1465
Megafauna. The world we have lost forever (30 photos + text)
The word "megafauna" means the totality of all animals with an average body weight exceeding 44 kg. However, in reality the boundaries of the concept rather conditional: for example, some researchers take the lower limit for the mass of 100 kg, some - 250, but few people doubt that a giant eagle from New Zealand or the world famous dodo - also part of the megafauna.
For us, the greatest interest is the Pleistocene megafauna. Pleistocene (1, 8 million - 11 thousand. Years ago - in fact, to this day) - the era in Earth's history has been marked by several major events: the emergence of Homo sapiens, several periods of severe cold spells and ... the extinction of most of the large animals around the world. Giants, who disappeared at the end of the Pleistocene epoch, and which we now hardly ever see with their own eyes, and is dedicated to this post. Before you - 30 amazing animals have disappeared over the last few thousand years, someone before, and someone - almost yesterday ... Almost all of them have seen with my own eyes the ancient people, they are the same in most cases, they had a hand in their rapid extinction.
1. mammoths, elephants, mastodons

Khobotnev, the largest land animals of the Quaternary period, animals and landscape-are the clearest indicator of the health of ecological communities, were distributed on four continents and a variety of offshore islands and the variety of species was not an example of the current . In our native Eurasian woolly mammoth met (genus Mammuthus), pryamobivnevy elephant (Palaeoloxodon), Stegodon (Stegodon) still alive and Asian elephant. America was inhabited by two species of mammoth - woolly and Columbia, as well as the mastodon (Mammut americanum) and gompotery (Cuvieronius). In Africa, the current living African elephant, and even earlier, in the early Pleistocene - a few species, including Asian. Elephants who had moved to isolated islands, eventually becoming ... dwarf; so it happened to Stegodon Islands Flores and Sulawesi (Indonesia), mammoths of Wrangel Island (Russia) and the Channel Islands National Park (USA), elephants on the islands of the Mediterranean (Corsica, Sardinia, Sicily, Cyprus, Malta, Crete and several Greek islands). The growth of these elephants sometimes barely reached 1 m ...
The disappearance of the great diversity of Proboscidea there are still many uncertainties; so, there is still an ongoing debate about the causes of extinction of mammoths in Siberia and the Arctic. Unquestionable activities of the two factors - climate change and active hunting of ancient people. Different species of elephants in different continents have disappeared at different times, respectively: US - 8-10 thous. Years ago, the Eurasian - a little earlier. Dwarf elephants lived to see the beginning of the Holocene (the Greek island of Tilos about - about 2000 BC), just before the extinct mammoths of Wrangel Island; the last representative gompoteriev - kyuveronius disappeared in South America, supposedly to 400 AD
2. Rhinos

Woolly Rhinoceros (Coelodonta antiquitatis) - the second most famous after the Pleistocene mammoth beast. Its length reaches 3, 5 m, weight - up to 3 m. On the face he had two horns, the longest of which, front, sometimes reaching more than 1 m in length. An important feature of this type - a long thick coat of brown, like the mammoth, which allowed a rhino to survive in inhospitable for heat-loving animals of northern and central Eurasia. Inhabited woolly rhinoceros on the cold plains, known as "mammoth steppe" - in their place is now a multitude of coniferous and deciduous forests. Extinct view about 10 thousand years ago, and possibly later. As in the case of the mammoth, there are two main hypotheses disappearance northern rhinos: rapid climate change and excessive hunting of ancient man. Most likely, both factors affected ...
Where less known are two other possible contemporary of ancient people - elasmotery (Elasmotherium, 3-4 species) and rhino Merck (Dicerorhinus kirchbergensis). Elasmotery was truly a giant beast: its growth at the withers reaching 2 to 3 m, and weight - up to 6 tons! On his head was only one horn, but long suspected it could reach up to two meters. Rhino Merck was similar to woolly in size and also had two-horned. Both of these animals became extinct before the woolly rhinoceros - may not withstand competition with him also; but some researchers believe that the relict populations elasmoteriev Merck and rhinos survived until the end of the Pleistocene, and met with the ancient people.
3. Bulls
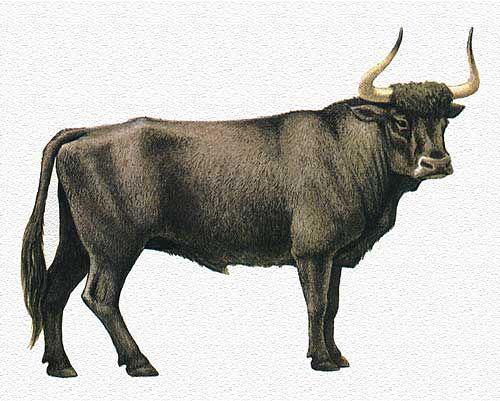
Subfamily oxen (Bovinae) in the last 10 thousand years, has lost some very interesting and often very colorful species. North America and Eurasia have lost several species of bison, the most famous of which - the steppe bison (Bison priscus), dwelt on both sides of the Atlantic and the extinct about 6000 years ago. Even in Africa, where the extinction of large animals was not of mass character, only 4 thousand years ago disappeared huge buffalo longhorned pelorovis (Pelorovis antiquus). Several species of oxen, in particular Baikal yak (Poephagus baicalensis) and the dwarf buffalo Philippines (Bubalus cebuensis), extinct in Asia. But the most famous view of the missing bulls, of course, is the tour (Bos primigenius) - wild ox from Europe and Asia, who became the ancestor of most breeds of cattle. This powerful animal black color with a light stripe on the back completely disappeared by 1627.
One of the main reasons for the sharp reduction in the number of wild bulls (and falling numbers of many surviving species) - the active pursuit of human beings; scenes of hunting bulls and bison often appear in cave paintings. In addition, the great influence of climatic factors on the reduction in the number of large hollow-horned ungulates, especially in northern latitudes.
4. Cave bear

Cave bear (Ursus spelaeus) - another extinct animal with the man, a well-known and widely far from paleontology and archeology circles. It is found in Europe - Western (larger species, to 3, 5 m in length) and East (no more brown). Cave bear gravitated mostly to the open spaces and not to forests, as well as caves. Another important difference: while the brown bear is a classic omnivore with superiority in the herbivorous, cave bear was almost complete vegetarian. Therefore ancient people could pose a risk only to the strength and size of this beast is hardly ever this type of bears hunted specifically on people.
Gone cave bear about 10 thousand. Years ago, and perhaps a little later. The most likely cause of its extinction is as follows: after the end of the last Ice Age steppe zone quickly covered with dense forests, depriving Bear usual habitat; individuals just choose a cave as a shelter, they were killed by people. In addition, in the past I hunted frightening, but not too dangerous giants meat and warm bear fur coat - good trophies.
5. Arktodus

Two types of long-legged, short-faced bear that lived in North America. In contrast to the relatively sluggish and omnivorous brown, black and cave bears, giant ploskomordy bear (Russian name of the larger species Arctodus simus) was a true predator and an active hunter, able to catch and kill very large prey, until the moose, camels, buffalo and young Mammoth - as do modern lions. Its dimensions were appropriate height at the withers - 1, 6 m height standing on its hind legs - more than 3 m, and weight - up to a ton.
Gone arktodusy about 10-12 thousand. Years ago, along with other members of the Pleistocene megafauna America. Possible reasons: competition with the brown bear (which is unlikely: arktodus was much stronger, and in the open spaces at the brown did not stand a chance - that the success of the hunt, in battle one on one) or a sharp reduction in food supply due to climatic or ( i) human factors (which is likely).
6. Lions

The present area of a lion (Panthera leo) is limited to sub-Saharan Africa and the tiny reserve in India. It is - only a small portion of the original habitat of a lion - or rather, some of its subspecies, and possibly species: cave lion (P. l. Spelaea) met in Eurasia - from England to Siberia and Turkmenistan, the lion Vereshchagin (P. l. Vereshchagini) - from Yakutia to Alaska, American Lion (P. l. atrox) inhabited the Americas - from Alaska in the north to the south of Peru. Two subspecies of lion (Barbary and Asian) lived in Europe and Central Asia.
The most well-known cave and American lions. How they look, we do not know; presumably their color was a pale, very likely - with spots or stripes. The presence of the male mane contested (my personal opinion - was a mane, it is warmer). Linear dimensions superior to African lions: American subspecies of the Siberian tiger was with even larger.
All Lions are active hunters and top predator of its biomes; Only American Lion inferior in size and strength ploskomordomu bear. They were prey to all sorts of hoofed animals, herds of millions roamed the steppes and woodlands Palearctic.
American and cave lions disappeared about 10 thousand. Years ago; some populations may live to ancient times. Probable cause of extinction - a famine due to a sharp reduction in the number of production; vigorous competition with the person; the combination of climatic and anthropogenic factors ... Barbary lion in the wild destroyed in 1922 .; Asiatic lion survived only in India (population size - about 300 individuals), and in several zoos around the world.
7. saber-toothed cats

These saber-toothed cats (Machairodontinae) - subfamily of large carnivores of the cat family, highly specialized in the production of herbivorous pachyderms such as bulls, giant sloths and elephants. In public, they are known as the saber-toothed tigers, but morphologically these animals are not relevant to the type of tiger (Panthera tigris), but directly related to cats. The main differences from the modern sabers big cats - a short tail and a unique jaw apparatus: upper canines were huge sizes (up to 17 cm), and the lower jaw relative to the top can be opened so wide that it was an angle of 120 °.
Until the late Pleistocene have lived at least two kinds of saber-toothed: Smilodon (Smilodon) and Homotherium (Homotherium). Smilodon, saber-toothed tiger classic, was the size of a large lion (height at the withers - up to 1, 2 m, weight - 300 kg) and lived in North and South America. Homotherium was a little less; Smilodon distinguished by its relatively short fangs and a lighter body structure. He lived in Africa, Eurasia and North America.
Recent saber-toothed cats have disappeared in North America 8-10 thousand years ago, and in Eurasia and Africa - even earlier. The reasons for the extinction of these powerful and dangerous predators not completely clear, but three versions are obvious: the fierce competition with these cats (lion, tiger, jaguar, etc.), Climate change and pressure from the man. Most likely, a combination of these three factors, and was fatal.
8. American cheetahs

At least two major North American cat species (genus Miracinonyx), morphologically very similar to the African cheetah, but are genetically closer to the cougar. Unlike the vast majority of other members of the megafauna, American cheetah is known only from fragments of skeletons, so much about its biology still remains unclear. But we know that it looks very interesting animal resembled the modern cheetah and hunting just catching prey in the sprint throw. As proof of this fact now living in the North American pronghorn antelope, can reach speeds of up to 100 km / h. None of the modern American predators can not run as fast, and that means only one thing - most recently existed-footed predator, for salvation from which it was necessary to develop a high-speed skills. This predator was an American cheetah - other contenders for this is not. And it died out relatively recently - 10-13 thousand. Years ago.
9. Deer

In today's time, there are many species of deer; However, much of the original diversity of these beautiful animals disappeared during the Pleistocene - early Holocene. Here are some of them: the largest and most famous - bolsherogy deer (Megaloceros giganteus) from Europe, North Africa and North-West Asia, majestic animal growth at the withers to 2, 1 m, 3 m, with huge beautiful horns scale to 3 6 m. Two kinds of his immediate family - Praemegaceros and Sinomegaceros - met at the end of the Pleistocene on the island of Sicily, and in East Asia, respectively. On both sides of the Atlantic lived Cervalces huge size of a large elk; North American deer were driven from the genera and Navahoceros Sangamona - average size, with a reindeer.
The disappearance of several genera of large and giant deer 9-12 happened thousands of years ago, some species have become extinct later. Probable cause - global climate change, pressure from the people and the competition with surviving species of deer and elk.
10. Horrible Wolf
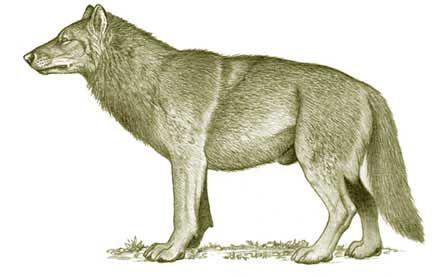
In North America, the time of its colonization by man lived not only well known to us the gray wolf. Hundreds of thousands of years ago, the continent appeared view, which was later people will call a terrible wolf (Canis dirus). It was larger and more massive than the gray wolf (1, 5 m in length, weighing up to 80 kg), has a more short legs and larger teeth. It was a gregarious predator, hunting for very large animals, such as horses and buffalo.
Dire wolf disappeared about 10,000 years ago - at a time when the mass extinction of large animals in North America, is the food great dogs. Last population of the species probably lived up to the 2nd millennium BC Ozark Mountain (Arkansas, USA).
The remains dire wolf are the most widespread findings in traps degtyanyh Ranch La Brea (California): there is found more than three thousand skeletons of this animal.
11. Giant beavers

Modern Beaver - one of the largest rodents of our time. If until now lived to its distant relative of the North American, he undoubtedly would have become an absolute champion: the length of the US giant beaver (Castoroides ohioensis) reached 2, 5 m, and weight - up to 220 kg! Besides the size, the giant beaver was different from the usual narrower tail, like the tail of a muskrat, and huge teeth protruding from the gums of almost 15 cm. The lifestyle of a giant beaver yet we can only guess. He could be a zealous builder (like its smaller cousin), and living in open countryside on the banks of major rivers and lakes, it is possible - in burrows near water.
Gone giant rodent about 9, 5 thousand years ago, presumably because of the reduction in his usual habitat and persecution by man.
The Pleistocene Europe lived another kind of giant beavers - trogontery (Trogontherium), but it became extinct much earlier and perhaps never crossed people.
12. Long-legged peccaries
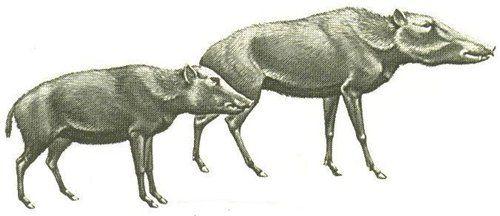
Two kinds of small pigs, close relatives of modern bakeries. In larger sizes (up to a meter or more), and long legs, thanks to which the animals were good runners. Rhode Platygonus differed shortened snout with large fangs and sharp, serve as a good means of defense from predators. Larger Mylohyus (up to 90 cm tall!), By contrast, had a long elongated front part of the head, resembling the extinct millions of years ago, giant carnivorous pigs entelodonov. We lived leggy bakers in North America, probably moving the prairies and woodlands in small groups, like antelopes.
Gone are the giant peccary, as well as many other members of the North American megafauna, about 9-12 thousand years ago.
13. marsupial lion
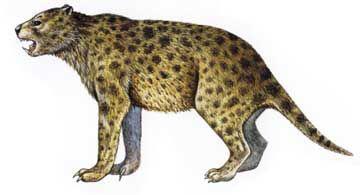
The largest marsupial predator of Australia, reaches the size of the modern jaguar length from the tip of the snout to the base of the tail - 110 cm, height at the withers - 70 cm, weight - 100 kg and more. The jaws of the marsupial lion (Thylacoleo carnifex) in bite force did not concede a lion, and a powerful musculature demonstrates the tremendous power of this beast, no doubt able to bring down the largest herbivores in the continent - such as DIPROTODON and giant kangaroos. Details marsupial lion skeleton give grounds to suppose that the animal could sit on his hind legs, relying on a strong tail, as do the kangaroo and climb trees in the manner of a leopard.
Gone marsupial lion 30-40 thousand. Years ago, at the same time with the rest of the Australian megafauna. Rumors that he could live up to historical times, still excite the minds cryptozoologists, nurturing the hope to find the mysterious "tiger cat Queensland." But the chances of enthusiasts luck now almost nil ...
14. DIPROTODON

DIPROTODON or "Tasmanian behemoth" (born Diprotodon) - a huge herbivore of Australia, the largest individuals that reach 3 meters in length and 1, 8 meters - high.
A source
For us, the greatest interest is the Pleistocene megafauna. Pleistocene (1, 8 million - 11 thousand. Years ago - in fact, to this day) - the era in Earth's history has been marked by several major events: the emergence of Homo sapiens, several periods of severe cold spells and ... the extinction of most of the large animals around the world. Giants, who disappeared at the end of the Pleistocene epoch, and which we now hardly ever see with their own eyes, and is dedicated to this post. Before you - 30 amazing animals have disappeared over the last few thousand years, someone before, and someone - almost yesterday ... Almost all of them have seen with my own eyes the ancient people, they are the same in most cases, they had a hand in their rapid extinction.
1. mammoths, elephants, mastodons

Khobotnev, the largest land animals of the Quaternary period, animals and landscape-are the clearest indicator of the health of ecological communities, were distributed on four continents and a variety of offshore islands and the variety of species was not an example of the current . In our native Eurasian woolly mammoth met (genus Mammuthus), pryamobivnevy elephant (Palaeoloxodon), Stegodon (Stegodon) still alive and Asian elephant. America was inhabited by two species of mammoth - woolly and Columbia, as well as the mastodon (Mammut americanum) and gompotery (Cuvieronius). In Africa, the current living African elephant, and even earlier, in the early Pleistocene - a few species, including Asian. Elephants who had moved to isolated islands, eventually becoming ... dwarf; so it happened to Stegodon Islands Flores and Sulawesi (Indonesia), mammoths of Wrangel Island (Russia) and the Channel Islands National Park (USA), elephants on the islands of the Mediterranean (Corsica, Sardinia, Sicily, Cyprus, Malta, Crete and several Greek islands). The growth of these elephants sometimes barely reached 1 m ...
The disappearance of the great diversity of Proboscidea there are still many uncertainties; so, there is still an ongoing debate about the causes of extinction of mammoths in Siberia and the Arctic. Unquestionable activities of the two factors - climate change and active hunting of ancient people. Different species of elephants in different continents have disappeared at different times, respectively: US - 8-10 thous. Years ago, the Eurasian - a little earlier. Dwarf elephants lived to see the beginning of the Holocene (the Greek island of Tilos about - about 2000 BC), just before the extinct mammoths of Wrangel Island; the last representative gompoteriev - kyuveronius disappeared in South America, supposedly to 400 AD
2. Rhinos

Woolly Rhinoceros (Coelodonta antiquitatis) - the second most famous after the Pleistocene mammoth beast. Its length reaches 3, 5 m, weight - up to 3 m. On the face he had two horns, the longest of which, front, sometimes reaching more than 1 m in length. An important feature of this type - a long thick coat of brown, like the mammoth, which allowed a rhino to survive in inhospitable for heat-loving animals of northern and central Eurasia. Inhabited woolly rhinoceros on the cold plains, known as "mammoth steppe" - in their place is now a multitude of coniferous and deciduous forests. Extinct view about 10 thousand years ago, and possibly later. As in the case of the mammoth, there are two main hypotheses disappearance northern rhinos: rapid climate change and excessive hunting of ancient man. Most likely, both factors affected ...
Where less known are two other possible contemporary of ancient people - elasmotery (Elasmotherium, 3-4 species) and rhino Merck (Dicerorhinus kirchbergensis). Elasmotery was truly a giant beast: its growth at the withers reaching 2 to 3 m, and weight - up to 6 tons! On his head was only one horn, but long suspected it could reach up to two meters. Rhino Merck was similar to woolly in size and also had two-horned. Both of these animals became extinct before the woolly rhinoceros - may not withstand competition with him also; but some researchers believe that the relict populations elasmoteriev Merck and rhinos survived until the end of the Pleistocene, and met with the ancient people.
3. Bulls

Subfamily oxen (Bovinae) in the last 10 thousand years, has lost some very interesting and often very colorful species. North America and Eurasia have lost several species of bison, the most famous of which - the steppe bison (Bison priscus), dwelt on both sides of the Atlantic and the extinct about 6000 years ago. Even in Africa, where the extinction of large animals was not of mass character, only 4 thousand years ago disappeared huge buffalo longhorned pelorovis (Pelorovis antiquus). Several species of oxen, in particular Baikal yak (Poephagus baicalensis) and the dwarf buffalo Philippines (Bubalus cebuensis), extinct in Asia. But the most famous view of the missing bulls, of course, is the tour (Bos primigenius) - wild ox from Europe and Asia, who became the ancestor of most breeds of cattle. This powerful animal black color with a light stripe on the back completely disappeared by 1627.
One of the main reasons for the sharp reduction in the number of wild bulls (and falling numbers of many surviving species) - the active pursuit of human beings; scenes of hunting bulls and bison often appear in cave paintings. In addition, the great influence of climatic factors on the reduction in the number of large hollow-horned ungulates, especially in northern latitudes.
4. Cave bear

Cave bear (Ursus spelaeus) - another extinct animal with the man, a well-known and widely far from paleontology and archeology circles. It is found in Europe - Western (larger species, to 3, 5 m in length) and East (no more brown). Cave bear gravitated mostly to the open spaces and not to forests, as well as caves. Another important difference: while the brown bear is a classic omnivore with superiority in the herbivorous, cave bear was almost complete vegetarian. Therefore ancient people could pose a risk only to the strength and size of this beast is hardly ever this type of bears hunted specifically on people.
Gone cave bear about 10 thousand. Years ago, and perhaps a little later. The most likely cause of its extinction is as follows: after the end of the last Ice Age steppe zone quickly covered with dense forests, depriving Bear usual habitat; individuals just choose a cave as a shelter, they were killed by people. In addition, in the past I hunted frightening, but not too dangerous giants meat and warm bear fur coat - good trophies.
5. Arktodus

Two types of long-legged, short-faced bear that lived in North America. In contrast to the relatively sluggish and omnivorous brown, black and cave bears, giant ploskomordy bear (Russian name of the larger species Arctodus simus) was a true predator and an active hunter, able to catch and kill very large prey, until the moose, camels, buffalo and young Mammoth - as do modern lions. Its dimensions were appropriate height at the withers - 1, 6 m height standing on its hind legs - more than 3 m, and weight - up to a ton.
Gone arktodusy about 10-12 thousand. Years ago, along with other members of the Pleistocene megafauna America. Possible reasons: competition with the brown bear (which is unlikely: arktodus was much stronger, and in the open spaces at the brown did not stand a chance - that the success of the hunt, in battle one on one) or a sharp reduction in food supply due to climatic or ( i) human factors (which is likely).
6. Lions

The present area of a lion (Panthera leo) is limited to sub-Saharan Africa and the tiny reserve in India. It is - only a small portion of the original habitat of a lion - or rather, some of its subspecies, and possibly species: cave lion (P. l. Spelaea) met in Eurasia - from England to Siberia and Turkmenistan, the lion Vereshchagin (P. l. Vereshchagini) - from Yakutia to Alaska, American Lion (P. l. atrox) inhabited the Americas - from Alaska in the north to the south of Peru. Two subspecies of lion (Barbary and Asian) lived in Europe and Central Asia.
The most well-known cave and American lions. How they look, we do not know; presumably their color was a pale, very likely - with spots or stripes. The presence of the male mane contested (my personal opinion - was a mane, it is warmer). Linear dimensions superior to African lions: American subspecies of the Siberian tiger was with even larger.
All Lions are active hunters and top predator of its biomes; Only American Lion inferior in size and strength ploskomordomu bear. They were prey to all sorts of hoofed animals, herds of millions roamed the steppes and woodlands Palearctic.
American and cave lions disappeared about 10 thousand. Years ago; some populations may live to ancient times. Probable cause of extinction - a famine due to a sharp reduction in the number of production; vigorous competition with the person; the combination of climatic and anthropogenic factors ... Barbary lion in the wild destroyed in 1922 .; Asiatic lion survived only in India (population size - about 300 individuals), and in several zoos around the world.
7. saber-toothed cats

These saber-toothed cats (Machairodontinae) - subfamily of large carnivores of the cat family, highly specialized in the production of herbivorous pachyderms such as bulls, giant sloths and elephants. In public, they are known as the saber-toothed tigers, but morphologically these animals are not relevant to the type of tiger (Panthera tigris), but directly related to cats. The main differences from the modern sabers big cats - a short tail and a unique jaw apparatus: upper canines were huge sizes (up to 17 cm), and the lower jaw relative to the top can be opened so wide that it was an angle of 120 °.
Until the late Pleistocene have lived at least two kinds of saber-toothed: Smilodon (Smilodon) and Homotherium (Homotherium). Smilodon, saber-toothed tiger classic, was the size of a large lion (height at the withers - up to 1, 2 m, weight - 300 kg) and lived in North and South America. Homotherium was a little less; Smilodon distinguished by its relatively short fangs and a lighter body structure. He lived in Africa, Eurasia and North America.
Recent saber-toothed cats have disappeared in North America 8-10 thousand years ago, and in Eurasia and Africa - even earlier. The reasons for the extinction of these powerful and dangerous predators not completely clear, but three versions are obvious: the fierce competition with these cats (lion, tiger, jaguar, etc.), Climate change and pressure from the man. Most likely, a combination of these three factors, and was fatal.
8. American cheetahs

At least two major North American cat species (genus Miracinonyx), morphologically very similar to the African cheetah, but are genetically closer to the cougar. Unlike the vast majority of other members of the megafauna, American cheetah is known only from fragments of skeletons, so much about its biology still remains unclear. But we know that it looks very interesting animal resembled the modern cheetah and hunting just catching prey in the sprint throw. As proof of this fact now living in the North American pronghorn antelope, can reach speeds of up to 100 km / h. None of the modern American predators can not run as fast, and that means only one thing - most recently existed-footed predator, for salvation from which it was necessary to develop a high-speed skills. This predator was an American cheetah - other contenders for this is not. And it died out relatively recently - 10-13 thousand. Years ago.
9. Deer

In today's time, there are many species of deer; However, much of the original diversity of these beautiful animals disappeared during the Pleistocene - early Holocene. Here are some of them: the largest and most famous - bolsherogy deer (Megaloceros giganteus) from Europe, North Africa and North-West Asia, majestic animal growth at the withers to 2, 1 m, 3 m, with huge beautiful horns scale to 3 6 m. Two kinds of his immediate family - Praemegaceros and Sinomegaceros - met at the end of the Pleistocene on the island of Sicily, and in East Asia, respectively. On both sides of the Atlantic lived Cervalces huge size of a large elk; North American deer were driven from the genera and Navahoceros Sangamona - average size, with a reindeer.
The disappearance of several genera of large and giant deer 9-12 happened thousands of years ago, some species have become extinct later. Probable cause - global climate change, pressure from the people and the competition with surviving species of deer and elk.
10. Horrible Wolf

In North America, the time of its colonization by man lived not only well known to us the gray wolf. Hundreds of thousands of years ago, the continent appeared view, which was later people will call a terrible wolf (Canis dirus). It was larger and more massive than the gray wolf (1, 5 m in length, weighing up to 80 kg), has a more short legs and larger teeth. It was a gregarious predator, hunting for very large animals, such as horses and buffalo.
Dire wolf disappeared about 10,000 years ago - at a time when the mass extinction of large animals in North America, is the food great dogs. Last population of the species probably lived up to the 2nd millennium BC Ozark Mountain (Arkansas, USA).
The remains dire wolf are the most widespread findings in traps degtyanyh Ranch La Brea (California): there is found more than three thousand skeletons of this animal.
11. Giant beavers

Modern Beaver - one of the largest rodents of our time. If until now lived to its distant relative of the North American, he undoubtedly would have become an absolute champion: the length of the US giant beaver (Castoroides ohioensis) reached 2, 5 m, and weight - up to 220 kg! Besides the size, the giant beaver was different from the usual narrower tail, like the tail of a muskrat, and huge teeth protruding from the gums of almost 15 cm. The lifestyle of a giant beaver yet we can only guess. He could be a zealous builder (like its smaller cousin), and living in open countryside on the banks of major rivers and lakes, it is possible - in burrows near water.
Gone giant rodent about 9, 5 thousand years ago, presumably because of the reduction in his usual habitat and persecution by man.
The Pleistocene Europe lived another kind of giant beavers - trogontery (Trogontherium), but it became extinct much earlier and perhaps never crossed people.
12. Long-legged peccaries

Two kinds of small pigs, close relatives of modern bakeries. In larger sizes (up to a meter or more), and long legs, thanks to which the animals were good runners. Rhode Platygonus differed shortened snout with large fangs and sharp, serve as a good means of defense from predators. Larger Mylohyus (up to 90 cm tall!), By contrast, had a long elongated front part of the head, resembling the extinct millions of years ago, giant carnivorous pigs entelodonov. We lived leggy bakers in North America, probably moving the prairies and woodlands in small groups, like antelopes.
Gone are the giant peccary, as well as many other members of the North American megafauna, about 9-12 thousand years ago.
13. marsupial lion

The largest marsupial predator of Australia, reaches the size of the modern jaguar length from the tip of the snout to the base of the tail - 110 cm, height at the withers - 70 cm, weight - 100 kg and more. The jaws of the marsupial lion (Thylacoleo carnifex) in bite force did not concede a lion, and a powerful musculature demonstrates the tremendous power of this beast, no doubt able to bring down the largest herbivores in the continent - such as DIPROTODON and giant kangaroos. Details marsupial lion skeleton give grounds to suppose that the animal could sit on his hind legs, relying on a strong tail, as do the kangaroo and climb trees in the manner of a leopard.
Gone marsupial lion 30-40 thousand. Years ago, at the same time with the rest of the Australian megafauna. Rumors that he could live up to historical times, still excite the minds cryptozoologists, nurturing the hope to find the mysterious "tiger cat Queensland." But the chances of enthusiasts luck now almost nil ...
14. DIPROTODON

DIPROTODON or "Tasmanian behemoth" (born Diprotodon) - a huge herbivore of Australia, the largest individuals that reach 3 meters in length and 1, 8 meters - high.
A source