Basic principles of green building
Ecohouse is not called thermal strength. It does not need neither heating nor air conditioning, no drafts, do not feel the cold, as the temperature difference between room air and internal surfaces of enclosing structures is negligible.

Ecohouse is an individual or blocked house with a plot of land, which is radically resource-efficient and low-waste, healthy and well-maintained, non-aggressive towards the natural environment. This is achieved mainly by the use of small Autonomous or collective life support engineering systems and rational construction design of the house. Importantly, these qualities he possesses not only as a separately taken, but the system — with all utilities and service of its production systems. Etoile — the key to the future.
THE BASIC PRINCIPLES OF ECO
• The natural surroundings. Building the "right" harmony with the landscape, that is, takes into account natural phenomena (sunrise, sunset etc.).
• Energy efficiency. The use of energy-saving appliances and engineering systems.
• Minimum energy loss. The use of new construction technologies, improved insulation. Improvement of the ventilation system, which is usually lost 1/3 of heat.
• Use of advanced engineering systems with a single control system. The use of modern high-tech products, and also products that use natural elements — solar panels, heat pumps etc.
• Low security impact devices, engineering networks on the inhabitants of the house.
• Applying new concepts of heating, leading role in which plays the thermoregulatory system. The use of "free" heat sources (solar heat, heat appliances, etc.).
• Ecological style interior items and household appliances. The possibility of recycling materials.
SOLAR ARCHITECTURE
Passive solar technology is a long — known method of design and construction of buildings for thousands of years used by people to get maximum benefits from solar radiation. Operation of solar collector is based on the greenhouse effect: absorb heat radiation of the sun greatly exceeds the heat radiation of the reservoir.
There are two types of solar collectors - flat and vacuum.
Vacuum the greenhouse effect is strengthened by the fact that heat radiation of the reservoir cannot pass through a vacuum — as in vacuum flask thermos household. As a result of vacuum manifold, in contrast to the flat, heats the coolant to a high temperature, even in cold weather, that is a decisive factor in favor of his choice for our country. But in winter, when short daylight hours and cloud cover, the amount of heat generated by the solar collector is greatly reduced.
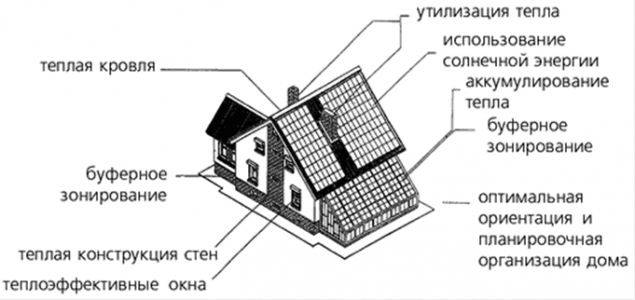
Architecture eco houses
AS HEAT-TRAPPING WALLS
From the point of view of eco friendliness for the most attractive can be considered a slab made of stone wool. They have the following advantages:
• non-toxic and non-carcinogenic unlike, for example, from a material such as asbestos fiber;
• basalt fiber does not break, it does not fray like fiberglass;
• not hygroscopic (water absorption is not more than 1.5%) with simultaneous high permeability;
• over time slabs of stone wool does not shrink in volume in contrast to glass wool or shlakovaty plates;
• material is not affected by fungi and insects;
• non-flammable and heat — resistant plates of stone wool can withstand temperatures up to 1000 °C.
The most important condition of maintaining the thermal contour of the building — the presence of supply and exhaust ventilation with heat recuperator (heat exchanger).
Principle: the external cold air enters a counter flow heat exchanger, which moves through tubes surrounded by the outside warm air coming out of the house in the opposite direction. As a result, the output from the heat exchanger outdoor air tends to acquire the temperature of the room, and the latter, on the contrary, before leaving the heat exchanger tends to outside temperature. So the problem is solved fairly intensive air exchange in a house without heat loss.
In Russia, where the climate is more severe than, for example, in Europe, to the main heat exchanger should be added, and dirt. Its feasibility is proven by the fact that in some Western ekodoma application of ground heat exchanger made it possible to abandon the air conditioner. Soil temperature at a depth of 8 m is a constant of about 8-12 °C. Therefore, it is necessary to bury the heat exchanger it is at this depth that the outdoor air passing in the soil, regardless of the time of year sought to adopt the appropriate temperature. On the street unable to stand either the July heat or January cold, but the house will always do the fresh air, the temperature of which optimum is about 17 °C.
THE "RIGHT" WINDOW
The coefficient of heat transfer resistance of Windows shall not be less than 1.5 °C • m2/W is another necessary condition for thermal integrity of eco.
