807
Graphene coating to improve the condensation of steam will help increase the efficiency of power plants
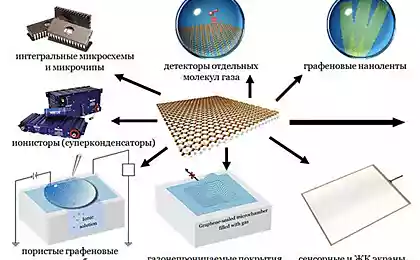
What can we do only with graphene today! It is used as a lubricant for moving parts , like water filter , as a means to obtain the hydrogen from the air . More slightly and fly to the stars with the help of graphene engines and construct elevator into space . But исследователи from MIT invented , how to use graphene coating to improve the condensation of moisture on the surface and thereby accelerate its cooling.
In thermal power plants is usually used water, which is heated by the selected source of energy is converted into steam to drive a turbine, and then condensed back into liquid. At the same time, the more effective will the cooling and condensing, the greater the overall efficiency of the plant.
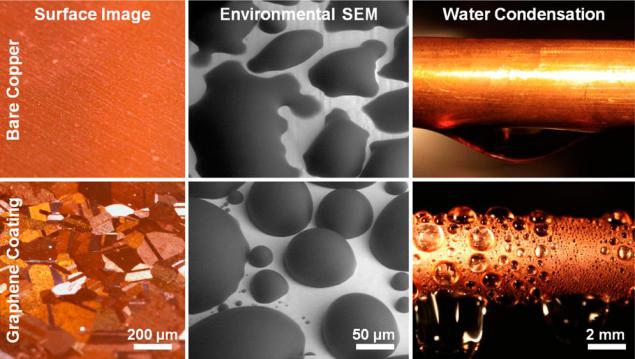
It is known that the droplet condensation occurring on hydrophobic surfaces effectively foil, which takes place on the wetted surfaces. But the coating surface transforms into the hydrophobic (typically polymer), usually either chemically unstable, or is too thick, resulting in a gain in efficiency of the whole is lost.
Scientists from MIT demonstrated , coating condensing surfaces to create a hydrophobic surface, providing effective condensation drip, while it chemically very stable and has good thermal conductivity. Compared with membrane condensation heat transfer is improved by 4 times. According to the calculations of scientists, in optimal conditions this figure can be increased up to 7 times. The experiment lasted two weeks, during which time a coating of graphene has not undergone any visible degradation.
The overall increase in the efficiency of power plants using such coatings will be only a few percent - but in absolute figures concerning both energy output and emissions of carbon dioxide (in the case when the power allocated under the CO 2 sub>), it will be felt .
At the same time, the process of applying the graphene coating, known as the химическое vapor deposition (Chemical vapor deposition, CVD), is already so well developed that it can begin to use in real applications within a year.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/251396/
Gamers have proven benefits for software verification
Meet Musio, cute robot who wants to be your friend