232
Osteopathic view of lymph
The main task of lymph is not to remove water from the tissues (this is good and the veins cope), but to remove excess protein, metabolic products and lipids.
This concept explains why lymphatic drainage so quickly go edema, despite the fact that the lymph current is quite slow.
Removing a few percent of the protein (reducing oncotic pressure) allows large amounts of previously protein-related water to escape into the bloodstream.
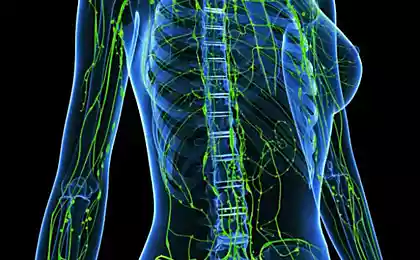
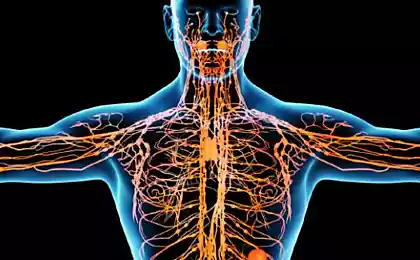
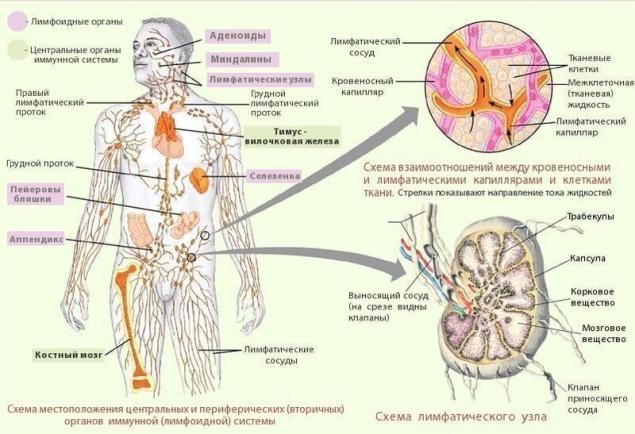
lymph It is formed in the tissues of the body from interstitial (tissue) fluid. Moving through the lymphatic vessels, it passes through the lymph nodes, where its composition changes significantly, mainly due to the entry into the lymph of formed elements - lymphocytes. It is therefore customary to distinguish:
The lymph performs or participates in the following functions:
(1) maintaining the consistency of the composition and volume of the interstitial fluid and the cell microenvironment;
2) the return of protein from the tissue medium to the blood;
(3) participation in the redistribution of body fluid;
4) providing a humoral connection between tissues and organs, the lymphoid system and blood;
(5) absorption and transport of food hydrolysis products, especially lipids from the gastrointestinal tract into the blood;
6) ensuring immunity mechanisms by transporting antigens and antibodies, transferring plasma cells, immune lymphocytes and macrophages from the lymphoid organs.
In addition, lymph is involved in the regulation of metabolism, through the transport of proteins and enzymes, minerals, water and metabolites, as well as in the humoral integration of the body and the regulation of functions, since lymph transports information macromolecules, biologically active substances and hormones.
The number, composition and properties of lymph
The volume of circulating lymph is difficult to determine, however, experimental studies show that a person has an average circulation of 1.5-2 liters of lymph.
Lymph consists of lymphoplasm and formed elements, and there are very few cells in the peripheral lymph, much more in the central lymph.
Similarly with blood: the ratio of the volume of formed elements to the total volume is called lymphocrit (for blood - hematocrit), lymphocrit even in the central lymph less than 1%.
Therefore, cellular elements in the central lymph are relatively small. The specific gravity of lymph is also lower than that of blood, and ranges from 1.010 to 1.023. The actual reaction is alkaline, the pH is in the range of 8.4-9.2.
The osmotic pressure of the lymph is close to the blood plasma, and the oncotic pressure is significantly lower due to the lower concentration of proteins in it. Accordingly, less and viscosity of the lymph. published
Author: Alexander Smirnov
Also interesting: Lymph is the living water of our body
Thick Blood: What You Need to Know!
P.S. And remember, just changing our consumption – together we change the world!
Source: www.facebook.com/metavitonica/posts/ 1827128014165450
This concept explains why lymphatic drainage so quickly go edema, despite the fact that the lymph current is quite slow.
Removing a few percent of the protein (reducing oncotic pressure) allows large amounts of previously protein-related water to escape into the bloodstream.
lymph It is formed in the tissues of the body from interstitial (tissue) fluid. Moving through the lymphatic vessels, it passes through the lymph nodes, where its composition changes significantly, mainly due to the entry into the lymph of formed elements - lymphocytes. It is therefore customary to distinguish:
- peripheral lymph, which has not passed through any lymph node,
- intermediate lymph, passed through one or two lymph nodes on the periphery,
- central lymph, before it enters the blood, for example, in the chest lymphatic duct.
The lymph performs or participates in the following functions:
(1) maintaining the consistency of the composition and volume of the interstitial fluid and the cell microenvironment;
2) the return of protein from the tissue medium to the blood;
(3) participation in the redistribution of body fluid;
4) providing a humoral connection between tissues and organs, the lymphoid system and blood;
(5) absorption and transport of food hydrolysis products, especially lipids from the gastrointestinal tract into the blood;
6) ensuring immunity mechanisms by transporting antigens and antibodies, transferring plasma cells, immune lymphocytes and macrophages from the lymphoid organs.
In addition, lymph is involved in the regulation of metabolism, through the transport of proteins and enzymes, minerals, water and metabolites, as well as in the humoral integration of the body and the regulation of functions, since lymph transports information macromolecules, biologically active substances and hormones.

The number, composition and properties of lymph
The volume of circulating lymph is difficult to determine, however, experimental studies show that a person has an average circulation of 1.5-2 liters of lymph.
Lymph consists of lymphoplasm and formed elements, and there are very few cells in the peripheral lymph, much more in the central lymph.
Similarly with blood: the ratio of the volume of formed elements to the total volume is called lymphocrit (for blood - hematocrit), lymphocrit even in the central lymph less than 1%.
Therefore, cellular elements in the central lymph are relatively small. The specific gravity of lymph is also lower than that of blood, and ranges from 1.010 to 1.023. The actual reaction is alkaline, the pH is in the range of 8.4-9.2.
The osmotic pressure of the lymph is close to the blood plasma, and the oncotic pressure is significantly lower due to the lower concentration of proteins in it. Accordingly, less and viscosity of the lymph. published
Author: Alexander Smirnov
Also interesting: Lymph is the living water of our body
Thick Blood: What You Need to Know!
P.S. And remember, just changing our consumption – together we change the world!
Source: www.facebook.com/metavitonica/posts/ 1827128014165450