950
Facts about the Soviet Lunokhod
Interesting facts about the last Soviet Lunokhod
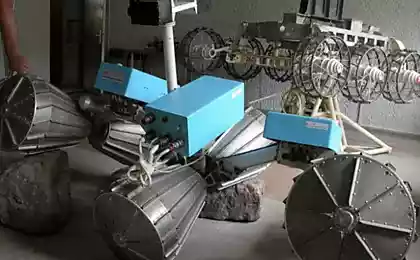
January 16, 1973 automatic station "Luna-21" was delivered to the Moon "Lunokhod-2" - the second in a series of Soviet lunar remote-controlled self-propelled vehicles, planetary rovers. "Lunokhod-2" became the latest E-series machine, which is being developed in the royal OKB-1. It was intended to study the mechanical properties of the lunar surface, photography and telephoto moon. Apparatus prilunilsya just 172 kilometers from the landing of the American "Apollo 17", in the southern part of the crater Le Monnier, located on the eastern edge of the Sea of Serenity. We decided to tell ten interesting facts about this self-propelled machine.
Distance traveled
During the development phase rover designers are faced with a challenge: to develop a device for movement on the lunar surface, which at that time did not know almost nothing. Nevertheless, the "Lunokhod-2" belong records for distance traveled: for four months the unit was 42 kilometers, including areas with very difficult terrain, loose soil and stone placers. Initially, the distance estimated at 37 kilometers, but scientists from MIIGAiK studying images from the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, have calculated that it is equal to 42, 1-42, 2 kilometers. This is a record for robots working outside the Earth.
NAVIGATION
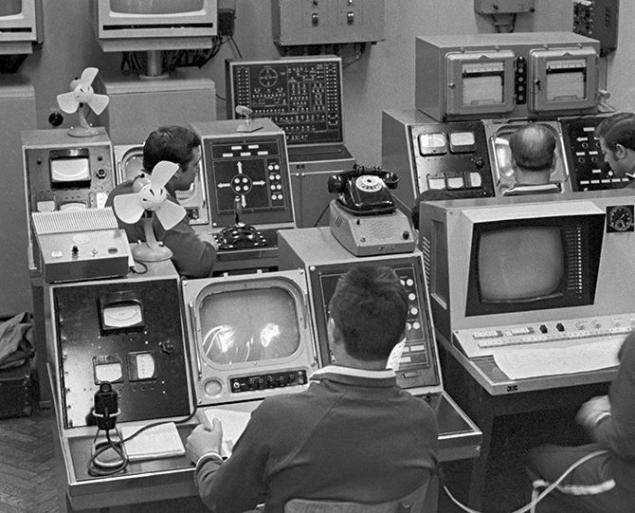
During the lunar landing navigation system "Lunokhod-2" was damaged, and 11 officers of the ground crew had to focus on the lunar rover surroundings, the stars and the sun. Position the housing is determined indirectly by downloads on wheels. There is an informal opinion that the move helped and detailed photocard district composed landing "Apollo 17", which came shortly before the flight at their disposal.
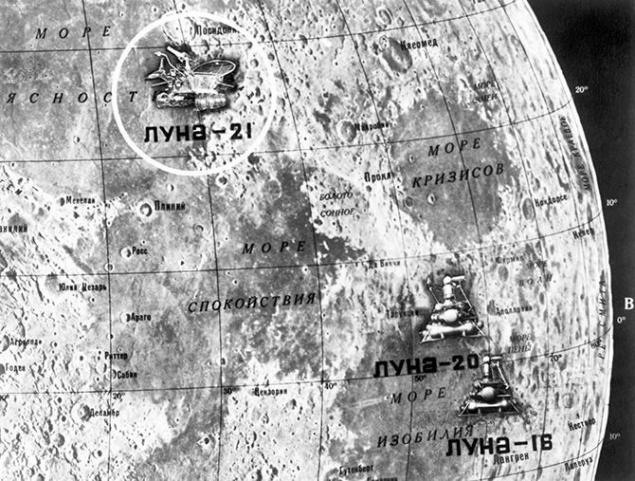

