1105
Rating poisons
Similar has already been more than once, but there is still a little different, and the figures.
Introduction.
"Everything is poison and nothing is devoid of toxicity. Poison from the drug dose is different »
Aureolus Philip Theophrastus von Hohenheim Bombastus (Paracelsus) 1493-1541. "Father" of toxicology.
In the animal world is constantly a struggle for survival. One nature has bestowed claws, teeth and hooves, and other skills to run quickly and deftly dodge Third Oliver Winchester and Mikhail Kalashnikov, but got the fourth most sophisticated weapons - poisons.
Small and seemingly defenseless, but people are able to kill a bunch of little animals have long attracted the attention of human rights and have been the object of study. And it is doing this ugliness science Toxicology. The main objectives of this science - detection and study of substances that can cause poisoning in humans, the study of the interaction of the poison to the body, as well as determining the range of the toxic effect of the venom from the safe to the minimum sufficient to completely discard hooves dose.
Information here

Classification of toxic living creatures.
Primary poisonous animals, those that produce the poison in the process of life. By way of development, they are divided into active and passive poison poisonous. First they have special glands to produce poison. These in turn are divided into armed (teeth, stings, etc.) and are not armed (which spit, release the skin, etc.). Passively toxic do not have special glands, the poison contained in their tissues and organs (liver, skin, etc.)
Secondary toxic (often fish and shellfish) venoms themselves do not synthesize but can accumulate toxins that enter them with food and water. Their toxicity is not constant and depends on many factors. According to the scientists, by animal this is not good not bad.
Approximately three-quarters of the planet yadnostsev are arthropods. The rest of the vast majority - are cold-blooded (reptiles, amphibians, fish and shellfish). Also, of course, there are birds and animals (such as the platypus). So if the next door on your floor lives a serial killer to show him respect and to be original, you can not call it a cold-blooded, and arthropods. And thanks to it will show you all what he can do.
Through years of research science has achieved good results. People poisons used in medicine. For example one of the latest achievements of science has been the allocation of omega-conotoxin, a component of the kind of shellfish poison Conus. This substance is 100-1000 times more potent than morphine and is not addictive !!! (if one has already started to gather on the hunt, the cones are found in coastal waters of the tropical Pacific Islands). Play the poison of an animal in the laboratory can not be entirely impossible. Scientists have learned how to synthesize only a few individual components (poisons animals contain all sorts of components and scientists are studying the effects on the body as a poison in a whole and its individual components). Therefore, they have all these little animals to catch, grow up on farms and then they were hard to milk.
Also one of the main objectives of toxicology - is the development of antidotes that after getting into the human body of poisons could save him. A variety syvortok against every poison. Serum idea is simple: zootoxins are foreign proteins - antigens, so they can unleash special proteins - antibodies. Scientists noticed (wonder why animals do not die from your poison) that the bodies of poisonous creatures present such antibodies, which protect themselves. In 1895, Albert Calmette developed the first serum antidote. To this day, it uses the same method of development: take a horse, pumped her a small amount of poison while she did not produce sufficient antibodies to resist. Then he introduced her to another, then another. Then the blood is drained from it and filtered out of her desired substance.
How often in the movies, bitten can give first aid to suck the venom out of the wound. But it is important to know a few things (suddenly someone come in handy). In the mouth, there should be no sores, tooth decay, ulcers and other tissue damage, or victims will have two. When a snake bite, this method is valid only for the first 5 minutes. Insect bites in 15 minutes. Cut with a knife, pull harness and cauterize the bite does not make sense, only hurt. Watering the bite alcohol is impossible, only intensify the poison. It is better to apply ice to the wound and ran to drag him to the hospital, where e mu introduce serum. Diagnostic methods for determining the type of poison does not exist, since toxic substances are changing rapidly in the body and determine the patient who was bitten as all shitty can be determined only on the symptoms and the testimony of witnesses.
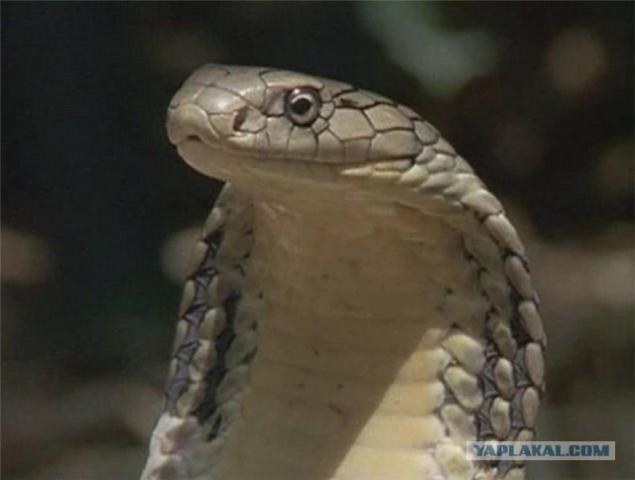
And so it is, who is the most poisonous in the world? To begin with, there are no instruments that determine these criteria. Everything is much simpler: take a mouse (not allowed to check on people all over the world) or rabbit (the dog) and exposed to the poison. (in the case of zootoxins most common method - intramuscular administration). Patient died? - Damn, write down how much of the next injected and drag. Still alive? - In the direction of it, albeit bounces back and write down how much you are stuck. And so millions of mice are killed in the name of science (the grateful people put them a few sites in several countries) .Tochnost determination of human exposure so small and amounts to 35% if the studies were conducted in rats and 53% - if the dogs. If pump poison all available test, the accuracy of matching human exposure increases to 70% (if all test subjects died). Based on these experiences to rank venomous animals you can make only one parameter: the mouse only, intramuscular administration only and evaluation only the individual components of poisons, and poisons are not whole. Value indicates the strength of poison is measured in milligrams per kilogram of body weight. DL50 - the average lethal dose causes death in half of the experimental mice. DL100- minimum amount of venom that was enough to kill anyone who will introduce him (again mouse). And so the list of the most poisonous animals on the DL50 for mice when administered intramuscularly. 10th
Neurotoxin II (0, 085 mg / kg)
Where to take Component Central Asian cobra venom (Naja oxiana)
It causes flaccid paralysis of skeletal and respiratory muscles due to non-depolarizing block N-cholinergic receptor striated muscle (kurarepodobnymi effect).
Short description: Central Asian cobra, which reaches a length of 1, 5-1, 6 m, distributed in the north-western India, Pakistan, Afghanistan and north-eastern Iran. In Central Asia, this snake is found in Turkmenistan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. The northern boundary of the range - the backbone of the Nura-Tau and Tau Mountain Belle-Ata, west - spurs of the Turkestan range.
Antidote: horse serum purified concentrated liquid