Requirements for Windows are as follows:
• profile design should have low thermal conductivity and have no "cold bridges"; the preferred three-chamber or five-chamber profiles with a thickness of 62-130 mm;
• window with a large area of glazing should face South direction;
• to reduce heat loss through Windows in winter time at night should close the shutters, roller blinds or blackout curtains.
For eco houses are best suited wooden Windows with triple glazing (three low-e glass, Interglass chamber filled with krypton). Glazing must have a thermal insulation with coefficient of heat transfer resistance of 2 °C • m2/W.
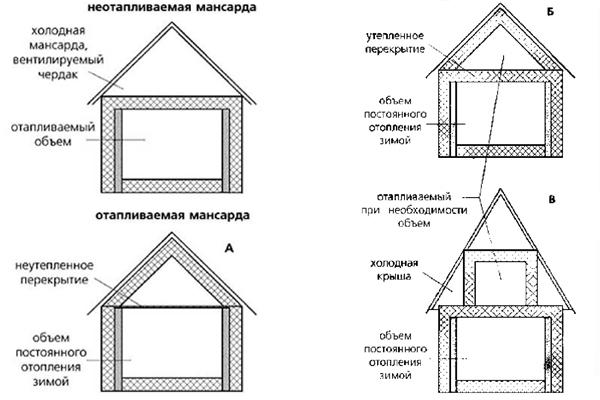
Insulation eco
INSULATION ECO
All internal heated space of eco needs to be insulated from the external environment to the heat loss for the year was less than the amount of heat that can be obtained for the year from the sun and accumulate in the house.
ROOF
Roof, as the Foundation determines the durability of the house. It protects the walls and foundations from rain, provide heat insulation of the interior. The roof can serve as a place to set up solar power — solar collectors for heating air, water, sun bateries the conversion of solar energy into electrical energy. With the surface of the roof can collect a significant amount of water for irrigation and other technical purposes.
Depending on desire it is possible to use a combined roof (insulated roof, is applied to the attic floor) and cold, which is traditionally used in the construction of homes in Russia, for the average single storey and two storey conventional houses (made of straw, reed, polybrene, boards).
FOUNDATIONS FOR ECO-HOMES
The Foundation is the basis of the durability of eco. The choice of design of the Foundation and its depth are determined depending on the soil type, weight of the house construction and location of groundwater. Traditionally, the following types of foundations: columnar, tape foundations of small blocks. The choice of Foundation must be done based on local traditions.
To increase the durability of the Foundation and protect it from groundwater, rain and melt water seeping from the ground around the Foundation is satisfied with the drainage system.
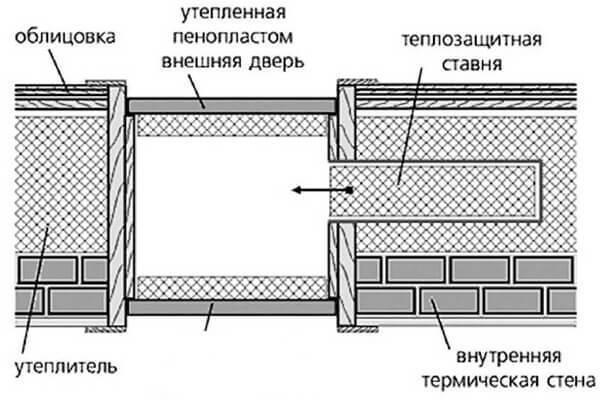
Insulated vestibule with additional insulated sliding door
ENTRANCE VESTIBULE
In the platform shall be installed internal and external insulated door. The vestibule can be done heated and unheated. To improve the thermal insulation, it is advisable to provide additional heat-efficient sliding door.
BUILDING MATERIALS
For eco building you can use all not forbidden sanitation and hygiene standards for construction materials. Necessary to maintain the final parameters of the house and its device described above.
However, there are certain preferences for materials, which are recommended for use in the construction of green buildings, and methods for their production.
The maximum preferred is the use of building materials from local raw materials produced on the site, and preparation of construction materials at the same construction site. In order to achieve the required quality and therefore the necessary parameters that make an ordinary house ekodoma materials are manufactured on a specially created mini-hardware (high technology in the production of building materials at minimum cost in manufacturing). This mini equipment can be used without overhaul within 10 construction seasons when storing it in the winter under a canopy.
INSIGHTS
The implementation of the "Ecodom" project and subsequent large-scale use of the underlying technology needs to solve the most urgent challenges of our time: ensuring residents comfortable housing, constructed and operated on the basis of resource - saving technologies using local materials, and greening household sector.
