461
How the gut flora controls the behavior of the person
Bacteria that form the microflora of the intestines, can control our nutrition to ensure an optimal environment such assumption was put forward by a group of biologists from the University of San Francisco, Arizona and new Mexico, published their report in the journal "BioEssays".
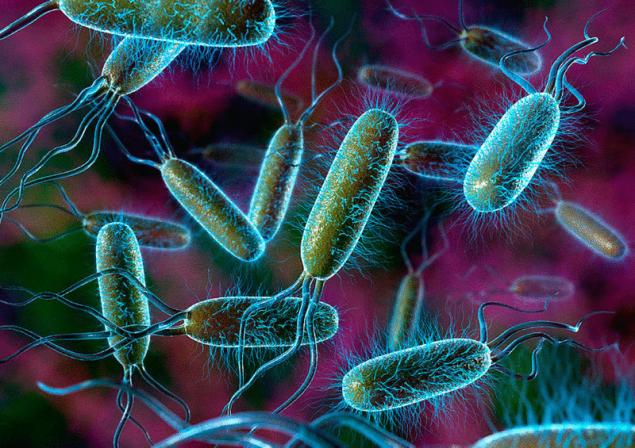
Their study aimed at the development of previous works to identify the relationship between intestinal microflora and human physiology, was carried out with the support of the American community in the fight against cancer, the Centre for lung cancer Bonnie J. The'addario, Institute for advanced study in Berlin and the National Institute of health, USA.
"Bacteria of the intestinal microflora have manipulative capabilities," says Dr. Carlo Mali. "There is a conflict of interest between various groups of bacteria of the microflora. Some of them coincide with our gastronomic purposes, others are contrary to them."
Can bacteria microflora to arouse our appetite?
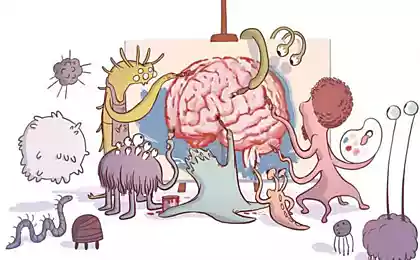
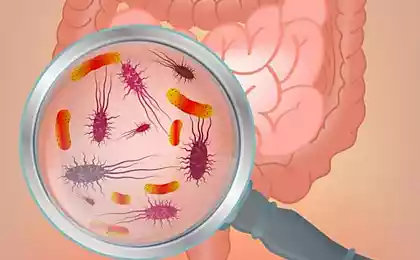
In the digestive tract of humans lives such a lot of bacteria (their number is hundreds of times greater than the number of our cells) that some scientists have come up with to describe the collective term for ecosystems – the "microbiome" or gut microbiota. Within this ecosystem of different types of microorganisms have different goals, so their number increases or decreases depending on the characteristics and composition of the habitat.
One of the main factors determining the state of our intestinal environment is the food we eat. Some gut bacteria prefer to eat fats, while others sugars. On this basis, scientists have suggested that intestinal bacteria probably are actively trying to manipulate the chemical composition of the environment for reasons of personal gain. This, in turn, may mean manipulation of our behavior by stimulating the appetite for other foods, our culinary preferences, or, conversely, the feeling of disgust when eating certain foods.
Despite the absence of direct evidence of such effects, the scientists were interested in the results of one study that found a difference in the composition of microbial metabolites (products of metabolism) in the urine of those people who recognize their passion for chocolate and those who consider themselves indifferent to it. These differences were recorded even in conditions where both groups of subjects received identical diet.
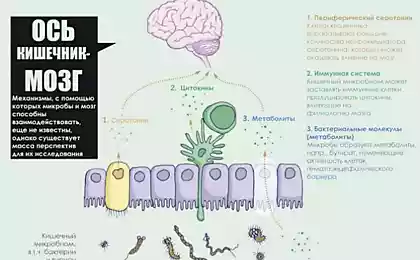
Still haven't found out what exactly is the mechanism by which bacteria can manipulate our behavior, there is a serious theoretical substantiation of this possibility. Studies have confirmed the existence of a strong relationship between the state of the microflora and the immune, nervous and endocrine (hormonal) systems of the human body. Some scientists believe that bacteria can distinguish certain signal molecules affecting the activity of the decimal cranial nerve extending from the bowel to the brain.
"Microbes have the ability to control our behavior and mood, sending various nerve signals decimal cranial nerve, changing taste receptors, producing toxins to make us feel unwell, as well as "chemical reward", causing a good feeling", said one of the leaders of the study Dr. Atena Octipus. Another study has revealed that people who consumed a probiotic drink with folic acid really improved the mood, but only in those cases where it was preceded by fatigue and depression.