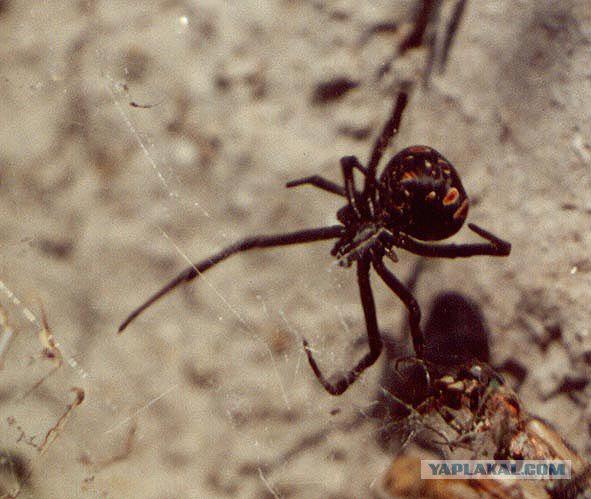
9th
Alpha-latrotoxin (0, 045 mg / kg)
Where to take: consisting armed with 31 species of spiders genus Latrodectus (karakurt)
Neurotoxin that causes the release of acetylcholine from presynaptic terminals, noradrenaline and other mediators with subsequent depletion of stocks.
Antidote: antitoxic serum "Antikarakurt»
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF WIDOW ("black widow") are found in tropical, subtropical and even temperate latitudes of all continents except Antarctica. The risk to humans of only females (the size of their body - up to 2 cm). Males are much smaller (0 to 5 cm) and are not able to bite through human skin. The toxicity of the venom has a pronounced seasonal dependence: September powerful May about ten times.

