789
Ty-22M-3 (15 pics + text)
In January 1974 the MIC USSR Council of Ministers adopted a decision on further modification of the Tu-22M2 by NK-25 engines. It was supposed to replace the engine, as well as introduce a number of significant improvements in the design and aerodynamics of the aircraft. June 26, 1974 the Resolution of the Council of Ministers № 534-187, determines the development of the Tu-22M with engines NK-25 airframe with improved aerodynamics, low weight of the empty aircraft and with improved tactical and operational characteristics.
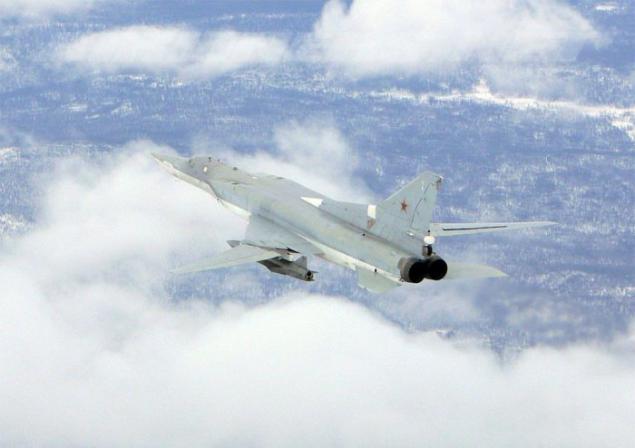

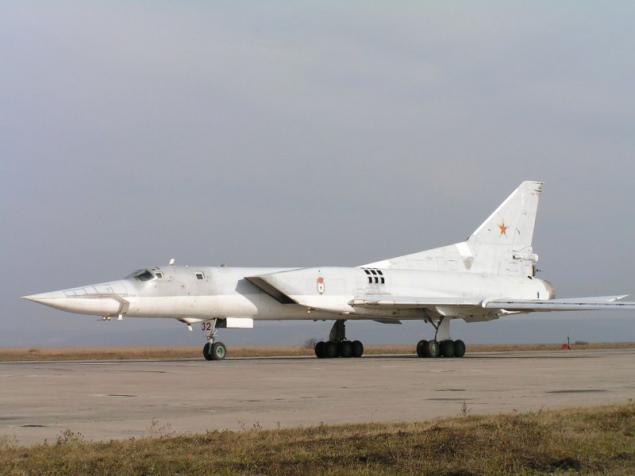
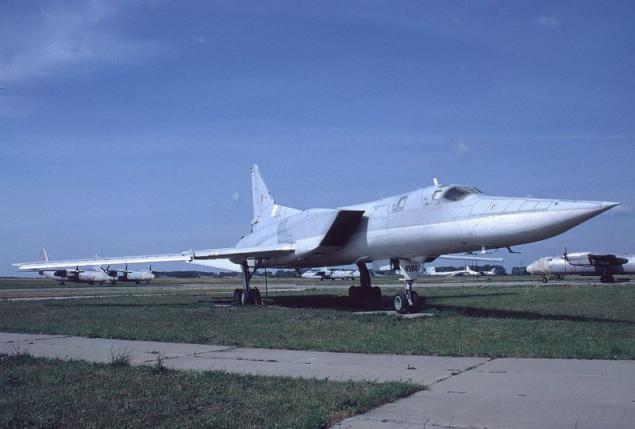
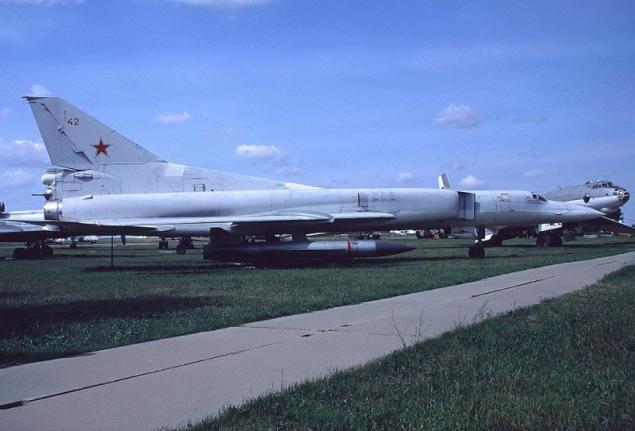
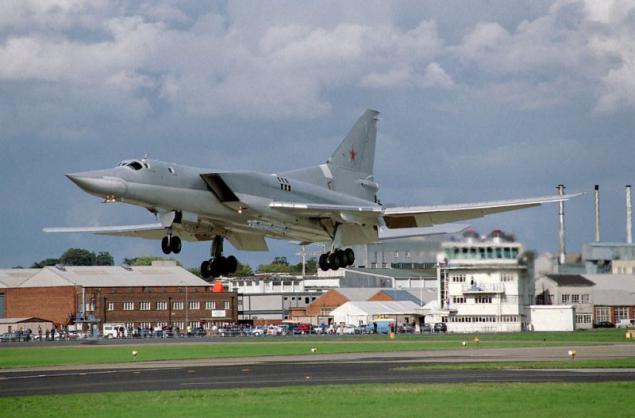
The new versions, called Tu-22M3 ("45-03") were replaced by engines made changes to the design of the air intake was increased maximum deflection angle of the rotary wing up to 65 °. The design of the forward fuselage was also redesigned, modified refueling boom. Coupled dvuhpushechnaya fodder plant has been replaced by odnopushechnuyu with improved aerodynamic shape. Carried out a set of measures to improve the aerodynamic performance and reduce the weight of the empty aircraft (in the constructions began to be widely used titanium). All measures to reduce weight, even with the heavier new engines were to provide a general decrease in the mass of the aircraft at 2300-2700 kg.

