662
The brain controls the production of new neurons
Stem cells in the adult brain are in subjection to special neurons that can speed up or slow down the emergence of new nerve cells.
That in the brain of adult mammals can appear new neurons, it became known some time ago, although it is still some time left for the scientific community recognized this fact. Adult neurogenesis is in the hippocampus, one of the main centers of memory and subventricular area, located close to the ventricles of the brain. A year ago researchers at the Karolinska Institute in Sweden have managed to prove that adult neurogenesis is not only in rodents but also in humans.

It is clear that new neurons must be obtained from special stem cells. But then there is not a simple question: how do these cells understand that the brain needs a party of new neurons? Stem cells have to work when you want, and however much you need, and to manage them must exist some special "Department". But where can he be and how would that look like?
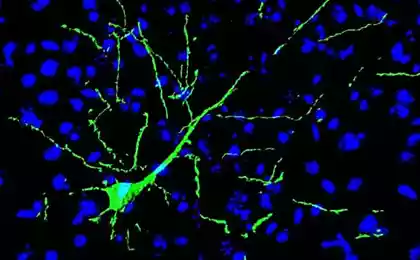
Partly this question was answered by researchers from Duke University which found in the brain in rodents a special population of neurons that control stem cells subventricular areas of the brain. According to Shay (Chay Kuo), he and his colleagues do not yet know how exactly the nervous chain is arranged with neurons, tutelary stem cells. However, there is no doubt that these neurons are their signals control the activity of neurogenesis.
The experiments lasted for five years, and as a result, the researchers found a group of cells, which are intensively synthesized acetylcholinesterase enzyme necessary for the production of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Acetylcholine involved in the transmission of neuromuscular signals, it is also required of the parasympathetic system and the memory centers and possibly neurogenesis also can't do without it. What is acetylcholine "factory" involved in the administration of the stem cells, the researchers found, regulating the work of these neurons if their activity is stimulated or suppressed, the stem cells produced more or less the precursors of neurons. The results of the experiments published in Nature Neuroscience. In rodents new nerve cells travel to the olfactory bulb. The sense of smell in the animal life plays a huge role, so it is very important that the nerve chain that is associated with the transfer and processing of olfactory signals did not lack in neurons. People not so dependent on smell, and the new brain cells can go into other areas. Earlier this year a group of researchers from the same Carolina University published an article which described the migration of the new neurons in the striatum, a complex subcortical structure, which influences and eating behavior, and complex motor responses, and perhaps some elements of consciousness.
Now the researchers are challenged to learn, as is the case with the regulation of stem cells in the human brain. Some data suggests that stem cells obey the dopamine and serotonin signals, so maybe the acetylcholine is not the only neurotransmitter that is involved here, and in the management of neurogenesis may be involved and other neurons. Increased interest in this issue is clear: if we know how to regulate stem cell activity of the brain, we will be able to use them to compensate for neural loss, which occurred due to trauma, stroke, Alzheimer's or some other disease.
Source: nkj.ru
That in the brain of adult mammals can appear new neurons, it became known some time ago, although it is still some time left for the scientific community recognized this fact. Adult neurogenesis is in the hippocampus, one of the main centers of memory and subventricular area, located close to the ventricles of the brain. A year ago researchers at the Karolinska Institute in Sweden have managed to prove that adult neurogenesis is not only in rodents but also in humans.

It is clear that new neurons must be obtained from special stem cells. But then there is not a simple question: how do these cells understand that the brain needs a party of new neurons? Stem cells have to work when you want, and however much you need, and to manage them must exist some special "Department". But where can he be and how would that look like?
Partly this question was answered by researchers from Duke University which found in the brain in rodents a special population of neurons that control stem cells subventricular areas of the brain. According to Shay (Chay Kuo), he and his colleagues do not yet know how exactly the nervous chain is arranged with neurons, tutelary stem cells. However, there is no doubt that these neurons are their signals control the activity of neurogenesis.
The experiments lasted for five years, and as a result, the researchers found a group of cells, which are intensively synthesized acetylcholinesterase enzyme necessary for the production of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Acetylcholine involved in the transmission of neuromuscular signals, it is also required of the parasympathetic system and the memory centers and possibly neurogenesis also can't do without it. What is acetylcholine "factory" involved in the administration of the stem cells, the researchers found, regulating the work of these neurons if their activity is stimulated or suppressed, the stem cells produced more or less the precursors of neurons. The results of the experiments published in Nature Neuroscience. In rodents new nerve cells travel to the olfactory bulb. The sense of smell in the animal life plays a huge role, so it is very important that the nerve chain that is associated with the transfer and processing of olfactory signals did not lack in neurons. People not so dependent on smell, and the new brain cells can go into other areas. Earlier this year a group of researchers from the same Carolina University published an article which described the migration of the new neurons in the striatum, a complex subcortical structure, which influences and eating behavior, and complex motor responses, and perhaps some elements of consciousness.
Now the researchers are challenged to learn, as is the case with the regulation of stem cells in the human brain. Some data suggests that stem cells obey the dopamine and serotonin signals, so maybe the acetylcholine is not the only neurotransmitter that is involved here, and in the management of neurogenesis may be involved and other neurons. Increased interest in this issue is clear: if we know how to regulate stem cell activity of the brain, we will be able to use them to compensate for neural loss, which occurred due to trauma, stroke, Alzheimer's or some other disease.
Source: nkj.ru