734
Real black death
It is rightly called the "Queen of the tumors." It changes its masks like a masquerade, deceiving even the most experienced professionals. Kills stealthily, like Palace intriguers, “poisoning” the human body in no time. Before her power trembles the global cancer community. It will teach to appreciate the aristocratic pallor.
Melanoma is the result of neoplastic transformation of melanocytes – cells that produce different variations of the pigment melanin. Melanocytes come from the neural crest, a group of marginal cells of the nerve of the gutter.
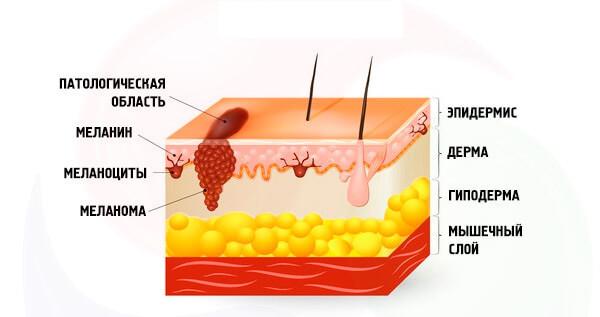
Cells of the neural crest are of high level of migration, and most of them are sent down from the neural tube, forming a variety of neural and endocrine structures. However, the melanoblast show your uniqueness even before the potential acquisition of the tumor phenotype and migrate down and to the sides of the neural tube.
The molecular mechanisms of this process remain unknown. The fate of melanoblast hard to call predefined: this element may subsequently develop into a neuron, leiomyza, and in the case of high level of melanocyte-glial potential in the glial component.
After differentiation in the melanocyte isolated body (soma) and processes, which are located in the basal and spinous layers of the epidermis, respectively. Under the action of melanocytestimulating and adrenocorticotropic hormone and sunlight in melanosomes synthesized (EU)melanin (and pheomelanin), whose function is to protect the nuclear apparatus of cells from damage by UV radiation.
The synthesized melanin is transported in the spiny layer of the epidermis on the tentacles of the melanocyte, later in the keratinocytes of the epidermis, giving the skin a tan. Some time later, this polymer gidrolizuyutza in the lysosomes, and the skin returns to its usual color.
This scenario can be called perfect. But what happens to those less fortunate? The key point of initiation of neoplastic transformation of the melanocyte is a non-lethal mutation in his genetic apparatus. The reason for this damage may have different effects: physical and chemical.
Like most tumors, the causes of the start of oncogenesis in melanoma, you can combine several ways:
1) Suppression of the activity of genes oncosuppressor;
2) Activation of proto-oncogenes;
3) Exogenous mutations, obtained a variety of ways.
What makes melanoma so dangerous? It would seem that outdoor localization, all known algorithms at the stage of self-examination, the high immunogenicity of the tumor should make the therapy as efficient as possible.
However, the unpredictability of the metastatic cascade coupled with the lack of specially designed therapy for metastatic melanoma, the unpredictability of the clinical and morphological – both micro-and macroscopic forms and higher frequency of recurrence lead to the fact that to date, the incidence of melanoma is increasing worldwide; the median survival with melanoma is not more than 8 months, and the effectiveness of radical surgical treatment do not exceed 65%. To answer the questions clinicians and patients can only scientists.
The possibility of sequencing the genome allowed us to deepen our understanding of carcinogenesis in cutaneous melanoma. The study of the processes originating in the transformation of melanocytes in the most aggressive of the existing tumor is the most important stage in the study of not only melanoma, but also all other tumors.
Only by identifying new targets possible purpose of targeted therapy, the expansion of diagnostic horizons as well as the possible revision of the classification, clinical-morphological forms with a preference for associations of subtypes of melanoma based on the nature of mutations. With this in mind, the review of mechanisms of carcinogenesis in melanoma need to pay special attention.
One of the most important achievements in the study of carcinogenesis in melanoma is considered the analysis of the mechanisms of signal transduction that are activated in the process of its development. Based on the etiological factors, the detection of certain mutations in melanoma of the skin may answer the question of the relationship of etiology and pathogenesis, clinical forms and therapeutic solutions.
What signaling pathway? This kind of "relay race" where in a strictly defined order enables a sequence of certain molecules involved in transmitting any kind of signal from the cell receptor into the cell. Signaling pathway can be activated by exogenous growth factors, neurotransmitters, hormones or endogenous by means of a signal-starters-activated for various reasons, inside the cage.
Epidemiology
The average age of patients with melanoma of the skin is about 45 years, but in recent years, melanoma has become increasingly occur in very young people (15-25 years). This tumor occurs in men and women, and in women 1.5-2 times more often. According to statistics, for every 100,000 healthy people accounts for 14 patients with melanoma.
In 2006 in Russia was 7.364 new patients with melanoma and 3.033 deaths. The annual number of cases of melanoma in Russia is 5,700 people, of which 2.200 are likely to die from this disease.
In different regions of the world the incidence of melanoma is significantly different. According to who, over the period 1988-2012. the highest standardized incidence rates for melanoma of the skin 25-29,8 o /oooo was characteristic of the white population of Australia and New Zealand. A fairly high incidence of 15-18,6 o /oooo observed among Europeans living in Zimbabwe, white men of the United States (Los Angeles, San Francisco), women, Austria, Norway.
High, by the standards of Europe, the level of 8.8–14,1 o /oooo was among the residents of Denmark, Italy, Switzerland, Sweden, men of Austria and Norway. The lowest standardized incidence rates for melanoma of the skin 0,1–1,5 o /oooo identified in Algeria, the Indians and black people in the US, Uganda, Zimbabwe, China, Korea, Japan.
On the occurrence of melanoma is affected by the race of man. According to who statistics, blacks are 4 times less likely to suffer from melanoma than Caucasians. There is an assumption that darker skin contains more melanin in the epidermis, which contributes to a stronger delay of UV radiation, and thus are better protected from its damaging effect on the melanocytes that developed evolutionary in accordance with the climatic conditions of those living in these areas of the globe people.
Accordingly, people with a weak natural hedge (less the amount of melanin in the skin) are more likely to suffer melanoma. For example, among residents of Kazakhstan noted an eightfold increase in the incidence of melanoma among visitors with white skin compared with the indigenous population.
Thus, the statistics of the who allow make sure natural the higher the number of melanocytes in the skin, the lower the risk of melanoma, hence the low level of pigmentation is a risk factor.
Evaluation of this factor is possible when ordinary clinical examination. People who belong to the “bright” phenotype, usually poorly susceptible to sun tan and is very prone to developing sunburn because of the high sensitivity to UV radiation, so the risk of developing melanoma increases them twice.
