909
What's inside
Hi, PL o /.
The theme will be fasting slowly. Please do not break, the end will tell.
Today I will try to start a series of three articles about the technology of storing information on optical media. Today will be a general theory. This introductory article will mnogobukoff and some explanatory illustrations.
If the first part will be of interest, the next two will be dedicated to the production of practice already with live pictures and videos. I understand that on the entertainment portal chances at the first part a bit, but still try.
It goes on R (RW) media!
Further discussion will be set out by the example of DVD, because I know the specifics DVD fullest. You can be absolutely sure that everything described is true for CD and Blu-Ray. Only different nuances.
Let's go.
Thus, the optical disc. You all know him, many people even think they know how it is arranged inside. Unfortunately most of representation are not even close to understanding the true state of affairs. Disc "in the context" is a kind of sandwich construction with CD, DVD and BR differ. For example, CD and DVD that's their construction:
THIS CD
As can be seen, one CD is actually round piece of plastic, the top of which displaced helical track carrying information. This surface is metallized to provide a reflection of the beam of the reader. Then a thin layer of metallization is covered with a protective varnish for the physical protection, as well as for protection against moisture and oxygen. Without varnish a thin layer of aluminum oxide and would have degraded within a short time and to read the disc has failed to. Well, quite on top of the drive is usually an image (hereinafter - print). If there is a desire and curiosity - can check presentation. Take the sandpaper and thoroughly unnecessary proshkurte a CD on top. You will see that very quickly dotrete drive to metalization and withdraw it.
But this DVD.
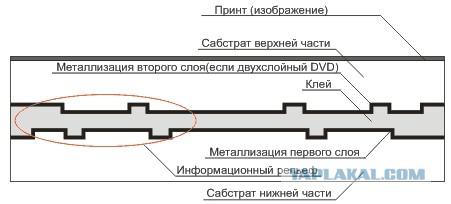
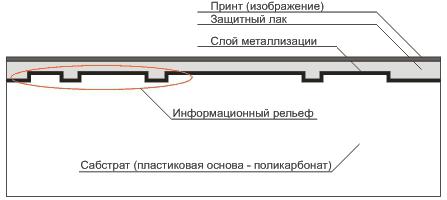
DVD, unlike CD consists of two halves sabstrata (plastic disc) bonded together. Information relief and metallization layer is located inside the sandwich and reliably protected polycarbonate layer. Again, for the inquisitive - bending can break the unnecessary DVD and you'll see that the disc consists of glued halves.
DVD can be performed in four different versions:
DVD5 - a standard single-layer disc, the information is found only on the lower half. Upper sabstrat often made of the same disc, has the same relief, but are not metallized, but simply glued to the bottom to ensure that the desired structure. In most cases, the print is on the top. Capacity about 4 75GB.
DVD10 - double-sided discs, the information contained above and below. This drive-shifter you want to read one side - turn right direction, inserted into the drive, read. They wanted the other side - was taken out, turned, put, read. A popular format for the content of various HS-type "12 movies on one." It is popular primarily because of the ease of production, and that allows you to stamp 100500 different collections, combining the contents of the upper and lower halves. Recognizable by the tiny printovke deposited only in the center. Capacity of about 4 GB 75h2.
Here's how it looks