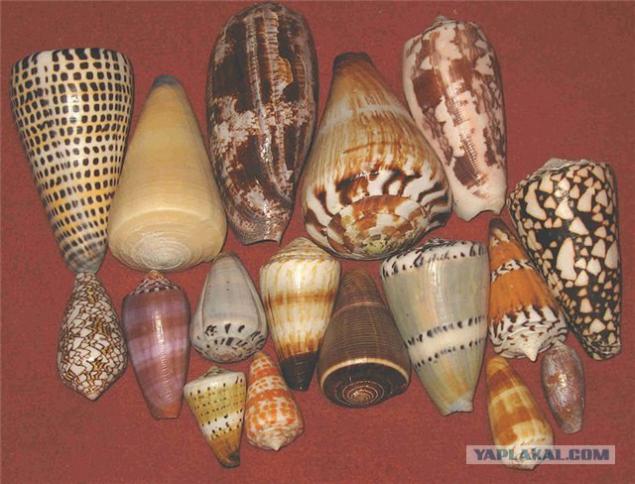
8th
Alpha-conotoxin (0, 012 mg / kg)
Where to take Component of a composite shellfish poison Conus geographus
Neurotoxin that blocks the N-cholinergic receptors of muscle and peripheral nerves.
Antidote: antitoxic serum in development as an antidote used anticholinesterase drugs
Description: Shells cones are 15-20 cm in length. Habitat - the eastern and northern coast of Australia, the eastern coast of Southeast Asia and China, and the Central Pacific.

7th
Chirikitotoksin (DL50 = 0, 01 mg / kg)
Where to take: produces skin toads Atelopus chiriquiensis
Structural analogs of tetrodotoxin - differs only in the replacement group CH2OH yet unidentified radical. Neurotoxin block sodium and potassium channels in the membranes of nerve endings.
Antidote: No specific antidote, spend detoxication and symptomatic therapy
Description: Small (males - about 3 cm, females - 3, 5-5 cm) toad with a beautiful name chirikita are found on the isthmus between North and South America - in Panama and Costa Rica. Type is endangered. The toxin produces leather Chiriqui and virulence, we recall, was evaluated when administered intramuscularly. But if you spread the boom ...
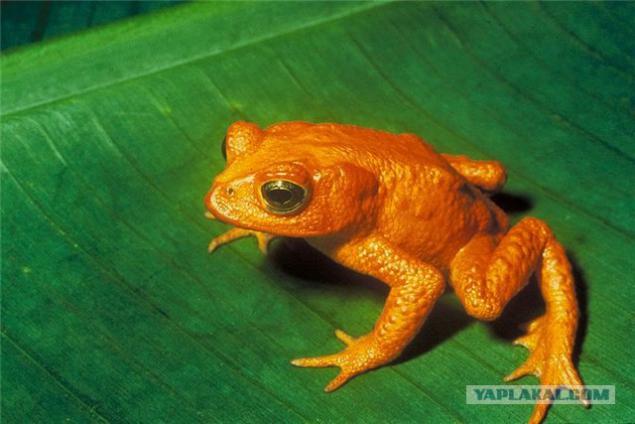

6th
Tityutoksin (0, 009 mg / kg)
Where do I get one of the components of scorpion venom yellow tolstohvostogo (Androctonus australis)
Neurotoxin slows the fast inactivation of sodium channels electrically excitable membranes, that leads to the development of persistent depolarization.
Antidote: antitoxic serum "Antiskorpion." As a little less effective replacement can be used serum "Antikarakurt»
Androctonus australis - medium sized scorpions, up to 10 cm. Australia has no relationship: australis in Latin - "southern" (a androctonus in Greek - "a murderer"). Meet in the Middle East, in the north and south-east Africa (Algeria, Tunisia, Lebanon, Israel, Egypt, Jordan, UAE, Iraq, Iran, etc.).
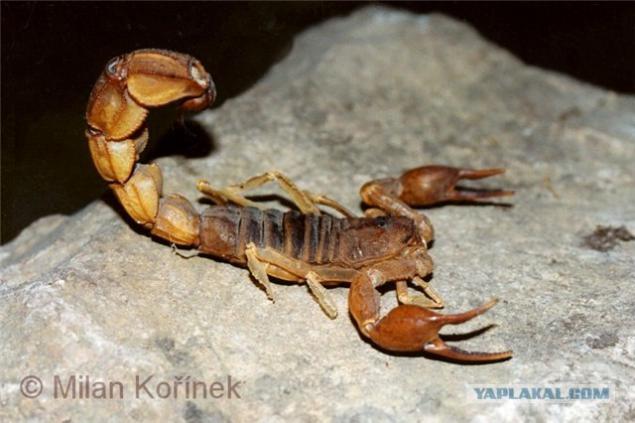