Photo and video
Over four months on the Moon to the Earth has been transferred 93 telephotometric panorama and about 89 thousand. Malokadrovogo television images. During the shooting obtained data of the most interesting features of the terrain, allowing a detailed study of their structure.
EQUIPMENT
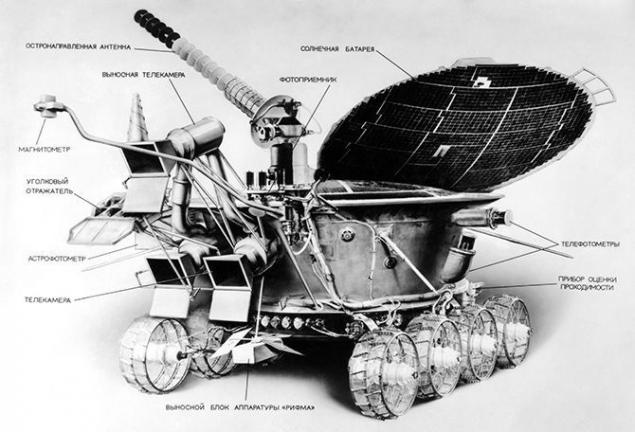
"Lunokhod-2" was equipped with an X-ray spectrometer "RHYME-M" to measure the chemical composition of the lunar soil, magnetometer SG-70A for the study of the magnetic field on the surface of the moon, astrophotometer to measure the luminosity of the lunar sky radiometer, a photodetector "Rubin-1", and and laser corner reflector. Also, the unit was equipped with the third television camera installed at the request of the crew at the level of the human eye, which significantly improves visibility while driving on the lunar surface.

WEIGHT
"Lunokhod-2" set a world record for the maximum mass of the automatic self-propelled unit on the surface of the moon - it was 836 kilograms.
CLEARANCE
On Lunokhod and lander were established State flag of the USSR, pennants with bas-relief of VI Lenin, USSR national emblem and the inscription "50 years of the USSR».

FAILURE
The last time telemetry information was taken from the "Lunokhod-2" May 10, 1973. It was said that the movement of the rover began to fracture due east to Cape Far. However, the path of the lunar rover landed in the crater, trying to get out of it in reverse, scooped up a plate of the dust from the walls of the crater, which is adhered to the solar cell and the cooling radiator. Because of the accident was broken thermal regime: one day the temperature in the compartment rose to +47 ° C. Equipment overheated and broke down.
LOCATION
The exact location of the "Lunokhod-2" could not be set for 37 years, although local experts have stated that the unit was not lost. Discover rover could after NASA announced in 2010, more than 100 thousand. Images of the lunar surface by the camera device LRO. Prior to their publication Canadian scientists from the University of Western Ontario failed to find traces of the lunar rover, and he thought the unit itself. However, later it turned out that dark spot, which the researchers took for "Lunokhod-2" - a place near the crater in which the rover was not long before the failure.

SALE OF TITLE
In 1973, at auction Sotheby's, devoted to space-related, "Lunokhod-2" was sold for 68,500 dollars Richard Garriott, an American collector of space artifacts, and the son of a NASA astronaut. Until now, the question remains unclear how the NPO. Lavochkin, created the "Lunokhod-2" could put it up for auction.
RECORDS
In addition to the records of self-propelled unit weight and distance traveled, "Lunokhod-2" also surpassed all devices such plan for the speed and duration of action. In 2013, the American Opportunity rover almost managed to catch up with the Soviet "Lunokhod-2" for the distance traveled: in 2004 he drove on Mars 35, 76 kilometers long and continues to move.
©
January 16, 1973 automatic station "Luna-21" was delivered to the Moon "Lunokhod-2" - the second in a series of Soviet lunar remote-controlled self-propelled vehicles, planetary rovers. "Lunokhod-2" became the latest E-series machine, which is being developed in the royal OKB-1. It was intended to study the mechanical properties of the lunar surface, photography and telephoto moon. Apparatus prilunilsya just 172 kilometers from the landing of the American "Apollo 17", in the southern part of the crater Le Monnier, located on the eastern edge of the Sea of Serenity. We decided to tell ten interesting facts about this self-propelled machine.

