165
How to maintain health in adulthood
There is a myth that vaccines made in childhood provide immunity for life. But that's not really true. Immunity to a number of diseases is not eternal, decreases with age and may disappear completely.

When examined in adults, an almost complete absence of antibodies to those infections from which they were vaccinated in childhood or adolescence is often found. So, the risk of getting sick in these people is the same as those who are not vaccinated.
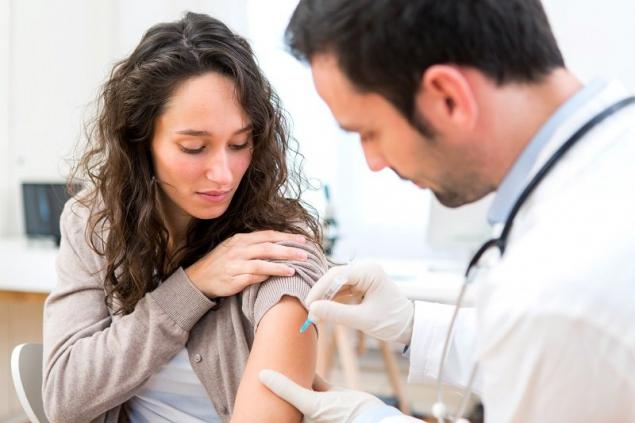
At the same time, do not forget that “childhood” diseases in adulthood are much more difficult. "Site" They will tell you how to avoid this danger and What vaccinations do adults need?To maintain and increase your health.
First of all, adults need to be vaccinated against diseases from which they did not receive protection in childhood. If you do not remember whether you were vaccinated, and there are no medical data on immunization, the doctor will send for appropriate tests.

Be sure to check the presence of vaccinations against measles, rubella and mumps. The lack of the necessary amount of antibodies to rubella is especially dangerous during pregnancy, and not so much for the woman herself as for the embryo.

Adults who have not had measles before, not vaccinated or vaccinated against measles once, are vaccinated before the age of 35 years. Up to 55 years inclusively vaccinated adults belonging to risk groups (health workers and workers of educational organizations).

Not only children, but also adults are vaccinated against diphtheria and tetanus. Immunity against these diseases lasts about 10 years. Therefore, all adults (without age limit) should be vaccinated against diphtheria and tetanus every 10 years.
Once in the period of 23-29 years should be vaccinated against tuberculosis. It is better to 30 years, later it makes sense only in contact with patients.
People born before the nineties are usually not yet vaccinated against hepatitis B. All of them should be fully vaccinated. Especially relevant vaccine health care providers and others who have contact with blood.
When preparing and conducting vaccination, a number of nuances should be taken into account.

This group includes those vaccinations that are optional. But that doesn't mean they're not needed. They are not allocated funds from the budget, and it is up to you to do them or not. An example is a vaccine against meningococcal infection, or a vaccination against infections caused by the human papillomavirus.
Do not forget that at one time it was mass prevention that negated many dangerous diseases, and now, when cases of refusal of vaccinations have become more frequent, some of them, for example, measles, return.
Editorial "Site" Every country has its own recipes for longevity, adhering to which people live happily ever after. We have collected for you the most precious secrets of centenarians from different parts of the world, which are worth adopting.
Hippocrates once said, “Tell me what you eat and I will tell you what you are sick.” To find a good figure and well-being, it is important to choose those products that bring the maximum benefit to the body.

When examined in adults, an almost complete absence of antibodies to those infections from which they were vaccinated in childhood or adolescence is often found. So, the risk of getting sick in these people is the same as those who are not vaccinated.

At the same time, do not forget that “childhood” diseases in adulthood are much more difficult. "Site" They will tell you how to avoid this danger and What vaccinations do adults need?To maintain and increase your health.
First of all, adults need to be vaccinated against diseases from which they did not receive protection in childhood. If you do not remember whether you were vaccinated, and there are no medical data on immunization, the doctor will send for appropriate tests.

Be sure to check the presence of vaccinations against measles, rubella and mumps. The lack of the necessary amount of antibodies to rubella is especially dangerous during pregnancy, and not so much for the woman herself as for the embryo.

Adults who have not had measles before, not vaccinated or vaccinated against measles once, are vaccinated before the age of 35 years. Up to 55 years inclusively vaccinated adults belonging to risk groups (health workers and workers of educational organizations).

Not only children, but also adults are vaccinated against diphtheria and tetanus. Immunity against these diseases lasts about 10 years. Therefore, all adults (without age limit) should be vaccinated against diphtheria and tetanus every 10 years.
Once in the period of 23-29 years should be vaccinated against tuberculosis. It is better to 30 years, later it makes sense only in contact with patients.

People born before the nineties are usually not yet vaccinated against hepatitis B. All of them should be fully vaccinated. Especially relevant vaccine health care providers and others who have contact with blood.
When preparing and conducting vaccination, a number of nuances should be taken into account.

- Vaccinations can only be given to a healthy person. It is necessary to first pass the basic analysis.
159765 - Alcohol can be consumed no earlier than 3 days after vaccination.
- Admission after vaccination of antihistamines and antipyretics will avoid allergic reactions.
- People with HIV are shown inactivated and live attenuated vaccines (this should be discussed with a doctor).
- Before traveling to countries with a hot climate, it is advisable to carry out a special vaccination. It is mandatory if you plan to visit places where dangerous infections spread: yellow fever, brucellosis, typhoid fever, Japanese encephalitis.
- Pregnant women should not be vaccinated with drugs that are based on the action of a live virus. Such vaccines include CCP (measles, rubella, mumps).

This group includes those vaccinations that are optional. But that doesn't mean they're not needed. They are not allocated funds from the budget, and it is up to you to do them or not. An example is a vaccine against meningococcal infection, or a vaccination against infections caused by the human papillomavirus.
Do not forget that at one time it was mass prevention that negated many dangerous diseases, and now, when cases of refusal of vaccinations have become more frequent, some of them, for example, measles, return.
Editorial "Site" Every country has its own recipes for longevity, adhering to which people live happily ever after. We have collected for you the most precious secrets of centenarians from different parts of the world, which are worth adopting.
Hippocrates once said, “Tell me what you eat and I will tell you what you are sick.” To find a good figure and well-being, it is important to choose those products that bring the maximum benefit to the body.