2119
Steam locomotives in the USSR
Nizhny Novgorod museum of steam locomotives - it is an open air museum, which is located in the village of sorting, now part of the Nizhny Novgorod. What to get into this museum should be to minimize the Moscow highway just after the store Carousel right (if coming from the Moscow side) all the time to go on the main road to the railway station, Gorky-sorting. The museum is located right next to the station. In total, the museum is 15 locomotives production of the USSR, Russia, Germany, Sweden.
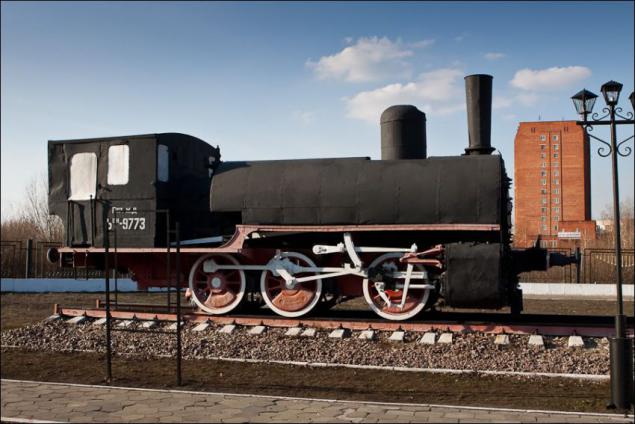
The locomotive VN-9773. Industrial steam locomotives of this series were built at the Nevsky Shipyard in St. Petersburg in the early 1900s. Design speed of the locomotive - 40 km / h, power - 300 horsepower, efficiency - 4%. By type of locomotive design refers to the tank engine, ie locomotives without tender - supply of fuel (oil) is stored at the locomotive. The locomotive had a saddle-shaped tank with a reserve of water 7m3, the oil tank is placed above the water tank. Locomotives of this series were produced for Transcaucasian, Mykolayiv and Privislinskoy railway, as several copies were produced for internal needs Nevsky Zavod.

Steam locomotive E-1112. Designed Lugansk Locomotive Works in 1910. Later locomotives built at Kharkov, Kolomna, Bryansk and Sormovo plants until 1957.
This series of locomotives is the most massive in the world - everything, including various modifications, was built about 11 thousand locomotives.
Design speed of the engine - 55 km / h. Maximum power - 1500 hp Efficiency - 8% Series E locomotives are among the most powerful and the most massive steam locomotives created at the beginning of the XX century. Project cargo locomotive passing the commission in February 1911 under consideration by the Engineering Council of the Ministry of Railways. Later, October 29, 1911 was approved by the working draft of the locomotive and, since 1912, has been adjusted their production.

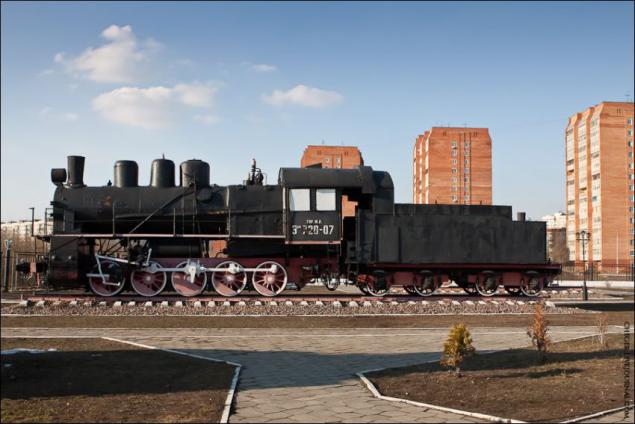
The locomotive EM720-07. Upgraded Series E, is being built in 1931-1935 gg Lugansk, Kharkov, Bryansk and Sormovo works. Total produced 2694 locomotives.
To increase the thrust was increased vapor pressure in the boiler while increasing the strength of the boiler and the strengthening of certain parts of the driving mechanism.
Design speed of the locomotive - 65 km / h. Maximum power - 1800 hp Efficiency - 7%.
Lokomotiv offers extra traction force by increasing the steam pressure in the boiler, which required the strengthening of the joints of the boiler and some parts of the driving mechanism. As a result, improvements have resulted in an increase in the total weight, which is why it was necessary to make a number of design changes. Locomotives were built without water purifier and nutritious cap, and with less smoke tubes (151 against 157 locomotives from the series Eu). But the active use of welding in the steam locomotive allowed to reduce the weight of the locomotive from 85 to 75 tons and replace the withdrawn units.

