865
Effect samoobnimaniya 16 man Reiss basic desires
Co time, I became alien
All human needs
- K. Loschevsky
In philosophy and motivational psychology, there are many models that describe the behavior of a person. Often they offer to reduce all the diversity of motives to a few basic reasons, sometimes to a few dozen. Sometimes they drive all the desires of one person (for example, to the pursuit of happiness) or two (for example, search for the emotional rewards and avoidance of suffering).
The diaries of Daniil Kharms has a record of the earthly interests - food, drink, warmth, woman - and heaven. Heavenly interest is in search of immortality, which people are trying to achieve, in turn, one of three ways: to continue the race, to immortalize the name or achieve eternal life through holiness
. Widely-known "Maslow's pyramid." Maslow suggested that in humans there needs physical, social, and the need for self-realization. Maslow believed that satisfy the need for food, sleep, warmth, the man then sexually puzzled question and social recognition, and then reaches a level where you can already do self-actualization.

The disadvantage of Maslow model is the fact that people are violating his scheme neglect "lower" needs for the sake of "higher", for example, enough sleep for the sake of education or risk life and limb for the sake of power.
Another important disadvantage: Maslow's pyramid describes some universal man, neglecting the important fact that the priorities of different people may differ significantly. Reiss calls himself a follower of Abraham Maslow, in the sense that the main merit of the latter is an attempt to consider all human nature with a motivational point of view.
Reiss found that the need to unite to achieve psychology (mainly methods) and philosophy (semantic concepts) to develop the most adequate theory of motivation
In 1998, American psychologist Steven Reiss offered its own model, in which a person is considered the focus of the sixteen primary needs, each of which operates independently of the others, and a unique set of display of force which varies from one to another.
The number "16" should not be misleading, basic desires - not psycho, Reiss and considered options with 10-D and 17-D grounds, but found them less functional
. Professor Reiss has created his theory after leaving the hospital, where he delivered a deadly diagnosis.
When we are faced with tragedy, we review what we have done, reflect what could be done, and ask the question, what does it mean. We learn who we are and what we really appreciate.
So, thinking about death, selfishness and duty, he came to a conclusion about the inadequacy of the concept, according to which a person runs a "pleasure principle." After all, one person prefers to stay on the job, and the other - to spend time with his family, and the fact that both of them are guided by the desire to feel good and avoid trouble, does not help us understand why they eventually take the opposite decision
<. br> Having studied the history of the problem, Reiss found that, according to Plato, a man driven by a desire for the truth, in Freudianism - Eros and Thanatos, Jung - the will to live, Adler - superiority and power. Carl Rogers suggested that the two main desires:. Self-realization and self-recognition
James is already creating a more detailed list of the basic instinctual desires: thrift, creativity, curiosity, self-respect, family, hunting, order, play, sex, shame, pain, gregariousness and revenge
. Later McDougall expands the list and continues to research and Murray pushed him to develop his own list in 1938 and offers a Thematic Apperception Test (TAT).

