216
What Causes Bladder Cancer: A Review of Causes and Prevention Methods
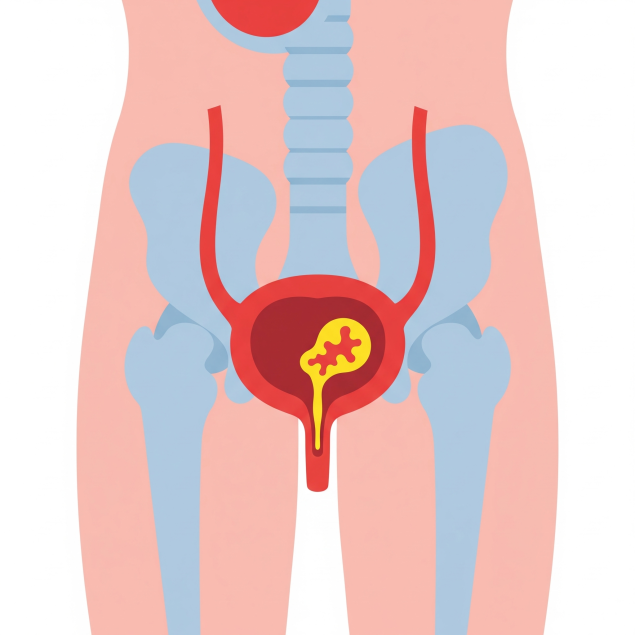
Bladder cancer is one of the most common malignant neoplasms of the urinary tract, especially among men over 50 years old. The disease is characterized by the development of a tumor in the mucous membrane of the organ and often proceeds secretively in the early stages. According to statistics, the main symptom of bladder cancer, which first attracts the attention of the patient, is blood in the urine (hematuria), but sometimes the tumor does not make itself felt for a long time.
Timely detection and individual selection of treatment can significantly improve the prognosis and quality of life of the patient with this form of oncology. Modern approaches to diagnosis and therapy provide high chances of cure, especially when the disease is detected at an early stage. More about the features of treatment of bladder cancer and prognosis can be read at the link https:/ /www.clinic-target.com/cancer/rak-mochevogo-puzyrya/.
Causes and risk factors
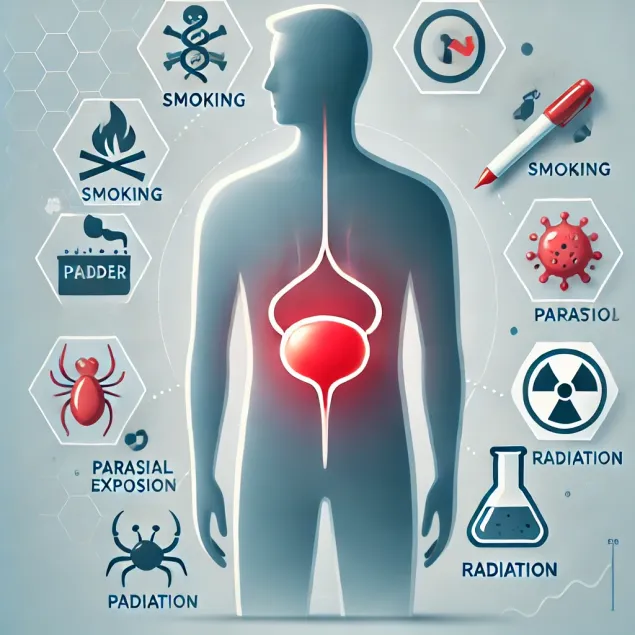
Bladder cancer can develop under the influence of various external and internal factors that contribute to malignant degeneration of cells of the mucous membrane of the organ. The main causes and risk factors include:
- Smoking. The most significant factor, since tobacco smoke contains carcinogens that are excreted by the kidneys and irritate the bladder mucosa. In smokers, the risk of the disease is 3-4 times higher than in non-smokers.
- Effects of chemicals. Working with aniline dyes, petroleum products, rubber, paints and organic solvents increases the risk of developing a malignant tumor. This form of oncology is often found in workers of the chemical and textile industry.
- Chronic inflammatory processes. Frequent cystitis, especially in men, urolithiasis and prolonged catheter presence can cause chronic irritation and inflammation of the mucosa, increasing the risk of mutations in the cells of the mucosa of the organ.
- Radiation. Previous radiation treatment of the pelvic organs (for example, in cancer) can provoke bladder cancer even years later.
- Uncontrolled drug and toxic effects. Certain medications (such as cyclophosphamide) and prolonged use of painkillers can negatively affect the urinary system.
- Parasitic infections. In endemic regions (Africa, Middle East), schistosoma haematobium infection is associated with an increased risk of squamous cell bladder cancer.
- Age and gender. The disease is more common in people older than 50 years, especially in men (by 3-4 times more often than in women).
- Hereditary predisposition. In rare cases, a family history of malignant urinary tumors may indicate an increased genetic vulnerability.
Early identification and elimination of risk factors plays a key role in the prevention of bladder cancer.

Symptoms of bladder cancer
In the early stages, bladder cancer can be asymptomatic. The main and often the first sign is hematuria - the appearance of blood in the urine, sometimes without pain. There may also be:
- frequent urination;
- burning or pain when urinating;
- Feeling of incomplete emptying.
In the later stages, pain in the lower abdomen, in the lower back, swelling of the legs and signs of renal failure in violation of urine outflow are possible. Symptoms depend on the stage and prevalence of the neoplasm.
Features of diagnostics
Diagnosis of bladder cancer is complex and may include:
- general and cytological analysis of urine;
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound);
- cystoscopy with a possible biopsy.
To clarify the stage of the disease is used CT or MRI of the pelvic organs. These methods allow to assess the depth of germination of the tumor and the presence of metastases.
Treatments bladder cancer
Treatment of bladder cancer requires an integrated and individual approach, taking into account the stage of the disease, the type of tumor, the age and general condition of the patient. The purpose of therapy is to remove the tumor, prevent recurrence and, if possible, preserve the function of the organ.
In modern oncology, such methods of treatment of bladder cancer are used:
- transurethral resection (TUR) - the main method of treatment of superficial tumors;
- cystectomy Complete removal of the bladder in invasive forms of cancer;
- chemotherapy intravesical (in the early stages) or systemic (in the spread of the disease);
- immunotherapy (introducing BCG vaccine) reduces the risk of recurrence in superficial forms;
- radiotherapy Used as an alternative to surgery or as part of a combination treatment.
Often a combination of several methods is used to achieve the best result.
Methods of preventing bladder cancer
Prevention of malignant bladder tumor plays an important role in reducing the risk of its development. Proper lifestyle, timely identification and elimination of risk factors, as well as regular medical examinations can significantly reduce the likelihood of cancer. Particular attention should be paid to people from high-risk groups - smokers, workers in the chemical industry and people with chronic urological pathologies.
The main methods of preventing bladder cancer include:
- Quit smoking. Smoking is the main risk factor, so quitting this habit significantly reduces the likelihood of getting sick.
- Compliance with safety rules when working with chemicals. The use of personal protective equipment and regular medical examinations when working with aniline dyes, solvents and other toxic substances.
- Control and treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases of the bladder. It is important to timely therapy of cystitis, urolithiasis and other urological pathologies to avoid prolonged irritation of the mucosa.
- Limiting the effects of radiation. Minimization and proper use of radiation exposure, especially in the treatment of other diseases.
- A balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle. A diet high in vegetables and fruits, maintaining a normal weight, regular physical activity contribute to strengthening immunity and reducing the risk of cancer.
- Regular medical examinations. For persons at risk - annual examinations, urine tests and, if necessary, cystoscopy allow to identify pathological changes at an early stage.
- Prevention of parasitic infections. In endemic regions, it is important to prevent infection with schistosomes through hygiene and the treatment of parasitic diseases.
Bladder cancer is a serious disease that requires timely diagnosis and comprehensive treatment. Early access to a doctor and adherence to preventive measures significantly increase the chances of a successful outcome. Therefore, it is important to monitor risk factors and undergo regular medical examinations.

What is the most important thing about being a parent?
5 things in life that we do not know how to foresee