198
How the disease is formed: The transfer of emotional damage to the body
Psycho-emotional factors play a big role in our lives. Modern osteopathy recognizes psycho-emotional damage as an important component in the development of osteopathic dysfunction as trauma or displacement in the vertebral-motor segment.
There are several mechanisms for the transfer of influence from the sphere of the psyche to the corporeal sphere of the musculoskeletal system.
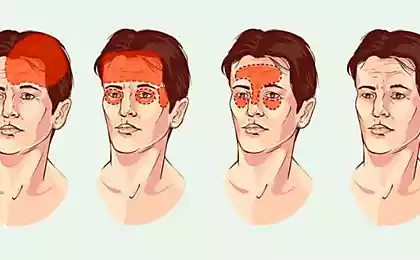
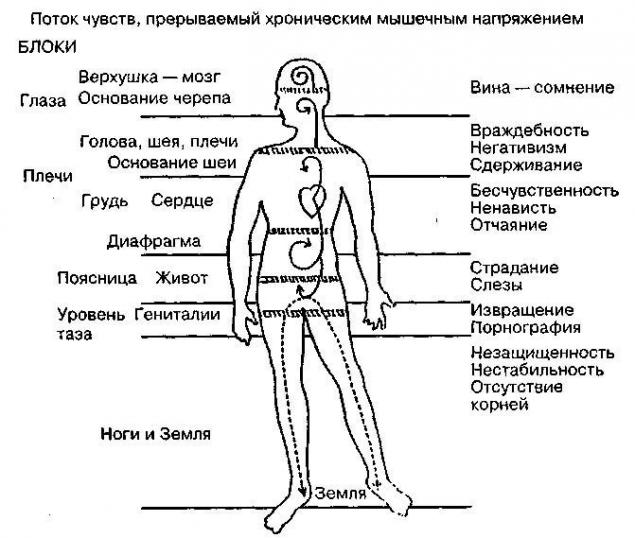
The first mechanism is the general tension of certain local muscle groups in the reflex response to stress.
In a nutshell, the like muscle tension is an echo of the bodily emotional reactions of our ancestors: tension of the muscles of the pelvis - a pinched tail in response to fear, tension of the shoulders and the collar area - standing on end hair in response to aggression, spasm jaw - grin as a manifestation of anger, etc.
Unfortunately, the mechanisms of arousal and inhibition in many people do not work effectively enough, and the spasm that arose on the emotional response lasts much longer than the time of exposure to stress. As a result, the displacement of adjacent structures and the “start” of the formation of the disease.
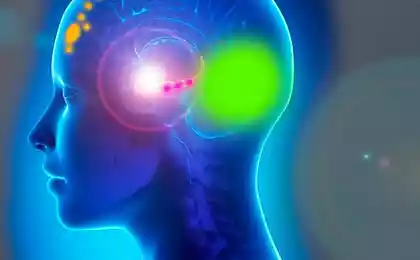
The second mechanism for transferring emotional damage to the body is associative fascial recording. The unfavorable situation experienced (sort, resentment, betrayal, fear, grief) is “recorded” as a spasm to the most weakened area of the body at the moment.