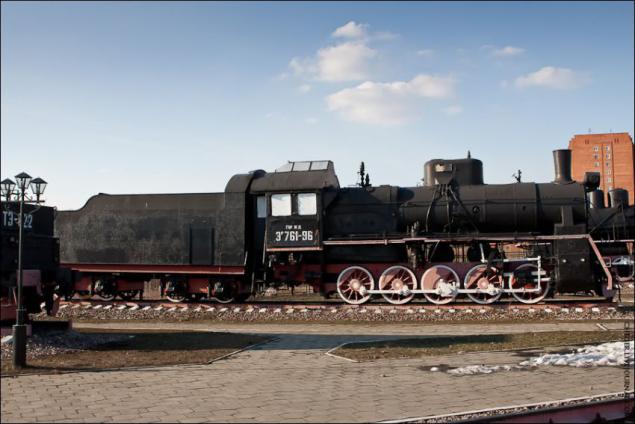
The locomotive ER761-96. EM Series reconstructed. Due to the elongation of the locomotive firebox power increased by 10%. Locomotives of this series were built by domestic factories in the 1930s and during the Great Patriotic War, and after the war production has been established in Romania (Resita plant), Poland (plant Tsegelskogo), Czechoslovakia (factory CKD) and Hungary (plant MÁVAG). Museum exhibit from Romania as evidenced by its nameplate. The last steam locomotive series was made in 1956 at the Hungarian plant MÁVAG. Also, a small number of locomotives of this series were produced during World War II the Kolomna Machine-Building Plant.
Design speed of the locomotive - 65 km / h. Maximum power - 2000 hp Efficiency - 7, 2%.

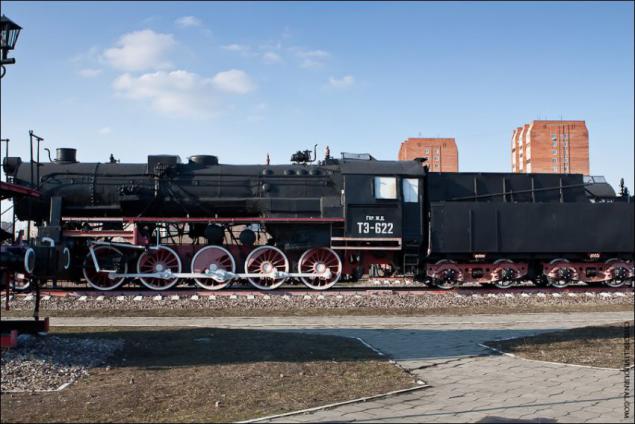
Steam locomotive TE-622. The name stands for TE Series trophy similar to the characteristics of the domestic series E.
Steam engines under the original name of the BR52 produced in Nazi Germany and occupied Europe. There were more than 6,000 locomotives, 2,200 of them came on the railways of the USSR as booty or by way of reparations.
The railways of the western part of the USSR locomotives TE actively exploited until the mid-1970s, after which most of them were transferred to industrial enterprises. During operation in the USSR series TE locomotives caused the Soviet railwaymen very positive feedback. As a general lack of marked fall in output when using low-grade domestic coal. In common parlance series TE locomotives called "Teshkami" or "Frau».
Design speed of the locomotive - 80 km / h. Maximum power - 1500 hp Efficiency - 7, 5%