DVD9 - dual-layer disc, the information contained above and below, but read only from below, without the need for revolution drive. And the first read information track sabstrata lower, then the drive head produces a refocusing on the upper track. The relative rarity. It requires excellent rebuilt production and high production culture. Above all - the roads, as the bottom of the plating is "translucent" and because of the specific nature not running aluminum, and silver. Learn more about all the specifics write the second part of the disc replication. The capacity of less than 4, 75h2 GB, since the density of the bottom of the tracks is usually somewhat lower than the standard. To the layman outwardly indistinguishable from DVD5.
DVD18 - Similar to DVD10, only both sides of the bilayer. I never held in the hands of such a disc, its production requires very specific machines that exist in nature only in the form of test systems and any application not found. It is extremely difficult to manufacture, consists of three parts. The upper and lower sabstraty identical to those of DVD9, central sabstrat has terrain and metallization from two sides. Thicker conventional DVD, climbs not all drives. External differences are not described in this instance you will never not fall. Capacity of about 4 GB 5x4.
Capacity available everywhere rough, and it is no coincidence. The amount of information can vary not only downwards but also in great. A good producer is able to lift track pitch (the distance between the tracks) trample down on the disc for more information. It is fraught with problems, but it is possible. If the first part of enough people interested in the second and third parts, I'll cover how to do this on a real production, but it is time to go further and ...
The device drive:
The disk, in addition to the information field comprises:
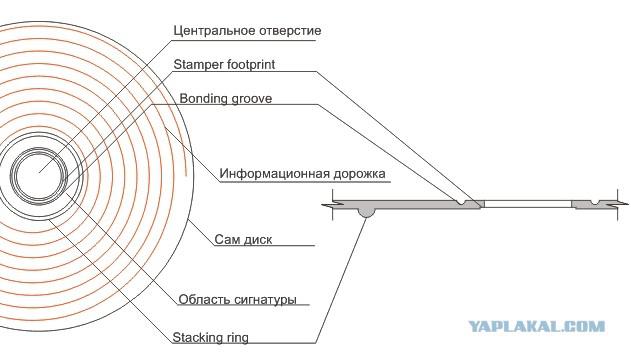
Stamper footprint. The tiny punching sabstrata due to flow technology, injection molding machines, some left little imprint, in principle, nothing to say, though traces of chipping or God forbid burr at this point is almost certainly talking about a very Khrenovoe production.
Here, if you look footpting barely, but still discernible

Bonding groove. The recess on the inner part sabstrata DVD. On CD course not. The technologically necessary to ensure that when the two halves gluing adhesive is flowed into the central portion. Symptom high production - you see that the glue is clear from this place is not flowing into the inner part and without giving too large pockets of air to the outside. However, even if the bonding is pretty sloppy, this may not be a sign of a bad disc. But if the glue has flowed inside right up to the central opening, this unique marriage.
The photo shows a gas pocket away from the bonding groove
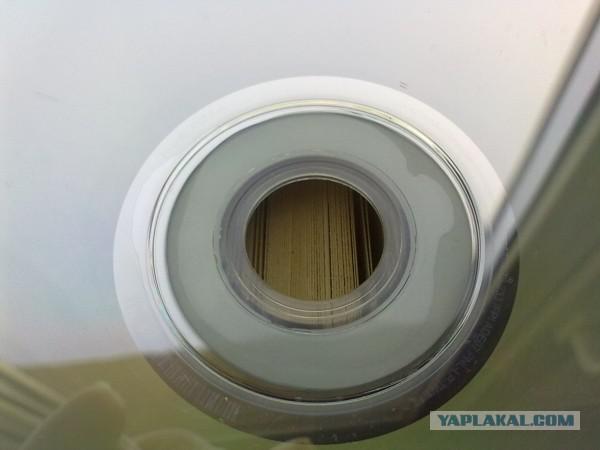

