321
Smoking
When you inhale cigarette smoke, it passes through your mouth and throat into the lungs. The smoke contains over 4 thousand. Chemicals including highly toxic and cancer-causing substances. For example, formaldehyde, benzene, arsenic, and others. These substances interact with body tissues when in contact with them. When the smoke reaches the lungs, it is deposited in the form of resins.

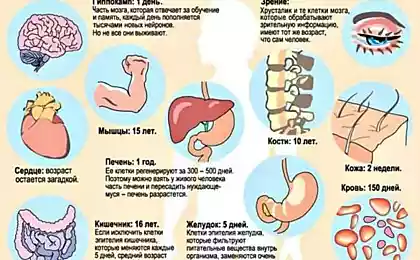
A large number of chemicals into the bloodstream through the lungs. Carbon monoxide (exactly the same manner as in automotive exhaust!) Replaces part of the oxygen in the blood. This causes lack of oxygen in all organs, including the brain.

One of the chemicals released into the bloodstream - nicotine. Its regular use leads to nicotine addiction. Nicotine, an alkaloid found in tobacco (up to 2 and some other plants. When smoking tobacco is absorbed into the body. A strong poison; in small doses, a stimulant effect on the nervous system, in large - causing her paralysis (cessation of breathing, cessation of cardiac activity). Repeated absorption of small doses of nicotine by smoking causes tabagism. nicotine sulfate is used to control pests of agricultural plants.

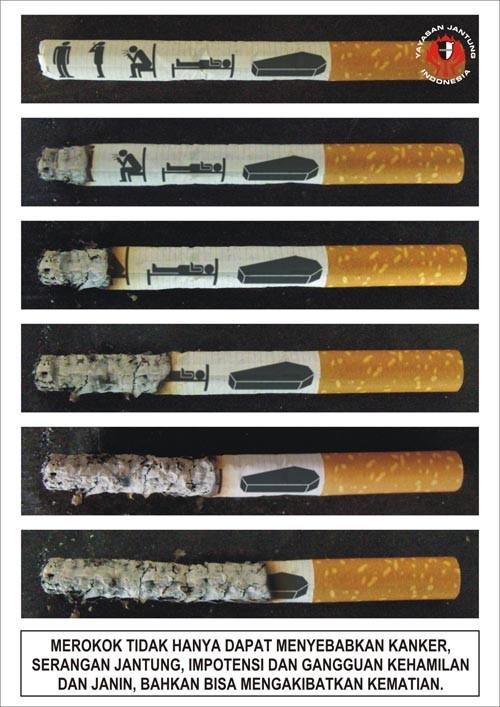
Cigarette smoke comes into direct contact with the lungs, greatly increasing the risk of cancer, pneumonia, emphysema, chronic bronchitis and other lung diseases, difficulty breathing. Fortunately, many of the changes are reversible.

The effect of chemical substances contained in tobacco smoke on the body is a major risk factor to be ill with myocardial infarction and other cardiac diseases. Myocardial infarction, cardiovascular disease characterized by the formation of a heart attack in the heart muscle as a result of violation of the coronary circulation (atherosclerosis, thrombosis, coronary artery spasm). Myocardial infarction (mostly against the background of angina attacks) contribute including smoking. The main manifestations: a long bout of severe compressive pain in the center or left side of the chest, feeling of fear, suffocation, collapse, fever, changes in blood and electrocardiogram. The patient in need of urgent hospitalization.


















































A large number of chemicals into the bloodstream through the lungs. Carbon monoxide (exactly the same manner as in automotive exhaust!) Replaces part of the oxygen in the blood. This causes lack of oxygen in all organs, including the brain.

One of the chemicals released into the bloodstream - nicotine. Its regular use leads to nicotine addiction. Nicotine, an alkaloid found in tobacco (up to 2 and some other plants. When smoking tobacco is absorbed into the body. A strong poison; in small doses, a stimulant effect on the nervous system, in large - causing her paralysis (cessation of breathing, cessation of cardiac activity). Repeated absorption of small doses of nicotine by smoking causes tabagism. nicotine sulfate is used to control pests of agricultural plants.

Cigarette smoke comes into direct contact with the lungs, greatly increasing the risk of cancer, pneumonia, emphysema, chronic bronchitis and other lung diseases, difficulty breathing. Fortunately, many of the changes are reversible.

The effect of chemical substances contained in tobacco smoke on the body is a major risk factor to be ill with myocardial infarction and other cardiac diseases. Myocardial infarction, cardiovascular disease characterized by the formation of a heart attack in the heart muscle as a result of violation of the coronary circulation (atherosclerosis, thrombosis, coronary artery spasm). Myocardial infarction (mostly against the background of angina attacks) contribute including smoking. The main manifestations: a long bout of severe compressive pain in the center or left side of the chest, feeling of fear, suffocation, collapse, fever, changes in blood and electrocardiogram. The patient in need of urgent hospitalization.