614
Brain ecology

In recent decades, the average life expectancy of a person has been continuously increasing. But this process is accompanied by a serious increase in the incidence of entire groups of diseases. And if earlier the average person did not even live to the age when these diseases begin to manifest themselves, now he is forced to take some actions in advance to avoid them in the future, if, of course, in old age he wants to remain sane and not be a burden to his relatives. We talked about this with Professor Alexei Danilov, head of the project “Brain Ecology”.
- Alexey, first of all, tell us what is the project "Brain Ecology" and what does the word "ecology" mean in this case?
The main idea of the project “Brain Ecology” is to motivate people to look at the problem of health from the point of view of their own capabilities. Today, when it comes to health, people tend to seek high-tech medical care. But the World Health Organization estimates that our health depends on the health system by only 10%, 20% is determined by genetics, and the remaining 70% is determined by our way of thinking, lifestyle and environment. That is, our health depends much less on the doctor than on what we eat, drink and dress, what we do, what we think about and where we live. And within the framework of the project, we developed a simple and understandable system that shows how the factors that surround us affect our health. For people, this should be a reason to change their attitude to health.
Since we consider health issues in the framework of human interaction with the environment, here we are closely in touch with the science of human ecology, which studies his relationship with nature and changing conditions of existence. For this reason, the word “ecology” is included in the name of the project. The word “brain” appeared there, of course, also not by accident. For most people, it is a very valuable organ. Woody Allen once said, “The brain is my second favorite organ.” Secondly, a wonderful American doctor, Dr. Amen Daniel, wrote a book, Change Your Brain, Change Your Life, and that idea came very close to us. We can't do anything about our genetics, we can't always influence politics or climate or anything else. But we can change ourselves and our relationship to the world.
- The famous satirist Ambrose Bierce said, “The brain is the organ with which we think we think.” In this regard, the question arises: what is the brain in terms of modern concepts of science?
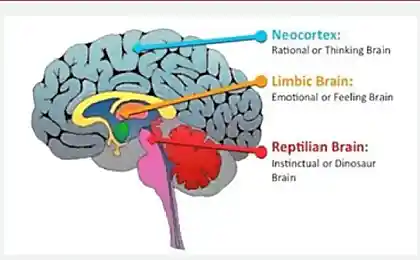
Another famous man, who is considered a great thinker and philosopher, at the end of his life said that “all I know is that I know nothing.” The same can be said about today’s ideas about the brain. While we are at the beginning of the way of understanding the mechanisms of its organization and action, there is an understanding that the brain is not an organ controlled by us, but a structure in which we ourselves are subordinate. The brain is the onboard computer of our body, it processes all the information received by a person, and only the brain depends on how it will dispose of it.
Ancient scientists thought the brain was just a large gland. For example, according to Aristotle, this gland produced the mucus necessary to cool the heat of the heart. One of the first who began to guess about the real role of the brain in our body was Claudius Galen, a doctor of the Roman Emperor Marcus Aurelius. He said that the brain is the focus of movement, sensitivity and mental activity.
The brain and its relationship with the body is a complex biochemical laboratory, but it can be argued that by changing our thinking, we can change the biochemistry and molecular biology of our body. For example, when a person smiles sincerely, thousands of endorphins are thrown out, which have a positive effect not only on the brain itself, but also on our blood vessels, cells, heart function and other organs. When a person is in fear, it leads to the release of other hormones and to completely different biochemical reactions. And they affect the body already negatively. That is, our thinking is a powerful tool that can make us stronger, stronger, more resilient, healthier or, conversely, lead to disease. Our life may be good or bad, but it is the brain that determines what it really is. Look around and you will see people who may be sweeping the streets, huddled in small rooms, have a small salary, but at the same time they smile, because they are quite happy with everything. And people with the same salary, but a different view of life, think it's terrible. So it's not life itself, it's not the facts themselves that make us happy or unhappy, but our ideas about them that are formed in our brains.
- Do we create ideals for ourselves and then pay for it with our health?
Health is largely determined by how happy we feel. There are countries like Bhutan, where everyone walks barefoot, lives in thatched houses, but is absolutely happy. Unfortunately, in Western culture, happiness is measured by a certain position in society, a certain social income, the presence of a car and a boat. And this boat must be several meters longer than the neighbor. And if you don't fit into that paradigm, you automatically become a loser and a loser. And from here arise stress, arterial hypertension, diabetes. Sometimes patients come to us who seem to have everything, but do not have happiness. And so they go to Tuva to the shamans, make bonfires there, live in dugouts, get closer to nature and two weeks later return completely different people!
The Roman emperor Diocletian (284-305), leaving fast, settled in his estate in the Salon and lived there alone for 8 years. When his associates once again tried to persuade him to return to power, he remarked: “If you had seen what kind of cabbage I grew, you would not have molested me with such trifles.”
