229
CELIACIA – Learn all about gluten intolerance!
Celiac disease (gluten enteropathy) - a disease characterized by chronic inflammation of the mucosa of the small intestine, accompanied by a violation of absorption and resulting from gluten intolerance (protein, which is contained in grains: wheat, rye and barley). The composition of gluten protein includes L-gliadin - a substance that has a toxic effect on the mucosa and leads to a violation of the absorption of nutrients in the intestine. Most often (in 85% of cases), the complete elimination of gluten from the diet causes the restoration of the functionality of the small intestine after 3-6 months.
With celiac disease, characteristic atrophic changes in the villi of the mucous membrane of the small intestine are noted. The disease is more typical for women, they suffer from celiac disease twice as often as men.

Etiology and pathogenesis of celiac disease
Celiac disease has a genetic predisposition. This is confirmed by the detection of violations of the small intestinal wall in 10-15% of family members (relatives of the first degree) of patients suffering from this disease.
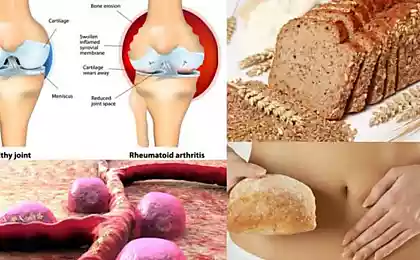
The dependence of morbidity on immune status was also noted. In the body of patients with celiac disease, an increase in antibody titers to L-gliadin, tissue transglutaminase and endomyosin (a protein contained in smooth muscle fibers) is noted. Confirm the immune dependence of the disease and often concomitant pathologies that have an autoimmune nature (type I diabetes, connective tissue diseases, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune thyroiditis, herpetiform dermatitis, Sjogren's syndrome).
Some congenital or acquired features of the small intestine contribute to the occurrence of increased sensitivity of intestinal epithelium cells to gliadin. Such conditions include enzyme deficiency, as a result of which peptides are poorly broken down (and there is no complete breakdown of gliadin). The accumulation of gliadin in the intestine contributes to the manifestation of its toxic effect.
Autoimmune disorders in cases where epithelial cells of the intestine become a target for their own antibodiesThey reduce their protective properties and increase sensitivity to gliadin. In addition, the factors contributing to the occurrence of gliadin intolerance are genetically determined specific characteristics of the receptors of the cell membrane of the intestinal epithelium, as well as the result of changes in the receptor apparatus by certain viruses.
Symptoms of Celiac Disease
Clinical signs of celiac disease are diarrhea, steatorrhea, weight loss, polyhypovitaminosis and other manifestations of malabsorption syndrome.
Celiac disease in children begins to appear usually at 9-18 months. There is a frequent and liquid stool with a large amount of fat and there is a decrease in body weight, stunting.
In adults, the deployment of clinical symptoms of celiac disease can be triggered by pregnancy, surgical interventions, infection.
People suffering from celiac disease are often noted tendency to drowsiness, reduced efficiency, often rumbling in the stomach, flatulence, instability of the chair (diarrhea, followed by constipation). In elderly patients, pain and aches in the bones, muscles may be noted.
The chair is usually frequent (5 or more times a day), liquid, frothy with the remains of undigested food. With prolonged diarrhea, there is a likelihood of developing signs of dehydration: dry skin and mucous membranes.
The progression of malabsorption syndrome leads to the development of severe disorders of internal homeostasis of the body.
In clinical gastroenterology differ celiac:
In women, the development of clinical symptoms begins in 30-40 years, in men in 40-50 years.
Complications of celiac disease
Patients with celiac disease belong to the group of increased risk of bowel cancer (intestinal lymphoma, adenocarcinoma). This type of malignant tumor develops in 6-8% of patients, most often after 50 years. The occurrence of a malignant neoplasm is suspected if the clinical manifestations of celiac disease resumed against the background of a gluten-free diet.
Another possible complication of celiac disease is ulcerative neinoileitis (inflammation with a tendency to ulcerate the wall of the skinny and ileum). It is characterized by the development of acute pain in the abdomen, fever. The development of this condition threatens with internal bleeding, perforation of the wall of the small intestine, peritonitis.