Another sign of abnormal level of pigmentation is the presence of a large number of freckles on the skin due to accumulation of proliferating melanocytes in the basal layer of the epidermis and the epithelium of the outer divisions of hair follicles.
Extremely heavy the degree of pigmentation disorders, characterized by complete lack of melanin in the body, is observed in albinos. Carcinogenic effects of UV radiation from them is so great that most 20 years, there are precancerous lesions or tumors of the skin, and is so detrimental that less than 10% of these people live up to 30 years.
Signaling pathways
To date, the most studied are the following signal paths:
The trouble starts when scientists try to track the strict specificity of signaling pathways and regulated process. It is a mistake to assume that the activation of these signaling pathways is a sign of neoplastic transformation in melanoma.
Firstly, these signaling pathways also exist in normal, regulating differentiation of cells in the antenatal and postnatal periods, ensure the reproduction of the effects of certain hormones and other typical processes aimed at maintaining normal functioning of the cell.
Second, the data paths involved not only in melanocytes: they are universal signaling systems involved in most cells in the human body. What's the matter? In any of the signaling pathways may occur one or another genetic or epigenetic damage, which will result in the negative regulation of signaling pathways with outcome in carcinogenesis.
MAPK
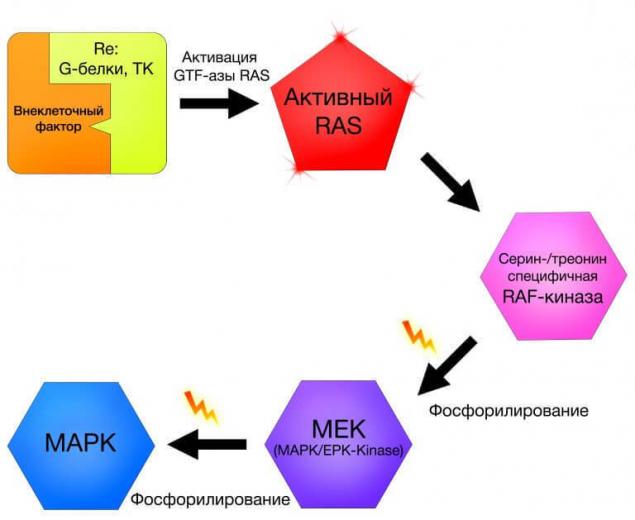
The cluster MARK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) are the intracellular signaling pathways of a variety of functions [8]. The criterion for inclusion in the MARC group is the presence of mitogen-activated protein kinases in the module, in which, in addition to kinases, contains proteinopathy and proteins-collectors auxiliary protein complexes [9].
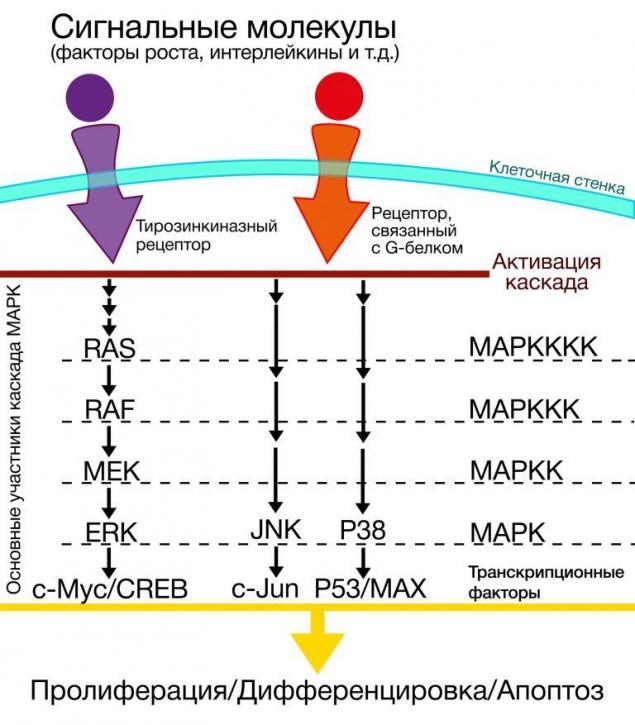
By themselves or MARK a cluster or its effects are not of particular interest in the context of carcinogenesis, however, those mutations that occur in genes of proteins involved in signaling pathways in cells of melanoma, require more detailed consideration. Among the many kinases involved in signal transmission in the cluster MARK there are so-called Raf kinase.
Raf is a family of serine-threonine dependent protein kinases, whose name is an acronym for Rapidly Accelerated Fibrosarcoma. But where fast-growing fibrosarcoma, and where the melanoma?
The fact that the underlying mechanisms of carcinogenesis often found Perekrest ways, such as in our case, including. In the context of this article makes no sense to focus on a detailed representation of the steps of carcinogenesis of fibrosarcoma we will be discussing features of the Raf in cutaneous melanoma.
BRAF
Notable in the family of Raf - we can be B-raf protein, which plays a role in MARK-cascade, whose effects are differentiation and cell division. The protein B-raf is encoded by the homonymous gene, which would be completely unremarkable if not for one "but": arising under the action of excessive UV radiation in this gene V600[x] mutation (under the [x] in this case, means the designation of nonsynonymous substitutions, leading to mutations), which consists in the substitution of valine for leucine (V600L), lysine (V600K) or glutamic acid (v600e was) 600-th position, is the starter neoplastic transformation in melanoma of the skin, and is also a target for the action of drugs, within the group of inhibitors of BRAF V600L. This so-called "nibi": imatinib, sorafenib, vemurafenib, etc.
In randomized clinical studies revealed an interesting feature: if the verified mutated BRAF status of the patient low molecular weight inhibitors of BRAF has led to the inhibition of melanoma, the consumption "-of nibav" patients, mutations of BRAF, which have raised doubts or were absent, led to the mutation of another of the cascade RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK, pathologically activating it and initiating the neoplastic transformation.
Thus, it can be concluded that low molecular BRAF inhibitors though are effective therapeutic tool still show a dangerous ambivalence in the case of lack of diagnosis or erroneous interpretation of the BRAF status of the patient.
C 2011 alternative to chemotherapy for patients with metastatic melanoma with the BRAF mutation v600e was is the drug vemurafenib (selrap). At the heart of its action is the inhibition of BRAF dimerization, while mutation v600e was the gain of the ERK signaling as a result of dimerization of the mutant kinase.
In phase I trials, the response to vemurafenib was obtained in 81 % of melanoma patients with the mutation v600e was (decrease in diameter of all tumor sites by 30 %). In phase III trials, overall survival at 6 months was observed in 84% of patients with metastatic melanoma, progression-free survival was 5-7 months.
