214
Intestinal microbiome and anxiety: an unexpected connection

Description: Research shows that the gut microbiome plays a key role in a person’s mental health. How can bacteria in the gut affect anxiety and even social phobia? We analyze scientific data and give practical advice.
Introduction
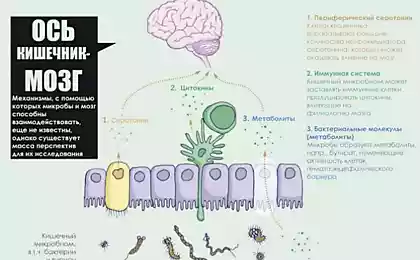
Have you ever wondered why anxiety can be accompanied by stomach discomfort? It turns out that our gut and brain are connected by a complex network of nerve endings and chemical signals called cerebral axis. But even more surprising, the microbes that inhabit the gut can affect our emotional state, including our anxiety levels.
How does the microbiome affect the psyche?

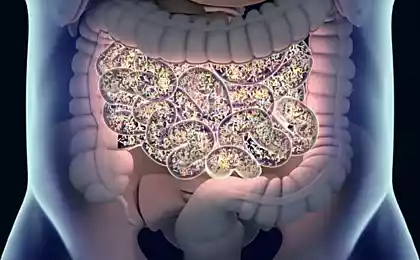
A microbiome is a collection of bacteria, viruses and fungi that inhabit our intestines. These microorganisms perform many functions:
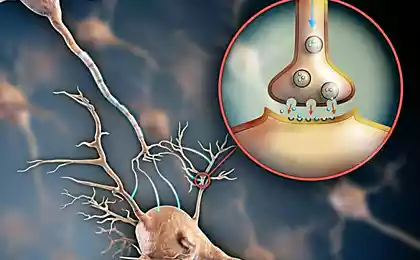
- They produce neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine.
- It affects the level of inflammation in the body.
- They communicate with the vagus nerve, transmitting signals to the brain.
Microbiome and social phobia
Some studies confirm that certain types of bacteria may be associated with social anxiety. For example, people with a deficiency of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium have elevated levels of cortisol, a stress hormone.
How to improve the microbiome to reduce anxiety?

1. Include probiotics and prebiotics
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria found in fermented foods such as kefir, yogurt, sauerkraut. Prebiotics are food for these bacteria found in vegetables, fruits and cereals.
2. Minimize stress
Chronic stress affects the microbiome, increasing the number of harmful bacteria. Practice meditation, yoga and breathing exercises.
3. Enjoy a variety of diets.
A varied diet maintains the balance of the microbiome. Eat more fiber and plant foods.
4. Avoid antibiotics without need
Antibiotics kill not only harmful, but also beneficial bacteria. Take them only as prescribed by a doctor.
Conclusion
Our gut and mental health are much more connected than is commonly believed. The balance of the microbiome can affect anxiety levels, depression, and social behavior. Eating the right foods and reducing stress can improve not only bowel function, but also mental state.
Glossary
- microbiome - a set of microorganisms that inhabit the intestine.
- cerebral axis The relationship between the intestine and the nervous system.
- Probiotics - live bacteria that are useful for the intestines.
- Prebiotics substances that promote the growth of beneficial bacteria.
- Neurotransmitters Chemical compounds that transmit signals in the brain.
AI Psychologist: Can an Algorithm Replace a Human?
The Art of Minimalism: How Fewer Things Improve Quality of Life