With severe insufficiency of iron absorption, iron deficiency anemia develops. Sometimes it becomes the only manifestation of the disease (with erased and latent form).
Fertility disorders, infertility can be the result of long-existing malabsorption syndrome. Also, a prolonged violation of absorption leads to polyhypovitaminses, protein deficiency, disorders of mineral metabolism.
Lack of vitamin D in combination with a reduced intake of calcium in the body helps to reduce bone density, their brittleness. In 30-35% of cases, patients with celiac disease decrease in the size of the spleen, 70% of patients note arterial hypotension.
Diagnosis of celiac disease
Most specific technique celiac is determination in the blood of antibodies to gliadin and tissue transglutaminase. The sensitivity of the technique is 100%, its specificity for this pathology is about 95-97%.
In addition, it is possible to biopsy the mucosa of the small intestine and determine the existing atrophy (smoothing) of villi, as well as the presence of clusters of lymphocytes in the mucosa.
Additional methods for clarifying the patient's condition are endoscopic examination of the small intestine, the Schilling test and a test with D-xylose, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, computed tomography, MRI angiography of mesenterial vessels, contrast radioscopy gut.
Treatment of celiac disease
The purpose of therapy for celiac disease is to restore bowel function, normalize body weight and correct the deficiency of necessary substances.
Pathogenetic treatment consists in compliance with the agluten diet, that is, direct avoidance of the damaging factor. A gluten-free diet is necessary throughout life. Most often (in 85% of cases), this measure leads to the subsidence of symptoms and the restoration of normal bowel activity. As a rule, the final recovery occurs no earlier than in 3-6 months, so adjust the content of substances necessary for the body is required throughout the recovery time. If necessary, parenteral nutrition, the introduction of iron and folic acid preparations, salt solutions, calcium, vitamins are prescribed.
Those patients who do not detect a positive effect of the diet are prescribed hormonal drugs (prednisolone) for 6-8 weeks as anti-inflammatory therapy.
The lack of positive dynamics in the exclusion of gluten from the diet for three months may indicate that the diet is not fully followed, with violations, or there are concomitant diseases. (insufficiency of disaccharidase, Addison’s disease, small intestinal lymphoma, ulcerative naynitis, giardiasis, lack of minerals in the diet: iron, calcium, magnesium).
In such cases, additional diagnostic measures are carried out to identify these conditions. If all possible reasons for the lack of improvement are excluded, hormone therapy is prescribed. After three months of the course of prednisolone, a biopsy of the small intestine is performed.
gluten-free diet
Gluten is found in the following products:
In small concentrations, gluten can be found in sausages and sausages, canned meat and fish, chocolate, ice cream, mayonnaise and ketchup, various sauces, instant coffee and cocoa powder, soy products, instant soups, broth cubes, products containing malt extract. From drinks it is necessary to abandon beer, kvass, vodka.
Often patients with celiac disease should limit the consumption of whole milkThey may have lactose (milk sugar) intolerance. Currently, there are special dietary gluten-free products (marked with crossed-out spike).
Prevention of celiac disease
There is no primary specific prevention of celiac disease. Secondary prevention of the development of clinical symptoms is to follow a gluten-free diet. With celiac disease in close relatives, it is desirable to conduct a periodic examination for the detection of specific antibodies.
Pregnant women suffering from celiac disease are at risk for developing heart defects in the fetus. Pregnancy in such women should be carried out with increased attention.
Prognosis and medical examination
It is not currently possible to correct the sensitivity of epithelium cells to gluten, so patients with celiac disease should follow a gluten-free diet throughout their lives. Careful adherence to it leads to the preservation of quality and life expectancy. With non-compliance with the diet, the survival rate drops sharply, cases of death among patients with celiac disease who violate the gluten-free diet are 10-30%, while with strict adherence to the diet, this figure does not exceed one percent.