However, 20-30% of patients receiving vemurafenib, side effects: malignant transformation of benign lesions and the appearance of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, which is associated with the activation of the MAPK route via RAS mutations in the suppression of RAF. Some patients in the treatment there are new foci of melanoma with wild type BRAF. Recent studies show that the MARK lends itself to a more effective inhibition when using not only BRAF (as monotherapy), and MEK-inhibitors.
This combination is not only more efficient, it prevents the development of resistance to therapy and the occurrence of the most serious adverse effect of BRAF-inhibitors – squamous cell carcinoma of the skin.
Suggest that the effect may be a combination of the drugs sorafenib and lonafarnib – inhibitor ferreiromania (reactions leading to the initiation of the carcinogenic activity of protein RAS) and "zakalivanie" RAS on the cell membrane.
In January 2014 registered a new targeted therapy dabravine for the treatment of melanoma with a mutation in 600-m BRAF codon. Unlike vemurafenib, gabroveni acts not only when replacing v600e was, but with the V600K mutation. Both BRAF inhibitors were the first drugs which had the effect in patients with brain metastases. Unfortunately, almost all patients responding to vemurafenib, over time there is resistance to therapy.
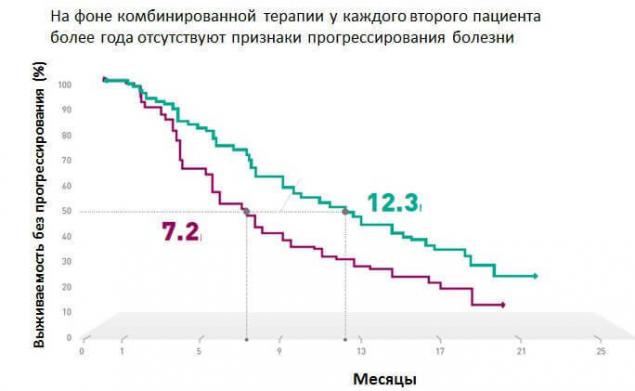
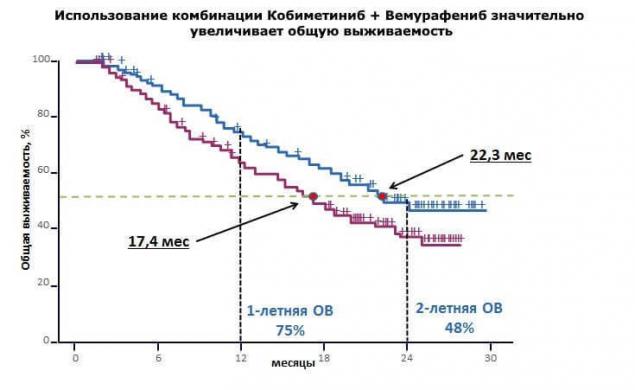
"In the clinical research study coBRIM, it was confirmed that combination therapy using the drugs vemurafenib and kabinetinin in 90% of cases allows to achieve response to therapy in patients with BRAF - positive metastatic melanoma. Every second patient over a year no evidence of disease progression, and overall survival approaching two years."
MEK
MEK is a serine-kinase treoninove MARK cluster, activated in response to changes in the upstream levels of the signal circuit.
The role of the MEK is to integrate signals from various growth factors with subsequent activation of proliferation. As part of the MARK-cascade, MEK is involved in the regulation of activity of transcription factors such as C-myc.
The Myc protein encoded by the homonymous gene, and is a proto-oncogene is not only a "canonical" example of transcripting factor, but also controls the chromatin structure by regulating acetylation of histones, which in turn affects the activity of gene expression. The mutant gene of the ICC, located in 8-th chromosome, is detected in many tumor types; a classic example of assetsfinancial t (8;14), leading to the emergence and development of Burkitt's lymphoma.
Experiments aimed at its inhibition, leading to lysis of tumor cells of the lung in mice. Therefore, the ICC is a therapeutic target, in particular, the development of selective allosteric inhibitors of the ICC is a relevant topic for clinical research.
NRAS
N-RAS (Neuroblastoma-Ras) is a gene that encodes the eponymous protein that is part of the so-called Ras superfamily of small GTP-AZ. Along with NRAS in this family includes the genes K-Ras, H-Ras (causing neoplastic transformation when infected with sarcoma virus Kristen and Harvey, respectively). To date, the function of NRAS is defined as the transmission of proliferative signals from growth factor receptors. NRAS, like all the superfamily involved in signaling pathways MARK.
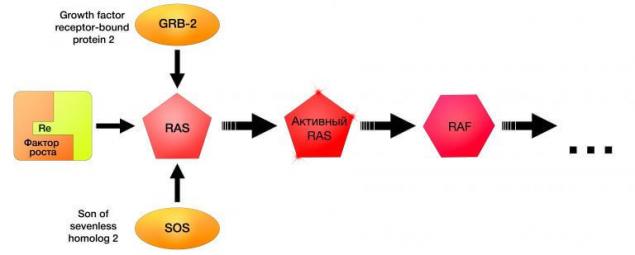
NRAS mutations were found in 10-26% of cases of melanoma of the skin, mainly of the irradiated UV. Inhibition of NRAS has opened new horizons in the treatment of melanoma, showing the practical importance of the close relationship of all parts of the signal path. The first drug targeted therapy of melanoma with NRAS mutation is an inhibitor MEK162, with which almost 70% of patients this category fails to treatment response and stabilization of disease.
c-KIT
The last considered in the context of this article link MARK-cascade will be the gene c-KIT. Last but not least: this gene is a proto-oncogene, a protein which is a receptor for growth factors of stem cells, is detected in one third of cases of melanoma of different locations: as the skin and mucous membranes.
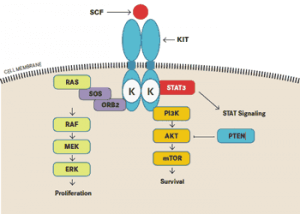
Scheme of signaling pathway Kit
Like many other mutations, there are drugs aimed to inhibit Kit mutations. Given the uninterrupted complementary connection parts of the signal path MARK, it is not surprising the fact that the Kit mutation is successfully inhibited, known for the targeted therapy of BRAF-positive melanomas "-nabami": Imatinib, Nilotinib and other drugs.
PI3K – phosphoinositol-3-kinany way
The following component of a proliferative signaling pathways that are pathologically activated in melanoma cells is PI3K – phosphoinositol-3-kinany way, often denoted in the literature as the "signaling pathway of PI3K/AKT/mTOR". This cascade of reactions, the main events which unfold around the following enzymes: phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K), a family of protein kinases, components of which are the serine-threonine kinase AKT 1, 2, 3, and another serine-tranisitional kinase, called "target rapamycin" and denoted by mTOR.
This signaling pathway is universal for most human cells and delivers cell proliferation, metabolism and differentiation.
In the context of carcinogenesis in cells of melanoma, the greatest interest represent the components of AKT and PTEN.
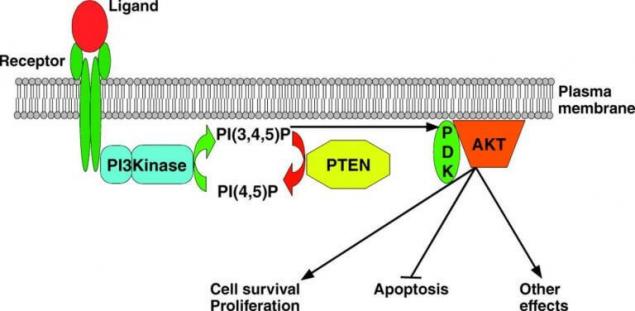
Classical pathway PTEN
PTEN
PTEN is a phosphatase enzyme, which is a negative regulator РІ3К-paths and encoded by the eponymous gene oncosuppressor. By cleavage of a phosphate group from phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate inhibits the enzyme (up to the complete blockade) conduction signal phosphoinositol-3-kinasemb way. Inactivation of PTEN is detected in many tumors leading to uncontrolled division with the loss of differentiation, failures in the cell metabolism and perverted synthesis. Inactivating PTEN mutations are found in 10-30% of melanomas.
ACT
Another component of the PI3K-signaling pathway considered in the development of melanoma, will be the family ACT.
The family ACT is a group of kinases, which by attaching residues of phosphoric acid to different proteins zitozolya control their activity. The family performs the classic functions such as the regulation of proliferation, differentiation and changes of the cytoskeleton and sensitive in the context of carcinogenesis function angioneogenesis, evade apoptosis and acquire resistance to cytostatic drugs .
The family ACT includes 3 subspecies of protein kinases: AKT-1, AKT-2 and AKT-3, which are products of the corresponding genes.
Akt1 — α-serine/treoninove protein kinase – a inhibition of apoptosis, protein biosynthesis (in the direction of "plus-tissue", hypertrophy of myocytes, etc.).
Akt2 — ß -serine/treoninove protein kinase is involved in the metabolism of insulin and induces glucose transport carried out GLUTE-4.
Akt3 — γ - serine/treoninove-kinase function is not known.
Different types ACT hyperexpression in 45-70% of melanomas. The experiments carried out with the PHLPP phosphatase, catalyzing the dephosphorylation of the molecule in the AKT-1 and subsequent inactivation of AKT-1 led to apoptosis and decrease proliferation in neoplasticeskih modified cells.
mTOR
This also shows protein kinase threonine-serine specificity, existing in the form of two intracellular complexes: TORC1 and TORC2. Target rapamycin is the first complex, which is the therapeutic target of immunosuppressant of the same name.
But Тarget mammalian Of Rapamycin interested in us now not as a target rapamycin, and as a component of the PI3K-signaling pathway that plays a key role in the process of cell growth. Despite the fact that the molecule is indivisible TOR derived its two subunits, the latter have completely different powers.
Damage the first set will not have any catastrophic consequences for the cell, and a violation of TOR2 lead to the so-called "arrest" (termination) of the cell cycle in phase G2/M phase in a few generations. If you suffer both subunits, the cell will "stand" in the G0 phase in the next generation. Thus, it becomes clear: whether alone, jointly with ТОR1, but somehow ТОR2 has the strongest influence on the cell cycle.
The following is discussed in this article component of the system of control of the cell cycle is the system tsiklinsky kinases CDKN2A, CDK4 and CDK6. Mutations, deletions, promoter hypermethioninemia are violations detected in 50% (CDKN2A) and 10-12% (CDK4) in melanoma, heritable germinal mutations in predisposition genes can determine the occurrence of familial melanoma in 15% of cases.
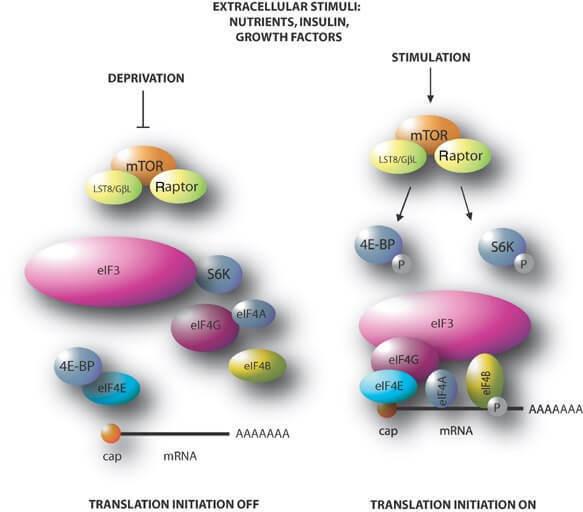
Figure 1 Mechanism of action target rapamycin
CDKN2A (cyclin-dependent kinase Inhibitor 2A) gene localized in the short arm of chromosome 9 and encodes two proteins that are oncosuppressor: P14 and P16. Using these proteins regulate the activity, perhaps the most famous of the p53 tumor suppressor and retinoblastoma protein.
In the case of CDKN2A mutations (duplication of codon R112) both products of this gene are exposed to damage. Interestingly, this mutation is dominant in cases of hereditary melanoma in families of Scandinavian nationalities. Mutations of this gene are detected in 30-40% of cases of melanoma, especially often they occur in the context of familial melanoma. Genetic polymorphism has value in determining the speed of tumor development and resistance to chemotherapy.
However, a mistake to assume that CDKN2A is responsible solely for family cases. Sporadic somatic mutations of CDKN2A are found in 50% of cases of cutaneous melanoma, implemented either by deactivating P16, or by promoter methylation (10%).
Protein complex of cyclin-D and CDK4 regulates retinoblastoma protein expression, affecting the activity of the cell cycle and cell proliferation. The following cascade of reactions schematically shows the sequence of events in the genetic system and the cell itself by the breakdown of more high mechanisms of regulation, in this case, the protein P16:
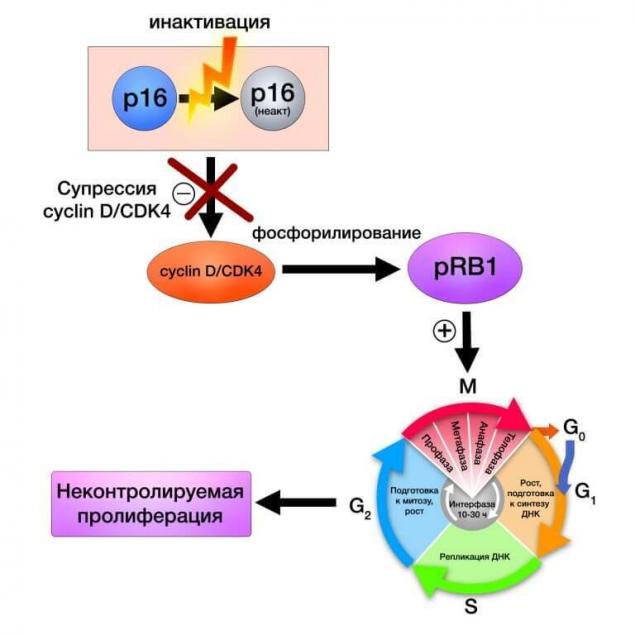
CDK4 (сyclin-dependent kinase 4) is an enzyme encoded by the homonymous gene and is part of the family of cyclin-dependent kinases. Being a link in the common system of control of the cell cycle, CDK4, and CDK6, associated with the appropriate proteins and the retinoblastoma protein.
In the context of carcinogenesis, these elements act as levers of the cell cycle, uncontrolled activity which may be the result of certain violations of the governing enzymes. Cdks as molecular target of interest not only to dermatooncology as CDK inhibitors as a drug class of anticancer drugs widely used for treating a variety of cancers such as estrogen-positive and HER-negative breast cancer, leukemia, thyroid cancer (pubiicly, letrozole, abamectin).
Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibit the activity of the corresponding enzyme alone complex "enzyme+cyclin"; these drugs are usually in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. The decrease in the activity of CDK can be achieved, for example, a reduction in the level of gene expression of cyclins or by increase of the degree of disintegration of cyclins.
The CDK inhibitor not only provide adequate cell growth, but also have the ability of stopping the cycle of G1 phase in response to DNA damage, adverse environmental conditions, etc.
WNT
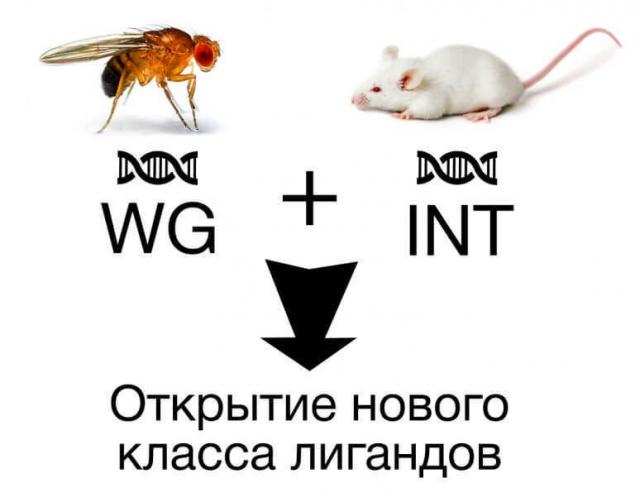
The WNT cascade is the example of classic signaling pathway regulating the proliferative activity and differentiation of cells. The name of this path received in the course of merge of the names of two genes: WG fruit flies, which inhibited the growth of the wings, and INT, which initially considered in the research of breast cancer in mice. In a single structure protein were pooled based on the number of features, which allowed to identify a new class of ligands.
According to the structure of the WNT is a complex, in the graphic image where you can see the similarity with an open palm. It should be noted that the level of glycosylation does not affect the secretory activity of this complex, however, N-glycosylation promotes the secretion of WNT.
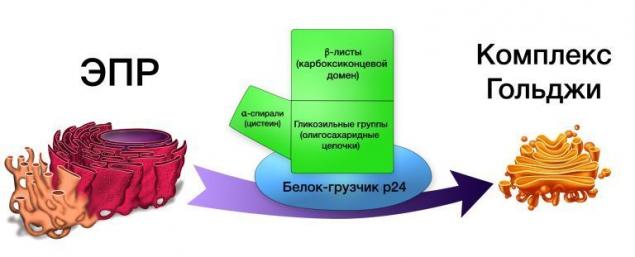
Protein WNT excreted proteins of the Golgi complex, such as, for example, GPR177, and transferred to the surface of cells using "protein-movers" p24.
To act on the cell can according to the canonical WNT or non-canonical ways, they — β-catenin dependent and β-catenin independent pathway, respectively. In the first case the concentration of the cellular β-catenin, the final link which makes the control of genetic expression affecting the morphogenesis of the cell, and in the second case is governed by the polarity of the cells by stimulating the reorganization of the cytoskeleton and changes in the intensity of calcium metabolism.
Canonical path is a sequence of reactions aimed at the accumulation of ß-catenin in the cell and direct its delivery to the nucleus, where he will act as a transcription factor.
The WNT path starts with compounds of WNT to the receptor for low density lipoprotein (Low-density lipoprotein Relater Protein-5, LRP-5), followed by activation of AXIN1 protein influence of APC (a negative regulator of the concentration of ß-catenin, mutations of which lead to the emergence and development of colorectal cancer), kinases GSK3, CK1 (kinase glycogen
Source: medach.pro/surgery/onkologiya-hirurgicheskie-distsiplinyi/melanoma/
Melanoma is the result of neoplastic transformation of melanocytes – cells that produce different variations of the pigment melanin. Melanocytes come from the neural crest, a group of marginal cells of the nerve of the gutter.

Cells of the neural crest are of high level of migration, and most of them are sent down from the neural tube, forming a variety of neural and endocrine structures. However, the melanoblast show your uniqueness even before the potential acquisition of the tumor phenotype and migrate down and to the sides of the neural tube.
The molecular mechanisms of this process remain unknown. The fate of melanoblast hard to call predefined: this element may subsequently develop into a neuron, leiomyza, and in the case of high level of melanocyte-glial potential in the glial component.
After differentiation in the melanocyte isolated body (soma) and processes, which are located in the basal and spinous layers of the epidermis, respectively. Under the action of melanocytestimulating and adrenocorticotropic hormone and sunlight in melanosomes synthesized (EU)melanin (and pheomelanin), whose function is to protect the nuclear apparatus of cells from damage by UV radiation.
The synthesized melanin is transported in the spiny layer of the epidermis on the tentacles of the melanocyte, later in the keratinocytes of the epidermis, giving the skin a tan. Some time later, this polymer gidrolizuyutza in the lysosomes, and the skin returns to its usual color.
This scenario can be called perfect. But what happens to those less fortunate? The key point of initiation of neoplastic transformation of the melanocyte is a non-lethal mutation in his genetic apparatus. The reason for this damage may have different effects: physical and chemical.
Like most tumors, the causes of the start of oncogenesis in melanoma, you can combine several ways:
1) Suppression of the activity of genes oncosuppressor;
2) Activation of proto-oncogenes;
3) Exogenous mutations, obtained a variety of ways.
What makes melanoma so dangerous? It would seem that outdoor localization, all known algorithms at the stage of self-examination, the high immunogenicity of the tumor should make the therapy as efficient as possible.
However, the unpredictability of the metastatic cascade coupled with the lack of specially designed therapy for metastatic melanoma, the unpredictability of the clinical and morphological – both micro-and macroscopic forms and higher frequency of recurrence lead to the fact that to date, the incidence of melanoma is increasing worldwide; the median survival with melanoma is not more than 8 months, and the effectiveness of radical surgical treatment do not exceed 65%. To answer the questions clinicians and patients can only scientists.
The possibility of sequencing the genome allowed us to deepen our understanding of carcinogenesis in cutaneous melanoma. The study of the processes originating in the transformation of melanocytes in the most aggressive of the existing tumor is the most important stage in the study of not only melanoma, but also all other tumors.
Only by identifying new targets possible purpose of targeted therapy, the expansion of diagnostic horizons as well as the possible revision of the classification, clinical-morphological forms with a preference for associations of subtypes of melanoma based on the nature of mutations. With this in mind, the review of mechanisms of carcinogenesis in melanoma need to pay special attention.
One of the most important achievements in the study of carcinogenesis in melanoma is considered the analysis of the mechanisms of signal transduction that are activated in the process of its development. Based on the etiological factors, the detection of certain mutations in melanoma of the skin may answer the question of the relationship of etiology and pathogenesis, clinical forms and therapeutic solutions.
What signaling pathway? This kind of "relay race" where in a strictly defined order enables a sequence of certain molecules involved in transmitting any kind of signal from the cell receptor into the cell. Signaling pathway can be activated by exogenous growth factors, neurotransmitters, hormones or endogenous by means of a signal-starters-activated for various reasons, inside the cage.
Epidemiology
The average age of patients with melanoma of the skin is about 45 years, but in recent years, melanoma has become increasingly occur in very young people (15-25 years). This tumor occurs in men and women, and in women 1.5-2 times more often. According to statistics, for every 100,000 healthy people accounts for 14 patients with melanoma.
In 2006 in Russia was 7.364 new patients with melanoma and 3.033 deaths. The annual number of cases of melanoma in Russia is 5,700 people, of which 2.200 are likely to die from this disease.
In different regions of the world the incidence of melanoma is significantly different. According to who, over the period 1988-2012. the highest standardized incidence rates for melanoma of the skin 25-29,8 o /oooo was characteristic of the white population of Australia and New Zealand. A fairly high incidence of 15-18,6 o /oooo observed among Europeans living in Zimbabwe, white men of the United States (Los Angeles, San Francisco), women, Austria, Norway.
High, by the standards of Europe, the level of 8.8–14,1 o /oooo was among the residents of Denmark, Italy, Switzerland, Sweden, men of Austria and Norway. The lowest standardized incidence rates for melanoma of the skin 0,1–1,5 o /oooo identified in Algeria, the Indians and black people in the US, Uganda, Zimbabwe, China, Korea, Japan.
On the occurrence of melanoma is affected by the race of man. According to who statistics, blacks are 4 times less likely to suffer from melanoma than Caucasians. There is an assumption that darker skin contains more melanin in the epidermis, which contributes to a stronger delay of UV radiation, and thus are better protected from its damaging effect on the melanocytes that developed evolutionary in accordance with the climatic conditions of those living in these areas of the globe people.
Accordingly, people with a weak natural hedge (less the amount of melanin in the skin) are more likely to suffer melanoma. For example, among residents of Kazakhstan noted an eightfold increase in the incidence of melanoma among visitors with white skin compared with the indigenous population.
Thus, the statistics of the who allow make sure natural the higher the number of melanocytes in the skin, the lower the risk of melanoma, hence the low level of pigmentation is a risk factor.
Evaluation of this factor is possible when ordinary clinical examination. People who belong to the “bright” phenotype, usually poorly susceptible to sun tan and is very prone to developing sunburn because of the high sensitivity to UV radiation, so the risk of developing melanoma increases them twice.
Another sign of abnormal level of pigmentation is the presence of a large number of freckles on the skin due to accumulation of proliferating melanocytes in the basal layer of the epidermis and the epithelium of the outer divisions of hair follicles.
Extremely heavy the degree of pigmentation disorders, characterized by complete lack of melanin in the body, is observed in albinos. Carcinogenic effects of UV radiation from them is so great that most 20 years, there are precancerous lesions or tumors of the skin, and is so detrimental that less than 10% of these people live up to 30 years.
Signaling pathways
To date, the most studied are the following signal paths:
- MARK
- PI3K
- CDK
- Wnt
The trouble starts when scientists try to track the strict specificity of signaling pathways and regulated process. It is a mistake to assume that the activation of these signaling pathways is a sign of neoplastic transformation in melanoma.
Firstly, these signaling pathways also exist in normal, regulating differentiation of cells in the antenatal and postnatal periods, ensure the reproduction of the effects of certain hormones and other typical processes aimed at maintaining normal functioning of the cell.
Second, the data paths involved not only in melanocytes: they are universal signaling systems involved in most cells in the human body. What's the matter? In any of the signaling pathways may occur one or another genetic or epigenetic damage, which will result in the negative regulation of signaling pathways with outcome in carcinogenesis.
MAPK
The cluster MARK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) are the intracellular signaling pathways of a variety of functions [8]. The criterion for inclusion in the MARC group is the presence of mitogen-activated protein kinases in the module, in which, in addition to kinases, contains proteinopathy and proteins-collectors auxiliary protein complexes [9].

By themselves or MARK a cluster or its effects are not of particular interest in the context of carcinogenesis, however, those mutations that occur in genes of proteins involved in signaling pathways in cells of melanoma, require more detailed consideration. Among the many kinases involved in signal transmission in the cluster MARK there are so-called Raf kinase.
Raf is a family of serine-threonine dependent protein kinases, whose name is an acronym for Rapidly Accelerated Fibrosarcoma. But where fast-growing fibrosarcoma, and where the melanoma?
The fact that the underlying mechanisms of carcinogenesis often found Perekrest ways, such as in our case, including. In the context of this article makes no sense to focus on a detailed representation of the steps of carcinogenesis of fibrosarcoma we will be discussing features of the Raf in cutaneous melanoma.
BRAF
Notable in the family of Raf - we can be B-raf protein, which plays a role in MARK-cascade, whose effects are differentiation and cell division. The protein B-raf is encoded by the homonymous gene, which would be completely unremarkable if not for one "but": arising under the action of excessive UV radiation in this gene V600[x] mutation (under the [x] in this case, means the designation of nonsynonymous substitutions, leading to mutations), which consists in the substitution of valine for leucine (V600L), lysine (V600K) or glutamic acid (v600e was) 600-th position, is the starter neoplastic transformation in melanoma of the skin, and is also a target for the action of drugs, within the group of inhibitors of BRAF V600L. This so-called "nibi": imatinib, sorafenib, vemurafenib, etc.
In randomized clinical studies revealed an interesting feature: if the verified mutated BRAF status of the patient low molecular weight inhibitors of BRAF has led to the inhibition of melanoma, the consumption "-of nibav" patients, mutations of BRAF, which have raised doubts or were absent, led to the mutation of another of the cascade RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK, pathologically activating it and initiating the neoplastic transformation.
Thus, it can be concluded that low molecular BRAF inhibitors though are effective therapeutic tool still show a dangerous ambivalence in the case of lack of diagnosis or erroneous interpretation of the BRAF status of the patient.
C 2011 alternative to chemotherapy for patients with metastatic melanoma with the BRAF mutation v600e was is the drug vemurafenib (selrap). At the heart of its action is the inhibition of BRAF dimerization, while mutation v600e was the gain of the ERK signaling as a result of dimerization of the mutant kinase.
In phase I trials, the response to vemurafenib was obtained in 81 % of melanoma patients with the mutation v600e was (decrease in diameter of all tumor sites by 30 %). In phase III trials, overall survival at 6 months was observed in 84% of patients with metastatic melanoma, progression-free survival was 5-7 months.

However, 20-30% of patients receiving vemurafenib, side effects: malignant transformation of benign lesions and the appearance of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, which is associated with the activation of the MAPK route via RAS mutations in the suppression of RAF. Some patients in the treatment there are new foci of melanoma with wild type BRAF. Recent studies show that the MARK lends itself to a more effective inhibition when using not only BRAF (as monotherapy), and MEK-inhibitors.
This combination is not only more efficient, it prevents the development of resistance to therapy and the occurrence of the most serious adverse effect of BRAF-inhibitors – squamous cell carcinoma of the skin.
Suggest that the effect may be a combination of the drugs sorafenib and lonafarnib – inhibitor ferreiromania (reactions leading to the initiation of the carcinogenic activity of protein RAS) and "zakalivanie" RAS on the cell membrane.
In January 2014 registered a new targeted therapy dabravine for the treatment of melanoma with a mutation in 600-m BRAF codon. Unlike vemurafenib, gabroveni acts not only when replacing v600e was, but with the V600K mutation. Both BRAF inhibitors were the first drugs which had the effect in patients with brain metastases. Unfortunately, almost all patients responding to vemurafenib, over time there is resistance to therapy.

"In the clinical research study coBRIM, it was confirmed that combination therapy using the drugs vemurafenib and kabinetinin in 90% of cases allows to achieve response to therapy in patients with BRAF - positive metastatic melanoma. Every second patient over a year no evidence of disease progression, and overall survival approaching two years."

MEK
MEK is a serine-kinase treoninove MARK cluster, activated in response to changes in the upstream levels of the signal circuit.
The role of the MEK is to integrate signals from various growth factors with subsequent activation of proliferation. As part of the MARK-cascade, MEK is involved in the regulation of activity of transcription factors such as C-myc.

The Myc protein encoded by the homonymous gene, and is a proto-oncogene is not only a "canonical" example of transcripting factor, but also controls the chromatin structure by regulating acetylation of histones, which in turn affects the activity of gene expression. The mutant gene of the ICC, located in 8-th chromosome, is detected in many tumor types; a classic example of assetsfinancial t (8;14), leading to the emergence and development of Burkitt's lymphoma.
Experiments aimed at its inhibition, leading to lysis of tumor cells of the lung in mice. Therefore, the ICC is a therapeutic target, in particular, the development of selective allosteric inhibitors of the ICC is a relevant topic for clinical research.
NRAS
N-RAS (Neuroblastoma-Ras) is a gene that encodes the eponymous protein that is part of the so-called Ras superfamily of small GTP-AZ. Along with NRAS in this family includes the genes K-Ras, H-Ras (causing neoplastic transformation when infected with sarcoma virus Kristen and Harvey, respectively). To date, the function of NRAS is defined as the transmission of proliferative signals from growth factor receptors. NRAS, like all the superfamily involved in signaling pathways MARK.

NRAS mutations were found in 10-26% of cases of melanoma of the skin, mainly of the irradiated UV. Inhibition of NRAS has opened new horizons in the treatment of melanoma, showing the practical importance of the close relationship of all parts of the signal path. The first drug targeted therapy of melanoma with NRAS mutation is an inhibitor MEK162, with which almost 70% of patients this category fails to treatment response and stabilization of disease.
c-KIT
The last considered in the context of this article link MARK-cascade will be the gene c-KIT. Last but not least: this gene is a proto-oncogene, a protein which is a receptor for growth factors of stem cells, is detected in one third of cases of melanoma of different locations: as the skin and mucous membranes.

Scheme of signaling pathway Kit
Like many other mutations, there are drugs aimed to inhibit Kit mutations. Given the uninterrupted complementary connection parts of the signal path MARK, it is not surprising the fact that the Kit mutation is successfully inhibited, known for the targeted therapy of BRAF-positive melanomas "-nabami": Imatinib, Nilotinib and other drugs.
PI3K – phosphoinositol-3-kinany way
The following component of a proliferative signaling pathways that are pathologically activated in melanoma cells is PI3K – phosphoinositol-3-kinany way, often denoted in the literature as the "signaling pathway of PI3K/AKT/mTOR". This cascade of reactions, the main events which unfold around the following enzymes: phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K), a family of protein kinases, components of which are the serine-threonine kinase AKT 1, 2, 3, and another serine-tranisitional kinase, called "target rapamycin" and denoted by mTOR.
This signaling pathway is universal for most human cells and delivers cell proliferation, metabolism and differentiation.
In the context of carcinogenesis in cells of melanoma, the greatest interest represent the components of AKT and PTEN.

Classical pathway PTEN
PTEN
PTEN is a phosphatase enzyme, which is a negative regulator РІ3К-paths and encoded by the eponymous gene oncosuppressor. By cleavage of a phosphate group from phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate inhibits the enzyme (up to the complete blockade) conduction signal phosphoinositol-3-kinasemb way. Inactivation of PTEN is detected in many tumors leading to uncontrolled division with the loss of differentiation, failures in the cell metabolism and perverted synthesis. Inactivating PTEN mutations are found in 10-30% of melanomas.
ACT
Another component of the PI3K-signaling pathway considered in the development of melanoma, will be the family ACT.
The family ACT is a group of kinases, which by attaching residues of phosphoric acid to different proteins zitozolya control their activity. The family performs the classic functions such as the regulation of proliferation, differentiation and changes of the cytoskeleton and sensitive in the context of carcinogenesis function angioneogenesis, evade apoptosis and acquire resistance to cytostatic drugs .
The family ACT includes 3 subspecies of protein kinases: AKT-1, AKT-2 and AKT-3, which are products of the corresponding genes.
Akt1 — α-serine/treoninove protein kinase – a inhibition of apoptosis, protein biosynthesis (in the direction of "plus-tissue", hypertrophy of myocytes, etc.).
Akt2 — ß -serine/treoninove protein kinase is involved in the metabolism of insulin and induces glucose transport carried out GLUTE-4.
Akt3 — γ - serine/treoninove-kinase function is not known.
Different types ACT hyperexpression in 45-70% of melanomas. The experiments carried out with the PHLPP phosphatase, catalyzing the dephosphorylation of the molecule in the AKT-1 and subsequent inactivation of AKT-1 led to apoptosis and decrease proliferation in neoplasticeskih modified cells.
mTOR
This also shows protein kinase threonine-serine specificity, existing in the form of two intracellular complexes: TORC1 and TORC2. Target rapamycin is the first complex, which is the therapeutic target of immunosuppressant of the same name.
But Тarget mammalian Of Rapamycin interested in us now not as a target rapamycin, and as a component of the PI3K-signaling pathway that plays a key role in the process of cell growth. Despite the fact that the molecule is indivisible TOR derived its two subunits, the latter have completely different powers.
Damage the first set will not have any catastrophic consequences for the cell, and a violation of TOR2 lead to the so-called "arrest" (termination) of the cell cycle in phase G2/M phase in a few generations. If you suffer both subunits, the cell will "stand" in the G0 phase in the next generation. Thus, it becomes clear: whether alone, jointly with ТОR1, but somehow ТОR2 has the strongest influence on the cell cycle.
The following is discussed in this article component of the system of control of the cell cycle is the system tsiklinsky kinases CDKN2A, CDK4 and CDK6. Mutations, deletions, promoter hypermethioninemia are violations detected in 50% (CDKN2A) and 10-12% (CDK4) in melanoma, heritable germinal mutations in predisposition genes can determine the occurrence of familial melanoma in 15% of cases.

Figure 1 Mechanism of action target rapamycin
CDKN2A (cyclin-dependent kinase Inhibitor 2A) gene localized in the short arm of chromosome 9 and encodes two proteins that are oncosuppressor: P14 and P16. Using these proteins regulate the activity, perhaps the most famous of the p53 tumor suppressor and retinoblastoma protein.
In the case of CDKN2A mutations (duplication of codon R112) both products of this gene are exposed to damage. Interestingly, this mutation is dominant in cases of hereditary melanoma in families of Scandinavian nationalities. Mutations of this gene are detected in 30-40% of cases of melanoma, especially often they occur in the context of familial melanoma. Genetic polymorphism has value in determining the speed of tumor development and resistance to chemotherapy.
However, a mistake to assume that CDKN2A is responsible solely for family cases. Sporadic somatic mutations of CDKN2A are found in 50% of cases of cutaneous melanoma, implemented either by deactivating P16, or by promoter methylation (10%).
Protein complex of cyclin-D and CDK4 regulates retinoblastoma protein expression, affecting the activity of the cell cycle and cell proliferation. The following cascade of reactions schematically shows the sequence of events in the genetic system and the cell itself by the breakdown of more high mechanisms of regulation, in this case, the protein P16:

CDK4 (сyclin-dependent kinase 4) is an enzyme encoded by the homonymous gene and is part of the family of cyclin-dependent kinases. Being a link in the common system of control of the cell cycle, CDK4, and CDK6, associated with the appropriate proteins and the retinoblastoma protein.
In the context of carcinogenesis, these elements act as levers of the cell cycle, uncontrolled activity which may be the result of certain violations of the governing enzymes. Cdks as molecular target of interest not only to dermatooncology as CDK inhibitors as a drug class of anticancer drugs widely used for treating a variety of cancers such as estrogen-positive and HER-negative breast cancer, leukemia, thyroid cancer (pubiicly, letrozole, abamectin).
Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibit the activity of the corresponding enzyme alone complex "enzyme+cyclin"; these drugs are usually in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. The decrease in the activity of CDK can be achieved, for example, a reduction in the level of gene expression of cyclins or by increase of the degree of disintegration of cyclins.
The CDK inhibitor not only provide adequate cell growth, but also have the ability of stopping the cycle of G1 phase in response to DNA damage, adverse environmental conditions, etc.
WNT
The WNT cascade is the example of classic signaling pathway regulating the proliferative activity and differentiation of cells. The name of this path received in the course of merge of the names of two genes: WG fruit flies, which inhibited the growth of the wings, and INT, which initially considered in the research of breast cancer in mice. In a single structure protein were pooled based on the number of features, which allowed to identify a new class of ligands.

According to the structure of the WNT is a complex, in the graphic image where you can see the similarity with an open palm. It should be noted that the level of glycosylation does not affect the secretory activity of this complex, however, N-glycosylation promotes the secretion of WNT.

Protein WNT excreted proteins of the Golgi complex, such as, for example, GPR177, and transferred to the surface of cells using "protein-movers" p24.
To act on the cell can according to the canonical WNT or non-canonical ways, they — β-catenin dependent and β-catenin independent pathway, respectively. In the first case the concentration of the cellular β-catenin, the final link which makes the control of genetic expression affecting the morphogenesis of the cell, and in the second case is governed by the polarity of the cells by stimulating the reorganization of the cytoskeleton and changes in the intensity of calcium metabolism.
Canonical path is a sequence of reactions aimed at the accumulation of ß-catenin in the cell and direct its delivery to the nucleus, where he will act as a transcription factor.
The WNT path starts with compounds of WNT to the receptor for low density lipoprotein (Low-density lipoprotein Relater Protein-5, LRP-5), followed by activation of AXIN1 protein influence of APC (a negative regulator of the concentration of ß-catenin, mutations of which lead to the emergence and development of colorectal cancer), kinases GSK3, CK1 (kinase glycogen
Source: medach.pro/surgery/onkologiya-hirurgicheskie-distsiplinyi/melanoma/
Today I called the wrong number and accidentally sent my dad the message
Bitter bread my mother's son