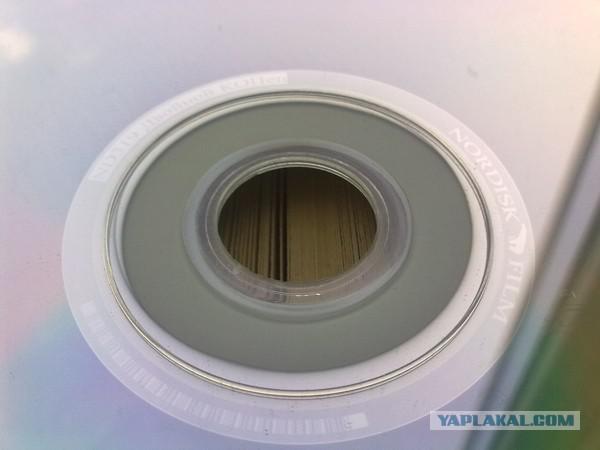
In the signature is placed on the service information, with a stamper (metal image, which forms during casting Information relief) made the drive. The fact is that in the production until the products are not painted all the discs look like twins, so as not to confuse the different discs to painting just this signature, and need. In the same area provides information on the manufacturer's license.
Stacking ring - just protruding above the surface of a common ring. It is necessary to discs in the stack does not rub against each other and do not scratch. That is sort of laying.
Information field. In fact that is where there is a spiral track containing information. The new disc when viewed at an angle to the surface should look like a mirror. A small curvature (deviation) in principle, be allowed, but if you pay attention to it, it is likely that the deviation is significant. Under no circumstances should not be allowed to the information field were visible tiny bumps (called "Baboon") Having Baboon - 100% marriage. How to watch: lift the disc information on the side of the eye level, and rotate it so you can see the reflection of a lamp on the front of the ceiling. If this inspection all perfectly clear.
I could not take a photo of the Baboon, so I messed up the drive to give a presentation. reduce this elephant 20 times. This will be the Baboon.
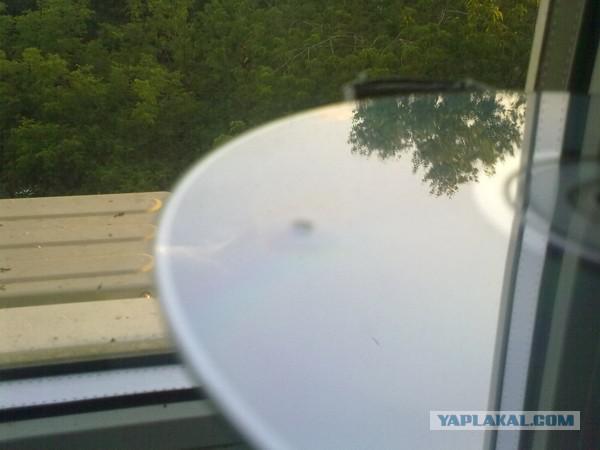

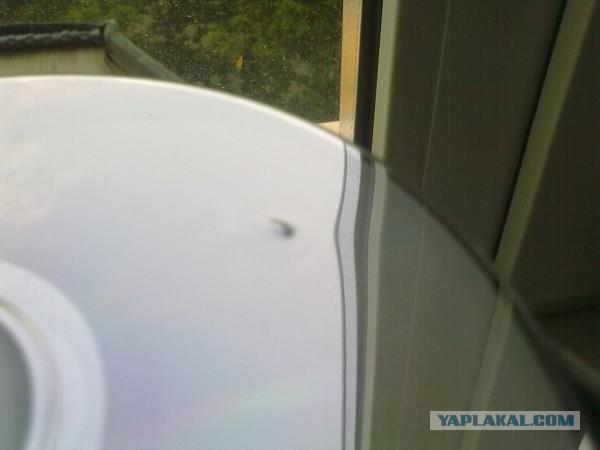
Another sign of the quality of the disc - plating begins immediately after the stacking ring and ends about a millimeter from the edge of the disc. Border metallization should be clear. If the boundary is blurry, the disc likely metallizovyvalsya hiking on well-masked, what a good production does not usually happen.
On Voto it shows how far gone ugly plating inside the signature area. Surely inner mask deformed