All faces, celiacshould be on the dispensary register with a gastroenterologist and be examined annually. For patients who react poorly to the exclusion of gluten from the diet, dispensary observation is indicated twice a year. The prognosis is noticeably worse if this disease is complicated by the occurrence of small intestinal lymphoma. published
P.S. And remember, just changing our consumption – together we change the world!
Join us on Facebook, VKontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: www.krasotaimedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_gastroenterologia/celiac
With celiac disease, characteristic atrophic changes in the villi of the mucous membrane of the small intestine are noted. The disease is more typical for women, they suffer from celiac disease twice as often as men.

Etiology and pathogenesis of celiac disease
Celiac disease has a genetic predisposition. This is confirmed by the detection of violations of the small intestinal wall in 10-15% of family members (relatives of the first degree) of patients suffering from this disease.
The dependence of morbidity on immune status was also noted. In the body of patients with celiac disease, an increase in antibody titers to L-gliadin, tissue transglutaminase and endomyosin (a protein contained in smooth muscle fibers) is noted. Confirm the immune dependence of the disease and often concomitant pathologies that have an autoimmune nature (type I diabetes, connective tissue diseases, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune thyroiditis, herpetiform dermatitis, Sjogren's syndrome).
Some congenital or acquired features of the small intestine contribute to the occurrence of increased sensitivity of intestinal epithelium cells to gliadin. Such conditions include enzyme deficiency, as a result of which peptides are poorly broken down (and there is no complete breakdown of gliadin). The accumulation of gliadin in the intestine contributes to the manifestation of its toxic effect.
Autoimmune disorders in cases where epithelial cells of the intestine become a target for their own antibodiesThey reduce their protective properties and increase sensitivity to gliadin. In addition, the factors contributing to the occurrence of gliadin intolerance are genetically determined specific characteristics of the receptors of the cell membrane of the intestinal epithelium, as well as the result of changes in the receptor apparatus by certain viruses.
Symptoms of Celiac Disease
Clinical signs of celiac disease are diarrhea, steatorrhea, weight loss, polyhypovitaminosis and other manifestations of malabsorption syndrome.
Celiac disease in children begins to appear usually at 9-18 months. There is a frequent and liquid stool with a large amount of fat and there is a decrease in body weight, stunting.
In adults, the deployment of clinical symptoms of celiac disease can be triggered by pregnancy, surgical interventions, infection.
People suffering from celiac disease are often noted tendency to drowsiness, reduced efficiency, often rumbling in the stomach, flatulence, instability of the chair (diarrhea, followed by constipation). In elderly patients, pain and aches in the bones, muscles may be noted.
The chair is usually frequent (5 or more times a day), liquid, frothy with the remains of undigested food. With prolonged diarrhea, there is a likelihood of developing signs of dehydration: dry skin and mucous membranes.
The progression of malabsorption syndrome leads to the development of severe disorders of internal homeostasis of the body.
In clinical gastroenterology differ celiac:
- typical (Develops in the first or second year of life, has characteristic clinical manifestations),
- erased(manifested by extraintestinal symptoms: iron deficiency, anemia, bleeding, osteoporosis),
- latent (without any complaints). Latent form often occurs in the elderly.
In women, the development of clinical symptoms begins in 30-40 years, in men in 40-50 years.
Complications of celiac disease
Patients with celiac disease belong to the group of increased risk of bowel cancer (intestinal lymphoma, adenocarcinoma). This type of malignant tumor develops in 6-8% of patients, most often after 50 years. The occurrence of a malignant neoplasm is suspected if the clinical manifestations of celiac disease resumed against the background of a gluten-free diet.
Another possible complication of celiac disease is ulcerative neinoileitis (inflammation with a tendency to ulcerate the wall of the skinny and ileum). It is characterized by the development of acute pain in the abdomen, fever. The development of this condition threatens with internal bleeding, perforation of the wall of the small intestine, peritonitis.
With severe insufficiency of iron absorption, iron deficiency anemia develops. Sometimes it becomes the only manifestation of the disease (with erased and latent form).
Fertility disorders, infertility can be the result of long-existing malabsorption syndrome. Also, a prolonged violation of absorption leads to polyhypovitaminses, protein deficiency, disorders of mineral metabolism.