5th
Tetrodotoxin (0, 008 mg / kg)
Shellfish BabyLonia japonica has a very beautiful shell of the classical spiral shapes in length of 40-85 mm. Habitat - the coast of the Korean Peninsula, Taiwan and Japan.
Toad Atelopus varius - small, 2, 5-4 cm, and stumble on them if "lucky" only in the jungles of Panama and Costa Rica
Habitat puffer fish - from the north coast to the north coast of Australia, Japan and the southern coast of China to the eastern islands of Oceania
Where to take: it is produced and accumulates in the tissues of fish of the family Tetraodontidae, shellfish BabyIonia japonica and close relatives of Chiriqui - toad Atelopus varius
Neurotoxin selectively blocking sodium channels in the membranes of nerve endings.
Antidote: No specific antidote, spend detoxication and symptomatic therapy
Some species of the family Tetraodontidae (chetyrehzubye, they also puffer fish, dogs and blowfish) reach a length of up to half a meter. And these fish, and a dish of them in Japan called "fugue". The poison is found in liver, milk, eggs, intestines and skin, so to cook fugu Only qualified chefs that remove toxic bodies separately for each type of procedure. According to the Japanese proverb, "He who eats fugue - a fool, but he who does not eat - too stupid."

4th
Taypoksin (taypotoksin) (0, 002 mg / kg)
Where to take Component venom of the poisonous snake on earth - the Australian Taipan (Oxyuranus scutellatus). Before the development of an antidote (1955) to 90% perished bitten
Presynaptic toxin possesses phospholipase activity and causes a characteristic change in the release of mediators of nerve impulse (weakening secretion increased and finally its complete inhibition). It has neurotoxic and miotoksicheskim action.
Antidote: antitoxic serum taypanovaya
Description: Taipan reach a length of 2 to 3, 6 m. Differ very aggressive nature, but, fortunately, found only in sparsely populated areas in the north-east coast of Australia and southern New Guinea.

3rd place
Batrachotoxin (0, 002 mg / kg)
Where to take: skin secretions of frogs, poison dart frogs genus Phyllobates
It has strong cardiotoxic causing arrhythmia and ventricular fibrillation of the heart, paralyzing the respiratory muscles, myocardium and skeletal muscles. Resistant and permanently increases the permeability of the resting membrane for sodium ions, blocking axonal transport.
Antidote: No specific antidote, spend detoxication and symptomatic therapy. Tetrodotoxin is a potent antagonist - like cures ...
Short description: Wood Frog does not exceed 5 cm in length, usually brightly colored in gold, black and orange, black and yellow tones (warning coloring). If you will bring to South America from Nicaragua to Colombia - do not grab their hands.

2nd place
Palytoxin (0, 00015 mg / kg)
Where to take: a six-rays found in coral polyps Palythoa toxica, P. tuberculosa, P. saribacorum
Cytotoxic venom. Damages sodium-potassium pump cell, disrupting the concentration gradient of the ions between the cell and the extracellular environment. Causes of chest pain is angina pectoris, tachycardia, shortness of breath, hemolysis. Death occurs within the first few minutes after the injection of the polyp.
Antidote: No specific antidote, symptomatic therapy (if you have time). Animal studies show that effective can be the simple vasodilators such as papaverine and isosorbide dinitrate.
Description: The body of these polyps - the inhabitants of the coral reefs of the Indian and Pacific oceans - is not out of eight, like ordinary corals, and six or more than eight, the amount placed on several rays corolla, usually a multiple of six.

Finally the winner
Diamphotoxin (0 000025Kmg / kg)
A single chain polypeptide opening "input" all sodium-potassium channels in the cell membrane, resulting in cell death due to intracellular electrolyte balance disturbances. Has neurotoxic and haemolytic effect is particularly pronounced, able in a short time to reduce the content of hemoglobin in the blood by 75% due to the massive destruction of erythrocytes. Bushmen now use crushed larvae diamfidy: Coat of manure boom can knock out 500-pound adult giraffe.
Description: Adult beetles reach 10-12 mm in length. Females lay eggs on the branches of plants Commifora (Commiphora). The larvae burrow into the ground, pupate and for several years to develop pupae. Therefore, to find cocoons Diamphidia for hunters is not a problem.
Antidote: There is no specific antidote. Spend detoxication and symptomatic therapy
Where to take: the most powerful poison of animal origin on the planet contained in the hemolymph ("blood") larvae South African leaf beetle genus Diamphidia (D.Klocusta, D.Knigro-ornata, D.Kfemoralis) belonging to the same family with all known Kartoshkin pest - Colorado potato beetle. Designed exclusively for protection from predators