Culture and education play a very important role. Grandparents, school, friends, television and the Internet are the environments that shape us, make us healthy or sick. Many diseases have a socio-cultural background. For example, the wave of obesity that swept the world, and one in three children suffer from it today, is primarily the result of a culture of food consumption imposed by society without corresponding energy expenditure. The reverse side is anorexia nervosa, when girls perceive themselves too fat. But in some cultures, for example, in Africa, this problem is not in principle, simply because they value completely different forms.
It also turns out that you can get your share of health, for example, by visiting a theater, reading a good book or simply walking in the park with your dog in the evening. There are studies that show that regular walks in the park, at least 3 times a week for 45 minutes, are equivalent to the action of antidepressants, but without the side effects that they have. We present the scientific evidence of how art, culture and education can help with health. Famous actress Ani Girardo at the end of her life suffered from Alzheimer's disease. She could not distinguish Pierre Richard from Alain Delon, but she remembered Shakespeare's sonnets, which she learned in her youth, and starred in films until the last days of her life. That is, our cultural level and intellectual potential help us cope with diseases when they arise. When we engage in intellectual activity, we increase the number of connections in our brain. In fact, the number and quality of connections between brain cells is what distinguishes one person from another. And if there is a problem, some of these connections can be broken, but the remaining consequences of the disease can be minimized. For example, if a person knows 5 foreign languages, then with a stroke, he may forget 3 languages, but the remaining two will still be able to speak. That is, he will not fall out of society. A woman speaks 21,000 words a day, a man only 7,000. Women, therefore, have more neural connections. Therefore, in the case of a stroke with left hemispheric lesions, speech disturbance in men will be observed 3 times more often than in women. Thus, women, training their brain, protect themselves from stroke.
After Einstein's death, his brain was removed from his body and placed in a formalin solution. Since Einstein was considered one of the most brilliant thinkers of the twentieth century, by studying his brain, scientists hoped to reveal patterns between genius and brain anatomy. However, no super features were identified. Einstein’s brain weighed 1,230 grams, which is even less than the average brain weight of an average adult male at that age of 1,400 grams. The researchers found that the regions of Einstein's brain responsible for speech and language were reduced, while the regions responsible for processing numerical and spatial information were enlarged. The concentration of neurons in 1 gram of the brain was higher than in average people. Einstein’s brain was also found to be 15 percent wider than that of a normal human.
Until recently, we had hoped that when the human genome was fully decoded, many of the problems we were talking about would be solved. But it turned out that only 2-3% of diseases have a clear genetic determinant. Most diseases - nervous, cardiovascular - have a polygenic nature, that is, different genes may be responsible for their clinical manifestation. It has been scientifically proven that the manifestation of many diseases is closely tied to our way of life. Epigenetics is the field of science that studies what happens to genes – what factors turn them on or off. So what we're actually looking for is the answer to the question, "How does a person's behavior in life affect the chances of a gene turning on or off?" For example, a person may be genetically predisposed to get diabetes at age 55. But if he is stressed, eats food, leads a sedentary lifestyle, he can accelerate this process and get sick at 45 years old. Or maybe vice versa - to give a delay, and then the disease will come only at 99 years. And scientists are now studying these mechanisms.
In recent years, scientists have made major strides in deciphering signals sent by the brain and creating brain-computer interfaces. Technology that allows you to control various electronic devices with the help of the power of thought has become a reality. One of the breakthrough projects in this area is conducted by the US Defense Advanced Research Agency. As part of the project, two probes were implanted in the brain of 55-year-old Jan Scheyerman, who suffers from paralysis of the arms and legs, in the area responsible for the movement of the right hand and arm. With their help, brain signals are read out, after decoding which the corresponding commands are fed to the mechanical hand. As soon as a woman thinks, “I raise my hand up,” the artificial hand immediately rises up. And during one of the latest experiments, the woman was entrusted with the management of flight simulators of the F-35 fighter and the single-engine Cessna aircraft. And Scheyerman coped with even this difficult task.
- Does the brain age with the body?
There are certain changes in the brain. Including, for example, the blood supply to the brain due to physiological extinction, some neurodegenerative diseases may wake up. But it is important to understand that the accumulation effect plays a fundamental role here. That is, some effects do not poison us immediately, but make themselves felt later, in older age. Even eating low-quality food can eventually lead to neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s disease. This is also a cumulative effect that makes itself felt in 20-30 years. Thinking about old age should be young.
Very often, we do not even realize that we are harming our brain, because we associate this or that factor with completely different organs. But along with these organs, the brain also suffers. When we breathe dirty air downtown, it's not just our lungs that suffer, it's our brains that suffer. When we wake up from the drill of an annoying neighbor at half past nine, not only the ears suffer, the brain suffers. When we drink an extra glass, we harm not only the liver, but also the brain. When we fight with our loved ones, the brain suffers too. And if we take even a little care of our brains, then all other organs will thank us.
