908
Can you trust robotic cars making hard decisions

In recent times ethical issues in relation to robotic equipment having the more often. In particular, if the robot car would be in a situation where a collision is unavoidable and he must choose who to bring down one man or the other, what will be his choice on what he will do? It is a modern variant of the selection problem, which many have taken an introductory philosophy course at the University.
Imagine that the robotic vehicle moves along the road and he ran out to meet two people, and to avoid collision with both is not possible. Suppose a person cannot get off the road, and the car – time to turn. These are the options suggested the people interviewed:
- the robot car could be a code to make a random decision.
- the robot car can pass control of the person to passenger.
- the robot car can make a decision based on a set of pre-programmed by the developers of the indicators or on the basis of a set of parameters programmed by the car owner.
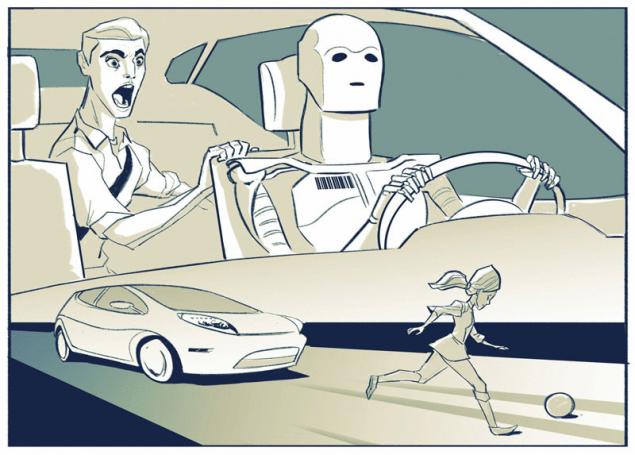
AS ROBOTIC CARS WILL MAKE ETHICAL DECISIONS?
For example, the owner can set the following settings: in the case of selecting between adult and child to knock down an adult. The car may even try to calculate importance of one another's lives, using the recognition system. That is, if the first person who can be knocked down, the car knows the offender, and the second a scientist working on the invention of a cure for cancer, it knocked at first.
In each of these examples, however, the computer leaves the decision to chance, giving the opportunity to take it to someone else.
People do the same thing: when faced with decisions, toss a coin, ask the advice of others or guided by the opinions of authorities in trying to find the right answer.
However, when faced with situations that require tough decisions, we also act differently. In particular, in ambiguous moments when the obvious choice we choose and justify our decision with logical reasons. However, the world is full of such hard decisions; how robotic vehicles (or robots in General) will cope with this kind of choice will be crucial for their development and adoption by society.
To find out how machines can make those difficult decisions, you need to learn how to take them people. It is a good idea. Dr. Ruth Chang says: tough decisions are determined by how the alternatives are related to each other.
When making easy decisions, for example, one alternative is clearly better than the other. If we prefer a natural color artificial, it is easy for us to choose a color, for example, for painting the walls of the room – we would prefer beige fluorescent pink. In the case of taking the hard decisions in favor of each choice have their reasons. But in General neither one nor the other are not ideal.
We may have to choose between taking a job offer in the countryside or to remain in our current positions in the city. We may equally appreciate the life in the city and would like to get a new job. Thus, both alternatives are equal. In this case, to make an important decision, we have to rethink our basic values and characteristics: what is really more important to us? Life in the city or a new job?
WHEN MAKING DIFFICULT DECISIONS CHOICES IT'S DIFFICULT TO COMPARE
It is important to note: when we made the decision, you need to justify his reasons.
If we prefer a beige or fluorescent color, country or a specific professional activity, these preferences cannot be measured, that is not to say that one is "more correct" than another. There is no objective reason to say, for example, that better beige bright pink, and that living in the countryside better. If you would be the factors that determine objectively that one is better than another, all people did would be the same choice. Instead, each of us comes up with reasons for taking their decisions (and when we do it all together, then create our laws, social norms and ethical system).
But the machine will never be able to do this... right? You will be surprised. Recently Google announced that, for example, was created an artificial intelligence that can learn and achieve success in video games. The program receives no commands, but instead playing over and over, gaining experience and making conclusions. Some believe that such a skill would be particularly useful for robotic vehicles.
HOW CAN IT WORK? Instead of robotic cars took random decisions (by external commands or using pre-programmed values and parameters), modern robots can use a variety of data that will be stored for them in the cloud, which will give them the opportunity when deciding to take into account local laws, the latest legal rulings, people and society, and the consequences that will eventually lead those or other decisions.
In short, robotic cars, like people, have to use the experience to generate their own reasons for the decisions taken.
The most interesting, tells Chang that in hard times people are engaged in a process that can be called "inventing excuses". We are talking about what people make up and choose the causes that justify their choice, and we view this as one of the highest forms of human development.
When we leave decision making to others, or give the situation to chance – this is a unique way to "go with the flow". But the definition and selection of the reasons why we make decisions in hard times also depend on the nature of man, busy position, ability to take responsibility for their actions; all this defines who you are and gives you the opportunity to be the author of his own life.
IN ADDITION, WHEN MAKING DECISIONS WE ALSO LOOK FORWARD TO OTHER PEOPLE
No one in their right sense would not trust my life, well-being or money to a person that takes random decisions, asks others to decided for him when the going gets tough, or for those who in the life of "drifting".
We trust the decisions of others when we know their values and know they will make a decision in accordance with these values. So we can trust that a serious selection technique, we need to be sure that it will also be governed by similar principles.
Unfortunately, the General public is far from understanding how artificial intelligence is making decisions. Perhaps the creators of robotic vehicles, unmanned aerial vehicles and other smart machines can keep this information secret or because of fears of the security of their intellectual property, either for security reasons as such. And today, many believe that artificial intelligence cannot be trusted and are afraid to trust such machines, the adoption of any important decisions.
And here we must return to the opinions and insights of Chang. As we are getting closer to era when we will be surrounded robotic cars, in our homes will be robots and UAVs will receive the approval of law enforcement agencies and the armed forces, we must not just go with the flow. Society must understand how robots make decisions, and the company and the government must make technical information more accessible and understandable to a broad range of potential users of such devices.
In some cases, as we have seen, robots can make better decisions than humans. At least, at the moment robotic cars show themselves more effective than human drivers — in April last year, the average figure was over 700,000 miles with no accidents (now more). For fast changing of the external circumstances, people can not always quickly and adequately to react and often follow my instincts, which not every time is correct.
AND WE STILL HAVE TO MAKE INCREASINGLY DIFFICULT DECISIONS
In a world where artificial intelligence can think, but not necessarily will pay attention to what will be punished or praised for the decision, we need to develop new mechanisms outside of our current system of justice and punishment that we apply to human society, to save the world. And if there is a big difference between humans and artificial intelligence, how we will comply with laws and to interpret their mechanical counterparts, is becoming increasingly important.
Faced with the necessity of making such difficult decisions, we must do more than just drift. We must decide what is most important to us as we will be the masters of their own lives in the world, which have to share with robots. Perhaps the question is not whether robots to make complex decisions and whether such decisions make people.
Source: www.robo-hunter.com/news/mojem-li-mi-doverit-robotizirovannim-avtomobilyam-prinyatie-nelegkih-reshenii
How to decorate a country station with led lights?
Stanford scientists have developed a new battery that would charge in a minute