Source:
Introduction.
"Everything is poison and nothing is devoid of toxicity. Poison from the drug dose is different »
Aureolus Philip Theophrastus von Hohenheim Bombastus (Paracelsus) 1493-1541. "Father" of toxicology.
In the animal world is constantly a struggle for survival. One nature has bestowed claws, teeth and hooves, and other skills to run quickly and deftly dodge Third Oliver Winchester and Mikhail Kalashnikov, but got the fourth most sophisticated weapons - poisons.
Small and seemingly defenseless, but people are able to kill a bunch of little animals have long attracted the attention of human rights and have been the object of study. And it is doing this ugliness science Toxicology. The main objectives of this science - detection and study of substances that can cause poisoning in humans, the study of the interaction of the poison to the body, as well as determining the range of the toxic effect of the venom from the safe to the minimum sufficient to completely discard hooves dose.
Information here

Classification of toxic living creatures.
Primary poisonous animals, those that produce the poison in the process of life. By way of development, they are divided into active and passive poison poisonous. First they have special glands to produce poison. These in turn are divided into armed (teeth, stings, etc.) and are not armed (which spit, release the skin, etc.). Passively toxic do not have special glands, the poison contained in their tissues and organs (liver, skin, etc.)
Secondary toxic (often fish and shellfish) venoms themselves do not synthesize but can accumulate toxins that enter them with food and water. Their toxicity is not constant and depends on many factors. According to the scientists, by animal this is not good not bad.
Approximately three-quarters of the planet yadnostsev are arthropods. The rest of the vast majority - are cold-blooded (reptiles, amphibians, fish and shellfish). Also, of course, there are birds and animals (such as the platypus). So if the next door on your floor lives a serial killer to show him respect and to be original, you can not call it a cold-blooded, and arthropods. And thanks to it will show you all what he can do.
Through years of research science has achieved good results. People poisons used in medicine. For example one of the latest achievements of science has been the allocation of omega-conotoxin, a component of the kind of shellfish poison Conus. This substance is 100-1000 times more potent than morphine and is not addictive !!! (if one has already started to gather on the hunt, the cones are found in coastal waters of the tropical Pacific Islands). Play the poison of an animal in the laboratory can not be entirely impossible. Scientists have learned how to synthesize only a few individual components (poisons animals contain all sorts of components and scientists are studying the effects on the body as a poison in a whole and its individual components). Therefore, they have all these little animals to catch, grow up on farms and then they were hard to milk.
Also one of the main objectives of toxicology - is the development of antidotes that after getting into the human body of poisons could save him. A variety syvortok against every poison. Serum idea is simple: zootoxins are foreign proteins - antigens, so they can unleash special proteins - antibodies. Scientists noticed (wonder why animals do not die from your poison) that the bodies of poisonous creatures present such antibodies, which protect themselves. In 1895, Albert Calmette developed the first serum antidote. To this day, it uses the same method of development: take a horse, pumped her a small amount of poison while she did not produce sufficient antibodies to resist. Then he introduced her to another, then another. Then the blood is drained from it and filtered out of her desired substance.
How often in the movies, bitten can give first aid to suck the venom out of the wound. But it is important to know a few things (suddenly someone come in handy). In the mouth, there should be no sores, tooth decay, ulcers and other tissue damage, or victims will have two. When a snake bite, this method is valid only for the first 5 minutes. Insect bites in 15 minutes. Cut with a knife, pull harness and cauterize the bite does not make sense, only hurt. Watering the bite alcohol is impossible, only intensify the poison. It is better to apply ice to the wound and ran to drag him to the hospital, where e mu introduce serum. Diagnostic methods for determining the type of poison does not exist, since toxic substances are changing rapidly in the body and determine the patient who was bitten as all shitty can be determined only on the symptoms and the testimony of witnesses.
And so it is, who is the most poisonous in the world? To begin with, there are no instruments that determine these criteria. Everything is much simpler: take a mouse (not allowed to check on people all over the world) or rabbit (the dog) and exposed to the poison. (in the case of zootoxins most common method - intramuscular administration). Patient died? - Damn, write down how much of the next injected and drag. Still alive? - In the direction of it, albeit bounces back and write down how much you are stuck. And so millions of mice are killed in the name of science (the grateful people put them a few sites in several countries) .Tochnost determination of human exposure so small and amounts to 35% if the studies were conducted in rats and 53% - if the dogs. If pump poison all available test, the accuracy of matching human exposure increases to 70% (if all test subjects died). Based on these experiences to rank venomous animals you can make only one parameter: the mouse only, intramuscular administration only and evaluation only the individual components of poisons, and poisons are not whole. Value indicates the strength of poison is measured in milligrams per kilogram of body weight. DL50 - the average lethal dose causes death in half of the experimental mice. DL100- minimum amount of venom that was enough to kill anyone who will introduce him (again mouse). And so the list of the most poisonous animals on the DL50 for mice when administered intramuscularly. 10th
Neurotoxin II (0, 085 mg / kg)
Where to take Component Central Asian cobra venom (Naja oxiana)
It causes flaccid paralysis of skeletal and respiratory muscles due to non-depolarizing block N-cholinergic receptor striated muscle (kurarepodobnymi effect).
Short description: Central Asian cobra, which reaches a length of 1, 5-1, 6 m, distributed in the north-western India, Pakistan, Afghanistan and north-eastern Iran. In Central Asia, this snake is found in Turkmenistan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. The northern boundary of the range - the backbone of the Nura-Tau and Tau Mountain Belle-Ata, west - spurs of the Turkestan range.
Antidote: horse serum purified concentrated liquid

9th
Alpha-latrotoxin (0, 045 mg / kg)
Where to take: consisting armed with 31 species of spiders genus Latrodectus (karakurt)
Neurotoxin that causes the release of acetylcholine from presynaptic terminals, noradrenaline and other mediators with subsequent depletion of stocks.
Antidote: antitoxic serum "Antikarakurt»
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF WIDOW ("black widow") are found in tropical, subtropical and even temperate latitudes of all continents except Antarctica. The risk to humans of only females (the size of their body - up to 2 cm). Males are much smaller (0 to 5 cm) and are not able to bite through human skin. The toxicity of the venom has a pronounced seasonal dependence: September powerful May about ten times.

8th
Alpha-conotoxin (0, 012 mg / kg)
Where to take Component of a composite shellfish poison Conus geographus
Neurotoxin that blocks the N-cholinergic receptors of muscle and peripheral nerves.
Antidote: antitoxic serum in development as an antidote used anticholinesterase drugs
Description: Shells cones are 15-20 cm in length. Habitat - the eastern and northern coast of Australia, the eastern coast of Southeast Asia and China, and the Central Pacific.

7th
Chirikitotoksin (DL50 = 0, 01 mg / kg)
Where to take: produces skin toads Atelopus chiriquiensis
Structural analogs of tetrodotoxin - differs only in the replacement group CH2OH yet unidentified radical. Neurotoxin block sodium and potassium channels in the membranes of nerve endings.
Antidote: No specific antidote, spend detoxication and symptomatic therapy
Description: Small (males - about 3 cm, females - 3, 5-5 cm) toad with a beautiful name chirikita are found on the isthmus between North and South America - in Panama and Costa Rica. Type is endangered. The toxin produces leather Chiriqui and virulence, we recall, was evaluated when administered intramuscularly. But if you spread the boom ...

6th
Tityutoksin (0, 009 mg / kg)
Where do I get one of the components of scorpion venom yellow tolstohvostogo (Androctonus australis)
Neurotoxin slows the fast inactivation of sodium channels electrically excitable membranes, that leads to the development of persistent depolarization.
Antidote: antitoxic serum "Antiskorpion." As a little less effective replacement can be used serum "Antikarakurt»
Androctonus australis - medium sized scorpions, up to 10 cm. Australia has no relationship: australis in Latin - "southern" (a androctonus in Greek - "a murderer"). Meet in the Middle East, in the north and south-east Africa (Algeria, Tunisia, Lebanon, Israel, Egypt, Jordan, UAE, Iraq, Iran, etc.).