Okay, go to the very tasty: Information and its representation on disk. Go-go-go!
Land, pits and Two Smoking Barrels
Track drive consists of a sequence of depressions, each of which is called "the pit." The spaces between the pits is called "Land" On the left picture, it looks like under magnification, with an approximate image of the laser beam reader:
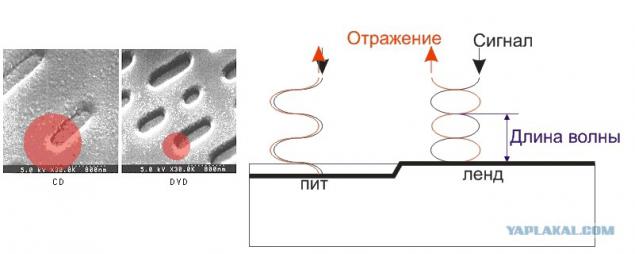
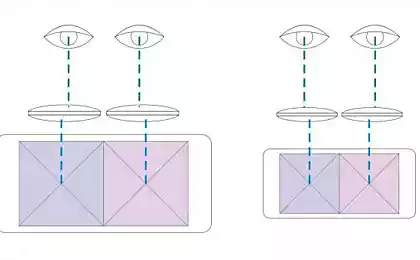
Some details: The depth of the pit should ideally correspond to a quarter of the wavelength of the actuator. What happens? Illustration on the right clearly illustrates that the signal reflected from the pit will be coming in the opposite of the signal reflected from the Land. What photodetector interpreted as a drop in power (in pita signal will weaken due to optical interference). That's what distinguishes the drive electronics and the pit of the Land. It would seem - well, that's nice, let the pit encoding unit, and Land zero - that's you and the whole principle (and by the way - many really believe that the information is encoded so), but we have a problem: Look at the size of the laser beam in the illustration on the left. See? Try to visualize as a pit sequence of "01010101". Understood? Pete turned too small compared to the beam of the reader, and this sequence could not be recognized. Or the size of the pits had to be increased to the size of the beam. This means that the pits (and information) on the same area of the disk would fit smaller. The following animations are all very clearly explained.
See? If the pits are too small, as shown in a central figure, it is impossible to select a sequence of ones and zeros. Either a pit will produce a series of units, or a series of zeros (will not be recognized). You can certainly increase the pit, but then increases the interval between tracks, as shown in the right illustration. So actually encoded information as shown on the left. The transition between Pete and Land (determined by the moment when the signal strength falls below a certain level, on Animation shown as a dashed line) codes 1. The rest of the time encoded zeros.
The read pattern is called EFM (Eight to Forteen Modulation) and its length for DVD is 16 bits, which are then converted into the standard byte in accordance with a special table. Why such a perversion? you ask? Because the minimum length of a pit sequence encodes a 100 (Animation in the top incidentally error "101" can not be). That is, at least two are always zero. This is necessary to ensure good detection and control of data reading, well, and in addition, the conversion table is compiled in a way that pits across quite often. A considerable interval between pits can allow the drive to lose track, and frequent pits provide good tracking (but more on that below)
Thus, the pits are different in length, incidentally referred to as their length I3 (100), I4 (1000), I5 (100 000) and so on, up to the maximum I16. What do they perform the function, in addition to purely informational? It's time to analyze how the drive.
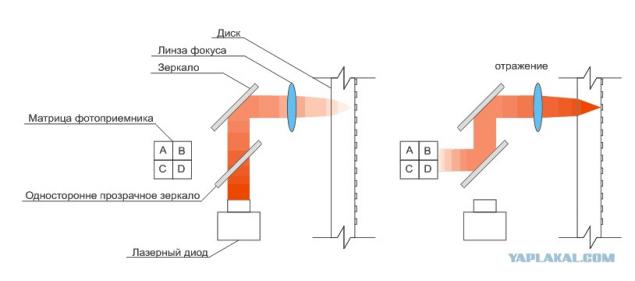
Classic disc drive is always the same solution:
Ray reader, having passed through the optical system is focused on the track is recorded, and passed way back falls on the photodetector array. Controller service matrix adds the signal from all four elements and the sum signal is building a Common EFM pattern. But not only. Focal drive system is designed so that if the focus of the beam on the path is broken, the reflected beam falls on the matrix is not "round spots" and extended diagonally. Thus the controller on the sum (A + D) - (C + B) constantly performs focus adjustment by controlling the position of the focus lens.
There are tracking. The geometry of the pit is that he had no vertical walls, and with a certain slope, so if the path begins to "run away" from the beam reflected immediately shifted from the center of the matrix. The controller automatically on the sum (A + C) - (B + D) biases the carriage, offsetting it. That is why it is very important that the pits were often in relief. On Land drive unable to determine the accuracy of positioning on the track.
We go further.
Error correction mechanism
DVD In a multilevel system error correction. The first barrier - interleaving. This non-linear distribution of the data track. It made for the fact that if the scratch or other defect on the disc does not read the data - lost significant linear array of data, and there are many, but small defects, smeared on the block information. Visually:
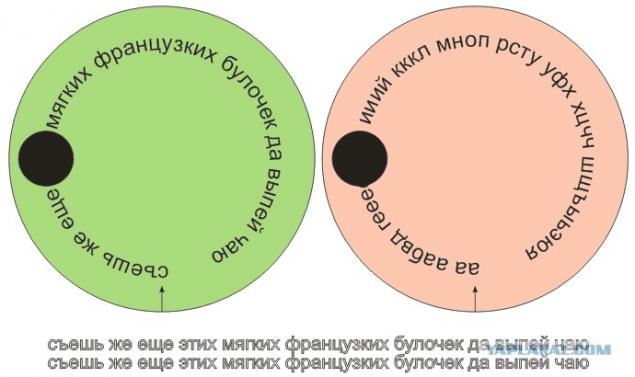
On a green sketch it shows that it would be without interleaving:
The read data would "eat else ???? of French soft drink tea buns yes "What ??? If you do not know the phrase, then place ???? You can assume anything from "ugly" to "Dad».
On the red - with interleaving:
These are: "Sh? NIL? ie even these soft France? FIR buloch? but to drink tea ».
That is, instead of losing a large block of data to be restored is already problematic, interleaving lost information distributed throughout the data set.
But that's not all)
After your EFM will work and interleaving - the information stored on the disc is supplemented checksums. I will not describe the mechanism of correction with absolute precision, but in general this mechanism:
The data stored on the disc are formed in blocks, each block of data is besides the amount counted by a certain algorithm for the rows and columns of the block. Well, something
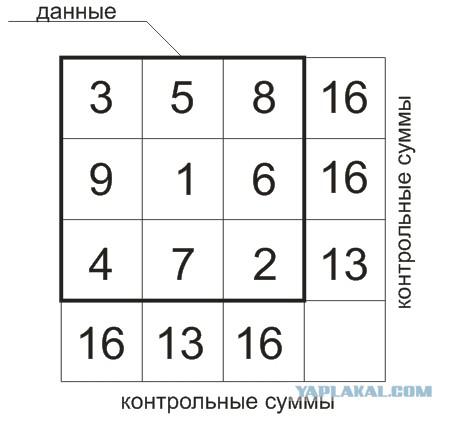
Remove any three digits in the data - you always restore their checksum. Remove even the entire checksum - you do not lose data when you have something.
I wanted to even describe in detail all the dirty tricks that occur in production and how it affects the quality of discs, but decided to postpone it for the individual dedicated to mastering and replication. There it would be more appropriate.
Here's one more goodbye Baboon (also in comparison to the real decrease in 20 times)
That's all I wanted to say.

