613
Building materials of the future
At that time, as some people believe that the old methods of construction — the best, the fact remains that the innovators in the construction industry create more and more simple and safe methods of erection of buildings and structures around the world. Development of innovative building materials allows architects and designers more fully realize the most daring ideas and builders to construct more complex and grandiose buildings, not fearing for the safety, strength and durability.
This area is developing continuously, therefore if you work in the construction industry or related areas, you will certainly need to know about new construction materials. At least in order to constantly stay "in the know". Now with the help of extrapolation, you can imagine which building materials and technological solutions will be in demand in the construction of buildings. We offer a short overview of the most promising of them.
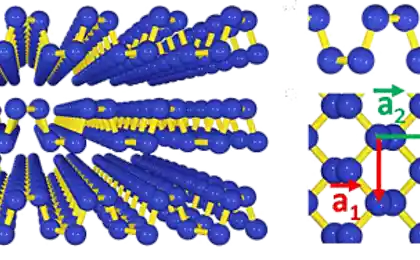
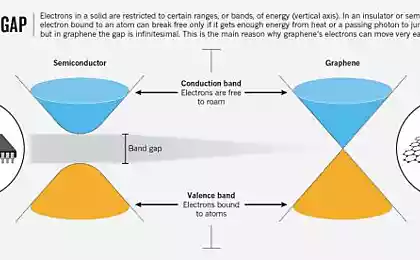
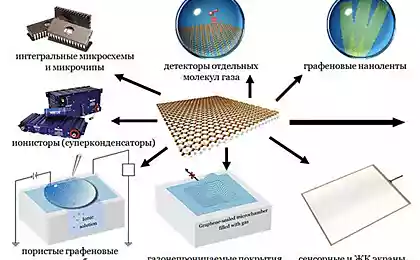
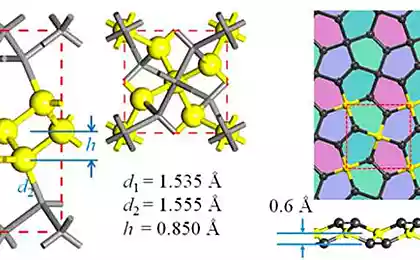
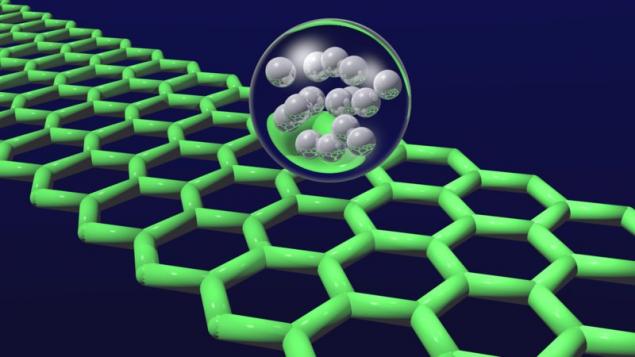
GrapheneDespite the fact that graphene is not a new material used it is not the most practical way, since opening. After all, in theory, graphene is an excellent building material because it has incredible lightness and strength, comparable with steel and carbon fiber. Potentially graphene can be combined with more traditional materials to create strong structures, beams and cables that will allow you to build impressive structures.
However, graphene is so difficult to produce that builders rarely use this material. In the best case, this happens in small fragments in the context of complex and expensive projects. But the situation may soon change. Currently, one of the research centers in the U.S. are developing a new method of production of graphene using chemical vapor deposition of this material from the vaporous state. Ivan Vlasyuk, project Manager, believes the new technology will "greatly expand the potential applications of graphene". The next step is to reduce production costs of graphene and improve its accessibility to the material to be used as widely as possible.
If the price of graphene is comparable to the prices of traditional building materials in construction can expect a real graphene revolution.
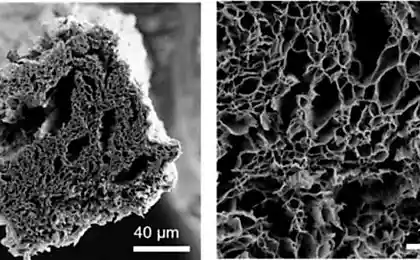
"Roman" the concreteBuildings of Ancient Rome were able to stand for a very long time, so building material, manufactured according to the same principles, today the focus of attention of scientists. Researchers from the University of California made a breakthrough by revealing the secret of long life of the buildings of Ancient Rome. It turns out the Roman builders used a special recipe for making concrete.

