175
Vitamin B5 - action, content, indications

What foods contain vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid)? How does this vitamin work in our body? What is the daily dose of calcium pantothenate, and what happens with hypo- and hypervitaminosis?
Pantothenic acid is a plastic substance, the color is light yellow, and the melting point of this vitamin is 75-80 ° C. The carbon atom is asymmetrical and has optical activity. Pantothenic acid is well soluble in ice acetic acid, dioxane, water and ethyl alcohol. This substance is easily destroyed when heated, in an acidic and alkaline environment, but the neutral medium tolerates well. Medicine uses salts of pantothenic acid, which are more stable. In 1933, the scientist Williams discovered pantothenic acid. Then it was given the name “pantoten”, which when translated from Greek means “everywhere”. The vitamin nature of this compound was proven by research in the 1940s. At first, it received another name - vitamin G, which was later changed to vitamin B5. Pantothenic acid has been found to cure alimentary dermatitis in chickens.
Once in the body, pantothenic acid is converted into panthetin, which is part of coenzyme A. This enzyme is involved in oxidation and acetylation. Coenzyme A is one of the few substances that simultaneously takes part in the metabolism of fats, proteins and carbohydrates.
One of the most important properties inherent in vitamin B5 is its ability to stimulate the production of glucocorticoids - these are adrenal hormones. This property allows it to be used in the treatment of colitis, arthritis, allergies and heart disease.
Vitamin B5 activates oxidative-reduction processes in the body, forms antibodies, helps to be absorbed by other vitamins, normalize lipid metabolism, synthesize neurotransmitters.
Interaction
- Calcium pantothenate has the ability to enhance the effectiveness of cardiac glucosides;
- This acid loses its useful properties during heat treatment - up to 50%;
- It's for metabolism.
- Neutralizes the toxic effect of drugs against tuberculosis and streptomycin.
For adults, the daily dose is approximately 4-7 mg. Increased need arises during heavy physical exertion, sometimes pregnancy and breastfeeding.
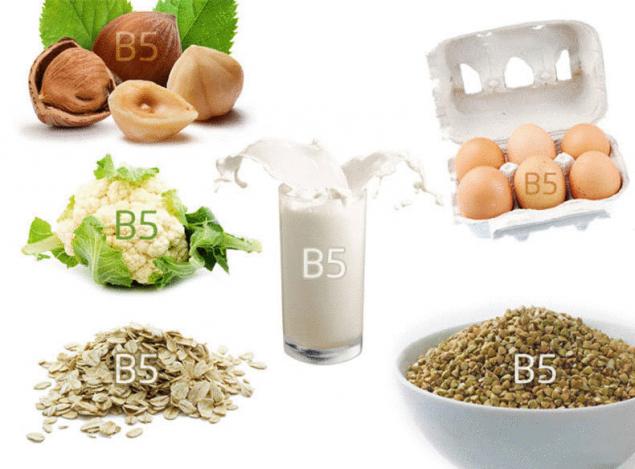
Products in which there is B5: whole grains, green leaf yeast, legumes, oatmeal, hazelnuts, buckwheat, eggs, cauliflower, fish eggs, milk.
Hypo- and hypervitaminosis The cause of vitamin B5 deficiency can be diseases of the small intestine, low content of fats and proteins in food, long-term use of antibiotics and sulfonamides. This is accompanied by fatigue, depression, nausea, sleep disorders, headaches, fatigue, redness of the skin of the feet, tingling, burning, muscle pain, numbness of the toes, dyspeptic disorders, gastric and duodenal ulcers.
The danger of overdose is reduced to zero, since the toxicity of pantothenic acid itself is reduced to zero.
Indications for taking B5B for medicinal purposes, vitamin B5 is used to treat the following diseases:
- Violated exchange processes;
- Paresthesia, polyneuritis, neuralgia;
- Burns, trophic ulcers;
- Bronchial asthma, bronchitis;
- Allergic reactions;
- TB;
- Hyperthyroidism;
- Toxicosis of pregnant women;
- Hypomotor dyskinesia of the intestine;
- Insufficient circulation;
- Chronic liver disease.
Source: lubim-zhizn.ru/