The first prototype of the Tu-22M3, made its first flight 20 June 1977. After the program flight-development tests Tu-22M3 1978 runs in serial production. C 1984 cease production of the early models of the Tu-22M and in mass production there is only a modification of the Tu-22M3. From 1981 to 1984, the aircraft took an additional set of tests in the version with advanced combat capabilities. The final form of the Tu-22M3 was adopted into service in March 1989.
All at the Kazan Aircraft Production Association was built 268 Tu-22M3.
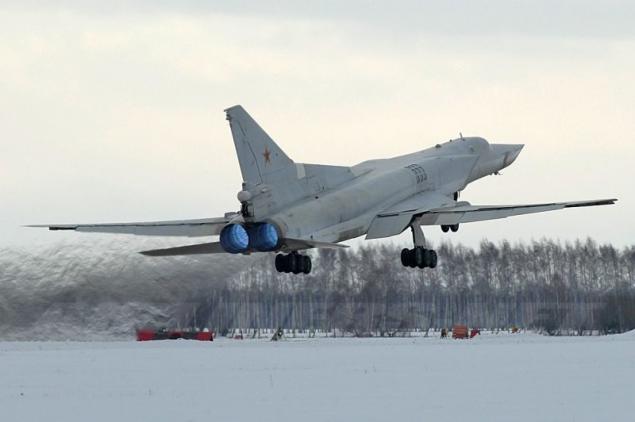