In contrast to modern concrete, the builders of Ancient Rome were used for the production of lime mortar of volcanic rock. Without going into the intricacies of technology, we note that these rocks create a more regular crystal grid in the setting process of the concrete, making it very homogeneous. This material is resistant to corrosion and bind the structure more firmly. It also reduces the risk of microcracks in the concrete over time, significantly increasing the life expectancy of the material up to 2000 years.
But "Rome" concrete is not only stronger than its modern counterpart, it is also environmentally friendly. As is known, in the manufacture of Portland cement ingredients is heated to a temperature exceeding 1,400 degrees Celsius, which contributes to massive carbon dioxide emission. According to some estimates, this makes up 7% of all global carbon emissions. But "Rome" concrete needs no such heating, and this means that the new material is stronger and more environmentally friendly than traditional analogue.
"Green" concrete,But researchers from mit went further and developed the technology, which involves completely exclude the cement from the concrete! Scientists at the Department of civil and environmental engineering has offered to issue so-called "green" concrete, which for the production of concrete uses such organic materials as bones, shells, sponges, etc.

This design eliminates two major disadvantages of Portland cement — a large amount of energy required for its production, and the inevitable appearance of microcracks in the concrete formed over time. The truth is, this concrete is very expensive.
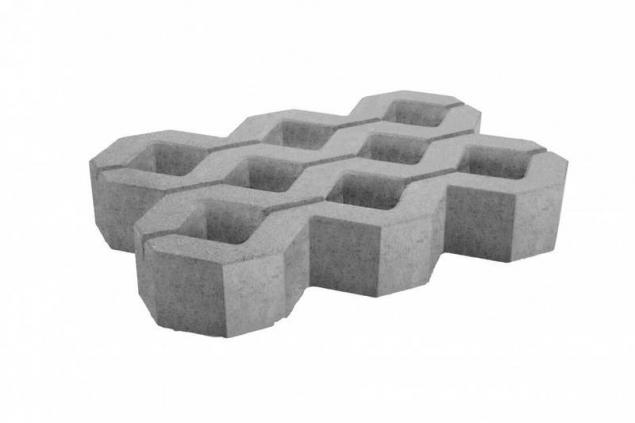

Another development, claiming the title of "green concrete", created by a team of specialists in one of Malaysian Universities. They went the other way and typical for the production of concrete components added recycled construction debris. The result is a cheap and environmentally friendly material, performs its function is not worse than the classical counterpart.
In fairness it should be noted that this technology of concrete production from construction waste appear everywhere, but hardly any of them comes to commercial use. It seems that the Malays had approached the closest.
Synthetic web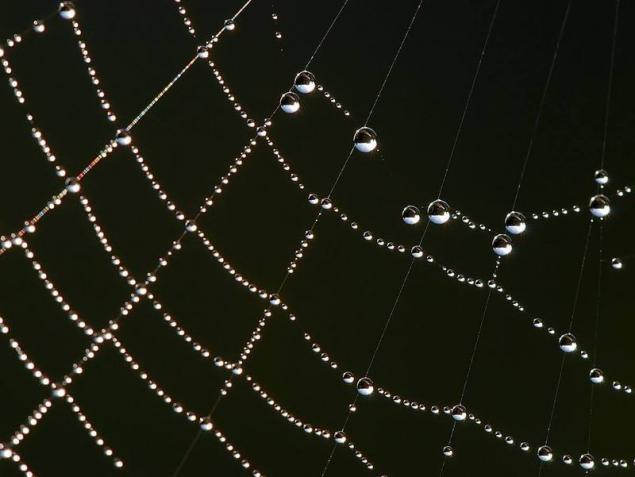
The web is one of the most impressive and mysterious materials in the natural world. Extremely high strength at relatively low weight make this material stronger and more reliable steel. Researchers have long wanted to create a synthetic version of the web, but until now all attempts were doomed.
The team from mit used 3D printing to create synthetic web to learn more about its structure. Researchers believe that this is the next step towards creation of fully artificial version. But work is just beginning.
"We are on track to develop a mathematical mechanism that makes the web so strong" — said the researcher of the University of Zhao Qing. published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: //estp-blog.ru/rubrics/rid-45367/