However, the theory of James and McDougall did not find any response in the camp of psychoanalysts nor behaviorist camp. The first did not like overly complicated scheme sets of instincts, and the second - the possibility of inheriting its degree
. Reiss found that the need to unite to achieve psychology (mainly methods) and philosophy (semantic concepts) to develop the most adequate theory. For this was formulated 328 original objectives, mixed by way of factor analysis to 16, as it was 15 - 16 categories covered the target with the highest degree of completeness and accuracy
. An important point was that vital needs that individual have manifestations (eg, the need for water), were excluded. 6,000 people were surveyed.
Samoobnimaniya effect - the tendency to project onto others their own motivational model, expecting that others should "be guided by the same, that you
An important concept of the theory is the effect samoobnimaniya. Samoobnimaniya effect is the tendency for people to project onto others their own motivational model, expecting other "must" be guided by the same. This problem - one of the deepest causes of misunderstandings and conflicts in human society, a collision with another
. Rice writes about this:
Your boss is experiencing basic desires completely differently than you. Parents experiencing basic desire is not so, their children. Wives experiencing basic desires a completely different way than their husbands. Sex gives men a much greater pleasure than others, partly due to the variety of individual genes that stimulate interest in sex.
Likewise, parenthood deliver much greater joy one over other. Since we can not survive themselves the degree of pleasure that another person receives from sex or paternity / maternity, we sometimes can not determine the extent to which these desires are or are not motivational for other people. We often do not understand why some people react to sex or paternity / maternity is different from us because we can not imagine how genetic differences between us produce different intensity of pleasure.
"Each of the 16 Wishes is actually a group of related motivations", - says Reiss
.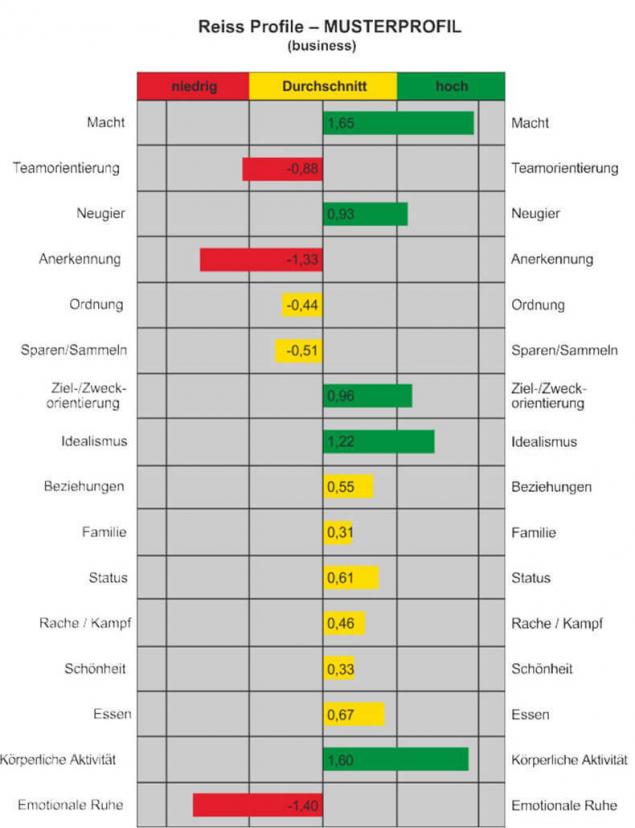
So, here are 16 basic desires for Reiss considering samoobnimaniya effect:
Recognition - the need for approval, accession to the group
. This same need is expressed in the desire to be loved. With a strong manifestation encourages people to avoid the attention of critics and public speaking, and challenges. Associated with self-esteem and self-esteem. samoobnimaniya effect to this need manifests itself in the fact that a person with a highly pronounced need for recognition perceives itself as a non-intrusive, with weak - both confident. The other, a man with a strong need for recognition, we will be perceived as being too sensitive or, on the contrary, self-satisfied.
Curiosity, or curiosity, - the need for training, the thirst for knowledge
. Reiss points out that it is not the intellect (the ability to easy knowledge of things), and then, what emotions the individual receives from the learning process. In addition, you can be curious, but not love intellectual games (chess, bridge), because they are not related to the search for truth. Curious people are more likely to ask questions. Effect samoobnimaniya appears as follows: I (intelligent / practical), the other (rustic / boring)
. Food - the need for food
. Also, drinking habits and hunting. Effect samoobnimaniya:. I (gourmet / wise), the other (limiting itself / glutton)
Family - the need to raise children, maternal and paternal instincts
. Effect samoobnimaniya:. I (executive / independent), the other (selfish / homebody)
Honor - the need for fidelity to the values of an ethnic group, clan and parents
. Associated with patriotism. Effect samoobnimaniya:. I (principal / rational), the other (the infamous / prude)
Idealism - the need for social justice and equality
. Of interest to the charity and politics. Effect samoobnimaniya: I (a compassionate, fair / realist), the other (the cynic / dreamer)
. Independence - the need for freedom, self-determination and to rely on their own strength
. Effect samoobnimaniya:. I (independence, autonomy / devotee), the other (immature / stubborn)
The order - the need for predictable and orderly environment, clean
. "Every person is inherent in their standard order as the most comfortable." Effect samoobnimaniya I (organized / flexible), the other (sleazy / perfectionist, perfectionist)
. Physical activity - the need to exercise
. People involved in sports, to varying degrees, make it for the benefit and pleasure. Effect samoobnimaniya:. I (active / quiet) and one (lazy athlete)
Power - the need for manifestation of the will, the desire to influence others to achieve success
. Ambition, dominance. Effect samoobnimaniya:. I (leader / located to the people), the other (lazy / overbearing)
Romance - the need for sex and, at the same time, the aesthetics
. Effect samoobnimaniya:. I (sensual / ascetic), the other (frigid / hedonist)
Frugality - need something to collect, accumulate
. Associated with such qualities as greed, extravagance and a penchant for collecting. Effect samoobnimaniya:. I (economy / enjoy life), other (wasteful / curmudgeon)
Communication - the need to communicate and friends (equal terms)
. Effect samoobnimaniya:. I (open / serious), the other (closed / surface)
Status - the need for social status / importance, attention to reputation and they produce the impression to the titles and awards, prestige, and consumption of premium-class
. High or low level of demand reflects both self-esteem and perception of others. Effect samoobnimaniya I (elite / open-minded), other (minor / snob)
. Peace - the need for security, emotional comfort
. This need is closely related to the intensity of the experience of pain, stress and fear. Effect samoobnimaniya:. I (cautious / bold), the other (adventurous / fearful)
Revenge - need to hit back, to compete and win
. Associated with anger and hatred. Effect samoobnimaniya:. I (winner / non-conflict), the other (passive / aggressive)

In the book, Reiss "16 desires to God" explores the psychology of religion: in his view, faith meets the basic needs of all sixteen
. (Photo © Tom Dodge)
Each person in need can be expressed in varying degrees. Reiss stopped at the border of three values: weak manifestation, medium and strong. The scheme provides a wide variety of human character types, as needs are regarded as independent of each other.
14 requirements may be greater or lesser extent have been found in animals, 12 are involved in religious practices, which is consistent theological position: religion can not keep within the framework of several psychosocial functions and should not be longer than a "form of culture»
.
With regard to the requirements of permanence, repeated studies have shown extreme stability over time, 16 basic desires in people. It seems that they are caused by genetic or are formed at an early age. "People can change, but to a certain extent and not so easy».
The differences are statistically averaged floors of private deviations. At the same time, the trend of men most to be aggressive and less in need of rest, although the strength of the parental instincts of both sexes vary slightly.
Reiss says that there was no correlation between the needs and ethnic groups, but acknowledges that the study were subjected to only the representatives of America, Canada and Japan.
Therefore, he is not prepared to draw conclusions about the role of culture and education in the formation of needs, while bowing to the fact that it considered still less than the role of genetics. In any case, professional tests revealed that the different professions attract different people.
Tests have been developed that involve more than one hundred questions, and sometimes even control a reconciliation with observers questionnaires that assess from the outside. The simplest test is composed of 16 questions of this kind: "you usually experience greater or lesser need for independence (as an example), than your peers?". In this embodiment, the accuracy depends simply on understanding yourself and others, as well as the essence of every need.

Reiss model is a valuable psychological and social tool has to adopt human resources departments of large corporations and is used in professional sports.
However, the reasons and the purpose of its creation were something more important: it is the author's contribution to the understanding of human nature
. So, Reiss says that 16 needs only have 6 areas to meet them: family, relationships, work, spiritual life, sports and happiness. It is proposed to distinguish between "sensual happiness", which brings pleasure in the present tense and "value-based happiness" that fills our life with meaning.
Some people focus on the first, but at some point may feel the devastation. And although there is no reason to abandon the simple pleasures, far more important than "value-based happiness" - the more so that it was to keep alive in the people caught up in disease situations, injuries, social upheaval and other factors which can not always choose <. br> Author: Anton Timohin
All human needs
- K. Loschevsky
In philosophy and motivational psychology, there are many models that describe the behavior of a person. Often they offer to reduce all the diversity of motives to a few basic reasons, sometimes to a few dozen. Sometimes they drive all the desires of one person (for example, to the pursuit of happiness) or two (for example, search for the emotional rewards and avoidance of suffering).
The diaries of Daniil Kharms has a record of the earthly interests - food, drink, warmth, woman - and heaven. Heavenly interest is in search of immortality, which people are trying to achieve, in turn, one of three ways: to continue the race, to immortalize the name or achieve eternal life through holiness
. Widely-known "Maslow's pyramid." Maslow suggested that in humans there needs physical, social, and the need for self-realization. Maslow believed that satisfy the need for food, sleep, warmth, the man then sexually puzzled question and social recognition, and then reaches a level where you can already do self-actualization.

The disadvantage of Maslow model is the fact that people are violating his scheme neglect "lower" needs for the sake of "higher", for example, enough sleep for the sake of education or risk life and limb for the sake of power.
Another important disadvantage: Maslow's pyramid describes some universal man, neglecting the important fact that the priorities of different people may differ significantly. Reiss calls himself a follower of Abraham Maslow, in the sense that the main merit of the latter is an attempt to consider all human nature with a motivational point of view.
Reiss found that the need to unite to achieve psychology (mainly methods) and philosophy (semantic concepts) to develop the most adequate theory of motivation
In 1998, American psychologist Steven Reiss offered its own model, in which a person is considered the focus of the sixteen primary needs, each of which operates independently of the others, and a unique set of display of force which varies from one to another.
The number "16" should not be misleading, basic desires - not psycho, Reiss and considered options with 10-D and 17-D grounds, but found them less functional
. Professor Reiss has created his theory after leaving the hospital, where he delivered a deadly diagnosis.
When we are faced with tragedy, we review what we have done, reflect what could be done, and ask the question, what does it mean. We learn who we are and what we really appreciate.
So, thinking about death, selfishness and duty, he came to a conclusion about the inadequacy of the concept, according to which a person runs a "pleasure principle." After all, one person prefers to stay on the job, and the other - to spend time with his family, and the fact that both of them are guided by the desire to feel good and avoid trouble, does not help us understand why they eventually take the opposite decision
<. br> Having studied the history of the problem, Reiss found that, according to Plato, a man driven by a desire for the truth, in Freudianism - Eros and Thanatos, Jung - the will to live, Adler - superiority and power. Carl Rogers suggested that the two main desires:. Self-realization and self-recognition
James is already creating a more detailed list of the basic instinctual desires: thrift, creativity, curiosity, self-respect, family, hunting, order, play, sex, shame, pain, gregariousness and revenge
. Later McDougall expands the list and continues to research and Murray pushed him to develop his own list in 1938 and offers a Thematic Apperception Test (TAT).

However, the theory of James and McDougall did not find any response in the camp of psychoanalysts nor behaviorist camp. The first did not like overly complicated scheme sets of instincts, and the second - the possibility of inheriting its degree
. Reiss found that the need to unite to achieve psychology (mainly methods) and philosophy (semantic concepts) to develop the most adequate theory. For this was formulated 328 original objectives, mixed by way of factor analysis to 16, as it was 15 - 16 categories covered the target with the highest degree of completeness and accuracy
. An important point was that vital needs that individual have manifestations (eg, the need for water), were excluded. 6,000 people were surveyed.
Samoobnimaniya effect - the tendency to project onto others their own motivational model, expecting that others should "be guided by the same, that you
An important concept of the theory is the effect samoobnimaniya. Samoobnimaniya effect is the tendency for people to project onto others their own motivational model, expecting other "must" be guided by the same. This problem - one of the deepest causes of misunderstandings and conflicts in human society, a collision with another
. Rice writes about this:
Your boss is experiencing basic desires completely differently than you. Parents experiencing basic desire is not so, their children. Wives experiencing basic desires a completely different way than their husbands. Sex gives men a much greater pleasure than others, partly due to the variety of individual genes that stimulate interest in sex.
Likewise, parenthood deliver much greater joy one over other. Since we can not survive themselves the degree of pleasure that another person receives from sex or paternity / maternity, we sometimes can not determine the extent to which these desires are or are not motivational for other people. We often do not understand why some people react to sex or paternity / maternity is different from us because we can not imagine how genetic differences between us produce different intensity of pleasure.
"Each of the 16 Wishes is actually a group of related motivations", - says Reiss
.

So, here are 16 basic desires for Reiss considering samoobnimaniya effect:
Recognition - the need for approval, accession to the group
. This same need is expressed in the desire to be loved. With a strong manifestation encourages people to avoid the attention of critics and public speaking, and challenges. Associated with self-esteem and self-esteem. samoobnimaniya effect to this need manifests itself in the fact that a person with a highly pronounced need for recognition perceives itself as a non-intrusive, with weak - both confident. The other, a man with a strong need for recognition, we will be perceived as being too sensitive or, on the contrary, self-satisfied.
Curiosity, or curiosity, - the need for training, the thirst for knowledge
. Reiss points out that it is not the intellect (the ability to easy knowledge of things), and then, what emotions the individual receives from the learning process. In addition, you can be curious, but not love intellectual games (chess, bridge), because they are not related to the search for truth. Curious people are more likely to ask questions. Effect samoobnimaniya appears as follows: I (intelligent / practical), the other (rustic / boring)
. Food - the need for food
. Also, drinking habits and hunting. Effect samoobnimaniya:. I (gourmet / wise), the other (limiting itself / glutton)
Family - the need to raise children, maternal and paternal instincts
. Effect samoobnimaniya:. I (executive / independent), the other (selfish / homebody)
Honor - the need for fidelity to the values of an ethnic group, clan and parents
. Associated with patriotism. Effect samoobnimaniya:. I (principal / rational), the other (the infamous / prude)
Idealism - the need for social justice and equality
. Of interest to the charity and politics. Effect samoobnimaniya: I (a compassionate, fair / realist), the other (the cynic / dreamer)
. Independence - the need for freedom, self-determination and to rely on their own strength
. Effect samoobnimaniya:. I (independence, autonomy / devotee), the other (immature / stubborn)
The order - the need for predictable and orderly environment, clean
. "Every person is inherent in their standard order as the most comfortable." Effect samoobnimaniya I (organized / flexible), the other (sleazy / perfectionist, perfectionist)
. Physical activity - the need to exercise
. People involved in sports, to varying degrees, make it for the benefit and pleasure. Effect samoobnimaniya:. I (active / quiet) and one (lazy athlete)
Power - the need for manifestation of the will, the desire to influence others to achieve success
. Ambition, dominance. Effect samoobnimaniya:. I (leader / located to the people), the other (lazy / overbearing)
Romance - the need for sex and, at the same time, the aesthetics
. Effect samoobnimaniya:. I (sensual / ascetic), the other (frigid / hedonist)
Frugality - need something to collect, accumulate
. Associated with such qualities as greed, extravagance and a penchant for collecting. Effect samoobnimaniya:. I (economy / enjoy life), other (wasteful / curmudgeon)
Communication - the need to communicate and friends (equal terms)
. Effect samoobnimaniya:. I (open / serious), the other (closed / surface)
Status - the need for social status / importance, attention to reputation and they produce the impression to the titles and awards, prestige, and consumption of premium-class
. High or low level of demand reflects both self-esteem and perception of others. Effect samoobnimaniya I (elite / open-minded), other (minor / snob)
. Peace - the need for security, emotional comfort
. This need is closely related to the intensity of the experience of pain, stress and fear. Effect samoobnimaniya:. I (cautious / bold), the other (adventurous / fearful)
Revenge - need to hit back, to compete and win
. Associated with anger and hatred. Effect samoobnimaniya:. I (winner / non-conflict), the other (passive / aggressive)

In the book, Reiss "16 desires to God" explores the psychology of religion: in his view, faith meets the basic needs of all sixteen
. (Photo © Tom Dodge)
Each person in need can be expressed in varying degrees. Reiss stopped at the border of three values: weak manifestation, medium and strong. The scheme provides a wide variety of human character types, as needs are regarded as independent of each other.
14 requirements may be greater or lesser extent have been found in animals, 12 are involved in religious practices, which is consistent theological position: religion can not keep within the framework of several psychosocial functions and should not be longer than a "form of culture»
.
With regard to the requirements of permanence, repeated studies have shown extreme stability over time, 16 basic desires in people. It seems that they are caused by genetic or are formed at an early age. "People can change, but to a certain extent and not so easy».
The differences are statistically averaged floors of private deviations. At the same time, the trend of men most to be aggressive and less in need of rest, although the strength of the parental instincts of both sexes vary slightly.
Reiss says that there was no correlation between the needs and ethnic groups, but acknowledges that the study were subjected to only the representatives of America, Canada and Japan.
Therefore, he is not prepared to draw conclusions about the role of culture and education in the formation of needs, while bowing to the fact that it considered still less than the role of genetics. In any case, professional tests revealed that the different professions attract different people.
Tests have been developed that involve more than one hundred questions, and sometimes even control a reconciliation with observers questionnaires that assess from the outside. The simplest test is composed of 16 questions of this kind: "you usually experience greater or lesser need for independence (as an example), than your peers?". In this embodiment, the accuracy depends simply on understanding yourself and others, as well as the essence of every need.

Reiss model is a valuable psychological and social tool has to adopt human resources departments of large corporations and is used in professional sports.
However, the reasons and the purpose of its creation were something more important: it is the author's contribution to the understanding of human nature
. So, Reiss says that 16 needs only have 6 areas to meet them: family, relationships, work, spiritual life, sports and happiness. It is proposed to distinguish between "sensual happiness", which brings pleasure in the present tense and "value-based happiness" that fills our life with meaning.
Some people focus on the first, but at some point may feel the devastation. And although there is no reason to abandon the simple pleasures, far more important than "value-based happiness" - the more so that it was to keep alive in the people caught up in disease situations, injuries, social upheaval and other factors which can not always choose <. br> Author: Anton Timohin
Aversion to lose why we care about the loss of more than acquisition
What is behind the desire to eat chalk