The house with the described properties are called a heat fortress. In mild climate does not need neither heating nor air conditioning, no drafts, do not feel the cold, as the temperature difference between room air and internal surfaces of enclosing structures is negligible. The house heats heat appliances, the bodies of the inhabitants, both owners and Pets, as well as solar energy. Since the building has no drying air heating equipment, the microclimate can be compared with the fertile summer weather anywhere on the mountain resorts of Switzerland. It has a positive effect, for example, those who suffer from allergies.
Many components of the passive house concept are feasible in Russia. So, the reconstruction of housing has already been successfully applied technologies that contribute to energy efficiency of buildings. It is the insulation of facades using modern heat insulation materials, schemes of forced ventilation and modern window systems. However, practical implementation of energy saving technologies at first, is not cheap. However, the calculations show that the large capital costs quickly pay for themselves through low operating costs. That is, investment in energy saving solutions can be considered long-term and very sound investment.
It is necessary to understand the construction of comfortable, healthy, ecological house today is not a utopia, but a necessary reality. published
Source: www.energy-fresh.ru/greenhouse/building/?id=2075

Ecohouse is an individual or blocked house with a plot of land, which is radically resource-efficient and low-waste, healthy and well-maintained, non-aggressive towards the natural environment. This is achieved mainly by the use of small Autonomous or collective life support engineering systems and rational construction design of the house. Importantly, these qualities he possesses not only as a separately taken, but the system — with all utilities and service of its production systems. Etoile — the key to the future.
THE BASIC PRINCIPLES OF ECO
• The natural surroundings. Building the "right" harmony with the landscape, that is, takes into account natural phenomena (sunrise, sunset etc.).
• Energy efficiency. The use of energy-saving appliances and engineering systems.
• Minimum energy loss. The use of new construction technologies, improved insulation. Improvement of the ventilation system, which is usually lost 1/3 of heat.
• Use of advanced engineering systems with a single control system. The use of modern high-tech products, and also products that use natural elements — solar panels, heat pumps etc.
• Low security impact devices, engineering networks on the inhabitants of the house.
• Applying new concepts of heating, leading role in which plays the thermoregulatory system. The use of "free" heat sources (solar heat, heat appliances, etc.).
• Ecological style interior items and household appliances. The possibility of recycling materials.
SOLAR ARCHITECTURE
Passive solar technology is a long — known method of design and construction of buildings for thousands of years used by people to get maximum benefits from solar radiation. Operation of solar collector is based on the greenhouse effect: absorb heat radiation of the sun greatly exceeds the heat radiation of the reservoir.
There are two types of solar collectors - flat and vacuum.
Vacuum the greenhouse effect is strengthened by the fact that heat radiation of the reservoir cannot pass through a vacuum — as in vacuum flask thermos household. As a result of vacuum manifold, in contrast to the flat, heats the coolant to a high temperature, even in cold weather, that is a decisive factor in favor of his choice for our country. But in winter, when short daylight hours and cloud cover, the amount of heat generated by the solar collector is greatly reduced.

Architecture eco houses
AS HEAT-TRAPPING WALLS
From the point of view of eco friendliness for the most attractive can be considered a slab made of stone wool. They have the following advantages:
• non-toxic and non-carcinogenic unlike, for example, from a material such as asbestos fiber;
• basalt fiber does not break, it does not fray like fiberglass;
• not hygroscopic (water absorption is not more than 1.5%) with simultaneous high permeability;
• over time slabs of stone wool does not shrink in volume in contrast to glass wool or shlakovaty plates;
• material is not affected by fungi and insects;
• non-flammable and heat — resistant plates of stone wool can withstand temperatures up to 1000 °C.
The most important condition of maintaining the thermal contour of the building — the presence of supply and exhaust ventilation with heat recuperator (heat exchanger).
Principle: the external cold air enters a counter flow heat exchanger, which moves through tubes surrounded by the outside warm air coming out of the house in the opposite direction. As a result, the output from the heat exchanger outdoor air tends to acquire the temperature of the room, and the latter, on the contrary, before leaving the heat exchanger tends to outside temperature. So the problem is solved fairly intensive air exchange in a house without heat loss.
In Russia, where the climate is more severe than, for example, in Europe, to the main heat exchanger should be added, and dirt. Its feasibility is proven by the fact that in some Western ekodoma application of ground heat exchanger made it possible to abandon the air conditioner. Soil temperature at a depth of 8 m is a constant of about 8-12 °C. Therefore, it is necessary to bury the heat exchanger it is at this depth that the outdoor air passing in the soil, regardless of the time of year sought to adopt the appropriate temperature. On the street unable to stand either the July heat or January cold, but the house will always do the fresh air, the temperature of which optimum is about 17 °C.