Source:
The theme will be fasting slowly. Please do not break, the end will tell.
Today I will try to start a series of three articles about the technology of storing information on optical media. Today will be a general theory. This introductory article will mnogobukoff and some explanatory illustrations.
If the first part will be of interest, the next two will be dedicated to the production of practice already with live pictures and videos. I understand that on the entertainment portal chances at the first part a bit, but still try.
It goes on R (RW) media!
Further discussion will be set out by the example of DVD, because I know the specifics DVD fullest. You can be absolutely sure that everything described is true for CD and Blu-Ray. Only different nuances.
Let's go.
Thus, the optical disc. You all know him, many people even think they know how it is arranged inside. Unfortunately most of representation are not even close to understanding the true state of affairs. Disc "in the context" is a kind of sandwich construction with CD, DVD and BR differ. For example, CD and DVD that's their construction:
THIS CD

As can be seen, one CD is actually round piece of plastic, the top of which displaced helical track carrying information. This surface is metallized to provide a reflection of the beam of the reader. Then a thin layer of metallization is covered with a protective varnish for the physical protection, as well as for protection against moisture and oxygen. Without varnish a thin layer of aluminum oxide and would have degraded within a short time and to read the disc has failed to. Well, quite on top of the drive is usually an image (hereinafter - print). If there is a desire and curiosity - can check presentation. Take the sandpaper and thoroughly unnecessary proshkurte a CD on top. You will see that very quickly dotrete drive to metalization and withdraw it.
But this DVD.

DVD, unlike CD consists of two halves sabstrata (plastic disc) bonded together. Information relief and metallization layer is located inside the sandwich and reliably protected polycarbonate layer. Again, for the inquisitive - bending can break the unnecessary DVD and you'll see that the disc consists of glued halves.
DVD can be performed in four different versions:
DVD5 - a standard single-layer disc, the information is found only on the lower half. Upper sabstrat often made of the same disc, has the same relief, but are not metallized, but simply glued to the bottom to ensure that the desired structure. In most cases, the print is on the top. Capacity about 4 75GB.
DVD10 - double-sided discs, the information contained above and below. This drive-shifter you want to read one side - turn right direction, inserted into the drive, read. They wanted the other side - was taken out, turned, put, read. A popular format for the content of various HS-type "12 movies on one." It is popular primarily because of the ease of production, and that allows you to stamp 100500 different collections, combining the contents of the upper and lower halves. Recognizable by the tiny printovke deposited only in the center. Capacity of about 4 GB 75h2.
Here's how it looks

DVD9 - dual-layer disc, the information contained above and below, but read only from below, without the need for revolution drive. And the first read information track sabstrata lower, then the drive head produces a refocusing on the upper track. The relative rarity. It requires excellent rebuilt production and high production culture. Above all - the roads, as the bottom of the plating is "translucent" and because of the specific nature not running aluminum, and silver. Learn more about all the specifics write the second part of the disc replication. The capacity of less than 4, 75h2 GB, since the density of the bottom of the tracks is usually somewhat lower than the standard. To the layman outwardly indistinguishable from DVD5.
DVD18 - Similar to DVD10, only both sides of the bilayer. I never held in the hands of such a disc, its production requires very specific machines that exist in nature only in the form of test systems and any application not found. It is extremely difficult to manufacture, consists of three parts. The upper and lower sabstraty identical to those of DVD9, central sabstrat has terrain and metallization from two sides. Thicker conventional DVD, climbs not all drives. External differences are not described in this instance you will never not fall. Capacity of about 4 GB 5x4.
Capacity available everywhere rough, and it is no coincidence. The amount of information can vary not only downwards but also in great. A good producer is able to lift track pitch (the distance between the tracks) trample down on the disc for more information. It is fraught with problems, but it is possible. If the first part of enough people interested in the second and third parts, I'll cover how to do this on a real production, but it is time to go further and ...
The device drive:
The disk, in addition to the information field comprises:

Stamper footprint. The tiny punching sabstrata due to flow technology, injection molding machines, some left little imprint, in principle, nothing to say, though traces of chipping or God forbid burr at this point is almost certainly talking about a very Khrenovoe production.
Here, if you look footpting barely, but still discernible

Bonding groove. The recess on the inner part sabstrata DVD. On CD course not. The technologically necessary to ensure that when the two halves gluing adhesive is flowed into the central portion. Symptom high production - you see that the glue is clear from this place is not flowing into the inner part and without giving too large pockets of air to the outside. However, even if the bonding is pretty sloppy, this may not be a sign of a bad disc. But if the glue has flowed inside right up to the central opening, this unique marriage.
The photo shows a gas pocket away from the bonding groove

In the signature is placed on the service information, with a stamper (metal image, which forms during casting Information relief) made the drive. The fact is that in the production until the products are not painted all the discs look like twins, so as not to confuse the different discs to painting just this signature, and need. In the same area provides information on the manufacturer's license.
Stacking ring - just protruding above the surface of a common ring. It is necessary to discs in the stack does not rub against each other and do not scratch. That is sort of laying.
Information field. In fact that is where there is a spiral track containing information. The new disc when viewed at an angle to the surface should look like a mirror. A small curvature (deviation) in principle, be allowed, but if you pay attention to it, it is likely that the deviation is significant. Under no circumstances should not be allowed to the information field were visible tiny bumps (called "Baboon") Having Baboon - 100% marriage. How to watch: lift the disc information on the side of the eye level, and rotate it so you can see the reflection of a lamp on the front of the ceiling. If this inspection all perfectly clear.
I could not take a photo of the Baboon, so I messed up the drive to give a presentation. reduce this elephant 20 times. This will be the Baboon.

Another sign of the quality of the disc - plating begins immediately after the stacking ring and ends about a millimeter from the edge of the disc. Border metallization should be clear. If the boundary is blurry, the disc likely metallizovyvalsya hiking on well-masked, what a good production does not usually happen.
On Voto it shows how far gone ugly plating inside the signature area. Surely inner mask deformed

Okay, go to the very tasty: Information and its representation on disk. Go-go-go!
Land, pits and Two Smoking Barrels
Track drive consists of a sequence of depressions, each of which is called "the pit." The spaces between the pits is called "Land" On the left picture, it looks like under magnification, with an approximate image of the laser beam reader:

