638
About human nature

Among the arguments against the policies of the left that I see again and again, is like "human nature will take its course" or "it is against human nature". I have even heard such an argument from the representative of the left movement — say, any system in the future should "consider human nature". It is quite obvious what it means — and do not have any additional questions. People are selfish. People are working solely in their own interests, and it is natural. But I'm sure it's not. In this post I hope to explain why.
The complexity of this topic, apparently, has always been recognized, but the approaches of philosophers, scientists and economists varied considerably over the centuries. In Ancient Greece it was believed that human nature is largely determined by destiny, because every person was created with the divine spark within.
As time went on, and a metaphysical look out of fashion, and philosophers began to rely on observation of human tendencies. Thomas Hobbes on this score were particularly pessimistic view of human nature is cruel to the core. After him, Rousseau noted that there is no predestination influencing human nature. He believed that morality is a natural and integral component of a person, and the establishment of institutions, languages and concepts (e.g., justice) is a necessary way of its development. Then the need for government and Commerce have undermined the foundations of human freedom.
After a massive recognition of the ideas of Darwin about evolution and natural selection, the idea that nature as a whole — there is a fierce competition, which confronts the individual with the individual for the sake of survival.
The complexity of Darwin's theory was quickly and wrongly reduced to a bad one, but a metaphorical slogan "Survival of the Fittest", and then (admittedly in hindsight) to words of Tennyson, "nature has claws and teeth covered in blood. Inevitably, this found an echo in the economic, social and political thought of the time. In fact, such a narrow view of evolution confirms class division and economic inequality of the Victorian Era. A society divided into classes and deeply unequal economic opportunity, suddenly finds justification and scientific rationale.
Darwin himself knew, of course, that this is a rough and excessive simplification and foresaw this misunderstanding, putting in the "Origin of species" that the phrase "survival of the fittest" was more a metaphor than an attempt to find a simple and clear formula of evolution.
The use of such ideas by the establishment to justify the status quo can be seen by returning to Ancient Greece. At that time, as the Greeks used the idea of metaphysical predetermination of the status quo, citizens, landowners and workers of non-citizens-slaves of capitalist society following the Industrial revolution used the same idea of "scientific power".
In the mid-twentieth century to explore the nature of man began to use game theory, and the first studies in this area have consequences, tangible even in the 21st century. Mathematicians working for the RAND Corporation, which developed the U.S. strategy for the cold war, embodied their ideas in game theory in General, and the idea that man is isolated, paranoid, and selfish creature. In addition, we have developed the idea that people acting solely in their own interests, is the cause of a stable society; the mathematician John Nash won the Nobel Prize by proving it mathematically.
The answer is that all rules of the games", developed at RAND, must be respected — that is, participants should behave selfishly and try to outwit other players. But when these ideas were tested in the RAND on real people, mathematicians found that in reality, people would rather cooperate than betray other members.
In particular, RAND developed a game designed to showcase it, is called "Prisoner's Dilemma" and can be described as follows:
"In the Prisoner's Dilemma is two criminals caught for a crime, but interrogated separately. The police have some evidence of only minor violations, but nothing that could be linked to more serious crime.
Prisoners agreed that would neither confess or to testify against each other if they are caught. If both criminals keep his word, they are guaranteed a small punishment. But the dilemma begins when the police offer each prisoner "to knock off" term in exchange for testimony against another criminal.
It seems that this is a good deal — confess and get a little time while your partner will get the maximum. But then you realize that it is suggested that you and your partner, so you both get the maximum sentence. That's the dilemma — whether to trust his partner, while keeping silent, or try to spend it to quickly get out of prison.
This game and how Nash used it to explain human nature, was picked up along with the paranoia of the time (at the peak of the Cold war). There has not been without its own paranoia Nash — he suffered from paranoid schizophrenia.
These ideas accidentally leaked in the minds of right-wing economists and politicians, culminating in the current neo-liberal economic thoughts in extremely individualistic Thatcherism and capitalism. Cooperation and altruism has been declared a myth, and it was assumed that each person will act solely in their own interests.
However in parallel with this, some biologists began to study what they considered unfounded and rejected poorly understood aspect of evolution. Biologists knew (in contrast to received wisdom) that the history of evolution is not consisted solely of violence, carnage and death. They knew that along with the competitive aspect, there was also cooperation and altruism, and some biologists tried to explain them from the point of view of evolution.
A significant contribution to the early 70s made by the American evolutionary biologist Robert Trivers, who proposed the theory of mutual (reciprocal) altruism and parental contribution. Reciprocal altruism can be described thus:
"...behavior in which the organism behaves in such a manner that temporarily reduces its fitness while the fitness of another organism increases, expecting that the second body will later behave in the same way."
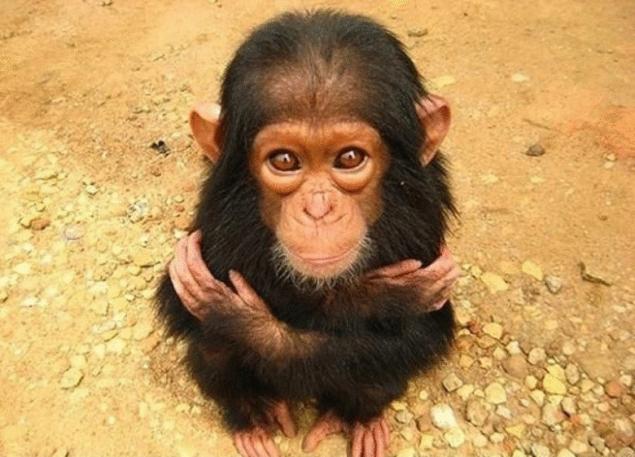
Examples of reciprocal altruism in nature due to, for example vampireville bats sometimes regurgitate blood to feed each other. Dolphins often come to the aid of people and animals. Chimpanzees, according to the research Institute of evolutionary anthropology, max Planck society, behave altruistically, even towards genetically distant individuals. According To Felix Warneken:
"Chimpanzees and their offspring demonstrate that up to a certain level of altruism is innate and is not just a factor of education. People say that we behave altruistic because our parents taught us this, and initially children are selfish. But it turns out that culture is not the only source of altruism."
And we know from our own experience that people work together all the time and in different situations, and often demonstrate selfless acts for the good of the group or another person. We see cooperation all around us — from trade unions to workplaces to the military associations during the war. All these actions require cooperation and sacrifice for the benefit of others.
As noted by Peter George. Richerson, Robert T. Boyd and Joseph Henrich in the work entitled "the Cultural evolution of human cooperation", the evidence of human cooperation is extensive and diverse". They cite studies of the prisoner's Dilemma, which show that "people tend to cooperate, even with strangers," and they often "make the altruistic choice, but such cooperation depends on many factors that have great influence on human behavior.
It may seem obvious, but as noted by Richardson associates, "people from different communities behave differently because their beliefs, skills, mental models, values, preferences and habits that they have absorbed from a long stay in societies with different institutions". This was confirmed during multiple repetitions of the prisoner's Dilemma and sudden manifestations of trust and consensus.
In the book Carl Sagan and Ann Druyan "shadows of forgotten ancestors: a Search for who we are", is an experiment in which macaques were fed only if they decide to pull the chain and shock an unrelated macaque whose agony can be directly see through the one way glass. Otherwise, monkeys would starve. After realizing this relationship quickly macaques refused to pull a chain: in one case, 13% of the monkeys agreed, the capital and 87% preferred to starve. Macaques who were electrocuted in previous experiments, showed even less desire to pull the chain."
In "the Evolution of mutual assistance" by Robert Axelrod and William D. Hamilton recognizes that mutual aid is widespread intra - and interspecific phenomenon. Based on the theories of Robert Trivers, Axelrod and Hamilton used the prisoner's Dilemma to suggest possible mechanisms of evolution of cooperation. The mechanism of "tit for tat", which had great success during these experiments is comparable to the idea of Triversa about reciprocal altruism. Indeed, the conclusion drawn in connection with these studies, States:
"Darwin's emphasis on individual advantage has been formalized in terms of game theory. This creates conditions in which may develop cooperation based on reciprocity"
In some situations, it seems understandable that people will cooperate, in others they will act in their own interests. Of course, there are a tremendous number of variables influencing it, in addition to the situation. Personality, her values and beliefs, among other things, play an important role. But on average case, it will be the importance of the political and economic status quo?
It seems that the issue has been exhausted. The media and the government have always been very influential. The impact of the previously mentioned experiments, RAND still felt. Paranoid view of the world embodied in these experiments, entrenched in the heart of the Western capitalist institutions for several decades, this was especially noticeable in the 80s in the UK and USA and most tragically in Chile under Pinochet. Despite this, people continue to interact in different circumstances, despite the duress (sometimes very cruel) to behave differently.
As mentioned earlier regarding the work of the "Cultural Evolution of Human cooperation" Richardson, a fellow of the Institute solve the problem." A number of conclusions about human societies that depend on social institutions in which we act.
Politics, media and social norms will influence individual behaviour to a greater or lesser extent. And if we turn our attention to the General tone closeinternal of individualism presented to us by politicians and mass media, we find that this view of humanity has seeped into the daily thought and it's not a coincidence, then where did public institutions is a complex topic seem to have realized recently. But companies and communities began their development much earlier as a consequence of the development of the human brain.
The human brain became more and more, women had to bear children earlier and earlier, and the more I become the brain, the more difficult was the process of childbirth. This in turn meant that human babies were born helpless and stay that way for a long time — for several years. Human babies are also born without a large amount of instinctive knowledge and behaviour, which they have to learn from my elders. Extended family members were living together for this purpose, and with the change of the number and type of necessary knowledge, companies and communities is changing.
The description of the General history of human institutions is not the purpose of this post. Different people at different times came to different solutions to the problems they faced. But as we can see, public institutions can compel the majority to work for the benefit of the interest of the minority. Capitalism, for example, have used Darwin's ideas and developed them to their logical conclusion — social Darwinism. Later the ideas of the mathematicians at RAND were also used to strengthen the grip of capitalism and to zacamintului in the minds of people the idea of war of all against all and the ego, which thrives capitalism. For the survival of capitalism requires the separation, inequality and greed, and the ideas came from RAND to the influence of neoliberal thought, it provided a mathematical basis, although these models are based on some initial assumptions, the falsity of which has been proven.
These ideas can be countered by many things — from changes in state and market intervention system to eliminate capitalism and create a workers ' state. Or until the elimination of capitalism and the state. It's just come to grips with where ideas come from "human nature". This argument seems to be self-sufficient and simple, but it is based on a mixture of erroneous assumptions and institutional propaganda. Capitalism has long used the combination of these arguments and coercion using laws and state violence in order to strengthen its status quo and to suppress opposition in all possible forms. People living under this yoke, to continue to resist this violence. Why is this happening?
Peter Kropotkin argued in "Mutual aid as a factor of evolution", that the natural tendency of man is far from battle, conflict and violence and cooperation and mutual aid are the key criteria of evolutionary success. Of course, Kropotkin somewhere might exaggerate, but in General was right. Stephen Jay Gould noted that the opinion of Kropotkin and many Russian intellectuals about the ideas of Darwin and their overall Malthusian tone was partly due to the cultural differences and their experiences of life in Russia, while Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace lived in the imperialist, industrial and deeply capitalist Britain.
Since then, we can see that the ideas of altruism and cooperation are studied in detail from the perspective of evolutionism. It turned out that humans, primates, and less complex types are actively cooperating with both related and unrelated individuals, and that humans and primates have a biological predisposition to altruism and even heroism.
It seems that this innate tendency is not a product only of culture, but culture and experience are able to build, develop and change the nature of the manifestations of these trends. "How can we implement these ideas, given the nature of man?" — this is incorrect formulation of the question. "As human nature can help these ideas?", "What aspects of human nature should inspire us?" — issues should sound that way.
The ideals of capitalism has brought man a lot of suffering. The concentration of wealth and private property, exploitation of labor, use of land for profit, the brutal suppression of the opposition, the exploitation of democracy, information control, the huge gap between rich and poor, excess food and medical supplies from the rich, while poor die of starvation and disease. However, attempts to counter this system with the help of the state also led to the suppression, poverty, injustice and cruelty — to all crimes committed capital. It is proved that such regimes are nothing but a travesty of the ideals of the left, no matter how good were the intentions of their initiators.
So, if the capitalist and Communist regimes inevitably lead to suppression, how can they be opposite each other? There may be a solution? Both modes require control of the minority over the majority. Both require strict laws and coercion to action. Both essentially serve the interests of the elite instead of interests of the masses, and both modes need paranoid ideas of conspiracy and even violent pressure to achieve their goals. Here's why you should root out conspiracy ideas and the cult of violence. The power and control elite need to replace direct democracy in which everyone can participate. The tyranny of capital must be eliminated. No work can not be operated for someone else's profit. Wealth should not concentrate in few hands. Wealth should belong to all.
People have the ability to individualize, and for cooperation, for altruism and heroism. The case in cultural terms, the level of education and in a specific situation — that is what determines what aspects of human nature manifest themselves. Society itself and its institutions significantly affect it. Cooperation, altruism and heroism must be valued above selfishness. If you manage to create such a society, we will be able to erase the boundary between altruism and selfishness, and to make this cooperation real.
materials libcom.org
Source: www.anarcho-news.com