THE "RIGHT" WINDOW
The coefficient of heat transfer resistance of Windows shall not be less than 1.5 °C • m2/W is another necessary condition for thermal integrity of eco.
Requirements for Windows are as follows:
• profile design should have low thermal conductivity and have no "cold bridges"; the preferred three-chamber or five-chamber profiles with a thickness of 62-130 mm;
• window with a large area of glazing should face South direction;
• to reduce heat loss through Windows in winter time at night should close the shutters, roller blinds or blackout curtains.
For eco houses are best suited wooden Windows with triple glazing (three low-e glass, Interglass chamber filled with krypton). Glazing must have a thermal insulation with coefficient of heat transfer resistance of 2 °C • m2/W.

Insulation eco
INSULATION ECO
All internal heated space of eco needs to be insulated from the external environment to the heat loss for the year was less than the amount of heat that can be obtained for the year from the sun and accumulate in the house.
ROOF
Roof, as the Foundation determines the durability of the house. It protects the walls and foundations from rain, provide heat insulation of the interior. The roof can serve as a place to set up solar power — solar collectors for heating air, water, sun bateries the conversion of solar energy into electrical energy. With the surface of the roof can collect a significant amount of water for irrigation and other technical purposes.
Depending on desire it is possible to use a combined roof (insulated roof, is applied to the attic floor) and cold, which is traditionally used in the construction of homes in Russia, for the average single storey and two storey conventional houses (made of straw, reed, polybrene, boards).
FOUNDATIONS FOR ECO-HOMES
The Foundation is the basis of the durability of eco. The choice of design of the Foundation and its depth are determined depending on the soil type, weight of the house construction and location of groundwater. Traditionally, the following types of foundations: columnar, tape foundations of small blocks. The choice of Foundation must be done based on local traditions.
To increase the durability of the Foundation and protect it from groundwater, rain and melt water seeping from the ground around the Foundation is satisfied with the drainage system.

Insulated vestibule with additional insulated sliding door
ENTRANCE VESTIBULE
In the platform shall be installed internal and external insulated door. The vestibule can be done heated and unheated. To improve the thermal insulation, it is advisable to provide additional heat-efficient sliding door.
BUILDING MATERIALS
For eco building you can use all not forbidden sanitation and hygiene standards for construction materials. Necessary to maintain the final parameters of the house and its device described above.
However, there are certain preferences for materials, which are recommended for use in the construction of green buildings, and methods for their production.
The maximum preferred is the use of building materials from local raw materials produced on the site, and preparation of construction materials at the same construction site. In order to achieve the required quality and therefore the necessary parameters that make an ordinary house ekodoma materials are manufactured on a specially created mini-hardware (high technology in the production of building materials at minimum cost in manufacturing). This mini equipment can be used without overhaul within 10 construction seasons when storing it in the winter under a canopy.
INSIGHTS
The implementation of the "Ecodom" project and subsequent large-scale use of the underlying technology needs to solve the most urgent challenges of our time: ensuring residents comfortable housing, constructed and operated on the basis of resource - saving technologies using local materials, and greening household sector.
The house with the described properties are called a heat fortress. In mild climate does not need neither heating nor air conditioning, no drafts, do not feel the cold, as the temperature difference between room air and internal surfaces of enclosing structures is negligible. The house heats heat appliances, the bodies of the inhabitants, both owners and Pets, as well as solar energy. Since the building has no drying air heating equipment, the microclimate can be compared with the fertile summer weather anywhere on the mountain resorts of Switzerland. It has a positive effect, for example, those who suffer from allergies.
Many components of the passive house concept are feasible in Russia. So, the reconstruction of housing has already been successfully applied technologies that contribute to energy efficiency of buildings. It is the insulation of facades using modern heat insulation materials, schemes of forced ventilation and modern window systems. However, practical implementation of energy saving technologies at first, is not cheap. However, the calculations show that the large capital costs quickly pay for themselves through low operating costs. That is, investment in energy saving solutions can be considered long-term and very sound investment.
It is necessary to understand the construction of comfortable, healthy, ecological house today is not a utopia, but a necessary reality. published
Source: www.energy-fresh.ru/greenhouse/building/?id=2075
Causes of male infertility: deficiency regimen, leptin, insulin
What to do if you get a call from the Bank's foreign debts. Usage instructions























