414
In Africa, opened the settlement age of about 70 thousand years
The remains of the long-term dwellings from Africa to refute the idea that the first such structures people began to build just after resettlement in the more harsh conditions of Europe and Asia.
During excavations in Northern Sudan, Polish archaeologists from the Institute of archaeology and Ethnology in poznań, have discovered the remains of settlements, whose age is estimated at 70 thousand years. According to the researchers, this finding contradicts the theory about the construction of permanent homes has been associated with the so-called Great Exodus from Africa and settling in the colder regions of Europe and Asia.

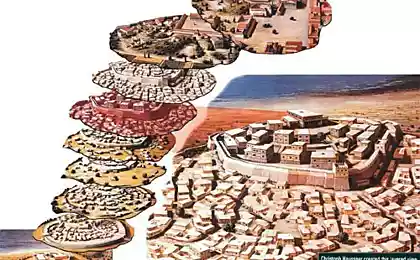
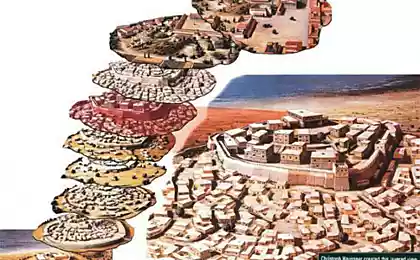
The monument, known as Affad 23 (Affad 23) is currently only known in the Nile valley, which preserved the long-term, larger dwellings of early Homo Sapiens that are well adapted to swampy terrain.
New evidence a much higher level of development and adaptation in Africa during the middle Paleolithic.
"The opening of Upfade unique for the middle Palaeolithic. Last season we found the remains of several wooden structures of the lungs. At the same time, in the course of research we were able to precisely locate the village and to establish new economic zones: the great flint "workshop" and a Playground for the butchering of carcasses of animals killed on the hunt," says the head of the excavation, Dr. Mar Supinska (Marta Osypińska).
The researchers found the types of animals that people hunted in that time. Despite the relatively simple flint tools, made in the technique Levallois, residents Affare could hunt large, dangerous mammals such as the hippopotamus, elephant and Buffalo, and small, nimble monkeys and cane hamsters.
This year the researchers also intend to determine exactly the time when Palaeolithic hunters lived here, using the method of optically stimulated luminescence Dating.
According to archaeologist Peter Osipovskogo, it is now known that the settlement dates from the end of a wet period. This, in particular, specifies the list of species hunted by people. But similar natural conditions were in the region at least as twice – about 75 thousand years ago and about 25 thousand years ago. Precise Dating of the settlement is now the most important task of the expedition, said the archaeologist.
The source: Past Horizons
Source: nkj.ru
During excavations in Northern Sudan, Polish archaeologists from the Institute of archaeology and Ethnology in poznań, have discovered the remains of settlements, whose age is estimated at 70 thousand years. According to the researchers, this finding contradicts the theory about the construction of permanent homes has been associated with the so-called Great Exodus from Africa and settling in the colder regions of Europe and Asia.

The monument, known as Affad 23 (Affad 23) is currently only known in the Nile valley, which preserved the long-term, larger dwellings of early Homo Sapiens that are well adapted to swampy terrain.
New evidence a much higher level of development and adaptation in Africa during the middle Paleolithic.
"The opening of Upfade unique for the middle Palaeolithic. Last season we found the remains of several wooden structures of the lungs. At the same time, in the course of research we were able to precisely locate the village and to establish new economic zones: the great flint "workshop" and a Playground for the butchering of carcasses of animals killed on the hunt," says the head of the excavation, Dr. Mar Supinska (Marta Osypińska).
The researchers found the types of animals that people hunted in that time. Despite the relatively simple flint tools, made in the technique Levallois, residents Affare could hunt large, dangerous mammals such as the hippopotamus, elephant and Buffalo, and small, nimble monkeys and cane hamsters.
This year the researchers also intend to determine exactly the time when Palaeolithic hunters lived here, using the method of optically stimulated luminescence Dating.
According to archaeologist Peter Osipovskogo, it is now known that the settlement dates from the end of a wet period. This, in particular, specifies the list of species hunted by people. But similar natural conditions were in the region at least as twice – about 75 thousand years ago and about 25 thousand years ago. Precise Dating of the settlement is now the most important task of the expedition, said the archaeologist.
The source: Past Horizons
Source: nkj.ru
Social status in baboons is dependent on the correct relatives
Largest solar power plant under construction in Pakistan