613
Available on the general analysis of blood: learn to understand their own analyzes
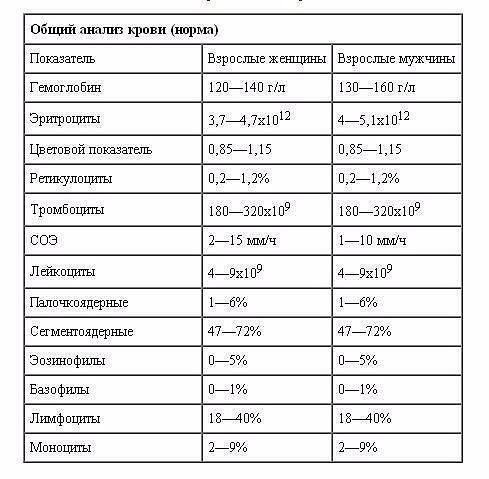
Indicators of general blood analysis are (in parentheses indicate the abbreviation of the indicator):
Hemoglobin (HGB) - inside the erythrocyte protein that is responsible for the oxygen saturation of the body. In the lungs it combines with oxygen, and delivers it to the organs. There the oxygen is replaced by carbon dioxide, which is delivered to the lungs. And gas exchange occurs. According to the norms of general blood tests measure hemoglobin differ for men and women - at first it should be mentioned
. Red blood cells (RBC) - cells containing hemoglobin. Complete blood count is a count, as "average content of hemoglobin in one erythrocyte» (MCH), which reflects the amount of this protein in a single red blood cell.
Hematocrit (HCT) - measure the density of blood
. Reticulocytes (RE) - young erythrocytes. The fall in hemoglobin and red blood cells is below normal may occur in anemia, after a long illness.
Platelets (PLT) provides blood clotting. An overall analysis reveals a decrease in platelet count and to prevent bleeding, which may fall under PLT lower than 50h109 / l.
White blood cells (WBC) - responsible for immunity. Indicators of leukocytes in general blood test to evaluate the state of immunity and even to determine the cause of the disease. Excess levels of white blood cells are often observed in acute bacterial infections, purulent inflammation. In the fall of the number of white blood cells is below normal probable viral infection, toxic condition, certain bacterial infections.
Thus, if the increased number of white blood cells fighting the virus - a disease caused by a viral infection, a lot of white blood cells fighting the bacteria, - disease of bacterial origin. The treatment in the first and second cases is significantly different.
The most active against bacteria neutrophils (NE), so the nature of bacterial inflammations their percentage in the blood increases. While the number of other types of leukocytes (again expressed in%) is decreased. In total, the percentage of all kinds of white blood cells is 100%.
The percentage of different types of white blood cells called leukocyte formula.
Extended CBC provides information about the different types of neutrophils. Adults neutrophils, which perform most of the work to fight infection - called segmented. During neutrophil maturation takes several forms: medullocell, metamyelocyte, stab neutrophil and only then segmented. The presence of a small amount of segmented and band neutrophils are absolutely normal.
Myelocytes and metamyelocytes appear in severe diseases, activation of the body's effort to fight the disease.
Eosinophils (EO) - an excess of in the overall analysis of blood eosinophils observed in parasitic infestations (eg, parasitic), allergic reactions, healing from severe bacterial infections
. Basophils (BA) - present in blood in small amounts. Increasing the content of basophils found in rare diseases.
Lymphocytes (LYMP) form the general and local immunity. In viral infections, lymphocyte content increases.
Monocytes (MON) utilize bacteria, dying cells, and other foreign elements. Increasing the number of monocytes seen with prolonged infections and infectious mononucleosis.
Plasma cells from healthy adult are absent. There are varicella, bark, infectious mononucleosis, rubella and some other viral infections.
An important indicator of blood count - ESR. In inflammatory processes ESR increases.
Complete blood count is necessary to pass in the morning on an empty stomach.