243
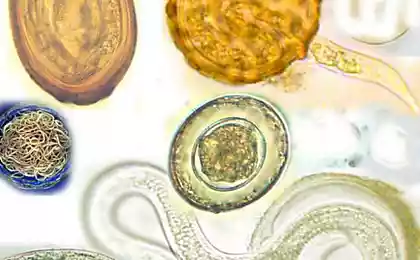
You'll be shocked! Top 10 Parasites Hiding in Our Food
In most cases, many diseases can be avoided by following simple hygiene rules – washing fruits and vegetables (even a ready-to-eat salad).. cook meat for a sufficient amount of time and monitor the purity of the pets.
According to a joint report by the United Nations and the World Health Organization (WHO), improved agricultural conditions and global food trade standards can help to avoid parasites in food. Experts have identified the 24 most dangerous parasites most commonly found in food. We took 10 of them.
1. Pork tapeworm
An adult pig tapeworm can reach ten meters in length. It is the largest of the tapeworms affecting humans. They enter the human body as a larvae through poorly cooked pork, then they attach to the stomach wall and quickly begin to grow. The adult inhabits the intestinal tract and feeds on products entering the gastrointestinal tract.
This condition is usually taken for indigestion. But if the body got eggs, and not larvae, then everything can be much more serious. Eggs, until the larvae form, spread throughout the body. The same thing happens in pigs. This process is called cysticercosis. This risks serious health problems. Especially with damage to the central nervous system (neurocysticercosis), which can cause epileptic seizures. Neurocysticercosis is considered the leading cause of epilepsy in countries below the poverty line.
2. Single-chamber echinococcus

Single-chamber echinococcus is another type of tapeworm, but reaching only three to seven millimeters in length and causing echinococcosis of the bladder. The life cycle of the worm circulates between carnivores (usually dogs) and livestock. Most often, people become infected by accidentally getting eggs through dog feces, through contaminated foods or soil, and through direct contact. Due to the hard shell, eggs can remain contagious for several months, even at sub-zero temperatures.
More than a million cases of bladder echinococcosis are reported worldwide each year, especially in areas where camels are in close contact with dogs. Once in the human body, the parasite migrates directly to the liver. Due to mild symptoms and slowly developing cysts, the disease may go unnoticed for several years. Cysts may contain several liters of fluid and many larvae. The rupture of such a cyst can even lead to death.
3. Multi-chambered echinococcus

The exact geographical distribution of this worm is difficult to determine, but it is found in both North America and Europe, where infection rates are slowly increasing. The life cycle usually includes foxes and small rodents, but sometimes affects dogs and even cats. In humans, it causes alveolar echinococcosis, in which cysts form in internal organs. Cysts can reproduce and spread like tumors. In the absence of treatment, this can lead to death. At risk are hunters who touch killed foxes, as well as collectors of berries and mushrooms affected by fox feces.
4. toxoplasm
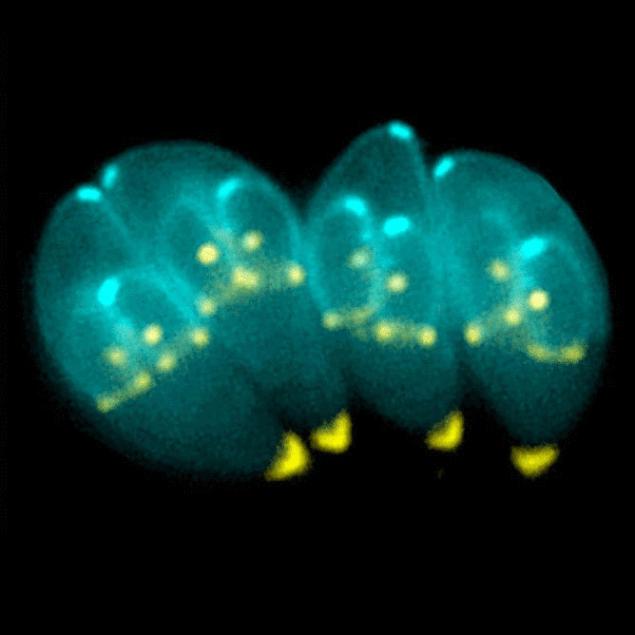
Toxoplasma is a single-celled parasite that affects all warm-blooded mammals, however, the life cycle usually includes cats and rodents. It is the most common parasite found in almost all countries. Human infection rates vary from 10 to 80% of the population in different parts of the world. The parasite is dormant for almost the entire life of the host. Most infected people have no symptoms and do not even know they are infected.
The most serious problems can occur in pregnant women. The parasite can penetrate the placenta, which threatens with abnormalities in the development of the fetus or even miscarriage. That is why being in an interesting position is necessary to avoid contact with cats and, especially, clean the cat toilet tray. Also at risk are people with reduced immunity, as well as patients preparing for organ transplantation. In such an organism, the parasite can begin uncontrolled reproduction.
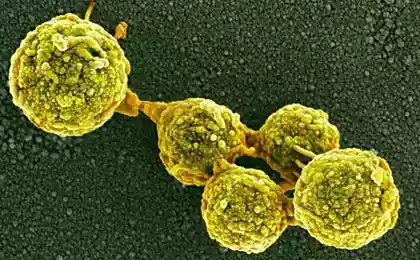
5. Cryptosporidium
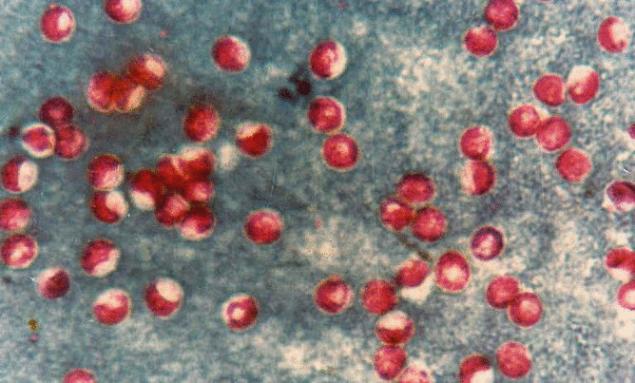
This one parasite It is transmitted through contaminated water or food that has been washed in such water. Some outbreaks were also caused by unpasteurized milk and apple juice, as well as contaminated shellfish. This parasite is found all over the world. A common cause is water contamination through livestock feces. Clear signs of infection may be watery diarrhea.
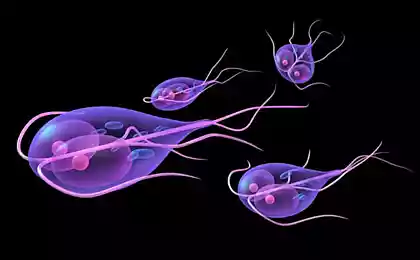
6. Dysentery amoeba

Dysentery amoeba is a simple parasite that affects the gastrointestinal tract and is the cause of amoeba dysentery. This disease is characterized by hemorrhagic diarrhea and abdominal pain, which can be life-threatening. More serious problems can occur when parasites spread from the intestines throughout the body, causing abscesses in the liver and other organs.
7. Trichinella
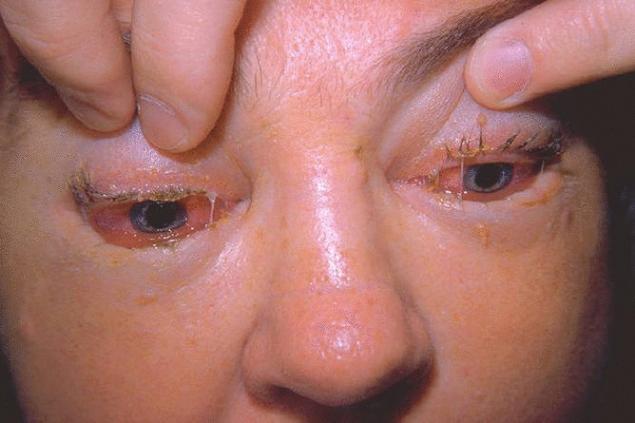
Trichinella is an intracellular roundworm, a causative agent of trichinosis (muscle infection caused by eating raw or poorly cooked pork or foods containing pork, such as sausages or sausages). Also, the parasite can enter the body through the meat of wild animals, for example, wild boar or even a walrus. Contaminated meat contains cysts invisible to the eye, which contain larvae. After such meat enters the body, the larvae turn into adults who continue to multiply and lay larvae, spreading through the muscle tissue and waiting for the current host to be eaten further along the food chain.
8. Opistorchids

Opistorchids belong to the flatworm family, most common in Southeast Asia (some species are found in Europe and Russia). The infection is transmitted by eating raw or poorly cooked freshwater fish, which in turn has been infected with snail larvae. Once in fish, these larvae turn into another form of larvae, and when eaten by a mammal (for example, humans), they become adult worms with a habitat in the bile duct and gallbladder. These worms reproduce eggs that are excreted from the body with feces and infect other snails when they enter fresh water sources.
The main carriers of infection are stray dogs and cats. Long-term chronic infection caused by opistorchids is often associated with the development of liver and gallbladder cancer. Freezing and heat treatment of fish will help to avoid infection. However, dried, salted, smoked and pickled fish can become sources of infection.
9. ascaris
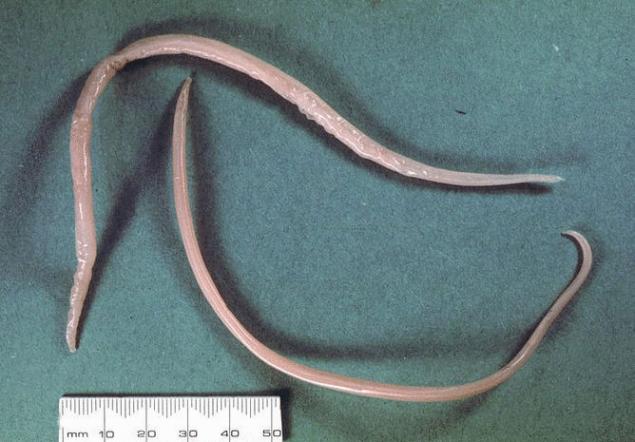

ascaris It is one of the largest gastrointestinal worms (up to 35 cm) and one of the most common among humans (25% of the world's population is affected by it). After entering the intestinal tract, larvae hatch from the eggs, which through the blood flow enter the lungs, then through the airways into the throat, where when swallowed they enter the stomach, and then into the intestinal tract, where they turn into adults. Every day every female produces worms.hundred thousand eggs, which with feces enter the environment and spread this disease further.
Previously, pig roundworm was thought to only affect pigs. But it can also be dangerous for people. The incidence rate and symptoms depend on the number of worms in the body.
10. Trypanosomes

TrypanosomeTrypanosoma cruziIt is the causative agent of Chagas disease. This disease is characterized by a slow course, with the defeat of various cells and organs, including the heart. Usually, for many years, the symptoms of the disease are almost not noticeable. This disease manifests itself only with significant damage to the intestines and heart.
Usually, this infection is transmitted through feces or triatomic bugs (also known as kissing bugs), which most often bite and drink human blood at night. When bitten by feces, bedbugs fall on human skin. Then, when combing the bite, feces enter the inside of the wound.
Trypanosomes are among the ten most common parasites. After all, it has recently been proven that you can get infected simply by eating food affected by the feces of these bedbugs. Several recent outbreaks have been linked to contaminated fruit juices. This makes it possible to turn trypanosomes into a global pathogen. published
P.S. And remember, just changing our consumption – together we change the world!
Join us on Facebook, VKontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: mixednews.ru/archives/67052
According to a joint report by the United Nations and the World Health Organization (WHO), improved agricultural conditions and global food trade standards can help to avoid parasites in food. Experts have identified the 24 most dangerous parasites most commonly found in food. We took 10 of them.
1. Pork tapeworm
An adult pig tapeworm can reach ten meters in length. It is the largest of the tapeworms affecting humans. They enter the human body as a larvae through poorly cooked pork, then they attach to the stomach wall and quickly begin to grow. The adult inhabits the intestinal tract and feeds on products entering the gastrointestinal tract.
This condition is usually taken for indigestion. But if the body got eggs, and not larvae, then everything can be much more serious. Eggs, until the larvae form, spread throughout the body. The same thing happens in pigs. This process is called cysticercosis. This risks serious health problems. Especially with damage to the central nervous system (neurocysticercosis), which can cause epileptic seizures. Neurocysticercosis is considered the leading cause of epilepsy in countries below the poverty line.
2. Single-chamber echinococcus

Single-chamber echinococcus is another type of tapeworm, but reaching only three to seven millimeters in length and causing echinococcosis of the bladder. The life cycle of the worm circulates between carnivores (usually dogs) and livestock. Most often, people become infected by accidentally getting eggs through dog feces, through contaminated foods or soil, and through direct contact. Due to the hard shell, eggs can remain contagious for several months, even at sub-zero temperatures.
More than a million cases of bladder echinococcosis are reported worldwide each year, especially in areas where camels are in close contact with dogs. Once in the human body, the parasite migrates directly to the liver. Due to mild symptoms and slowly developing cysts, the disease may go unnoticed for several years. Cysts may contain several liters of fluid and many larvae. The rupture of such a cyst can even lead to death.
3. Multi-chambered echinococcus

The exact geographical distribution of this worm is difficult to determine, but it is found in both North America and Europe, where infection rates are slowly increasing. The life cycle usually includes foxes and small rodents, but sometimes affects dogs and even cats. In humans, it causes alveolar echinococcosis, in which cysts form in internal organs. Cysts can reproduce and spread like tumors. In the absence of treatment, this can lead to death. At risk are hunters who touch killed foxes, as well as collectors of berries and mushrooms affected by fox feces.
4. toxoplasm

Toxoplasma is a single-celled parasite that affects all warm-blooded mammals, however, the life cycle usually includes cats and rodents. It is the most common parasite found in almost all countries. Human infection rates vary from 10 to 80% of the population in different parts of the world. The parasite is dormant for almost the entire life of the host. Most infected people have no symptoms and do not even know they are infected.
The most serious problems can occur in pregnant women. The parasite can penetrate the placenta, which threatens with abnormalities in the development of the fetus or even miscarriage. That is why being in an interesting position is necessary to avoid contact with cats and, especially, clean the cat toilet tray. Also at risk are people with reduced immunity, as well as patients preparing for organ transplantation. In such an organism, the parasite can begin uncontrolled reproduction.
5. Cryptosporidium

This one parasite It is transmitted through contaminated water or food that has been washed in such water. Some outbreaks were also caused by unpasteurized milk and apple juice, as well as contaminated shellfish. This parasite is found all over the world. A common cause is water contamination through livestock feces. Clear signs of infection may be watery diarrhea.
6. Dysentery amoeba

Dysentery amoeba is a simple parasite that affects the gastrointestinal tract and is the cause of amoeba dysentery. This disease is characterized by hemorrhagic diarrhea and abdominal pain, which can be life-threatening. More serious problems can occur when parasites spread from the intestines throughout the body, causing abscesses in the liver and other organs.
7. Trichinella

Trichinella is an intracellular roundworm, a causative agent of trichinosis (muscle infection caused by eating raw or poorly cooked pork or foods containing pork, such as sausages or sausages). Also, the parasite can enter the body through the meat of wild animals, for example, wild boar or even a walrus. Contaminated meat contains cysts invisible to the eye, which contain larvae. After such meat enters the body, the larvae turn into adults who continue to multiply and lay larvae, spreading through the muscle tissue and waiting for the current host to be eaten further along the food chain.
8. Opistorchids

Opistorchids belong to the flatworm family, most common in Southeast Asia (some species are found in Europe and Russia). The infection is transmitted by eating raw or poorly cooked freshwater fish, which in turn has been infected with snail larvae. Once in fish, these larvae turn into another form of larvae, and when eaten by a mammal (for example, humans), they become adult worms with a habitat in the bile duct and gallbladder. These worms reproduce eggs that are excreted from the body with feces and infect other snails when they enter fresh water sources.
The main carriers of infection are stray dogs and cats. Long-term chronic infection caused by opistorchids is often associated with the development of liver and gallbladder cancer. Freezing and heat treatment of fish will help to avoid infection. However, dried, salted, smoked and pickled fish can become sources of infection.
9. ascaris

ascaris It is one of the largest gastrointestinal worms (up to 35 cm) and one of the most common among humans (25% of the world's population is affected by it). After entering the intestinal tract, larvae hatch from the eggs, which through the blood flow enter the lungs, then through the airways into the throat, where when swallowed they enter the stomach, and then into the intestinal tract, where they turn into adults. Every day every female produces worms.hundred thousand eggs, which with feces enter the environment and spread this disease further.
Previously, pig roundworm was thought to only affect pigs. But it can also be dangerous for people. The incidence rate and symptoms depend on the number of worms in the body.
10. Trypanosomes

TrypanosomeTrypanosoma cruziIt is the causative agent of Chagas disease. This disease is characterized by a slow course, with the defeat of various cells and organs, including the heart. Usually, for many years, the symptoms of the disease are almost not noticeable. This disease manifests itself only with significant damage to the intestines and heart.
Usually, this infection is transmitted through feces or triatomic bugs (also known as kissing bugs), which most often bite and drink human blood at night. When bitten by feces, bedbugs fall on human skin. Then, when combing the bite, feces enter the inside of the wound.
Trypanosomes are among the ten most common parasites. After all, it has recently been proven that you can get infected simply by eating food affected by the feces of these bedbugs. Several recent outbreaks have been linked to contaminated fruit juices. This makes it possible to turn trypanosomes into a global pathogen. published
P.S. And remember, just changing our consumption – together we change the world!
Join us on Facebook, VKontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: mixednews.ru/archives/67052