324
What tests for COVID-19 will tell you if you have coronavirus
To effectively fight coronavirus infection, we all need to become a little medical. Including to understand the features of methods of prevention and testing of COVID-19, one of which is a rapid test for antibodies to coronavirus.

GettyImages Express test for antibodies to coronavirus Why do you need antibody tests? Antibodies are special molecules that our body’s immune system produces when it encounters pathogens or viruses. These molecules are called immunoglobulins (abbreviated Ig). Each foreign element has its own specific antibodies.

Therefore, determining their presence in the blood, you can judge the current or previous infections. In particular, the presence of antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 virus may indicate that the patient's immune system is fighting it right now or has encountered it before.
What is the difference between antibody tests and PCR tests? PCR test (polymerase chain reaction) refers to direct testing methods. It can detect the presence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the body at the moment. An antibody test can only detect the immune system response, not the virus itself.

GettyImages PCR is highly sensitive even in the earliest stages of the disease. It helps detect COVID-19 before symptoms appear. To do this, the patient takes a smear from the nasopharynx. The sample is then examined for the presence of coronavirus RNA.
View this post on Instagram
A post shared by EmmiAndMaria! (@emmiandmaria)
The analysis for antibodies is carried out differently: a drop of the patient’s blood is applied to the test strip. If there are no antibodies, the test shows one strip. To detect IgM or IgG antibodies indicate two or three strips.

It should be clarified that all rapid tests are only for testing by specialists in medical institutions. Even a small deviation from the standard algorithm of actions can radically change the result. Therefore, do not trust the sellers of express tests in private hands.
IgM and IgG immunoglobulins in COVID-19 begin to form only 7-14 days after contact with the virus. It is important to understand that they may not be at the initial stage of the disease. Therefore, the antibody test in such a situation can be negative.
The presence in the patient's body of various types of antibodies (IgM and IgG) allows us to judge the stage of infection. So, immunoglobulins of class M (IgM) appear after 1-2 weeks from the moment of infection and disappear after 2-3 months.
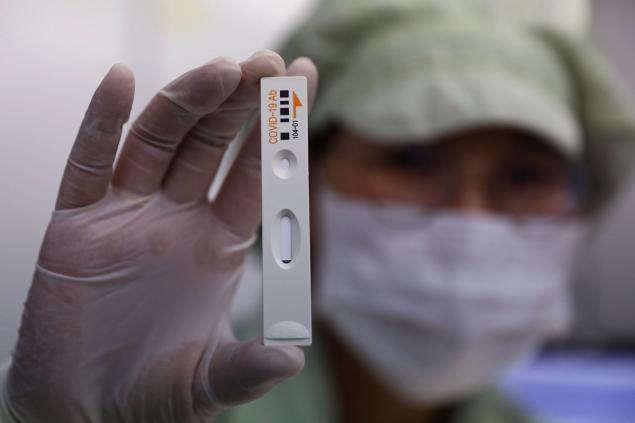
Grade G immunoglobulins (IgG) are formed in the body after 3-4 weeks and remain active for several years. Thus, the detection of IgM antibodies indicates an active stage of the disease or a recent infection, and IgG indicates a past disease.
If a person has a high fever and cough, the presence of IgG antibodies allows you to understand that a person has already had a coronavirus infection before. Antibody tests also show how many people are asymptomatic. This allows doctors to estimate the period necessary for the formation of herd immunity.
Rapid tests allow us to determine in about 15 minutes whether there are antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the blood. Plus the method in speed, minus in insufficient accuracy. Antibody tests could play an important role in diagnosing COVID-19, but their results are highly dependent on the time of testing.
1917
The highest accuracy (up to 90%) is in the third or more week since infection. In patients in the second week, it decreases to 70%, and in the first – to 30%. All this suggests that tests alone for diagnostic conclusions are not enough in any case. The doctor makes the final conclusions by comparing the test results with the general picture of the disease.
Photo preview and article .

GettyImages Express test for antibodies to coronavirus Why do you need antibody tests? Antibodies are special molecules that our body’s immune system produces when it encounters pathogens or viruses. These molecules are called immunoglobulins (abbreviated Ig). Each foreign element has its own specific antibodies.

Therefore, determining their presence in the blood, you can judge the current or previous infections. In particular, the presence of antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 virus may indicate that the patient's immune system is fighting it right now or has encountered it before.
What is the difference between antibody tests and PCR tests? PCR test (polymerase chain reaction) refers to direct testing methods. It can detect the presence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the body at the moment. An antibody test can only detect the immune system response, not the virus itself.

GettyImages PCR is highly sensitive even in the earliest stages of the disease. It helps detect COVID-19 before symptoms appear. To do this, the patient takes a smear from the nasopharynx. The sample is then examined for the presence of coronavirus RNA.
View this post on Instagram
A post shared by EmmiAndMaria! (@emmiandmaria)
The analysis for antibodies is carried out differently: a drop of the patient’s blood is applied to the test strip. If there are no antibodies, the test shows one strip. To detect IgM or IgG antibodies indicate two or three strips.

It should be clarified that all rapid tests are only for testing by specialists in medical institutions. Even a small deviation from the standard algorithm of actions can radically change the result. Therefore, do not trust the sellers of express tests in private hands.
IgM and IgG immunoglobulins in COVID-19 begin to form only 7-14 days after contact with the virus. It is important to understand that they may not be at the initial stage of the disease. Therefore, the antibody test in such a situation can be negative.
The presence in the patient's body of various types of antibodies (IgM and IgG) allows us to judge the stage of infection. So, immunoglobulins of class M (IgM) appear after 1-2 weeks from the moment of infection and disappear after 2-3 months.

Grade G immunoglobulins (IgG) are formed in the body after 3-4 weeks and remain active for several years. Thus, the detection of IgM antibodies indicates an active stage of the disease or a recent infection, and IgG indicates a past disease.
If a person has a high fever and cough, the presence of IgG antibodies allows you to understand that a person has already had a coronavirus infection before. Antibody tests also show how many people are asymptomatic. This allows doctors to estimate the period necessary for the formation of herd immunity.
Rapid tests allow us to determine in about 15 minutes whether there are antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the blood. Plus the method in speed, minus in insufficient accuracy. Antibody tests could play an important role in diagnosing COVID-19, but their results are highly dependent on the time of testing.
1917
The highest accuracy (up to 90%) is in the third or more week since infection. In patients in the second week, it decreases to 70%, and in the first – to 30%. All this suggests that tests alone for diagnostic conclusions are not enough in any case. The doctor makes the final conclusions by comparing the test results with the general picture of the disease.
Photo preview and article .
How to host guests for Christmas lying mother-in-law
For what the hostess exchanged the annoying "Foat" for "Ruby"