Lack of vitamin D in combination with a reduced intake of calcium in the body helps to reduce bone density, their brittleness. In 30-35% of cases, patients with celiac disease decrease in the size of the spleen, 70% of patients note arterial hypotension.
Diagnosis of celiac disease
Most specific technique celiac is determination in the blood of antibodies to gliadin and tissue transglutaminase. The sensitivity of the technique is 100%, its specificity for this pathology is about 95-97%.
In addition, it is possible to biopsy the mucosa of the small intestine and determine the existing atrophy (smoothing) of villi, as well as the presence of clusters of lymphocytes in the mucosa.
Additional methods for clarifying the patient's condition are endoscopic examination of the small intestine, the Schilling test and a test with D-xylose, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, computed tomography, MRI angiography of mesenterial vessels, contrast radioscopy gut.
Treatment of celiac disease
The purpose of therapy for celiac disease is to restore bowel function, normalize body weight and correct the deficiency of necessary substances.
Pathogenetic treatment consists in compliance with the agluten diet, that is, direct avoidance of the damaging factor. A gluten-free diet is necessary throughout life. Most often (in 85% of cases), this measure leads to the subsidence of symptoms and the restoration of normal bowel activity. As a rule, the final recovery occurs no earlier than in 3-6 months, so adjust the content of substances necessary for the body is required throughout the recovery time. If necessary, parenteral nutrition, the introduction of iron and folic acid preparations, salt solutions, calcium, vitamins are prescribed.
Those patients who do not detect a positive effect of the diet are prescribed hormonal drugs (prednisolone) for 6-8 weeks as anti-inflammatory therapy.
The lack of positive dynamics in the exclusion of gluten from the diet for three months may indicate that the diet is not fully followed, with violations, or there are concomitant diseases. (insufficiency of disaccharidase, Addison’s disease, small intestinal lymphoma, ulcerative naynitis, giardiasis, lack of minerals in the diet: iron, calcium, magnesium).
In such cases, additional diagnostic measures are carried out to identify these conditions. If all possible reasons for the lack of improvement are excluded, hormone therapy is prescribed. After three months of the course of prednisolone, a biopsy of the small intestine is performed.
gluten-free diet
Gluten is found in the following products:
- bread and any products of wheat, oatmeal, barley and rye flour,
- pasta,
- semolina.
In small concentrations, gluten can be found in sausages and sausages, canned meat and fish, chocolate, ice cream, mayonnaise and ketchup, various sauces, instant coffee and cocoa powder, soy products, instant soups, broth cubes, products containing malt extract. From drinks it is necessary to abandon beer, kvass, vodka.
Often patients with celiac disease should limit the consumption of whole milkThey may have lactose (milk sugar) intolerance. Currently, there are special dietary gluten-free products (marked with crossed-out spike).
Prevention of celiac disease
There is no primary specific prevention of celiac disease. Secondary prevention of the development of clinical symptoms is to follow a gluten-free diet. With celiac disease in close relatives, it is desirable to conduct a periodic examination for the detection of specific antibodies.
Pregnant women suffering from celiac disease are at risk for developing heart defects in the fetus. Pregnancy in such women should be carried out with increased attention.
Prognosis and medical examination
It is not currently possible to correct the sensitivity of epithelium cells to gluten, so patients with celiac disease should follow a gluten-free diet throughout their lives. Careful adherence to it leads to the preservation of quality and life expectancy. With non-compliance with the diet, the survival rate drops sharply, cases of death among patients with celiac disease who violate the gluten-free diet are 10-30%, while with strict adherence to the diet, this figure does not exceed one percent.
All faces, celiacshould be on the dispensary register with a gastroenterologist and be examined annually. For patients who react poorly to the exclusion of gluten from the diet, dispensary observation is indicated twice a year. The prognosis is noticeably worse if this disease is complicated by the occurrence of small intestinal lymphoma. published
P.S. And remember, just changing our consumption – together we change the world!
Join us on Facebook, VKontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: www.krasotaimedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_gastroenterologia/celiac