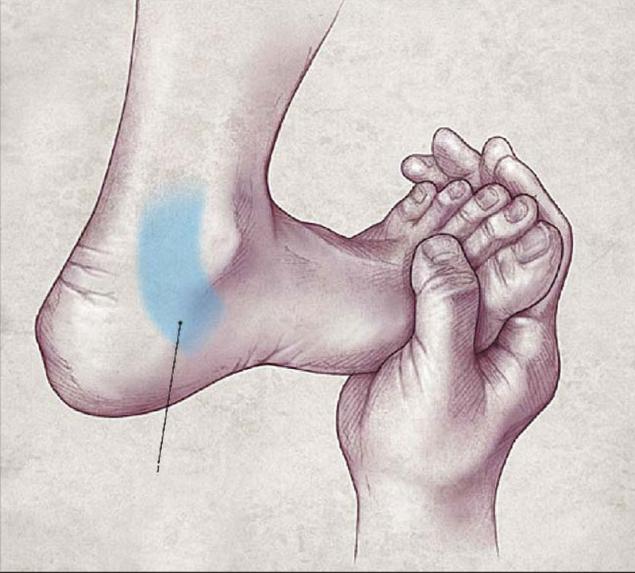
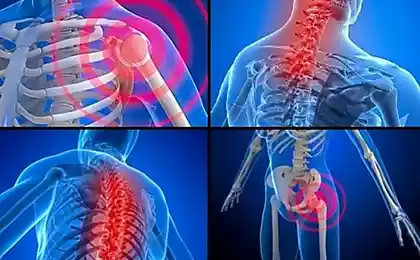
For example, 3 hours or even 3 days before the onset of a stressful situation, you twisted your leg. By the time of stress, the pain has already passed, and you have forgotten about the injury, but the area in the brain subthreshold, unconsciously signaling damage and maintaining a small protective spasm in the foot, persists. You get a psycho-emotional trauma, and a powerful surge of central pathological impulses is "recorded" on the already damaged, prepared for this area of the brain. Subthreshold impulse becomes permanent and persists for many years, creating conditions for muscle-fascial spasm, simulating ongoing damage to the foot. In response to this damage, the knee, hip joints, pelvic bones, sacrum and lumbar calf of the spine respond. The result is pain in the lower back.
An experienced osteopath is able to identify the connection of the disturbing area with the primary focus of the violation on the foot. But simple mechanical correction of the foot and relaxation of its muscles will not lead to the desired effect of recovery.
The osteopath may have several sessions with the foot. a pathological spasm will return - because it is supported by an impulse from the brain of the "seated" emotion, a long psycho-emotional experience.. To resolve this vicious circle, it is necessary to get to the cause of the defeat. Alternatively, you can ask the patient to mentally go through the traumatic emotional events of the past. At the moment when he remembers a situation that affects the foot, the fascial spasm will increase noticeably.
If you ask the patient to neutrally “observe” the remembered situation or use other psychotechnics of neutralization and disactualization, you can achieve the cessation of impulses from the brain and, as a result, the removal of pathological muscle tension. This will serve as a prerequisite for the restoration of normal functioning of the joints of the lumbar region and recovery. Such a primary effect of psychotrauma in the development of bodily diseases is not uncommon.
The above is one of the theories, sufficiently confirmed in practice, but does not reveal all the secrets why such a “record” occurs. By what criteria, whether in a random order or according to certain features from the list of injured areas of the body selected site for “recording”? Other osteopaths may have other points of view on this issue, it is only important that in practice All osteopaths recognize the importance of the psycho-emotional factor in the development of bodily diseases.
There is also an inverse relationship between constant pain and suffering in the body and the state of the mental sphere of a person.. Many patients seeking osteopathic care show signs of borderline psychiatry in the form of subdepressions, neuroses. It is not surprising, because the constant presence of discomfort, the need to limit your motor activity significantly reduce the quality of life and are a factor of permanent internal emotional “disorder”. In such situations, osteopathic care, the elimination of pain impulses and the restoration of body mobility lead to rapid normalization of mood, the return of joy and the ability to smile.
Also interesting: Osteopathy technique to restore vision
Remove back pain: gymnastics, recovery and treatment of the lower back, neck from the osteopath
The topic of psycho-emotional status and osteopathy is very broad, requires an individual dialogue with each patient.In some cases, a constant factor of exacerbation are relations in the family, with loved ones. In such situations, in addition to osteopathic help to the body, psychological work with the patient is necessary, explaining the causes to him and finding ways to change reactions to everyday stresses. (educating “neutrality”) or involving all parties to the conflict (children, spouses) for a joint solution, finding a compromise. published
Source: vk.com/wall-23903469?w=wall-23903469_4583
There are several mechanisms for the transfer of influence from the sphere of the psyche to the corporeal sphere of the musculoskeletal system.
