136
Experts emphasize the importance of vitamin E in the first 1000 days after conception
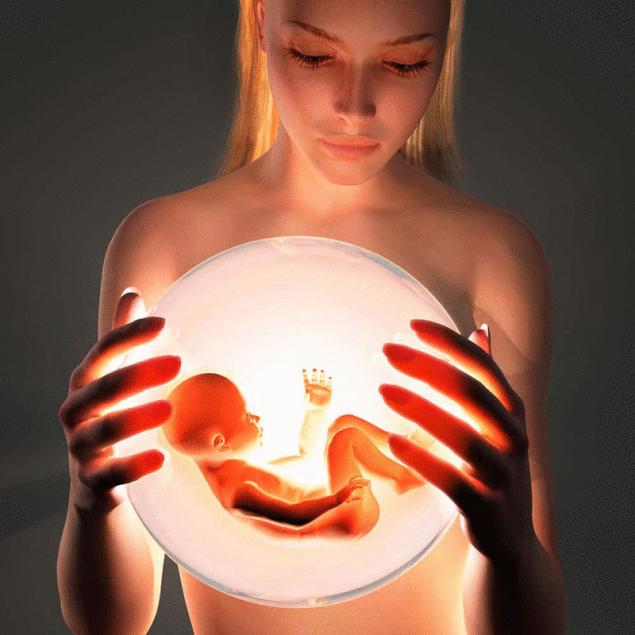

Scientists at the University of Oregon argue that the importance of vitamin E is underestimated, especially in the first thousand days after conception.
Professor Maret Traber said: Some critics have raised a false alarm about excessive vitamin E intake, when in fact most people’s diets are not saturated enough. Many people believe that vitamin E deficiency never happens. That's not true. This happens with alarming frequency, both in the United States and around the world. But some results of underconsumption are less obvious, such as its effects on the nervous system and brain development or resistance to infection.”
Experts, based on a review of numerous studies, presented conclusions. Among them, the most important are the importance of vitamin E during prenatal development and in the first years of life; the correlation between adequate intake and dementia later in life; the difficulty of assessing the adequacy of vitamin E by measuring only a blood test. The results are:
Vitamin E deficiency is associated with increased infection, anemia, stunted growth and adverse outcomes during pregnancy, for the infant and mother.
Deficiency, especially in children, can cause neurological disorders, muscle deterioration, and even cardiomyopathy.
Animal studies show that vitamin E is critical for early neurodevelopment in embryos, in part because it protects the function of omega-3 fatty acids, especially DHA, which is very important for brain health. The most sensitive organs are the head, eyes and brain.
One study found that higher concentrations of vitamin E at birth were associated with improved cognitive function in two-year-olds.
The findings of diseases that are increasing in the developed world, such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetes, suggest that obesity does not necessarily reflect adequate micronutrient intake.
Vitamin E supplements do not prevent the onset of Alzheimer’s disease, but have shown an advantage in slowing its progression.
Data from older adults have shown that lifelong eating leads to higher levels of vitamins B, C, D and E, which are associated with greater brain size and higher cognitive function.
Vitamin E protects critical fatty acids such as DHA throughout life, and one study found that people in the top quarter of DHA concentrations had a 47 percent reduced risk of developing all causes of dementia.
Traber added: It is important throughout life, but the strongest evidence for the benefits of vitamin E is in the first 1,000 days after conception. It is crucial for neurological reactions and brain development that occur only during this period. This is not something you can do later.”
He recommends the supplement for all people, but this vitamin is especially important for children two years old, women who are pregnant or may become pregnant, for the elderly.
Source: nauka24news.ru/