This area is developing continuously, therefore if you work in the construction industry or related areas, you will certainly need to know about new construction materials. At least in order to constantly stay "in the know". Now with the help of extrapolation, you can imagine which building materials and technological solutions will be in demand in the construction of buildings. We offer a short overview of the most promising of them.
GrapheneDespite the fact that graphene is not a new material used it is not the most practical way, since opening. After all, in theory, graphene is an excellent building material because it has incredible lightness and strength, comparable with steel and carbon fiber. Potentially graphene can be combined with more traditional materials to create strong structures, beams and cables that will allow you to build impressive structures.
However, graphene is so difficult to produce that builders rarely use this material. In the best case, this happens in small fragments in the context of complex and expensive projects. But the situation may soon change. Currently, one of the research centers in the U.S. are developing a new method of production of graphene using chemical vapor deposition of this material from the vaporous state. Ivan Vlasyuk, project Manager, believes the new technology will "greatly expand the potential applications of graphene". The next step is to reduce production costs of graphene and improve its accessibility to the material to be used as widely as possible.
If the price of graphene is comparable to the prices of traditional building materials in construction can expect a real graphene revolution.
"Roman" the concreteBuildings of Ancient Rome were able to stand for a very long time, so building material, manufactured according to the same principles, today the focus of attention of scientists. Researchers from the University of California made a breakthrough by revealing the secret of long life of the buildings of Ancient Rome. It turns out the Roman builders used a special recipe for making concrete.

In contrast to modern concrete, the builders of Ancient Rome were used for the production of lime mortar of volcanic rock. Without going into the intricacies of technology, we note that these rocks create a more regular crystal grid in the setting process of the concrete, making it very homogeneous. This material is resistant to corrosion and bind the structure more firmly. It also reduces the risk of microcracks in the concrete over time, significantly increasing the life expectancy of the material up to 2000 years.
But "Rome" concrete is not only stronger than its modern counterpart, it is also environmentally friendly. As is known, in the manufacture of Portland cement ingredients is heated to a temperature exceeding 1,400 degrees Celsius, which contributes to massive carbon dioxide emission. According to some estimates, this makes up 7% of all global carbon emissions. But "Rome" concrete needs no such heating, and this means that the new material is stronger and more environmentally friendly than traditional analogue.
"Green" concrete,But researchers from mit went further and developed the technology, which involves completely exclude the cement from the concrete! Scientists at the Department of civil and environmental engineering has offered to issue so-called "green" concrete, which for the production of concrete uses such organic materials as bones, shells, sponges, etc.

This design eliminates two major disadvantages of Portland cement — a large amount of energy required for its production, and the inevitable appearance of microcracks in the concrete formed over time. The truth is, this concrete is very expensive.

Another development, claiming the title of "green concrete", created by a team of specialists in one of Malaysian Universities. They went the other way and typical for the production of concrete components added recycled construction debris. The result is a cheap and environmentally friendly material, performs its function is not worse than the classical counterpart.
In fairness it should be noted that this technology of concrete production from construction waste appear everywhere, but hardly any of them comes to commercial use. It seems that the Malays had approached the closest.
Synthetic web

The web is one of the most impressive and mysterious materials in the natural world. Extremely high strength at relatively low weight make this material stronger and more reliable steel. Researchers have long wanted to create a synthetic version of the web, but until now all attempts were doomed.
The team from mit used 3D printing to create synthetic web to learn more about its structure. Researchers believe that this is the next step towards creation of fully artificial version. But work is just beginning.
"We are on track to develop a mathematical mechanism that makes the web so strong" — said the researcher of the University of Zhao Qing. published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: //estp-blog.ru/rubrics/rid-45367/
Fancy scooter with a ball instead of wheels
The Ulta Chaata device is able to collect solar energy and rainwater