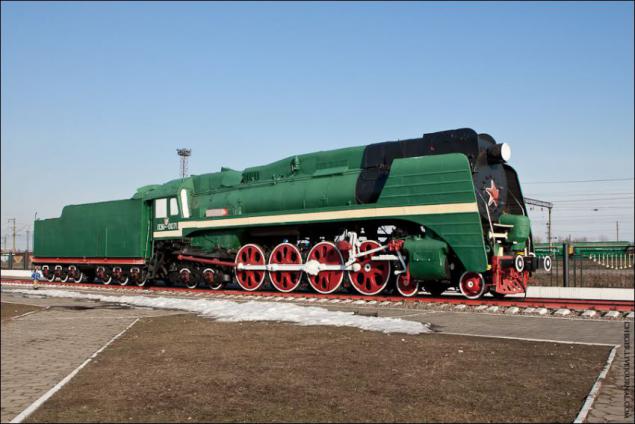
The locomotives P36 series, probably the most beautiful among domestic locomotives. This series was comparable to locomotives series of IP, but had less stress on the axles on the track (18ts), whereby it was possible to use these engines in most of the country's railways. Successful testing and trial operation of the first locomotive type 2-4-2 resulted in an experimental batch of the order in 1953 at the Kolomna Machine-Building zavode.Ekspluatatsionnye test locomotives took place at the Moscow-Kursk and Krasnoyarsk railways. In the second half of 1954 Kolomna factory produced pilot batch of locomotives will include minor structural improvements compared to the prototypes. At the end of 1954 the locomotive Series P36 was accepted for serial production. Locomotives of this series were sent to work with long-distance passenger trains on the main lines of Krasnoyarsk, Kalinin, Belarusian, Stalin, October, Kuibyshev and Northern railways. Since the beginning of the 70s, these locomotives were gradually replaced by electric and diesel locomotives. 1974 is considered the last year of operation of steam locomotives P36 series.
The steam locomotive P36-0071. Passenger locomotive design and manufacture of Kolomna Plant (251 locomotive, 1950-1956).
The last steam locomotive of the series at the same time became the last steam locomotive built in the USSR. He is now at the Museum of St. Petersburg.
The longest locomotives in this series worked on the Trans-Baikal Railway. Here, they were withdrawn from service in 1974.
Design speed - 125 km / h. Maximum power - 3000 hp Efficiency - 8, 2%.

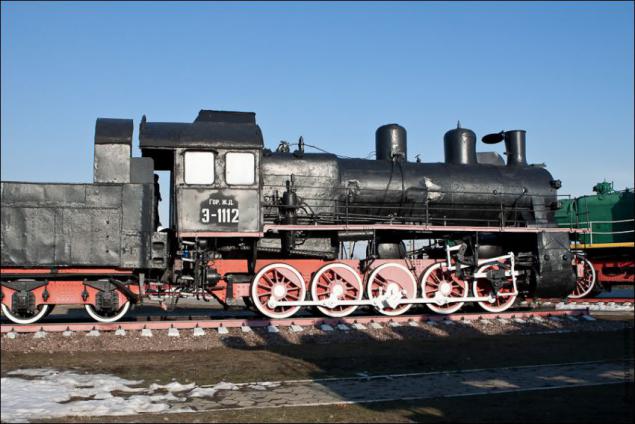
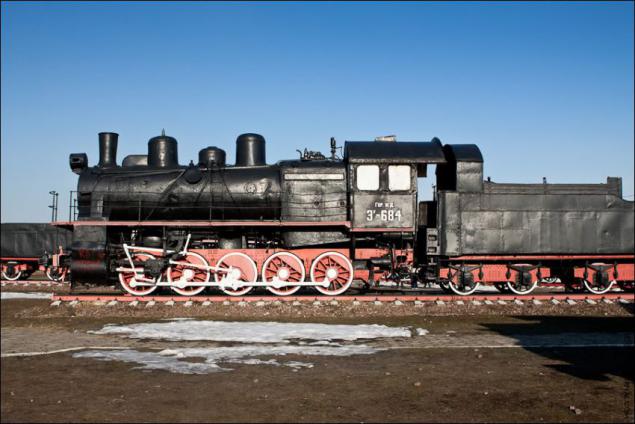
The locomotive EU684-52. Reinforced ("Y") version of the Series E, is produced from 1926 to 1931 Kolomna, Luhansk, Kharkiv, Bryansk and Sormovo works. Total built 2475 locomotives.
Design speed of the locomotive - 65 km / h. Maximum power - 1500 hp Efficiency - 7%

