815
10 space objects that are difficult to imagine.

Space is fine, but, in general, very strange. Planets revolve around stars that are dying and going out again, and everything revolves around the galaxy, the supermassive black hole, slowly draw all that gets too close. But sometimes it throws up so much space strange things that you twist your mind into a pretzel trying to figure it out.
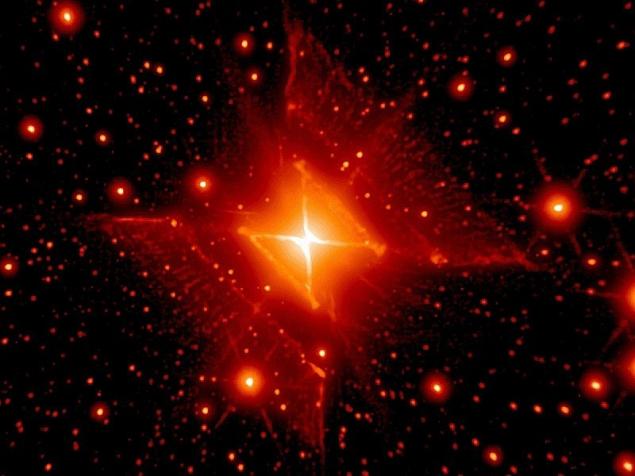
Red Square nebula
Objects in space, for the most part very rounded. Planets, stars, galaxies and the shape of the orbit - all reminiscent of the circle. But the Red Square nebula, a gas cloud forms an interesting, uh, square. Of course, astronomers are very, very surprised, because the objects in space do not have to be square.
In fact, it is not quite square. If you look closely at the picture, you'll notice that across the shape formed by two cones at the point of contact. But again, in the night sky are not many cones. The nebula an hourglass glows very brightly, as at the very center is the brightest star - where touching the cones. It is possible that this star exploded and became a supernova, leaving the ring at the base of the cones began to glow intensely.
Pillars of Creation
As Douglas Adams once wrote, "the big space. Really big. You can not even imagine how mind-bogglingly big it is. " We all know that the units of measure to measure distances in space, it is a light year, but few people think about what this means. Light year - it's so much distance that light - something that is moving fastest in the universe - passes this distance only for a year.
This means that when we look at objects in space that are really far away, like the Pillars of Creation (formation in the Eagle Nebula), we look back in time. How so? The light from the Eagle Nebula reaches the Earth for 7,000 years, and we see it the way it was 7,000 years ago, because what we see - is the reflected light.
The consequences are looking into the past rather strange. For example, astronomers believe that the Pillars of Creation were destroyed supernova about 6,000 years ago. That is, these pillars is simply not there. But we see them.
Collision of galaxies
In space, everything is constantly moving - in an orbit around its axis or just rushing through space. For this reason - and because of the incredible force of gravity - galaxies collide constantly. Perhaps it will not surprise you - just look at the moon, and to understand that the cosmos loves to keep small items near large. When two galaxies containing billions of stars collide, a local disaster occurs, yes?
In fact, collisions of galaxies in the likelihood that the two stars collide, is practically zero. The fact that apart from the fact that the space itself is high (and galaxies too), as it is in itself quite empty. Therefore, it is called "outer space." Although our galaxy and look solid from a distance, do not forget that the nearest star is at a distance of 4, 2 light-years away. It is very far away.
The problem horizon
Space - a solid mystery, everywhere you look. For example, if we look at a point on the east of our sky and measure the background radiation, and then do the same at the point on the west, which will be separated from the first 28 billion light years away, we see that the background radiation at the two points of equal temperature. < br />
It seems impossible, because nothing can travel faster than light, and even the world would have taken too long to fly from one point to another. How could the microwave background to stabilize almost uniformly throughout the universe?
This may explain the theory of inflation, which suggests that the universe is spread out over long distances immediately after the Big Bang. According to this theory, the universe was formed by stretching its edges, but space-time itself stretched like chewing gum, in a split second. In this infinite short time in this space I covered nanometer light years. It is not against the law that nothing can travel faster than light, because nothing and did not move. It just expanded.
Imagine the universe as the original one pixel in an image editing program. Now scale the image by a factor of 10 billion. Since the whole point is composed of the same material, its properties - temperature and including - homogeneous.
How do you kill a black hole
Black holes are so massive that the material starts to behave strangely close to him. One can imagine that to be drawn into the black hole - then spend the rest of eternity (or spend the remainder of the air), desperately crying in the tunnel of emptiness. But do not worry, monstrous gravity will deprive you of this hopelessness.
The force of gravity is stronger, the closer you are to the source of it, and when the source is a powerful body, the quantities can seriously change even for short distances - say, the height of a man. If you fall into a black hole feet first, the force of gravity acting on your feet will be so strong that you will see how your body is pulled into the spaghetti lines of atoms that are drawn into the center of the hole. You never know, suddenly, this information will be useful to you when you want to dive into the belly of a black hole.
The cells of the brain and the universe
Recently, physicists have created a simulation of the beginning of the universe, which began with the Big Bang and the sequence of events that led to what we see today. Bright yellow cluster galaxies tightly packed in the center and "network" less dense galaxies, stars, dark matter and so-forth.
At the same time, Brandeis University of student to investigate the relationship of neurons in the brain, studying thin plate mouse brain under the microscope. The image that he got yellow contains neurons related red "network" connections. Nothing resembles?
The two images, although very different in its scope (nanometers and light years), are strikingly similar. What is this, the usual case of the fractal recursive in nature or the universe really is a cell of the brain inside another vast universe?
The missing baryons
According to the Big Bang theory, the amount of matter in the universe will eventually create enough gravitational pull to slow the expansion of the universe to a complete stop. However, baryonic matter (what we see - stars, planets, galaxies and nebulae) is only 1 to 10 percent of all the matter that should be. Theorists balanced equation of hypothetical dark matter (which we can not see), to save the situation.
Each theory that tries to explain the absence of strange baryons, left with nothing. The most common theory is that the missing matter consists of the intergalactic medium (gas and particulate atoms floating in the voids between galaxies), but even so we still have plenty of the missing baryons. We do not have any idea of the whereabouts of most of the matter, which should actually be.
Cold Star
The fact that the stars are hot, no doubt. It's as logical as the fact that snow is white, and twice two is four. When visiting stars, we would be more worried about how not to burn, not how to stay warm - in most cases. Brown dwarfs - are stars that are very cold by the standards of stars. Not so long ago, astronomers discovered type of star called Y-dwarfs, which are the coldest star in the family of a subspecies of brown dwarfs. Y-dwarfs are cooler than the human body. At a temperature of 27 degrees Celsius, you can safely touch of the brown dwarf, to touch him, if only his incredible gravity does not turn you into a mess.
These stars are devilishly hard to detect because they do not emit almost no visible light, so look for them only in the infrared spectrum. There are even rumors that the brown-and Y-dwarfs - this is the same "dark matter", which has disappeared from our Universe.
The problem of the solar corona
The farther away the object from the heat source, so it is colder. That's why the strange thing is that the surface temperature of the Sun is about 2760 degrees Celsius, and its crown (something like its atmosphere) is 200 times hotter.
Even if they can be any processes that explain the difference in temperature, none of them can not explain the difference is so great. Scientists believe that this has something to do with small patches of magnetic fields that appear, disappear, and move along the surface of the sun. Since the magnetic lines can not intersect with each other, blotches rebuilt each time too close, and this process heats the corona.
While this explanation may seem neat, it is far from elegant. Experts can not agree in opinion on how to live a long time, these inclusions, not to mention the processes by which they could heat the corona. Even if the answer to the question lies in this, no one knows what causes these random blotches of magnetism in general appear.
Black Hole Eridani
Hubble Deep Space Field - This photo taken by the Hubble telescope, which show thousands of distant galaxies. However, when we look into the "empty" space in the constellation Eridanus, we see nothing. At all. Just a black void, stretched out on billions of light years. Almost any "vacuum" in the night sky returned pictures of galaxies, albeit blurry, but the existing ones. We have several methods that help determine what dark matter could be, but they leave us empty-handed when we look into the void Eridani.
One controversial theory suggests that the void contains a supermassive black hole, around which all the nearest galaxy clusters and high-speed rotation is aligned with the "illusion" of an expanding universe. Another theory says that all matter ever glued together to form galaxy clusters and between the clusters are formed with time drifting empty.
But this does not explain the second void discovered by astronomers in the southern night sky, which at this time about 3, 5 billion light-years wide. It is so broad that it can hardly explain even the Big Bang theory, the universe existed since long enough to have time to such a huge void formed by conventional galactic drift. Maybe someday all these riddles of the universe will just seeds in a glass, but not today and not tomorrow.