- Why do some people manage to maintain clarity of thought until old age, while others lose this ability? What is the key to brain health and what should be done to keep the brain young in old age?
In our project, we rely on three whales. The basis of health and longevity is a culture of nutrition, it is Brain fitness, that is, gymnastics for the mind, and it is stress management, that is, stress management.
Food is like fuel for a car. But when we refuel the car, we take care that the gasoline was good, the car worked properly and did not break down. But without hesitation, we pour actually 76th or even 72nd gasoline into ourselves. Any car would immediately break down, and the body endures, but for the time being. Nerve cells are made up of what we eat. And if our nerves are covered with trans fats, the brain will give rise to some thoughts, and if we consume olive oil, it is completely different.
Exercise for the mind is just as important as muscle training, so people who maintain intellectual activity and do it regularly live longer. Remember the academician Likhachev, who looked brilliant in his old age, had a beautiful clear mind, a good speech. When you think about it, it activates certain areas of your brain. The blood supply increases, the brain develops. After all, when we pull up on the bar, our biceps become more powerful – with the brain the same thing. As an intellectual training, there can be a solution to crossword puzzles, and the resolution of some life problems, just treat them calmly, with understanding. We cannot completely get rid of stress or avoid it either, but you can learn to manage it and even enjoy it. There are special techniques for this. They don’t remove stress factors, but they train our brains to react differently to unfavorable stimuli.
Even a perfect tool like the brain can be fooled. And they do this with the help of optical illusions – errors in visual perception caused by the inaccuracy of the processes of unconscious correction of the visual image. One of the most famous illusions is Ames’s room. People of ordinary height in it seem dwarfs or giants. The secret of this amazing room is the location of its walls. The side farthest from the viewer is at an acute angle to one side and at a blunt angle to the other.
- And how effective are drugs for preventing and treating brain diseases, especially when compared to other ways, like the same brain training you just talked about?
The idea of our approach is not to contrast modern medicine and pharmacology with some alternative methods, but to use them in an integrative way. Depending on the situation, neurosurgical operations may be necessary, but sometimes we can help with other interventions. As an illustration, I will tell you about a special preparation "Tanakan", obtained from the tree of gingko biloba. It is a powerful antioxidant that is used to increase concentration, improve memory, thinking, blood circulation. So it was used in a very interesting experiment. One group of patients was given a placebo, that is, a pacifier, another group - Tanakan, a third group - placebo plus mental gymnastics, and the fourth group - Tanakan plus mental gymnastics. It turned out that the placebo along with mental gymnastics was slightly more effective than Tanakan. Tanakan was slightly more effective than placebo. But Tanakan together with mental gymnastics was 4 times more effective than just Tanakan, and 3 times more effective than just mental gymnastics. That is, the effect of the drug exists, but in parallel, gymnastics increases it several times.
The eye is a fairly simple optical system. But according to the laws of optics, the image on the retina is formed inverted. “Rightens” it our brain, thereby allowing you to better adapt to the world around you. However, this does not happen immediately – newborns see the world upside down.
In 1896, American psychologist George Stratton designed an invertoscope (pictured) – special glasses with which a normal, inverted image is projected onto the retina. But the person who dresses them “out of habit” will see everything upside down. However, if you wear these glasses all the time, after a few days the brain will again adapt us to reality and turn the image.
- Should the brain rest?
This is an extremely important issue, since the main, if I may say so, the disease of civilization is a violation of the regime of work and rest. Today it is proved that if a person has at least 4 breaks of 15 minutes, then for 7 hours of work in the office he will do more than 10 hours of continuous work. Therefore, in all offices, we recommend creating a stress management room where people can briefly step out of the context of their environment, close their eyes, listen to music, distract themselves. Then, returning to the workplace with a new energy boost, a person can do much more. This prevents the appearance of headache, the development of chronic fatigue syndrome.
Some offices even have sleep capsules installed. And if a person is given 15-20 minutes of sleep during the day, then after lunch his productivity doubles. And it's expensive. Sleep is also good skin, good mood and a long life.
Google's rest room.
- Does the statement “The best rest is a change of activity” work for the brain?
It works because it's the brain that gets tired of monotony and routine. In childhood, a frequent change of mental activity is especially necessary. A person’s concentration cycle is about 15-20 minutes, although it also depends on the person’s temperament and abilities.
- In conclusion, there are three main recommendations that you would give to our readers.
Love, live sincerely and do what you like.
5 rules for the collection and storage of seeds
The incredible story of three brothers cheetahs. It's hard to believe!