Distance traveled
During the development phase rover designers are faced with a challenge: to develop a device for movement on the lunar surface, which at that time did not know almost nothing. Nevertheless, the "Lunokhod-2" belong records for distance traveled: for four months the unit was 42 kilometers, including areas with very difficult terrain, loose soil and stone placers. Initially, the distance estimated at 37 kilometers, but scientists from MIIGAiK studying images from the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, have calculated that it is equal to 42, 1-42, 2 kilometers. This is a record for robots working outside the Earth.
NAVIGATION
During the lunar landing navigation system "Lunokhod-2" was damaged, and 11 officers of the ground crew had to focus on the lunar rover surroundings, the stars and the sun. Position the housing is determined indirectly by downloads on wheels. There is an informal opinion that the move helped and detailed photocard district composed landing "Apollo 17", which came shortly before the flight at their disposal.

Photo and video
Over four months on the Moon to the Earth has been transferred 93 telephotometric panorama and about 89 thousand. Malokadrovogo television images. During the shooting obtained data of the most interesting features of the terrain, allowing a detailed study of their structure.
EQUIPMENT
"Lunokhod-2" was equipped with an X-ray spectrometer "RHYME-M" to measure the chemical composition of the lunar soil, magnetometer SG-70A for the study of the magnetic field on the surface of the moon, astrophotometer to measure the luminosity of the lunar sky radiometer, a photodetector "Rubin-1", and and laser corner reflector. Also, the unit was equipped with the third television camera installed at the request of the crew at the level of the human eye, which significantly improves visibility while driving on the lunar surface.

WEIGHT
"Lunokhod-2" set a world record for the maximum mass of the automatic self-propelled unit on the surface of the moon - it was 836 kilograms.
CLEARANCE
On Lunokhod and lander were established State flag of the USSR, pennants with bas-relief of VI Lenin, USSR national emblem and the inscription "50 years of the USSR».

FAILURE
The last time telemetry information was taken from the "Lunokhod-2" May 10, 1973. It was said that the movement of the rover began to fracture due east to Cape Far. However, the path of the lunar rover landed in the crater, trying to get out of it in reverse, scooped up a plate of the dust from the walls of the crater, which is adhered to the solar cell and the cooling radiator. Because of the accident was broken thermal regime: one day the temperature in the compartment rose to +47 ° C. Equipment overheated and broke down.
LOCATION
The exact location of the "Lunokhod-2" could not be set for 37 years, although local experts have stated that the unit was not lost. Discover rover could after NASA announced in 2010, more than 100 thousand. Images of the lunar surface by the camera device LRO. Prior to their publication Canadian scientists from the University of Western Ontario failed to find traces of the lunar rover, and he thought the unit itself. However, later it turned out that dark spot, which the researchers took for "Lunokhod-2" - a place near the crater in which the rover was not long before the failure.

SALE OF TITLE
In 1973, at auction Sotheby's, devoted to space-related, "Lunokhod-2" was sold for 68,500 dollars Richard Garriott, an American collector of space artifacts, and the son of a NASA astronaut. Until now, the question remains unclear how the NPO. Lavochkin, created the "Lunokhod-2" could put it up for auction.
RECORDS
In addition to the records of self-propelled unit weight and distance traveled, "Lunokhod-2" also surpassed all devices such plan for the speed and duration of action. In 2013, the American Opportunity rover almost managed to catch up with the Soviet "Lunokhod-2" for the distance traveled: in 2004 he drove on Mars 35, 76 kilometers long and continues to move.
©