In December 1985 began flight tests of long-range reconnaissance aircraft Tu-22M3R, designed on the basis of the Tu-22M3. In 1989 reconnaissance plane under the designation Tu-22MR transferred into production. Constructed or converted into a reconnaissance version of the Tu-22M3 12 aircraft. There were other projects for the development of the Tu-22M based on the use of upgraded engines, new equipment and weapons systems - Tu-22M4 (1990) and Tu-22M5.
Russian Air Force has 70 Tu-22M3, 83 aircraft are available to aviation Russian Navy.
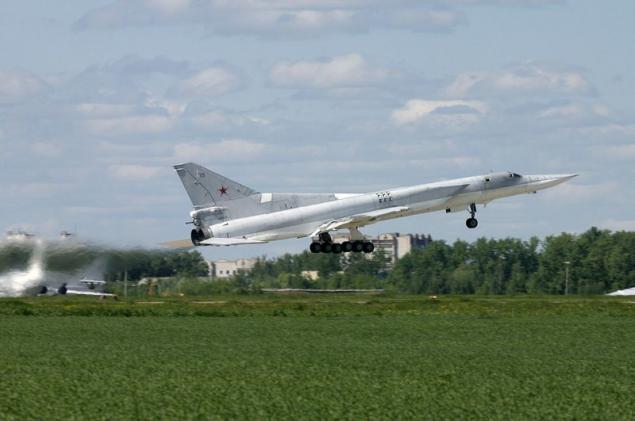
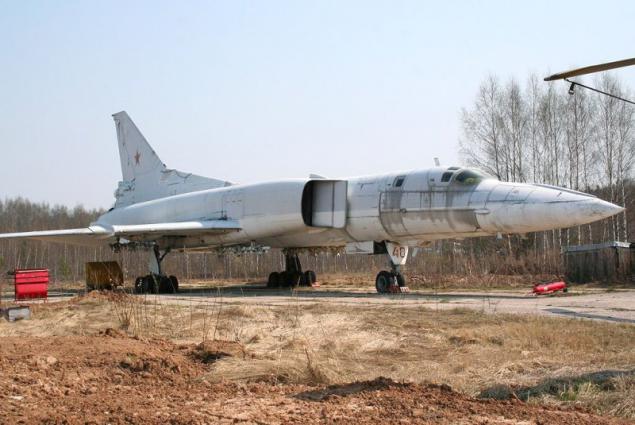
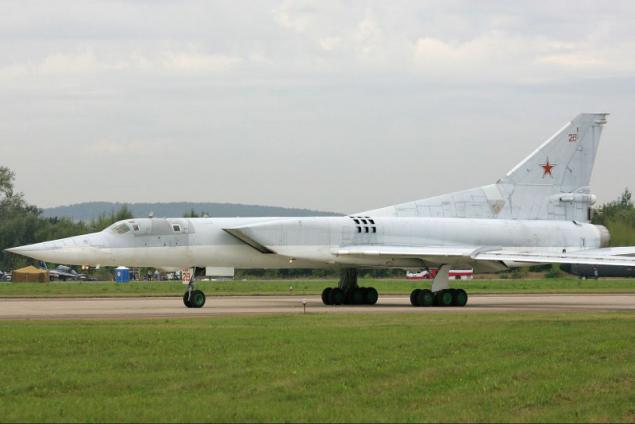
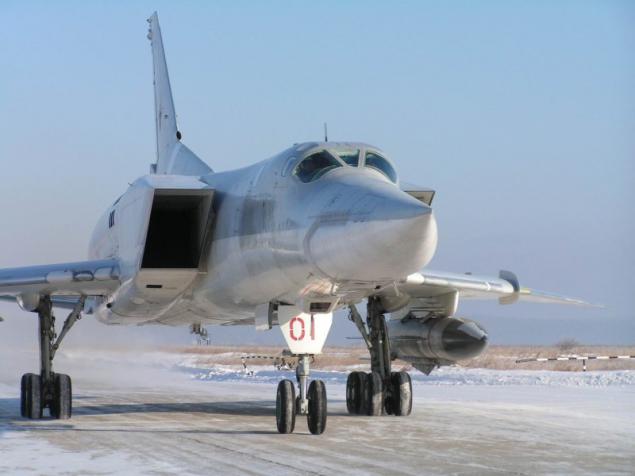
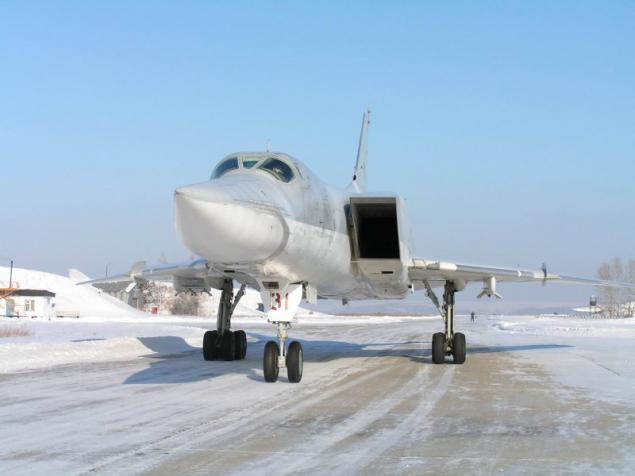














The new versions, called Tu-22M3 ("45-03") were replaced by engines made changes to the design of the air intake was increased maximum deflection angle of the rotary wing up to 65 °. The design of the forward fuselage was also redesigned, modified refueling boom. Coupled dvuhpushechnaya fodder plant has been replaced by odnopushechnuyu with improved aerodynamic shape. Carried out a set of measures to improve the aerodynamic performance and reduce the weight of the empty aircraft (in the constructions began to be widely used titanium). All measures to reduce weight, even with the heavier new engines were to provide a general decrease in the mass of the aircraft at 2300-2700 kg.

The first prototype of the Tu-22M3, made its first flight 20 June 1977. After the program flight-development tests Tu-22M3 1978 runs in serial production. C 1984 cease production of the early models of the Tu-22M and in mass production there is only a modification of the Tu-22M3. From 1981 to 1984, the aircraft took an additional set of tests in the version with advanced combat capabilities. The final form of the Tu-22M3 was adopted into service in March 1989.
All at the Kazan Aircraft Production Association was built 268 Tu-22M3.

In December 1985 began flight tests of long-range reconnaissance aircraft Tu-22M3R, designed on the basis of the Tu-22M3. In 1989 reconnaissance plane under the designation Tu-22MR transferred into production. Constructed or converted into a reconnaissance version of the Tu-22M3 12 aircraft. There were other projects for the development of the Tu-22M based on the use of upgraded engines, new equipment and weapons systems - Tu-22M4 (1990) and Tu-22M5.
Russian Air Force has 70 Tu-22M3, 83 aircraft are available to aviation Russian Navy.