The potential changes of the diet
Even if the bacteria can really affect our behavior, we are still far from defenseless. Because diet is a major factor in determining the predominant type of bacteria in our gut. For example, in the intestines of people living in Japan contains a special type of bacteria that promotes digestion of seafood and seaweed.
In fact, the experiments show that we can change the composition of gut microbiota in the space of 24 hours after changing our diet. "Our diet has a huge impact on populations of microorganisms in the gut," says Dr. Mali. "It's a complete ecosystem and it is able to respond to change in a matter of minutes."
Scientists were able to confirm that the changes of microflora caused on the one hand a change of diet or probiotic preparations, or on the other hand, taking antibiotics – can have a huge impact on human health.
"Studies of the microbiome can have a great potential to prevent a number of diseases, from obesity and diabetes to cancer of the gastrointestinal tract," says Dr. Octipus. In his opinion, scientists today are only on the distant approaches to the understanding of the importance of gut microbiota for human health and life.
source: mixednews.ru
Source: /users/1077

Their study aimed at the development of previous works to identify the relationship between intestinal microflora and human physiology, was carried out with the support of the American community in the fight against cancer, the Centre for lung cancer Bonnie J. The'addario, Institute for advanced study in Berlin and the National Institute of health, USA.
"Bacteria of the intestinal microflora have manipulative capabilities," says Dr. Carlo Mali. "There is a conflict of interest between various groups of bacteria of the microflora. Some of them coincide with our gastronomic purposes, others are contrary to them."
Can bacteria microflora to arouse our appetite?
In the digestive tract of humans lives such a lot of bacteria (their number is hundreds of times greater than the number of our cells) that some scientists have come up with to describe the collective term for ecosystems – the "microbiome" or gut microbiota. Within this ecosystem of different types of microorganisms have different goals, so their number increases or decreases depending on the characteristics and composition of the habitat.
One of the main factors determining the state of our intestinal environment is the food we eat. Some gut bacteria prefer to eat fats, while others sugars. On this basis, scientists have suggested that intestinal bacteria probably are actively trying to manipulate the chemical composition of the environment for reasons of personal gain. This, in turn, may mean manipulation of our behavior by stimulating the appetite for other foods, our culinary preferences, or, conversely, the feeling of disgust when eating certain foods.
Despite the absence of direct evidence of such effects, the scientists were interested in the results of one study that found a difference in the composition of microbial metabolites (products of metabolism) in the urine of those people who recognize their passion for chocolate and those who consider themselves indifferent to it. These differences were recorded even in conditions where both groups of subjects received identical diet.
Still haven't found out what exactly is the mechanism by which bacteria can manipulate our behavior, there is a serious theoretical substantiation of this possibility. Studies have confirmed the existence of a strong relationship between the state of the microflora and the immune, nervous and endocrine (hormonal) systems of the human body. Some scientists believe that bacteria can distinguish certain signal molecules affecting the activity of the decimal cranial nerve extending from the bowel to the brain.
"Microbes have the ability to control our behavior and mood, sending various nerve signals decimal cranial nerve, changing taste receptors, producing toxins to make us feel unwell, as well as "chemical reward", causing a good feeling", said one of the leaders of the study Dr. Atena Octipus. Another study has revealed that people who consumed a probiotic drink with folic acid really improved the mood, but only in those cases where it was preceded by fatigue and depression.
The potential changes of the diet
Even if the bacteria can really affect our behavior, we are still far from defenseless. Because diet is a major factor in determining the predominant type of bacteria in our gut. For example, in the intestines of people living in Japan contains a special type of bacteria that promotes digestion of seafood and seaweed.
In fact, the experiments show that we can change the composition of gut microbiota in the space of 24 hours after changing our diet. "Our diet has a huge impact on populations of microorganisms in the gut," says Dr. Mali. "It's a complete ecosystem and it is able to respond to change in a matter of minutes."
Scientists were able to confirm that the changes of microflora caused on the one hand a change of diet or probiotic preparations, or on the other hand, taking antibiotics – can have a huge impact on human health.
"Studies of the microbiome can have a great potential to prevent a number of diseases, from obesity and diabetes to cancer of the gastrointestinal tract," says Dr. Octipus. In his opinion, scientists today are only on the distant approaches to the understanding of the importance of gut microbiota for human health and life.
source: mixednews.ru
Source: /users/1077
Exercise “Golden fish” for the spine, Katsudzo Niche
Products with high iron content at night disrupt circadian cycle in the liver.