Some details: The depth of the pit should ideally correspond to a quarter of the wavelength of the actuator. What happens? Illustration on the right clearly illustrates that the signal reflected from the pit will be coming in the opposite of the signal reflected from the Land. What photodetector interpreted as a drop in power (in pita signal will weaken due to optical interference). That's what distinguishes the drive electronics and the pit of the Land. It would seem - well, that's nice, let the pit encoding unit, and Land zero - that's you and the whole principle (and by the way - many really believe that the information is encoded so), but we have a problem: Look at the size of the laser beam in the illustration on the left. See? Try to visualize as a pit sequence of "01010101". Understood? Pete turned too small compared to the beam of the reader, and this sequence could not be recognized. Or the size of the pits had to be increased to the size of the beam. This means that the pits (and information) on the same area of the disk would fit smaller. The following animations are all very clearly explained.
See? If the pits are too small, as shown in a central figure, it is impossible to select a sequence of ones and zeros. Either a pit will produce a series of units, or a series of zeros (will not be recognized). You can certainly increase the pit, but then increases the interval between tracks, as shown in the right illustration. So actually encoded information as shown on the left. The transition between Pete and Land (determined by the moment when the signal strength falls below a certain level, on Animation shown as a dashed line) codes 1. The rest of the time encoded zeros.
The read pattern is called EFM (Eight to Forteen Modulation) and its length for DVD is 16 bits, which are then converted into the standard byte in accordance with a special table. Why such a perversion? you ask? Because the minimum length of a pit sequence encodes a 100 (Animation in the top incidentally error "101" can not be). That is, at least two are always zero. This is necessary to ensure good detection and control of data reading, well, and in addition, the conversion table is compiled in a way that pits across quite often. A considerable interval between pits can allow the drive to lose track, and frequent pits provide good tracking (but more on that below)
Thus, the pits are different in length, incidentally referred to as their length I3 (100), I4 (1000), I5 (100 000) and so on, up to the maximum I16. What do they perform the function, in addition to purely informational? It's time to analyze how the drive.

Classic disc drive is always the same solution:
Ray reader, having passed through the optical system is focused on the track is recorded, and passed way back falls on the photodetector array. Controller service matrix adds the signal from all four elements and the sum signal is building a Common EFM pattern. But not only. Focal drive system is designed so that if the focus of the beam on the path is broken, the reflected beam falls on the matrix is not "round spots" and extended diagonally. Thus the controller on the sum (A + D) - (C + B) constantly performs focus adjustment by controlling the position of the focus lens.
There are tracking. The geometry of the pit is that he had no vertical walls, and with a certain slope, so if the path begins to "run away" from the beam reflected immediately shifted from the center of the matrix. The controller automatically on the sum (A + C) - (B + D) biases the carriage, offsetting it. That is why it is very important that the pits were often in relief. On Land drive unable to determine the accuracy of positioning on the track.
We go further.
Error correction mechanism
DVD In a multilevel system error correction. The first barrier - interleaving. This non-linear distribution of the data track. It made for the fact that if the scratch or other defect on the disc does not read the data - lost significant linear array of data, and there are many, but small defects, smeared on the block information. Visually:

On a green sketch it shows that it would be without interleaving:
The read data would "eat else ???? of French soft drink tea buns yes "What ??? If you do not know the phrase, then place ???? You can assume anything from "ugly" to "Dad».
On the red - with interleaving:
These are: "Sh? NIL? ie even these soft France? FIR buloch? but to drink tea ».
That is, instead of losing a large block of data to be restored is already problematic, interleaving lost information distributed throughout the data set.
But that's not all)
After your EFM will work and interleaving - the information stored on the disc is supplemented checksums. I will not describe the mechanism of correction with absolute precision, but in general this mechanism:
The data stored on the disc are formed in blocks, each block of data is besides the amount counted by a certain algorithm for the rows and columns of the block. Well, something

Remove any three digits in the data - you always restore their checksum. Remove even the entire checksum - you do not lose data when you have something.
I wanted to even describe in detail all the dirty tricks that occur in production and how it affects the quality of discs, but decided to postpone it for the individual dedicated to mastering and replication. There it would be more appropriate.
Here's one more goodbye Baboon (also in comparison to the real decrease in 20 times)
That's all I wanted to say.

Source: