899
Using natural communication capabilities of the organism, biologists were able to command the heart recover after a heart attack
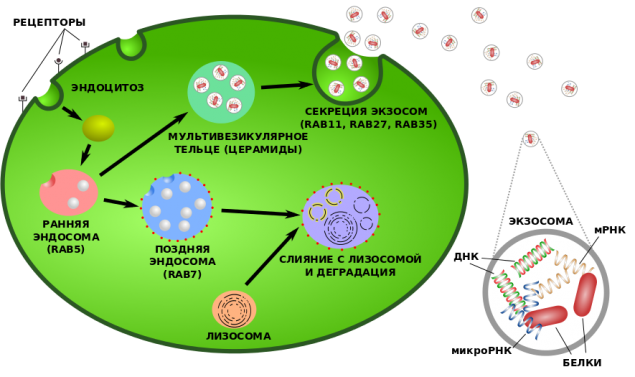
How are exosomes / Wikipedia i>
Работа biologists led by Dr. Raj Kishore Biology from Temple University School of Medicine sheds light on the role of exosomes in the functioning of the body and potentially able to make a new step in the treatment of widespread diseases - инфаркта myocardial , or heart attack.
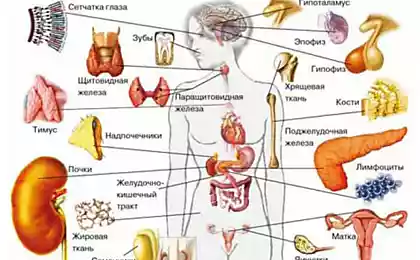
Экзосомы - Microscopic extracellular vesicles (blisters) up to 100 nm in diameter secreted into the extracellular space by cells of various tissues and organs. They were discovered in the 80s of the last century, and at first thought that the way cells get rid of unwanted waste products.
But later, when studying the work of cancer cells, biologists have found that it does not waste a unique means of communication - like notes in bottles thrown into the water. Using them cancers communicated with distant metastases. Later it became clear that almost all cells in the body use a mechanism to communicate with each other. In addition, exosomes are involved in many other processes, and fully their role has not yet been studied.
Biologists at Temple University have been studying ways to restore the heart after a heart attack. It is known that the heart almost can not heal itself - damage resulting from myocardial scar on the heart, it has to operate in emergency mode to provide the blood pumping, heart tissue grow, and the compressive force is reduced.
It would seem that the disease just need to try to cure using stem cells - those that are pluripotent (can turn into any desired cell a >). Unfortunately, the simple introduction of stem cells in heart tissue does nothing - usually, most of them simply died. And surviving cells have another risk - they can become тератому, a tumor in which there is porridge from completely different body tissues. In some cases, this tumor appears in the body as a result of the presence of immature parasitic Siamese twin.
Biologists led Kishore for several years trying to explore the role of exosomes in the body. These vesicles contained the DNA, mRNA , microRNAs and various proteins. mRNA, also known as messenger RNA - is actually an instruction on which new proteins are synthesized. Therefore, a team of biologists wondered - is it possible to use these exosomes as a team for the heart cells to self-repair?
The researchers took two groups of mice. One received exosomes extracted from stem cells. Another indicator - exosomes fibroblasts. Hearts mice were amazed infarction. And the first group of mice showed better results conclusively recovery from illness.
They have survived more than muscle tissue at heart appeared less scarring, fewer cardiac tissue withered away. In the area of lesions was observed much better development of the vascular system, which was the reason for the improvement of blood circulation and oxygen supply to the muscle tissue of the heart. Heart to produce more of their own stem cells, which are then turned into muscle cells. Heart of the first group of mice fought actively not grown as much as the other group.
"Our work shows that the best way to restore the heart - is strengthening its ability to heal itself and increase its ability to be treated, - said Dr. Kishore. - So you can avoid the risks associated with the occurrence of teratomas and other complications of stem cell therapy. This is a very exciting development in the theory of heart disease ».
In the continuation of the study, scientists tested does not bear any responsibility for these processes are most commonly found in exosomes miRNA molecule that regulates genes - miR-294. With the introduction of this molecule in the stem cells of the heart, which then turn into muscle cells, it was seen several processes similar to those that occurred after the introduction of as much as exosomes. But it became clear that not alone this molecule is responsible for all their good work.
Future research will help develop ekzosomnuyu therapy, in theory lead us to its use in the treatment of heart attacks in humans.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/252252/