The first mechanism is the general tension of certain local muscle groups in the reflex response to stress.
In a nutshell, the like muscle tension is an echo of the bodily emotional reactions of our ancestors: tension of the muscles of the pelvis - a pinched tail in response to fear, tension of the shoulders and the collar area - standing on end hair in response to aggression, spasm jaw - grin as a manifestation of anger, etc.
Unfortunately, the mechanisms of arousal and inhibition in many people do not work effectively enough, and the spasm that arose on the emotional response lasts much longer than the time of exposure to stress. As a result, the displacement of adjacent structures and the “start” of the formation of the disease.
The second mechanism for transferring emotional damage to the body is associative fascial recording. The unfavorable situation experienced (sort, resentment, betrayal, fear, grief) is “recorded” as a spasm to the most weakened area of the body at the moment.

For example, 3 hours or even 3 days before the onset of a stressful situation, you twisted your leg. By the time of stress, the pain has already passed, and you have forgotten about the injury, but the area in the brain subthreshold, unconsciously signaling damage and maintaining a small protective spasm in the foot, persists. You get a psycho-emotional trauma, and a powerful surge of central pathological impulses is "recorded" on the already damaged, prepared for this area of the brain. Subthreshold impulse becomes permanent and persists for many years, creating conditions for muscle-fascial spasm, simulating ongoing damage to the foot. In response to this damage, the knee, hip joints, pelvic bones, sacrum and lumbar calf of the spine respond. The result is pain in the lower back.
An experienced osteopath is able to identify the connection of the disturbing area with the primary focus of the violation on the foot. But simple mechanical correction of the foot and relaxation of its muscles will not lead to the desired effect of recovery.
The osteopath may have several sessions with the foot. a pathological spasm will return - because it is supported by an impulse from the brain of the "seated" emotion, a long psycho-emotional experience.. To resolve this vicious circle, it is necessary to get to the cause of the defeat. Alternatively, you can ask the patient to mentally go through the traumatic emotional events of the past. At the moment when he remembers a situation that affects the foot, the fascial spasm will increase noticeably.
If you ask the patient to neutrally “observe” the remembered situation or use other psychotechnics of neutralization and disactualization, you can achieve the cessation of impulses from the brain and, as a result, the removal of pathological muscle tension. This will serve as a prerequisite for the restoration of normal functioning of the joints of the lumbar region and recovery. Such a primary effect of psychotrauma in the development of bodily diseases is not uncommon.
The above is one of the theories, sufficiently confirmed in practice, but does not reveal all the secrets why such a “record” occurs. By what criteria, whether in a random order or according to certain features from the list of injured areas of the body selected site for “recording”? Other osteopaths may have other points of view on this issue, it is only important that in practice All osteopaths recognize the importance of the psycho-emotional factor in the development of bodily diseases.

There is also an inverse relationship between constant pain and suffering in the body and the state of the mental sphere of a person.. Many patients seeking osteopathic care show signs of borderline psychiatry in the form of subdepressions, neuroses. It is not surprising, because the constant presence of discomfort, the need to limit your motor activity significantly reduce the quality of life and are a factor of permanent internal emotional “disorder”. In such situations, osteopathic care, the elimination of pain impulses and the restoration of body mobility lead to rapid normalization of mood, the return of joy and the ability to smile.
Also interesting: Osteopathy technique to restore vision
Remove back pain: gymnastics, recovery and treatment of the lower back, neck from the osteopath
The topic of psycho-emotional status and osteopathy is very broad, requires an individual dialogue with each patient.In some cases, a constant factor of exacerbation are relations in the family, with loved ones. In such situations, in addition to osteopathic help to the body, psychological work with the patient is necessary, explaining the causes to him and finding ways to change reactions to everyday stresses. (educating “neutrality”) or involving all parties to the conflict (children, spouses) for a joint solution, finding a compromise. published
Source: vk.com/wall-23903469?w=wall-23903469_4583
Women 40+ don't let the hormones get the better of you!
6 best exercises to strengthen the lower back