5th
Tetrodotoxin (0, 008 mg / kg)
Shellfish BabyLonia japonica has a very beautiful shell of the classical spiral shapes in length of 40-85 mm. Habitat - the coast of the Korean Peninsula, Taiwan and Japan.
Toad Atelopus varius - small, 2, 5-4 cm, and stumble on them if "lucky" only in the jungles of Panama and Costa Rica
Habitat puffer fish - from the north coast to the north coast of Australia, Japan and the southern coast of China to the eastern islands of Oceania
Where to take: it is produced and accumulates in the tissues of fish of the family Tetraodontidae, shellfish BabyIonia japonica and close relatives of Chiriqui - toad Atelopus varius
Neurotoxin selectively blocking sodium channels in the membranes of nerve endings.
Antidote: No specific antidote, spend detoxication and symptomatic therapy
Some species of the family Tetraodontidae (chetyrehzubye, they also puffer fish, dogs and blowfish) reach a length of up to half a meter. And these fish, and a dish of them in Japan called "fugue". The poison is found in liver, milk, eggs, intestines and skin, so to cook fugu Only qualified chefs that remove toxic bodies separately for each type of procedure. According to the Japanese proverb, "He who eats fugue - a fool, but he who does not eat - too stupid."

4th
Taypoksin (taypotoksin) (0, 002 mg / kg)
Where to take Component venom of the poisonous snake on earth - the Australian Taipan (Oxyuranus scutellatus). Before the development of an antidote (1955) to 90% perished bitten
Presynaptic toxin possesses phospholipase activity and causes a characteristic change in the release of mediators of nerve impulse (weakening secretion increased and finally its complete inhibition). It has neurotoxic and miotoksicheskim action.
Antidote: antitoxic serum taypanovaya
Description: Taipan reach a length of 2 to 3, 6 m. Differ very aggressive nature, but, fortunately, found only in sparsely populated areas in the north-east coast of Australia and southern New Guinea.

3rd place
Batrachotoxin (0, 002 mg / kg)
Where to take: skin secretions of frogs, poison dart frogs genus Phyllobates
It has strong cardiotoxic causing arrhythmia and ventricular fibrillation of the heart, paralyzing the respiratory muscles, myocardium and skeletal muscles. Resistant and permanently increases the permeability of the resting membrane for sodium ions, blocking axonal transport.
Antidote: No specific antidote, spend detoxication and symptomatic therapy. Tetrodotoxin is a potent antagonist - like cures ...
Short description: Wood Frog does not exceed 5 cm in length, usually brightly colored in gold, black and orange, black and yellow tones (warning coloring). If you will bring to South America from Nicaragua to Colombia - do not grab their hands.

2nd place
Palytoxin (0, 00015 mg / kg)
Where to take: a six-rays found in coral polyps Palythoa toxica, P. tuberculosa, P. saribacorum
Cytotoxic venom. Damages sodium-potassium pump cell, disrupting the concentration gradient of the ions between the cell and the extracellular environment. Causes of chest pain is angina pectoris, tachycardia, shortness of breath, hemolysis. Death occurs within the first few minutes after the injection of the polyp.
Antidote: No specific antidote, symptomatic therapy (if you have time). Animal studies show that effective can be the simple vasodilators such as papaverine and isosorbide dinitrate.
Description: The body of these polyps - the inhabitants of the coral reefs of the Indian and Pacific oceans - is not out of eight, like ordinary corals, and six or more than eight, the amount placed on several rays corolla, usually a multiple of six.

Finally the winner
Diamphotoxin (0 000025Kmg / kg)
A single chain polypeptide opening "input" all sodium-potassium channels in the cell membrane, resulting in cell death due to intracellular electrolyte balance disturbances. Has neurotoxic and haemolytic effect is particularly pronounced, able in a short time to reduce the content of hemoglobin in the blood by 75% due to the massive destruction of erythrocytes. Bushmen now use crushed larvae diamfidy: Coat of manure boom can knock out 500-pound adult giraffe.
Description: Adult beetles reach 10-12 mm in length. Females lay eggs on the branches of plants Commifora (Commiphora). The larvae burrow into the ground, pupate and for several years to develop pupae. Therefore, to find cocoons Diamphidia for hunters is not a problem.
Antidote: There is no specific antidote. Spend detoxication and symptomatic therapy
Where to take: the most powerful poison of animal origin on the planet contained in the hemolymph ("blood") larvae South African leaf beetle genus Diamphidia (D.Klocusta, D.Knigro-ornata, D.Kfemoralis) belonging to the same family with all known Kartoshkin pest - Colorado potato beetle. Designed exclusively for protection from predators

Source: