1117
Zeppelins
Or air giants, who had no prospects.
28 pics + infa
Ferdinand Zeppelin (Ferdinand Zeppelin, 1838-1917), German designer of airships. Zeppelin was born July 8, 1838 in Konstanz (Baden).
It was in his head was born the idea of creating a flying ship, which would significantly outperform balloon. His life was intertwined with the army. At the age of 16 years he became a graduate of the Military Academy, which was located in Ludwigsburg, Germany, and after 3 years, he was promoted to an officer that is worthy of respect, because then Ferdinand Zeppelin was only 19 years old. Then fate brought him to distant America, which at that time torn apart by the war between the North and the South. After the end of hostilities Graf Zeppelin embarked on intensive research, during which for the first time in his life felt that this, to be in a hot air balloon high above the ground. Who knows, maybe this event and has left its mark on the fate of the then young German. However, before becoming a designer, Zeppelin had a little more to war ... the Austro-Prussian and Franco-Prussian war of Ferdinand Zeppelin made a hero, because after these wars, he already had the rank of General, with him, he got 33 years! Zeppelin retired and started development and testing of airships. In 1900, the first successful flight of the Zeppelin airship hard. Ferdinand Zeppelin airships military used in World War 1914-1918.

Even before the outbreak of World War representatives Kaiser fleet showed an active interest in airships and their possible use in the fighting. Aircraft then were still in the "child" status and their combat use was highly problematic. Airship same could be many hours in the air to rise to greater heights and to carry military cargo. Has played a decisive role, and the fact that the planes on all these parameters significantly inferior airships. Marine General Staff was ready to believe that with the help of the airship rigid structure of Count Zeppelin can be guaranteed to get the latest information on the strategic position of the sea and from the air to conduct offensive military operations. In addition, to build the airship was much cheaper and faster than a cruiser.
in 1900, after the first successful flights of Count Zeppelin airships, the General Staff of the Kaiser "High Seas Fleet," as well, and representatives of the Army, could hope that he will be a weapon, the action is not limited to any front line. By 1912 there were already 26 huge pavilions for land and naval forces. June 1, 1913 in Berlin-Yohanninstale was formed "Naval Air Battalion Task» («Marine-Luftschifferabteilung»).
To this we must add that conducted the glorification of airships as a symbol of the German Teutonic creative spirit and power, as well as a miracle - weapons that can not be countered equivalent enemy.
But in practice, it all came together a little differently ... Zeppelin LZ 24 - L3
type: hard, had a duralumin enclosure Three engine 210 PS Maybach 150 hp Volume: 22,470 cubic meters. Capacity: 9, 2 tons Length: 158 m. Speed: 80 km / h Maximum diameter: 14, 86 m.
The first flight made May 11, 1914 May 16, 1914 reached an altitude of 3125 meters. Was assigned to the Navy. During the war he made 24 reconnaissance missions over the North Sea.
On the night of January 19, 1915 under the command of Lieutenant-Commander Hans Fritz made the first raid on England. In the raid was also attended by airships L4 and L6. L6 because of problems with the engines returned to base. L3 bombarded the port of Yarmouth (Yarmouth), who was considered a military objective. 7 L3 dropped bombs, two people were killed and three were wounded. L4 moved deep into England, and dropped bombs on Kings Lynn. Two people were killed and 13 were wounded. A total of 24 bombs dropped by 50 kg. and some grenades weighing 3 kg. Caused damage 7740 pounds.
After flying in the UK started to panic, and in Germany the news of the raid was met with enthusiasm.
February 17, 1915 L3 made an emergency landing on the coast of Denmark near Fano. The crew was taken prisoner, and the airship was destroyed.

...
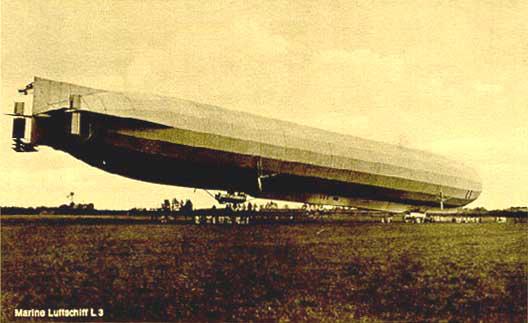
Zeppelin LZ 48 (L15)
Type: Hard Four engine rated at 154 kW. Volume: 31,900 cubic meters. m. Capacity: 16, 2 tons. Length: 163 m. Maximum speed: 96 km / h. The maximum diameter of 19 m.
The first flight made September 9, 1915 The photograph L15 during an emergency landing at Nordholz, Germany, October 1915
Made 8 reconnaissance flight. During three raids on England dropped 5780 kg. bombs. Shot down by air defense fire from the ground during a raid on London on 31 March - 1 April 1916 he began to sink in the delta of the River Thames. 17 crew members were taken prisoner. One person was killed.
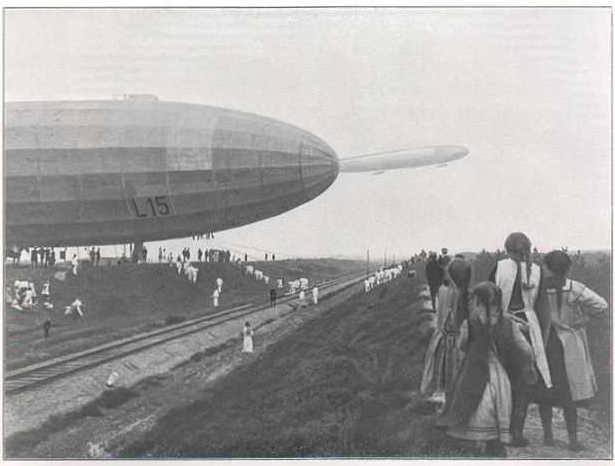

Zeppelin LZ-95 - L-48
Type: Hard Five Maybach engines rated at 177 kW. Volume: 55,800 cubic meters. m. Capacity: 39 tons. Length: 196 m. Maximum speed: 107 km / h. The maximum diameter of 24 m.
Covershil first flight May 22, 1917
In 1916, Great Britain was able to create quite an effective anti-aircraft defenses. German airships were forced to move their activities to a higher altitude (6000 meters or more) is not available searchlights, anti-aircraft guns and enemy aircraft. In January 1917, the navy of Germany to develop requirements for new airships capable of lifting at high altitude. In March 1917, during the test L-42 rose to a height of 6000 m with a bomb load of 2000 kg.
British Army changed its tactics to combat airships. It was decided to attack airships over the North Sea, where they have not yet gained a great height. In addition, British planes were more likely to attack the base of airships.
48 was shot down over the coastal town of Yarmouth, and fell near Leiston (Suffolk). In the destruction of L-48 for the first time three crew members to use a parachute airship (according to other sources were saved 2 people). Parachutes were hung near windows gondolas. Prior to that, the crews did not take parachutes and increased bomb load - parachutes were not reliable, and if they do vzvryve hydrogen useless.

Zeppelin LZ-95 - L-48
Type: Hard Five Maybach engines rated at 177 kW. Volume: 55,800 cubic meters. m. Capacity: 39 tons. Length: 196 m. Maximum speed: 107 km / h. The maximum diameter of 24 m.
Covershil first flight May 22, 1917
In 1916, Great Britain was able to create quite an effective anti-aircraft defenses. German airships were forced to move their activities to a higher altitude (6000 meters or more) is not available searchlights, anti-aircraft guns and enemy aircraft. In January 1917, the navy of Germany to develop requirements for new airships capable of lifting at high altitude. In March 1917, during the test L-42 rose to a height of 6000 m with a bomb load of 2000 kg.
British Army changed its tactics to combat airships. It was decided to attack airships over the North Sea, where they have not yet gained a great height. In addition, British planes were more likely to attack the base of airships.
48 was shot down over the coastal town of Yarmouth, and fell near Leiston (Suffolk). In the destruction of L-48 for the first time three crew members to use a parachute airship (according to other sources were saved 2 people). Parachutes were hung near windows gondolas. Prior to that, the crews did not take parachutes and increased bomb load - parachutes were not reliable, and if they do vzvryve hydrogen useless.
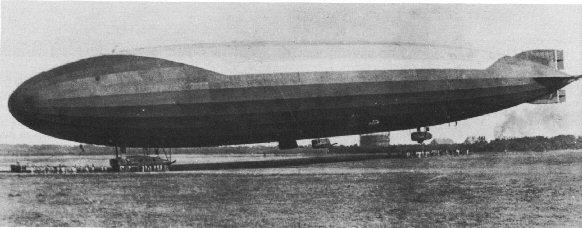
...
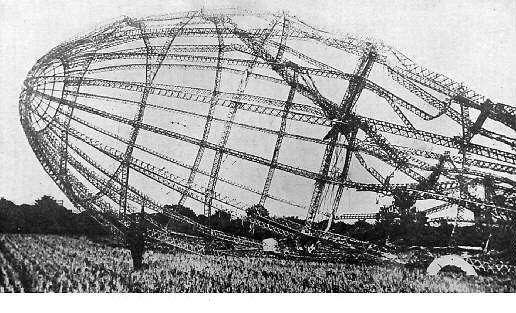
Zeppelin LZ59- L20
Type: Hard 4 Maybach engine capacity of 154 hp Volume: 31,900 cubic meters. m. Capacity: 16 tons 2 Length: 163 m. The maximum diameter of 19 m. The maximum speed: 96 km / h.
The first flight made November 21, 1915 Commander - kapitanleytenant Stabbert.
6 made reconnaissance missions, 2 raid on England. Dropped 2,864 kg. bombs.
May 4, 1916, returning from a raid on England crashed and sank in the Norwegian city of Stavanger (Stavanger). The crew was captured. The commander escaped from captivity after 6 months.

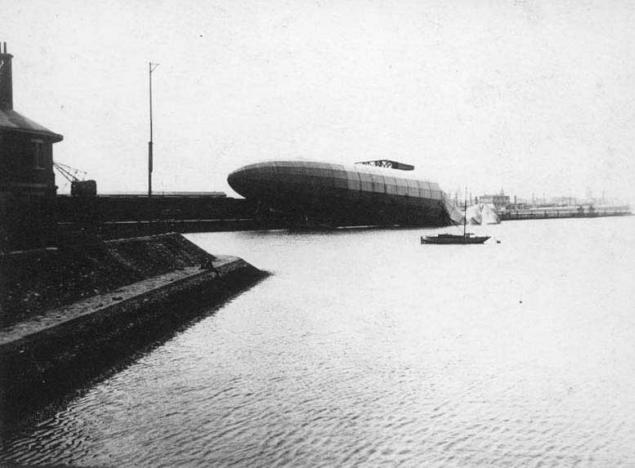
Zeppelin LZ-43
Type: Hard Four Maybach engine rated at 154 kW. Volume: 31,900 cubic meters. m. Capacity: 16, 2 tons. Length: 163 m. Maximum speed: 96 km / h. The maximum diameter of 19 m.
Zeppelin LZ-43 - L-12 made its first flight 21 June 1915
July 20, 1915 the French air force flew a raid on the German city of Karlsruhe. On this day in Germany celebrated the feast of Corpus Christi. Killing 110 people, injuring 123 people. One bomb hit the square, where children were given a theatrical performance. In Germany, a wave of hatred against the Entente.
August 9, 1915 in the bombing of England went from two bases Zeppelin L-9, L-12, L-13, L-10 and L-11. Crews wanted revenge. On board the L-10 was the commander of Division airships Peter Strasser. It was the first massive raid on London airships. Airships were carrying 440 bombs. Their goal was the London docks and factories in the northern part of the city. Bad weather and visibility prevented Zeppelin achieve goals.
By three o'clock in the morning August 10, 1915 the crew jettisoned the radio, empty fuel tanks, handrails from the gondola, the front part of the engine that has stopped due to lack of fuel. Before dawn the airship down on the water of La Manche. The wind began to treat him in the direction of England. The crew gathered in the aft nacelle, which continued to hang in the air. Then came the tug from the shore, and an hour later he delivered the L-12 in the Belgian port of Ostend.
The commander decided to repair the damaged tanks for hydrogen and deliver the airship to the nearest base for repair.
British intelligence received information that in the harbor of Ostend is airship. W. Churchill ordered the destruction of Zeppelin. August 11, 1915 six British flying boats tried to attack the L-12. Flak hit by a British aircraft, the rest flew harmlessly L-12.
Later command decided not to repair badly damaged L-12. The ship was dismantled.
In total during its operation L-12 made 5 reconnaissance flight.

Interesting technically the fact that the frame Zeppelin consisted of duralumin constructions, covered with cotton soaked material. To frame fastened gondola control motors (up to 7 motors). Lift force created 17 special gas cylinders attached to the body, which was hydrogen. The walls of these compartments from 1908 made of so-called "golden skin» («Goldschlagerhaut»). We are talking about the upper shell of the cecum cattle. Only one airship needed skins with 80,000 head of cattle.
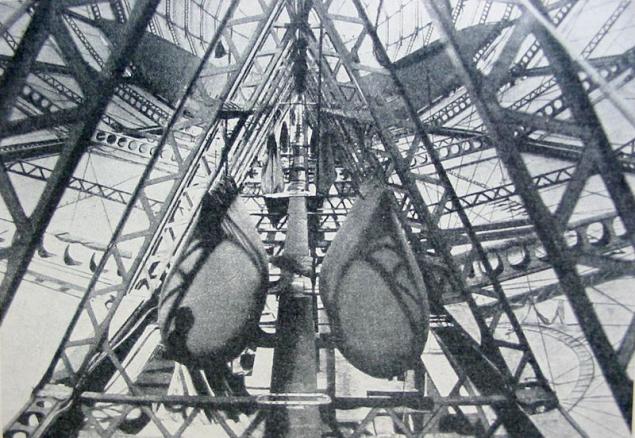
Each zeppelin took on board 1,000 kg of water ballast. It is reset to when needed extra lift. In accordance with the law of Archimedes, the airship filled with light gas, rises, where the so-called "soft heights", the lift becomes close to zero, and the pressure in compartments - close to atmospheric. Weight airship while accurately match the weight of the displaced air. Depending on weather conditions, the lift force increased with increasing atmospheric pressure and air temperature. Furthermore, the correctness of the weather condition of the crew depended on who was in an open cockpit and who should be afraid of detonating gas. At high altitudes balloonists had to endure temperatures up to -40 (S. And the wind at a speed of 36 m / s, usually at such altitudes, more like a hurricane. The crew started in the usual naval uniform, but later put on leather suits and coats, for to escape from the cold. Despite this, some balloonists were returning from frostbitten limbs. At an altitude of about 5000 m lack of oxygen often led to nosebleeds, loss of consciousness or vomiting. Eating during combat flight was largely impossible. ...
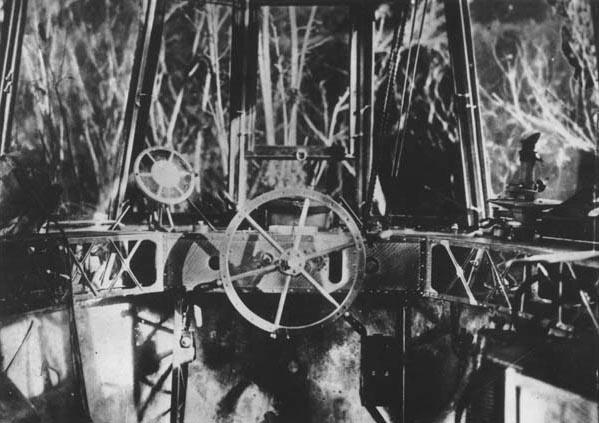
...
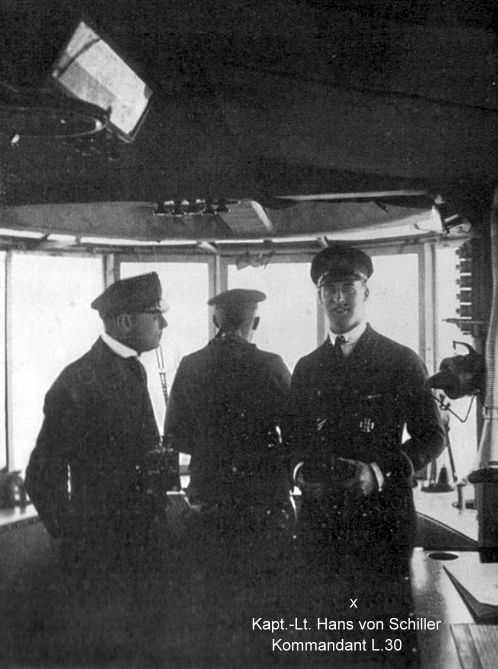

...
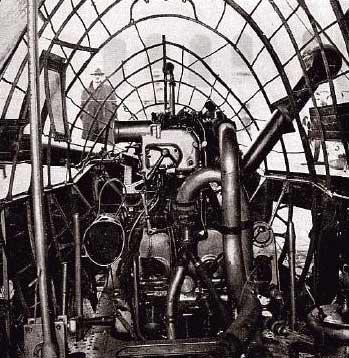
...

Crew Zeppelin
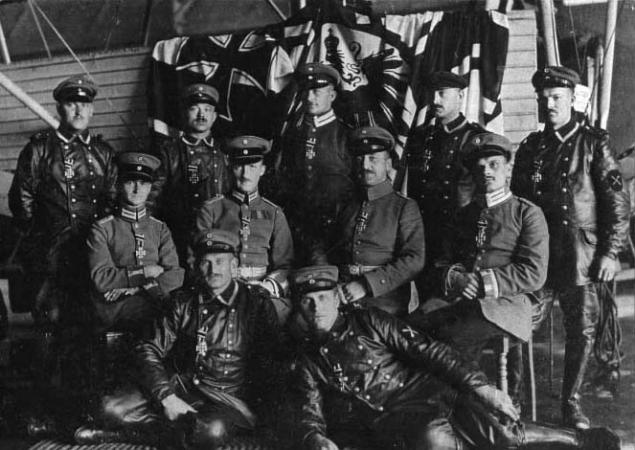

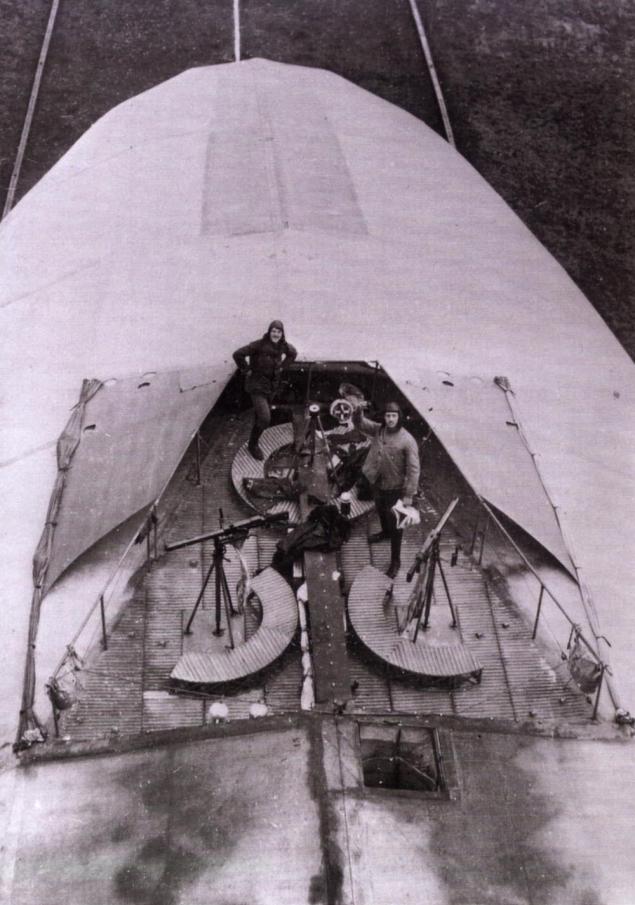
To save weight parachutes with them did not take, but at the same time on board were machine guns. They were installed in the aft nacelle and control. However, the fire of which can be opened only with the permission of the commander not to accidentally caught fire released exhaust gas

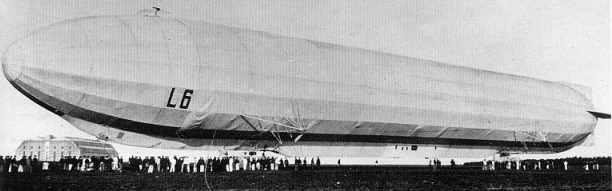
Zeppelin LZ 31 - L6
type: hard, had a duralumin enclosure Three engine 210 PS Maybach 150 hp Volume: 22,470 cubic meters. Capacity: 9, 2 tons Length: 158 m. Speed: 80 km / h Maximum diameter: 14, 86 m.
The first flight made 3 November 1914
Played an important role in fending off an attack fleet on the coast of the UK Germany 25 December 1914
Made 36 reconnaissance flights over the North Sea, spotted minefields.
Made a successful raid on England, during which dropped to 700 kg. bombs.
Burned during refueling gas based Fuhlsbuttel.
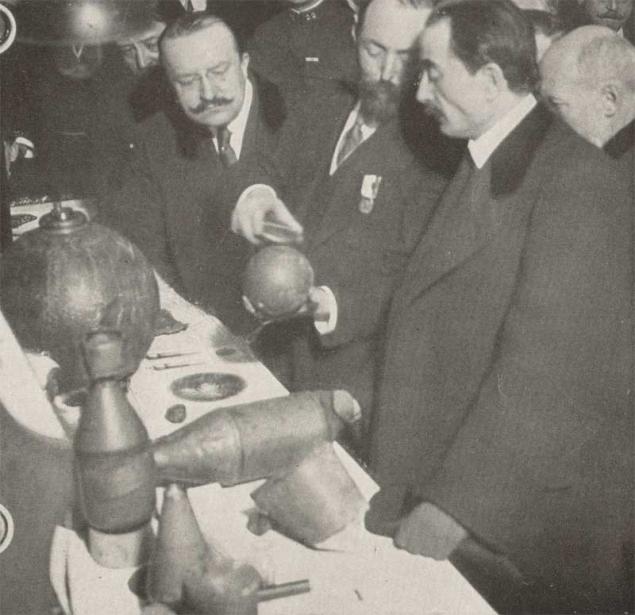
Bombs dropped from Zeppelins over London.
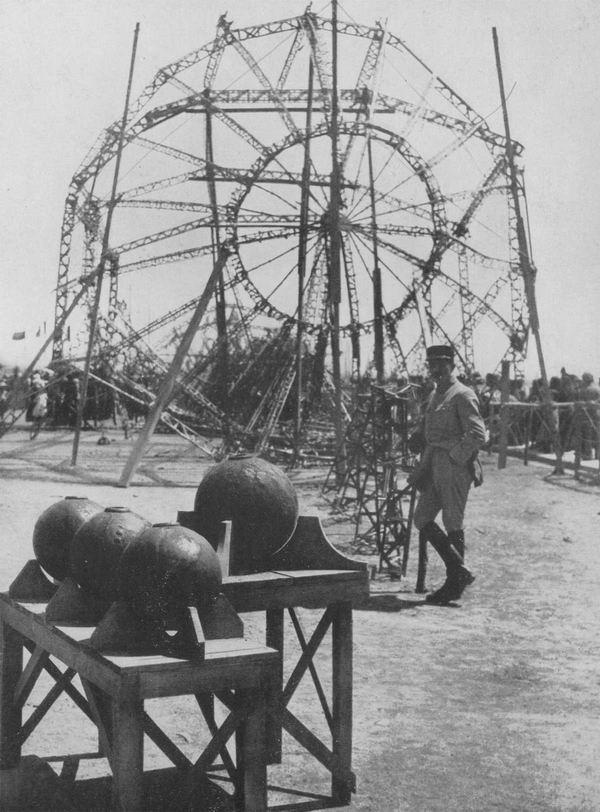

...

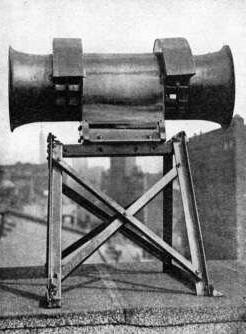
Banshee
They provide notice of the approach of Londovtsev zeppelins.
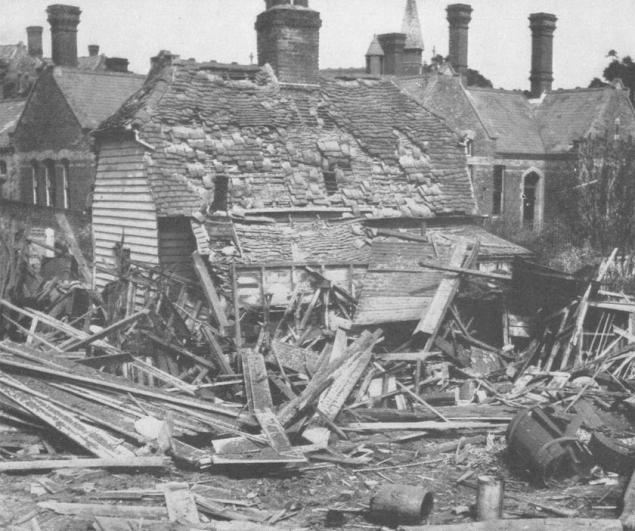
Result Zeppelin raid. White Swan Alley, London, September 9, 1915

...

...

...
Dobavleno1 in [mergetime] 1252596712 [/ mergetime]
British defense pounded German airships all great heights, and British fighter planes were becoming better equipped and more accurately hit the target. Flak also increasingly shot down by German airships. The British capital and other major cities have at their disposal a large number of powerful anti-aircraft installations and spotlights, which quickly found a giant aerial targets and shoot them down, despite a higher altitude. Defeat in a dogfight in almost all cases ended tragically for the crew. The use of airships over the sea is not always saved the crew from death zeppelin.
At sea, the situation was not nearly lutshe.Lish a limited number of times they were able to convey a message about the submarine sighted or detected by mine fields, and in doing so zeppelin was no absolutely no strategic advantage in conducting intelligence, as well as in sea battles.

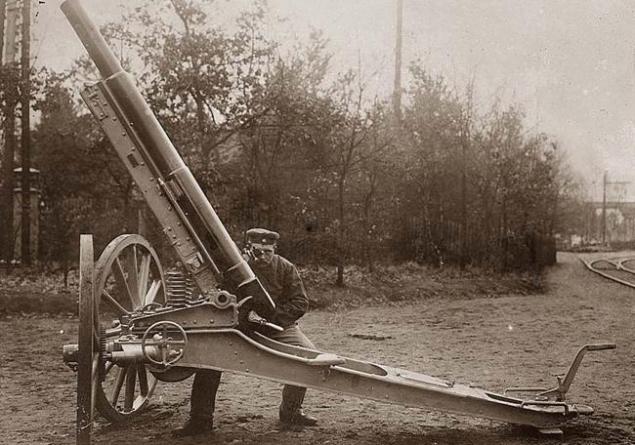
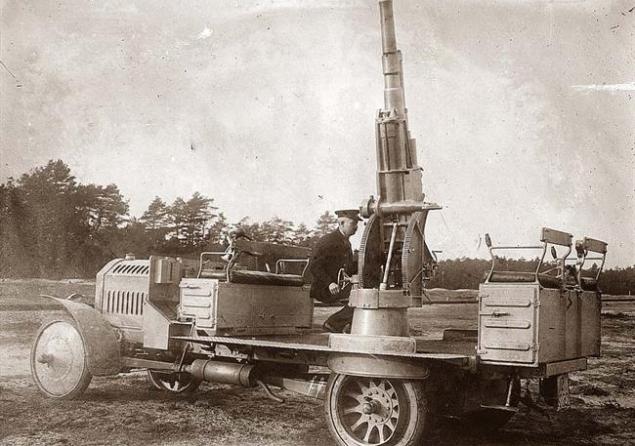
Antiaircraft guns

...

The first Zeppelin raid on London was held May 31, 1915 with the result. LZ-38 killed and wounded 42 people. Such insults Winston Churchill could not endure, and exactly one week LZ-38 was destroyed by British flying boat right at its base near Brussels.
In July 1915 the Kaiser Wilhelm III ordered to organize raids on Britain, but not bomb the buildings belonging to the royal family.
The first airships flying at an altitude of 10,000 feet (about 3,000 m.), But in the UK at the beginning had no means of defense. The first Zeppelin L-8 was shot down by anti-aircraft fire, March 5, 1915 in the area of Newport. June 7, 1915, the first air combat aircraft and airship. Shooter LZ-37 was not experienced, and shot all their ammunition from a distance, without causing damage to the British aircraft. Lieutenant Reginald Uornerford dropped down on defenseless airship 6 bombs. The wreckage of the airship fell convent on the outskirts of Ghent. Killed three nuns. Of the crew survived one person - falling, he struck the roof of the monastery, and fell into bed, which slept nun.
Downed Zeppelin Zeppelin LZ-93- L-44 and the body of his commander.
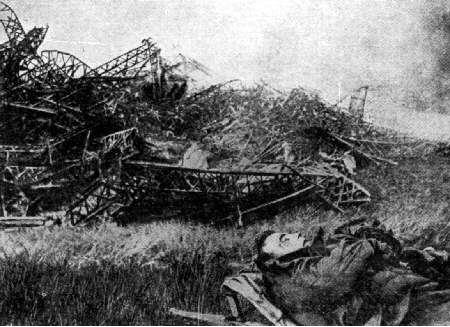
Last Zeppelin raid on Britain on 5 August 1918. It was attended by 5 Zeppelin R type. The flagship was shot over the North Sea by British aircraft DH4. The commander Peter Strasser and 23 crew members were killed. The rest of the Zeppelins dropped bombs in the sea, and went home.
Just raids on Britain from 1915 to 1918 was attended by about 50 airships. There were 12 raids on London, and 40 to the rest of the UK.
Without a doubt, the airship rigid structure was a great discovery, an important step in the world of aviation. Unfortunately, this is an interesting technical innovation was almost exclusively used for military purposes during the imperialist war. Passion for airships to have them in constant readiness, cost huge amounts of money in Germany. UK losses from air raids can be estimated as insignificant. For example, the construction of airships Germany invested funds is 5 times more than the cost of damage caused to air raids UK. The main effect was psychological. Britain was forced to divert from the Western Front over 10 000 people, planes, searchlights, anti-aircraft and other equipment.
Zeppelin raids were very expensive and ineffective, only the recruitment and training of the crew of the airship required four years, and all the crew consisted of 20-25 people of different military specialties. In addition, significant staffing required for ground handling, for example, to lift into the air and into the hangar institution with strong gusts of wind, the required effort of 200 people held a blimp for guys. Ground technicians usually consisted of 20-25 people.
Yet at the end of the First World War the construction of large airships continued. But that's another story.
Source:
28 pics + infa
Ferdinand Zeppelin (Ferdinand Zeppelin, 1838-1917), German designer of airships. Zeppelin was born July 8, 1838 in Konstanz (Baden).
It was in his head was born the idea of creating a flying ship, which would significantly outperform balloon. His life was intertwined with the army. At the age of 16 years he became a graduate of the Military Academy, which was located in Ludwigsburg, Germany, and after 3 years, he was promoted to an officer that is worthy of respect, because then Ferdinand Zeppelin was only 19 years old. Then fate brought him to distant America, which at that time torn apart by the war between the North and the South. After the end of hostilities Graf Zeppelin embarked on intensive research, during which for the first time in his life felt that this, to be in a hot air balloon high above the ground. Who knows, maybe this event and has left its mark on the fate of the then young German. However, before becoming a designer, Zeppelin had a little more to war ... the Austro-Prussian and Franco-Prussian war of Ferdinand Zeppelin made a hero, because after these wars, he already had the rank of General, with him, he got 33 years! Zeppelin retired and started development and testing of airships. In 1900, the first successful flight of the Zeppelin airship hard. Ferdinand Zeppelin airships military used in World War 1914-1918.

Even before the outbreak of World War representatives Kaiser fleet showed an active interest in airships and their possible use in the fighting. Aircraft then were still in the "child" status and their combat use was highly problematic. Airship same could be many hours in the air to rise to greater heights and to carry military cargo. Has played a decisive role, and the fact that the planes on all these parameters significantly inferior airships. Marine General Staff was ready to believe that with the help of the airship rigid structure of Count Zeppelin can be guaranteed to get the latest information on the strategic position of the sea and from the air to conduct offensive military operations. In addition, to build the airship was much cheaper and faster than a cruiser.
in 1900, after the first successful flights of Count Zeppelin airships, the General Staff of the Kaiser "High Seas Fleet," as well, and representatives of the Army, could hope that he will be a weapon, the action is not limited to any front line. By 1912 there were already 26 huge pavilions for land and naval forces. June 1, 1913 in Berlin-Yohanninstale was formed "Naval Air Battalion Task» («Marine-Luftschifferabteilung»).
To this we must add that conducted the glorification of airships as a symbol of the German Teutonic creative spirit and power, as well as a miracle - weapons that can not be countered equivalent enemy.
But in practice, it all came together a little differently ... Zeppelin LZ 24 - L3
type: hard, had a duralumin enclosure Three engine 210 PS Maybach 150 hp Volume: 22,470 cubic meters. Capacity: 9, 2 tons Length: 158 m. Speed: 80 km / h Maximum diameter: 14, 86 m.
The first flight made May 11, 1914 May 16, 1914 reached an altitude of 3125 meters. Was assigned to the Navy. During the war he made 24 reconnaissance missions over the North Sea.
On the night of January 19, 1915 under the command of Lieutenant-Commander Hans Fritz made the first raid on England. In the raid was also attended by airships L4 and L6. L6 because of problems with the engines returned to base. L3 bombarded the port of Yarmouth (Yarmouth), who was considered a military objective. 7 L3 dropped bombs, two people were killed and three were wounded. L4 moved deep into England, and dropped bombs on Kings Lynn. Two people were killed and 13 were wounded. A total of 24 bombs dropped by 50 kg. and some grenades weighing 3 kg. Caused damage 7740 pounds.
After flying in the UK started to panic, and in Germany the news of the raid was met with enthusiasm.
February 17, 1915 L3 made an emergency landing on the coast of Denmark near Fano. The crew was taken prisoner, and the airship was destroyed.

...

Zeppelin LZ 48 (L15)
Type: Hard Four engine rated at 154 kW. Volume: 31,900 cubic meters. m. Capacity: 16, 2 tons. Length: 163 m. Maximum speed: 96 km / h. The maximum diameter of 19 m.
The first flight made September 9, 1915 The photograph L15 during an emergency landing at Nordholz, Germany, October 1915
Made 8 reconnaissance flight. During three raids on England dropped 5780 kg. bombs. Shot down by air defense fire from the ground during a raid on London on 31 March - 1 April 1916 he began to sink in the delta of the River Thames. 17 crew members were taken prisoner. One person was killed.

Zeppelin LZ-95 - L-48
Type: Hard Five Maybach engines rated at 177 kW. Volume: 55,800 cubic meters. m. Capacity: 39 tons. Length: 196 m. Maximum speed: 107 km / h. The maximum diameter of 24 m.
Covershil first flight May 22, 1917
In 1916, Great Britain was able to create quite an effective anti-aircraft defenses. German airships were forced to move their activities to a higher altitude (6000 meters or more) is not available searchlights, anti-aircraft guns and enemy aircraft. In January 1917, the navy of Germany to develop requirements for new airships capable of lifting at high altitude. In March 1917, during the test L-42 rose to a height of 6000 m with a bomb load of 2000 kg.
British Army changed its tactics to combat airships. It was decided to attack airships over the North Sea, where they have not yet gained a great height. In addition, British planes were more likely to attack the base of airships.
48 was shot down over the coastal town of Yarmouth, and fell near Leiston (Suffolk). In the destruction of L-48 for the first time three crew members to use a parachute airship (according to other sources were saved 2 people). Parachutes were hung near windows gondolas. Prior to that, the crews did not take parachutes and increased bomb load - parachutes were not reliable, and if they do vzvryve hydrogen useless.

Zeppelin LZ-95 - L-48
Type: Hard Five Maybach engines rated at 177 kW. Volume: 55,800 cubic meters. m. Capacity: 39 tons. Length: 196 m. Maximum speed: 107 km / h. The maximum diameter of 24 m.
Covershil first flight May 22, 1917
In 1916, Great Britain was able to create quite an effective anti-aircraft defenses. German airships were forced to move their activities to a higher altitude (6000 meters or more) is not available searchlights, anti-aircraft guns and enemy aircraft. In January 1917, the navy of Germany to develop requirements for new airships capable of lifting at high altitude. In March 1917, during the test L-42 rose to a height of 6000 m with a bomb load of 2000 kg.
British Army changed its tactics to combat airships. It was decided to attack airships over the North Sea, where they have not yet gained a great height. In addition, British planes were more likely to attack the base of airships.
48 was shot down over the coastal town of Yarmouth, and fell near Leiston (Suffolk). In the destruction of L-48 for the first time three crew members to use a parachute airship (according to other sources were saved 2 people). Parachutes were hung near windows gondolas. Prior to that, the crews did not take parachutes and increased bomb load - parachutes were not reliable, and if they do vzvryve hydrogen useless.

...

Zeppelin LZ59- L20
Type: Hard 4 Maybach engine capacity of 154 hp Volume: 31,900 cubic meters. m. Capacity: 16 tons 2 Length: 163 m. The maximum diameter of 19 m. The maximum speed: 96 km / h.
The first flight made November 21, 1915 Commander - kapitanleytenant Stabbert.
6 made reconnaissance missions, 2 raid on England. Dropped 2,864 kg. bombs.
May 4, 1916, returning from a raid on England crashed and sank in the Norwegian city of Stavanger (Stavanger). The crew was captured. The commander escaped from captivity after 6 months.

Zeppelin LZ-43
Type: Hard Four Maybach engine rated at 154 kW. Volume: 31,900 cubic meters. m. Capacity: 16, 2 tons. Length: 163 m. Maximum speed: 96 km / h. The maximum diameter of 19 m.
Zeppelin LZ-43 - L-12 made its first flight 21 June 1915
July 20, 1915 the French air force flew a raid on the German city of Karlsruhe. On this day in Germany celebrated the feast of Corpus Christi. Killing 110 people, injuring 123 people. One bomb hit the square, where children were given a theatrical performance. In Germany, a wave of hatred against the Entente.
August 9, 1915 in the bombing of England went from two bases Zeppelin L-9, L-12, L-13, L-10 and L-11. Crews wanted revenge. On board the L-10 was the commander of Division airships Peter Strasser. It was the first massive raid on London airships. Airships were carrying 440 bombs. Their goal was the London docks and factories in the northern part of the city. Bad weather and visibility prevented Zeppelin achieve goals.
By three o'clock in the morning August 10, 1915 the crew jettisoned the radio, empty fuel tanks, handrails from the gondola, the front part of the engine that has stopped due to lack of fuel. Before dawn the airship down on the water of La Manche. The wind began to treat him in the direction of England. The crew gathered in the aft nacelle, which continued to hang in the air. Then came the tug from the shore, and an hour later he delivered the L-12 in the Belgian port of Ostend.
The commander decided to repair the damaged tanks for hydrogen and deliver the airship to the nearest base for repair.
British intelligence received information that in the harbor of Ostend is airship. W. Churchill ordered the destruction of Zeppelin. August 11, 1915 six British flying boats tried to attack the L-12. Flak hit by a British aircraft, the rest flew harmlessly L-12.
Later command decided not to repair badly damaged L-12. The ship was dismantled.
In total during its operation L-12 made 5 reconnaissance flight.

Interesting technically the fact that the frame Zeppelin consisted of duralumin constructions, covered with cotton soaked material. To frame fastened gondola control motors (up to 7 motors). Lift force created 17 special gas cylinders attached to the body, which was hydrogen. The walls of these compartments from 1908 made of so-called "golden skin» («Goldschlagerhaut»). We are talking about the upper shell of the cecum cattle. Only one airship needed skins with 80,000 head of cattle.

Each zeppelin took on board 1,000 kg of water ballast. It is reset to when needed extra lift. In accordance with the law of Archimedes, the airship filled with light gas, rises, where the so-called "soft heights", the lift becomes close to zero, and the pressure in compartments - close to atmospheric. Weight airship while accurately match the weight of the displaced air. Depending on weather conditions, the lift force increased with increasing atmospheric pressure and air temperature. Furthermore, the correctness of the weather condition of the crew depended on who was in an open cockpit and who should be afraid of detonating gas. At high altitudes balloonists had to endure temperatures up to -40 (S. And the wind at a speed of 36 m / s, usually at such altitudes, more like a hurricane. The crew started in the usual naval uniform, but later put on leather suits and coats, for to escape from the cold. Despite this, some balloonists were returning from frostbitten limbs. At an altitude of about 5000 m lack of oxygen often led to nosebleeds, loss of consciousness or vomiting. Eating during combat flight was largely impossible. ...

...

...

...

Crew Zeppelin

To save weight parachutes with them did not take, but at the same time on board were machine guns. They were installed in the aft nacelle and control. However, the fire of which can be opened only with the permission of the commander not to accidentally caught fire released exhaust gas

Zeppelin LZ 31 - L6
type: hard, had a duralumin enclosure Three engine 210 PS Maybach 150 hp Volume: 22,470 cubic meters. Capacity: 9, 2 tons Length: 158 m. Speed: 80 km / h Maximum diameter: 14, 86 m.
The first flight made 3 November 1914
Played an important role in fending off an attack fleet on the coast of the UK Germany 25 December 1914
Made 36 reconnaissance flights over the North Sea, spotted minefields.
Made a successful raid on England, during which dropped to 700 kg. bombs.
Burned during refueling gas based Fuhlsbuttel.

Bombs dropped from Zeppelins over London.

...

Banshee
They provide notice of the approach of Londovtsev zeppelins.

Result Zeppelin raid. White Swan Alley, London, September 9, 1915

...

...

...
Dobavleno1 in [mergetime] 1252596712 [/ mergetime]
British defense pounded German airships all great heights, and British fighter planes were becoming better equipped and more accurately hit the target. Flak also increasingly shot down by German airships. The British capital and other major cities have at their disposal a large number of powerful anti-aircraft installations and spotlights, which quickly found a giant aerial targets and shoot them down, despite a higher altitude. Defeat in a dogfight in almost all cases ended tragically for the crew. The use of airships over the sea is not always saved the crew from death zeppelin.
At sea, the situation was not nearly lutshe.Lish a limited number of times they were able to convey a message about the submarine sighted or detected by mine fields, and in doing so zeppelin was no absolutely no strategic advantage in conducting intelligence, as well as in sea battles.

Antiaircraft guns

...

The first Zeppelin raid on London was held May 31, 1915 with the result. LZ-38 killed and wounded 42 people. Such insults Winston Churchill could not endure, and exactly one week LZ-38 was destroyed by British flying boat right at its base near Brussels.
In July 1915 the Kaiser Wilhelm III ordered to organize raids on Britain, but not bomb the buildings belonging to the royal family.
The first airships flying at an altitude of 10,000 feet (about 3,000 m.), But in the UK at the beginning had no means of defense. The first Zeppelin L-8 was shot down by anti-aircraft fire, March 5, 1915 in the area of Newport. June 7, 1915, the first air combat aircraft and airship. Shooter LZ-37 was not experienced, and shot all their ammunition from a distance, without causing damage to the British aircraft. Lieutenant Reginald Uornerford dropped down on defenseless airship 6 bombs. The wreckage of the airship fell convent on the outskirts of Ghent. Killed three nuns. Of the crew survived one person - falling, he struck the roof of the monastery, and fell into bed, which slept nun.
Downed Zeppelin Zeppelin LZ-93- L-44 and the body of his commander.

Last Zeppelin raid on Britain on 5 August 1918. It was attended by 5 Zeppelin R type. The flagship was shot over the North Sea by British aircraft DH4. The commander Peter Strasser and 23 crew members were killed. The rest of the Zeppelins dropped bombs in the sea, and went home.
Just raids on Britain from 1915 to 1918 was attended by about 50 airships. There were 12 raids on London, and 40 to the rest of the UK.
Without a doubt, the airship rigid structure was a great discovery, an important step in the world of aviation. Unfortunately, this is an interesting technical innovation was almost exclusively used for military purposes during the imperialist war. Passion for airships to have them in constant readiness, cost huge amounts of money in Germany. UK losses from air raids can be estimated as insignificant. For example, the construction of airships Germany invested funds is 5 times more than the cost of damage caused to air raids UK. The main effect was psychological. Britain was forced to divert from the Western Front over 10 000 people, planes, searchlights, anti-aircraft and other equipment.
Zeppelin raids were very expensive and ineffective, only the recruitment and training of the crew of the airship required four years, and all the crew consisted of 20-25 people of different military specialties. In addition, significant staffing required for ground handling, for example, to lift into the air and into the hangar institution with strong gusts of wind, the required effort of 200 people held a blimp for guys. Ground technicians usually consisted of 20-25 people.
Yet at the end of the First World War the construction of large airships continued. But that's another story.
Source:






