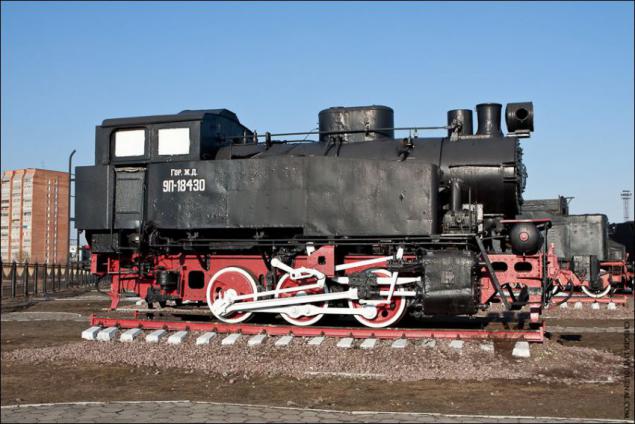
Steam locomotive 9P-18430. Another massive shunting and industrial tank engine. It was built in the Soviet Union from 1935 to 1957. Total produced more than 3 million cars.
Design speed of the engine - 25 km / h. Maximum power - 320 hp
As of the year 2007 in museums or as a locomotive-preserved monuments of the 34 locomotive serii.Parovozy series 9P improved design produced Kolomna plant from 1939 to 1941. and Murom Locomotive Plant. Dzerzhinsky from 1945 to 1955. Steam locomotives working on ways to many industrial enterprises in the country and is well proven.
Shunting tank locomotive of this series was immediately taken to the mass production despite a number of shortcomings.
Later, in 1939, when the program of the Kolomna Machine-Building Plant was again included the construction of these locomotives, the plant designers have revised drawings to address deficiencies.

To reduce pressure on the rails, in 1948, it was decided to develop a series based on L. After lengthy trials, in 1952 the first steam locomotive, designed to Voroshilovgrad locomotive plant im.Oktyabrskoy Revolution, received the designation OR18-01 entered the railroad. Although similar to a series of parameters A series of PR units was a new, more modern type of locomotive with significant structural differences between a number of nodes and their trailer thermal characteristics. On a steam train set a different water heater and wheel sets have been strengthened. During the test, the locomotive showed an increase in capacity of 24% compared to locomotives series L. During 1953 locomotive OR18-01 passed performance tests on a plot Lublin Serpukhov-Moscow-Kursk-Donbass railway. In 1954, the factory built Voroshilovgradsky initial batch of five cars (numbers 0005-0010) in the process of creating a series that has received a new designation LP - The locomotive was built based on a series of drawings A Voroshylovgrad plant.
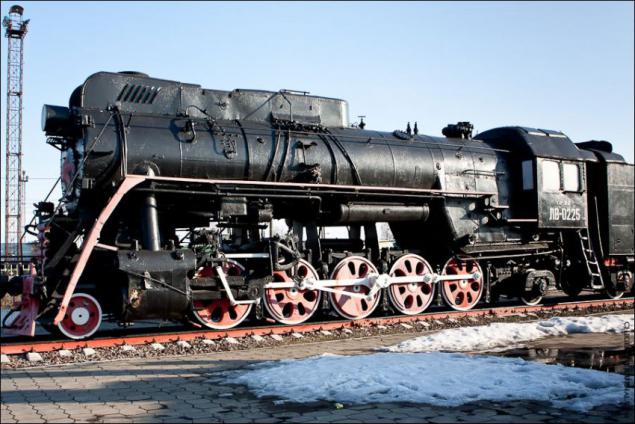
Steam locomotive LV-0225. Freight locomotive manufacturing plant Voroshylovgrad based on a series of LA were built from 1952 to 1956. Total 522 locomotive.
Produced in China until the mid-1990s, the locomotive series QJ had much in common with the Soviet LP.
Design speed - 90 km / h. Maximum power - 2420 hp Efficiency - 8%

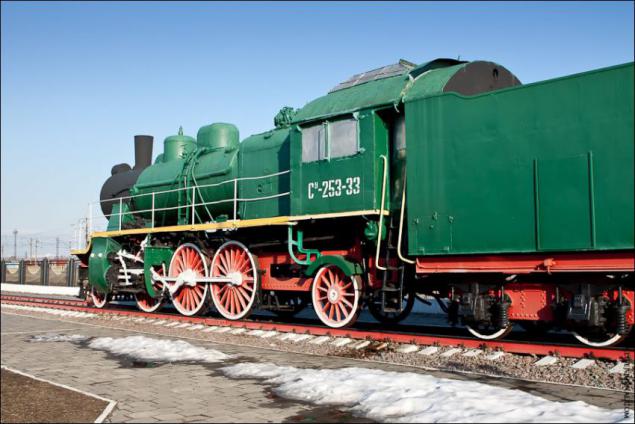
The locomotive SU253-33. Passenger locomotives series Su produced in the USSR from 1924 to 1940. Project locomotive developed by the Leningrad factory "Red Putilovets».
Museum locomotive built directly into the city of Gorky (formerly so-called Nizhny Novgorod) plant "Red Sormovo" produces such locomotives from 1947 to 1951 (a total of 411 locomotives).
Design speed - 115 km / h. Maximum power - 1500 hp Efficiency - 7, 8%. The locomotive passenger, so the emphasis is on speed and not on the thrust and towing weight

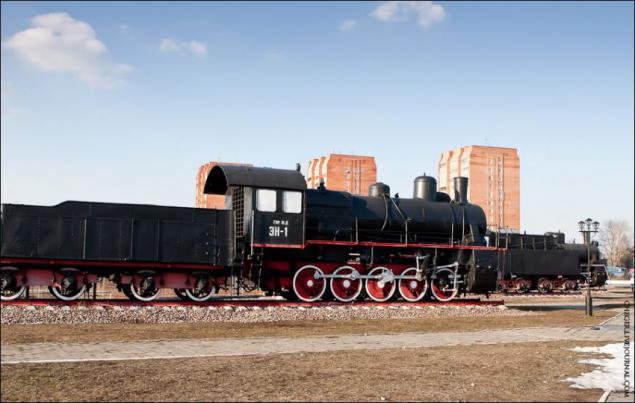
The locomotive EN-1. Modification E series, produced Nevsky Shipyard in Petrograd from 1916 to 1920. Total built 63 steam locomotive.
During the war 1914-1918. and in the postwar period, the state iron and steel industry has deteriorated sharply, and after 1917 was in general very poor. In view of the absence of metal for the repair of existing locomotives and the inability to increase the locomotive fleet, by 1920 the country's leadership decided to order a large batch of freight locomotives abroad. It was originally planned to order 1,000 locomotives in Sweden, part of which had to be made on the basis of Swedish locomotives Series R, and the other by the type of more appropriate operating conditions of domestic railways. But in the end we decided to order locomotives E series of drawings of Lugansk plant.
In Sweden ordered 500 locomotives, and, simultaneously, in Germany has been ordered 700 locomotives. The first locomotives were built in strict accordance with the drawings of Lugansk plant, but later began to make small changes in the light of experience and features of operation.

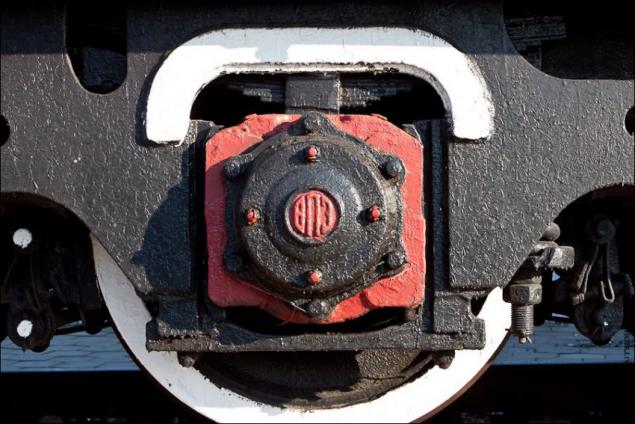
On the wheels of a steam locomotive - the emblem Voroshylovgrad plant

Source:
The locomotive VN-9773. Industrial steam locomotives of this series were built at the Nevsky Shipyard in St. Petersburg in the early 1900s. Design speed of the locomotive - 40 km / h, power - 300 horsepower, efficiency - 4%. By type of locomotive design refers to the tank engine, ie locomotives without tender - supply of fuel (oil) is stored at the locomotive. The locomotive had a saddle-shaped tank with a reserve of water 7m3, the oil tank is placed above the water tank. Locomotives of this series were produced for Transcaucasian, Mykolayiv and Privislinskoy railway, as several copies were produced for internal needs Nevsky Zavod.

Steam locomotive E-1112. Designed Lugansk Locomotive Works in 1910. Later locomotives built at Kharkov, Kolomna, Bryansk and Sormovo plants until 1957.
This series of locomotives is the most massive in the world - everything, including various modifications, was built about 11 thousand locomotives.
Design speed of the engine - 55 km / h. Maximum power - 1500 hp Efficiency - 8% Series E locomotives are among the most powerful and the most massive steam locomotives created at the beginning of the XX century. Project cargo locomotive passing the commission in February 1911 under consideration by the Engineering Council of the Ministry of Railways. Later, October 29, 1911 was approved by the working draft of the locomotive and, since 1912, has been adjusted their production.

The locomotive EM720-07. Upgraded Series E, is being built in 1931-1935 gg Lugansk, Kharkov, Bryansk and Sormovo works. Total produced 2694 locomotives.
To increase the thrust was increased vapor pressure in the boiler while increasing the strength of the boiler and the strengthening of certain parts of the driving mechanism.
Design speed of the locomotive - 65 km / h. Maximum power - 1800 hp Efficiency - 7%.
Lokomotiv offers extra traction force by increasing the steam pressure in the boiler, which required the strengthening of the joints of the boiler and some parts of the driving mechanism. As a result, improvements have resulted in an increase in the total weight, which is why it was necessary to make a number of design changes. Locomotives were built without water purifier and nutritious cap, and with less smoke tubes (151 against 157 locomotives from the series Eu). But the active use of welding in the steam locomotive allowed to reduce the weight of the locomotive from 85 to 75 tons and replace the withdrawn units.

The locomotive ER761-96. EM Series reconstructed. Due to the elongation of the locomotive firebox power increased by 10%. Locomotives of this series were built by domestic factories in the 1930s and during the Great Patriotic War, and after the war production has been established in Romania (Resita plant), Poland (plant Tsegelskogo), Czechoslovakia (factory CKD) and Hungary (plant MÁVAG). Museum exhibit from Romania as evidenced by its nameplate. The last steam locomotive series was made in 1956 at the Hungarian plant MÁVAG. Also, a small number of locomotives of this series were produced during World War II the Kolomna Machine-Building Plant.
Design speed of the locomotive - 65 km / h. Maximum power - 2000 hp Efficiency - 7, 2%.

Steam locomotive TE-622. The name stands for TE Series trophy similar to the characteristics of the domestic series E.
Steam engines under the original name of the BR52 produced in Nazi Germany and occupied Europe. There were more than 6,000 locomotives, 2,200 of them came on the railways of the USSR as booty or by way of reparations.
The railways of the western part of the USSR locomotives TE actively exploited until the mid-1970s, after which most of them were transferred to industrial enterprises. During operation in the USSR series TE locomotives caused the Soviet railwaymen very positive feedback. As a general lack of marked fall in output when using low-grade domestic coal. In common parlance series TE locomotives called "Teshkami" or "Frau».
Design speed of the locomotive - 80 km / h. Maximum power - 1500 hp Efficiency - 7, 5%

The locomotives P36 series, probably the most beautiful among domestic locomotives. This series was comparable to locomotives series of IP, but had less stress on the axles on the track (18ts), whereby it was possible to use these engines in most of the country's railways. Successful testing and trial operation of the first locomotive type 2-4-2 resulted in an experimental batch of the order in 1953 at the Kolomna Machine-Building zavode.Ekspluatatsionnye test locomotives took place at the Moscow-Kursk and Krasnoyarsk railways. In the second half of 1954 Kolomna factory produced pilot batch of locomotives will include minor structural improvements compared to the prototypes. At the end of 1954 the locomotive Series P36 was accepted for serial production. Locomotives of this series were sent to work with long-distance passenger trains on the main lines of Krasnoyarsk, Kalinin, Belarusian, Stalin, October, Kuibyshev and Northern railways. Since the beginning of the 70s, these locomotives were gradually replaced by electric and diesel locomotives. 1974 is considered the last year of operation of steam locomotives P36 series.
The steam locomotive P36-0071. Passenger locomotive design and manufacture of Kolomna Plant (251 locomotive, 1950-1956).
The last steam locomotive of the series at the same time became the last steam locomotive built in the USSR. He is now at the Museum of St. Petersburg.
The longest locomotives in this series worked on the Trans-Baikal Railway. Here, they were withdrawn from service in 1974.
Design speed - 125 km / h. Maximum power - 3000 hp Efficiency - 8, 2%.

The locomotive EU684-52. Reinforced ("Y") version of the Series E, is produced from 1926 to 1931 Kolomna, Luhansk, Kharkiv, Bryansk and Sormovo works. Total built 2475 locomotives.
Design speed of the locomotive - 65 km / h. Maximum power - 1500 hp Efficiency - 7%

Steam locomotive 9P-18430. Another massive shunting and industrial tank engine. It was built in the Soviet Union from 1935 to 1957. Total produced more than 3 million cars.
Design speed of the engine - 25 km / h. Maximum power - 320 hp
As of the year 2007 in museums or as a locomotive-preserved monuments of the 34 locomotive serii.Parovozy series 9P improved design produced Kolomna plant from 1939 to 1941. and Murom Locomotive Plant. Dzerzhinsky from 1945 to 1955. Steam locomotives working on ways to many industrial enterprises in the country and is well proven.
Shunting tank locomotive of this series was immediately taken to the mass production despite a number of shortcomings.
Later, in 1939, when the program of the Kolomna Machine-Building Plant was again included the construction of these locomotives, the plant designers have revised drawings to address deficiencies.

To reduce pressure on the rails, in 1948, it was decided to develop a series based on L. After lengthy trials, in 1952 the first steam locomotive, designed to Voroshilovgrad locomotive plant im.Oktyabrskoy Revolution, received the designation OR18-01 entered the railroad. Although similar to a series of parameters A series of PR units was a new, more modern type of locomotive with significant structural differences between a number of nodes and their trailer thermal characteristics. On a steam train set a different water heater and wheel sets have been strengthened. During the test, the locomotive showed an increase in capacity of 24% compared to locomotives series L. During 1953 locomotive OR18-01 passed performance tests on a plot Lublin Serpukhov-Moscow-Kursk-Donbass railway. In 1954, the factory built Voroshilovgradsky initial batch of five cars (numbers 0005-0010) in the process of creating a series that has received a new designation LP - The locomotive was built based on a series of drawings A Voroshylovgrad plant.
Steam locomotive LV-0225. Freight locomotive manufacturing plant Voroshylovgrad based on a series of LA were built from 1952 to 1956. Total 522 locomotive.
Produced in China until the mid-1990s, the locomotive series QJ had much in common with the Soviet LP.
Design speed - 90 km / h. Maximum power - 2420 hp Efficiency - 8%

The locomotive SU253-33. Passenger locomotives series Su produced in the USSR from 1924 to 1940. Project locomotive developed by the Leningrad factory "Red Putilovets».
Museum locomotive built directly into the city of Gorky (formerly so-called Nizhny Novgorod) plant "Red Sormovo" produces such locomotives from 1947 to 1951 (a total of 411 locomotives).
Design speed - 115 km / h. Maximum power - 1500 hp Efficiency - 7, 8%. The locomotive passenger, so the emphasis is on speed and not on the thrust and towing weight

The locomotive EN-1. Modification E series, produced Nevsky Shipyard in Petrograd from 1916 to 1920. Total built 63 steam locomotive.
During the war 1914-1918. and in the postwar period, the state iron and steel industry has deteriorated sharply, and after 1917 was in general very poor. In view of the absence of metal for the repair of existing locomotives and the inability to increase the locomotive fleet, by 1920 the country's leadership decided to order a large batch of freight locomotives abroad. It was originally planned to order 1,000 locomotives in Sweden, part of which had to be made on the basis of Swedish locomotives Series R, and the other by the type of more appropriate operating conditions of domestic railways. But in the end we decided to order locomotives E series of drawings of Lugansk plant.
In Sweden ordered 500 locomotives, and, simultaneously, in Germany has been ordered 700 locomotives. The first locomotives were built in strict accordance with the drawings of Lugansk plant, but later began to make small changes in the light of experience and features of operation.

On the wheels of a steam locomotive - the emblem Voroshylovgrad plant

Source: