709
The world in 2030: what will change in science, technology and the labour market
In the twenty-first century technology, dramatically affecting our lives, growing fast, and governments are interested in qualitative predictions. Mathew burrows, the author of the book "the Future declassified. What will the world in 2030," ten years worked on the report "Global trends" — a futuristic material for the White house and the U.S. Department of defense. Published several excerpts from the book about the most important trends that determine how the world will look like in 15 years.

© Atelier Teratoma
Food let's face it: we expect a significant deficiency, if not taken preventive measures. The extrapolation of current trends on consumption of food and water per capita shows the estimated magnitude of the problem for the next couple of decades. The demand for food will grow by 2030 by more than 35%, but most grains such as wheat or rice, the average growth rate of production slowed down from 2% a year in the 70s and 80s to 1% per year since 1990, According to McKinsey Global Institute, "growth trends of resource prices since 2000 has changed drastically and dramatically". In the twentieth century in real terms prices have fallen since 2000, they increased by more than two times, although the last couple of years has decreased slightly. They are still close to historic highs. Mankind has consumed more food than was produced over many years of the previous decade.
One large international study found that global annual demand for water will by 2030 reach 6900 billion m3, 40% more than current sustainable water supplies. Agriculture, consuming about 3100 billion m3 of water per year (about 70% of the total volume today in the world) by 2030 will require is already 4500 billion m3, while the performance will not improve. About 40% of humanity lives inside or in the immediate vicinity of the basin of the rivers of international importance. Of these basins, more than 200 shared between more than two countries, increasing the dependence on changes in demand and availability of water and vulnerability. Based on the current dynamics of the Organization for economic cooperation and development (OECD) suggests that by 2030 nearly half of humanity will inhabit areas with acute water shortage. Now people have cultivated the fertile land. Given the limited availability of new irrigated lands to meet the global need for food, it is essential to increase yields.
Of particular concern is Africa. It is necessary to increase the efficiency of agriculture to avoid food shortages. In contrast to South Asia and South America, where they recorded the growth of production per capita, Africa has recently returned to the figures of the ' 70s. many States there are no conditions for agriculture, including the necessary infrastructure and a transport system for delivery of seed and fertilizer from the ports inland; there are serious problems with the management. Even minor improvements in the supply chain of food can lead to serious decrease waste and reduce the pressures from a growing population.
Wheat is likely to continue to show high price volatility. A large proportion of production comes from the grain regions with water scarcity and climate risk, such as China, India, Pakistan and Australia. In General, the most vulnerable to the inflation of prices for food products will be import-dependent poor countries, such as Bangladesh, Egypt, Djibouti and Sudan. Their first line of defense in the fight against rising food prices will increase subsidies on basic foodstuffs. It was a difficult decision, especially in view of the fact that many of them intend to fight against inflation of the budget. China, India and Russia is also likely to face the problem of increasing food prices, but they are better able to fend for themselves. Russia and China are the major producers of grain. They have a more healthy situation with the budget, they can afford the payment of subsidies and under control to cope with spikes in food prices. Rich countries can also purchase food on international markets.
Today we are experiencing a new turning point, and it is difficult to predict the full scale of the imminent changes or their consequences. We don't just explore the creation, as it was in Darwin's time. Today we change the very nature of man. In other words, we no longer need to wait for God or natural selection will do the trick. On the other hand, as noted by ray Kurzweil, author of the book "the Singularity is coming": "Understanding the information process underlying life, we begin to learn to reprogram our biology, to manage at a virtual level to halt the disease, to achieve incredible growth of human capabilities and the notable extension of life expectancy".And it's not just that biological science has stepped to a new level. This technological revolution is characterized by the convergence and synergies of several major technologies, namely nano-, bio-, it, 3D printing, artificial intelligence, new materials and robotics.
For the first time feeling what is coming is something totally new, visited me, when I started to work on the project "Global trends" and went to the conference to hear the presentation of the doctor of Kli - Nicky Johns Hopkins. It was about implants and prosthetics, designed to help returning from war zones to soldiers with amputations and paralyzed limbs. Implanted brain chips are used to control robotic arms. The implant receives signals of a brain of the patient, decrypts them and through the cable connection moves the robotic hand. In the future, scientists hope that this connection will be wireless. According to scientists from the Institute of brain science, brown universities, the main goal is to restore the mobility of the own limbs of the patient.
Jeffrey Stibel, President of Braingate, a developer of technology brain computer interface, spoke about the progress in the field of restoration of lost vision: "you will Have a brain implant connected to a device similar to sunglasses. Sunglasses, in fact, do what we do when we look only in this case, the beholder is blind and glasses transmit the information through the computer chip directly into the brain to have a feeling that he really sees something. It works." According to Stibel, there is still a lot of work to improve the implants, but we are already on the way to the universe where "mind over matter".
BrainGate implant, © Stanford Neural Prosthetics Translational Laboratory
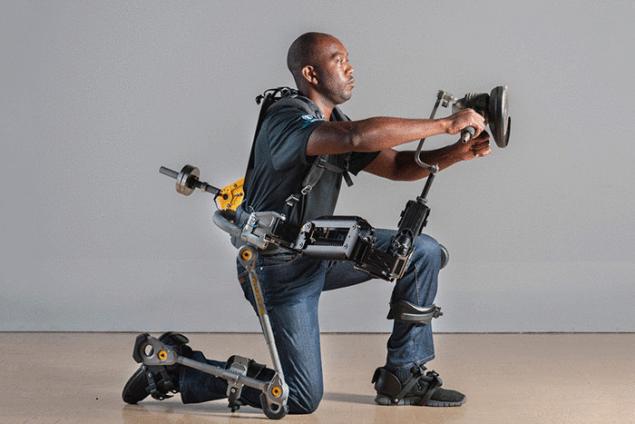

exoskeleton, ©Lockheed Martin/wired.com
Exoskeletons — another invention that extends our physical capabilities. As a rule, they consist of an outer frame that is attached to the soldier's feet. Using the system, driven by motors or hydraulics, the soldiers can carry heavy loads up to 100 kg. Over time, when the technology of production of batteries will step forward, the limited amount of electricity will cease to be a deterrent. As brain implants designed to enhance mental capabilities, exoskeletons expand the capabilities of the physical. This will allow civil and military work more effectively in such environments that were previously unavailable. The elderly may be useful mechanized exoskeletons that help in simple activities (walking, lifting). This would improve the health and quality of life of the aging population.
Successful development in the field of prosthetics probably will be directly integrated into the human body. Brain computer interfaces can provide superhuman capabilities, increase strength and speed, and to perform functions previously inaccessible to man. For example, the brain can send signals, bypassing the damaged fragments of the spinal cord will activate the nerves in idle hands or feet. As technology is advancing replacement of limbs, people will have the opportunity to expand their physical abilities (as well as with the help of plastic medicine in our days to improve the appearance). Future implants in the retina will give us the ability to see at night, and neurological enhancements could provide us with a better memory or speed of thought. Neuropharmaceutical will allow people to concentrate for longer periods and improve learning ability. It would be a step ahead of wearable computer Google Glass with a transparent display, which is mounted on the head and allows a person to have a constant connection to the Internet. Augmented reality system — for example, those that increase intelligence or improve your ability to see in the dark can significantly increase your mental or physical ability and speed that will allow you to better cope with situations in real life.
Life expectancy No less important and rising trend in life expectancy that we see in the world. In may 2013, the world health organization (who), the United Nations released data showing the "increase in life expectancy in the world with 64 years in 1990 to 70 years in 2011", and this is a significant increase. The decrease was observed only in North Korea, South Africa, Lesotho, Zimbabwe and Libya.
Rapidly ageing countries may experience a slowdown in GDP growth and even stagnation. "Old" States will not be easy to reform pension and health systems — and arrange funding to support needy seniors — while not burdening the young generation, who are forced to pay for pension programs. The governments of countries with relatively high average age is 45-50 years — may be forced to significantly reduce spending and raise taxes. Some analysts believe that an ageing society will seek to avoid risks and find yourself in a pinch. Some European and rapidly aging East Asian States decide that can't afford a massive armed force or show of force to other countries. Then the cuts in defence spending seen in Europe over the past 10 years, would be only the tip of the iceberg. Rapid increase in the population of Asian and African minorities in Western European countries with low fertility more risks to undermine national harmony and to stimulate the growth of reactionary sentiment in politics. And we don't know where all this will lead.

An aging society may not be the catastrophe it would be if physical labor was still a vital need as in many historical stages. Progress in the field of health, which was discussed just above, will certainly improve the quality of life of the elderly that will allow them to stay longer employable. And some polls show that, for example, in the U.S. the generation of baby boomers remains wish to work — albeit with a less rigid schedule, even if they financially can afford to retire and maintain your normal standard of living.
Artificial intelligence In the beginning of 2014 it has been reported that one of the most powerful supercomputers in the world — Japan K. has created the most accurate simulation of the human brain that ever existed, which required 40 minutes to render one second of human brain activity. Scientists suggest that the simulation of the brain will be fully possible when there is an even more powerful computers. Most likely, this will happen in the next 10 years. Understanding the human brain and the ability to reproduce it have broad use in medicine in the treatment of diseases such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and many other disorders of the brain. It will also give significant impetus to the work on the creation of artificial intelligence and the application of big data. The first researchers in artificial intelligence have developed algorithms that step by step imitated the thinking of people when they put a puzzle or make logical conclusions. However, people solve most of their problems using fast, intuitive judgments, and not conscious of sequential logic, which is able to simulate artificial intelligence at the initial stage.

Research in the field of artificial intelligence have made some headway in regard to simulation of brain activity, but successful simulation of activities of human brain, made not so long ago, the Japanese computer will help us move forward in its understanding. Here it is also necessary to take a step forward in the development of algorithms that uses a computer program to recreate the functioning of the brain. The search for more efficient algorithms for finding a solution to the problem was for research in the field of artificial intelligence a priority. My colleague at the Atlantic Union Dr. Banning Garrett investigated the problem of the world, manipulated by algorithms, and the risks associated with it. He notes that progress in the field of algorithms has attracted much less public attention than the increase in microprocessor performance (and the speed of the development of algorithms substantially beyond Moore's law). The speed of processors has accelerated 1000 times, but during the same period, between 1988 and 2003, the work algorithms had improved as much as 43 thousands of times.
Algorithms and the Internet of things, which is increasingly called the Internet of everything — a match made in heaven, making a substantial contribution in science, health, resource efficiency and smart cities. However, big data and algorithms can lead to a massive attack on personal information. Moreover, there is a huge potential for abuse prediction algorithms. "Already today, insurance companies and the Commission on early conditional release use predictive algorithms to calculate risks; in the United States more and more places where the police work is based on the prediction, after processing data out of the street, groups or individuals who become objects of greater attention," said Garrett. As explained by Garrett, the main limiting factor for the analysis of algorithms is that results are based on correlations, not causal dependence. In his book on big data Viktor Mayer-Schoenberg and Kenneth Cukier explain that correlation is good, if you can detect "much faster and cheaper than causal dependence". However, about correlation can lead to erroneous assessment with all the consequences: for example, harassment by law enforcement of innocent citizens on the basis of a predicted propensity to commit crimes.
The labour market Even in developing countries, robots can replace the local workforce in areas such as electronics, which will adversely affect the level of local salaries. Foxconn — the Chinese manufacturer of Apple products — as you know, plans to replace 80% of the staff robots. The company is worried about rising labour costs and difficulties in finding reliable employees for little money. The retention percentage of employees began to decline as soon as began to appear numerous opportunities in other areas and increased salary demands of the Chinese workers.
The use of robots is not confined to the workplace or everyday life. Autonomous motor vehicles, including the iconic unmanned vehicle from Google may have in the next 10 years to fill our freeways. Long-term consequence of the introduction of unmanned vehicles and other Autonomous vehicles can become a radical change in the ways of car use, which will affect transportation infrastructure and use of urban areas. Unmanned vehicles would encourage the reorganization of cities and changes in urban lifestyle. Robotic vehicles, especially if together with their appearance, change the schema of possession and use, would have devastating consequences for the global economy primarily the automotive industry. Some producers could benefit from the situation (or there would be a new manufacturers), but can completely change the very idea of what a car is, if people will start to appreciate it for convenience, not status.
A greater threat to the promise of breakthroughs in software, the emergence of programs that can do the work of highly skilled workers faster and more accurately. Incredible features of search engines such as Google Search or Microsoft Bing, based on powerful ranking algorithms significantly surpass human: the search engines can sift through billions of data points in search of an answer to the request. Other powerful algorithms replace lawyers with eDiscovery, scanning millions of legal documents with great speed, incredible accuracy and lower material costs than men. X-rays computers are described much more accurately than radiologists. Constantly improving the quality of online translator Google Translate by analyzing huge amounts of data and advanced algorithms. In short, a profession or even areas of activity will be completely eliminated with the advent of revolutionary software.
This brings us to an important question: will this create more jobs than it destroyed. In fact, no one with certainty can not say, but concerns voiced, even those economists whose theories predict the emergence from the ashes of the destroyed jobs of these new professions, which we can't imagine. A recent OECD report has opened our eyes to some startling facts: according to studies, a new technology was 80% to blame for what happened over the last 20 years a 4% decrease in the share of global GDP attributable to the working class. But those few who have the skills and talent in those areas, where they began to apply new technologies — as well as the management and owners of corporations — reinvested his fortune. I here's optimistic and believe that there will be a new professional direction.published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: theoryandpractice.ru

© Atelier Teratoma
Food let's face it: we expect a significant deficiency, if not taken preventive measures. The extrapolation of current trends on consumption of food and water per capita shows the estimated magnitude of the problem for the next couple of decades. The demand for food will grow by 2030 by more than 35%, but most grains such as wheat or rice, the average growth rate of production slowed down from 2% a year in the 70s and 80s to 1% per year since 1990, According to McKinsey Global Institute, "growth trends of resource prices since 2000 has changed drastically and dramatically". In the twentieth century in real terms prices have fallen since 2000, they increased by more than two times, although the last couple of years has decreased slightly. They are still close to historic highs. Mankind has consumed more food than was produced over many years of the previous decade.
One large international study found that global annual demand for water will by 2030 reach 6900 billion m3, 40% more than current sustainable water supplies. Agriculture, consuming about 3100 billion m3 of water per year (about 70% of the total volume today in the world) by 2030 will require is already 4500 billion m3, while the performance will not improve. About 40% of humanity lives inside or in the immediate vicinity of the basin of the rivers of international importance. Of these basins, more than 200 shared between more than two countries, increasing the dependence on changes in demand and availability of water and vulnerability. Based on the current dynamics of the Organization for economic cooperation and development (OECD) suggests that by 2030 nearly half of humanity will inhabit areas with acute water shortage. Now people have cultivated the fertile land. Given the limited availability of new irrigated lands to meet the global need for food, it is essential to increase yields.
Of particular concern is Africa. It is necessary to increase the efficiency of agriculture to avoid food shortages. In contrast to South Asia and South America, where they recorded the growth of production per capita, Africa has recently returned to the figures of the ' 70s. many States there are no conditions for agriculture, including the necessary infrastructure and a transport system for delivery of seed and fertilizer from the ports inland; there are serious problems with the management. Even minor improvements in the supply chain of food can lead to serious decrease waste and reduce the pressures from a growing population.
Wheat is likely to continue to show high price volatility. A large proportion of production comes from the grain regions with water scarcity and climate risk, such as China, India, Pakistan and Australia. In General, the most vulnerable to the inflation of prices for food products will be import-dependent poor countries, such as Bangladesh, Egypt, Djibouti and Sudan. Their first line of defense in the fight against rising food prices will increase subsidies on basic foodstuffs. It was a difficult decision, especially in view of the fact that many of them intend to fight against inflation of the budget. China, India and Russia is also likely to face the problem of increasing food prices, but they are better able to fend for themselves. Russia and China are the major producers of grain. They have a more healthy situation with the budget, they can afford the payment of subsidies and under control to cope with spikes in food prices. Rich countries can also purchase food on international markets.
Today we are experiencing a new turning point, and it is difficult to predict the full scale of the imminent changes or their consequences. We don't just explore the creation, as it was in Darwin's time. Today we change the very nature of man. In other words, we no longer need to wait for God or natural selection will do the trick. On the other hand, as noted by ray Kurzweil, author of the book "the Singularity is coming": "Understanding the information process underlying life, we begin to learn to reprogram our biology, to manage at a virtual level to halt the disease, to achieve incredible growth of human capabilities and the notable extension of life expectancy".And it's not just that biological science has stepped to a new level. This technological revolution is characterized by the convergence and synergies of several major technologies, namely nano-, bio-, it, 3D printing, artificial intelligence, new materials and robotics.
For the first time feeling what is coming is something totally new, visited me, when I started to work on the project "Global trends" and went to the conference to hear the presentation of the doctor of Kli - Nicky Johns Hopkins. It was about implants and prosthetics, designed to help returning from war zones to soldiers with amputations and paralyzed limbs. Implanted brain chips are used to control robotic arms. The implant receives signals of a brain of the patient, decrypts them and through the cable connection moves the robotic hand. In the future, scientists hope that this connection will be wireless. According to scientists from the Institute of brain science, brown universities, the main goal is to restore the mobility of the own limbs of the patient.
Jeffrey Stibel, President of Braingate, a developer of technology brain computer interface, spoke about the progress in the field of restoration of lost vision: "you will Have a brain implant connected to a device similar to sunglasses. Sunglasses, in fact, do what we do when we look only in this case, the beholder is blind and glasses transmit the information through the computer chip directly into the brain to have a feeling that he really sees something. It works." According to Stibel, there is still a lot of work to improve the implants, but we are already on the way to the universe where "mind over matter".

BrainGate implant, © Stanford Neural Prosthetics Translational Laboratory

exoskeleton, ©Lockheed Martin/wired.com
Exoskeletons — another invention that extends our physical capabilities. As a rule, they consist of an outer frame that is attached to the soldier's feet. Using the system, driven by motors or hydraulics, the soldiers can carry heavy loads up to 100 kg. Over time, when the technology of production of batteries will step forward, the limited amount of electricity will cease to be a deterrent. As brain implants designed to enhance mental capabilities, exoskeletons expand the capabilities of the physical. This will allow civil and military work more effectively in such environments that were previously unavailable. The elderly may be useful mechanized exoskeletons that help in simple activities (walking, lifting). This would improve the health and quality of life of the aging population.
Successful development in the field of prosthetics probably will be directly integrated into the human body. Brain computer interfaces can provide superhuman capabilities, increase strength and speed, and to perform functions previously inaccessible to man. For example, the brain can send signals, bypassing the damaged fragments of the spinal cord will activate the nerves in idle hands or feet. As technology is advancing replacement of limbs, people will have the opportunity to expand their physical abilities (as well as with the help of plastic medicine in our days to improve the appearance). Future implants in the retina will give us the ability to see at night, and neurological enhancements could provide us with a better memory or speed of thought. Neuropharmaceutical will allow people to concentrate for longer periods and improve learning ability. It would be a step ahead of wearable computer Google Glass with a transparent display, which is mounted on the head and allows a person to have a constant connection to the Internet. Augmented reality system — for example, those that increase intelligence or improve your ability to see in the dark can significantly increase your mental or physical ability and speed that will allow you to better cope with situations in real life.
Life expectancy No less important and rising trend in life expectancy that we see in the world. In may 2013, the world health organization (who), the United Nations released data showing the "increase in life expectancy in the world with 64 years in 1990 to 70 years in 2011", and this is a significant increase. The decrease was observed only in North Korea, South Africa, Lesotho, Zimbabwe and Libya.
Rapidly ageing countries may experience a slowdown in GDP growth and even stagnation. "Old" States will not be easy to reform pension and health systems — and arrange funding to support needy seniors — while not burdening the young generation, who are forced to pay for pension programs. The governments of countries with relatively high average age is 45-50 years — may be forced to significantly reduce spending and raise taxes. Some analysts believe that an ageing society will seek to avoid risks and find yourself in a pinch. Some European and rapidly aging East Asian States decide that can't afford a massive armed force or show of force to other countries. Then the cuts in defence spending seen in Europe over the past 10 years, would be only the tip of the iceberg. Rapid increase in the population of Asian and African minorities in Western European countries with low fertility more risks to undermine national harmony and to stimulate the growth of reactionary sentiment in politics. And we don't know where all this will lead.

An aging society may not be the catastrophe it would be if physical labor was still a vital need as in many historical stages. Progress in the field of health, which was discussed just above, will certainly improve the quality of life of the elderly that will allow them to stay longer employable. And some polls show that, for example, in the U.S. the generation of baby boomers remains wish to work — albeit with a less rigid schedule, even if they financially can afford to retire and maintain your normal standard of living.
Artificial intelligence In the beginning of 2014 it has been reported that one of the most powerful supercomputers in the world — Japan K. has created the most accurate simulation of the human brain that ever existed, which required 40 minutes to render one second of human brain activity. Scientists suggest that the simulation of the brain will be fully possible when there is an even more powerful computers. Most likely, this will happen in the next 10 years. Understanding the human brain and the ability to reproduce it have broad use in medicine in the treatment of diseases such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and many other disorders of the brain. It will also give significant impetus to the work on the creation of artificial intelligence and the application of big data. The first researchers in artificial intelligence have developed algorithms that step by step imitated the thinking of people when they put a puzzle or make logical conclusions. However, people solve most of their problems using fast, intuitive judgments, and not conscious of sequential logic, which is able to simulate artificial intelligence at the initial stage.

Research in the field of artificial intelligence have made some headway in regard to simulation of brain activity, but successful simulation of activities of human brain, made not so long ago, the Japanese computer will help us move forward in its understanding. Here it is also necessary to take a step forward in the development of algorithms that uses a computer program to recreate the functioning of the brain. The search for more efficient algorithms for finding a solution to the problem was for research in the field of artificial intelligence a priority. My colleague at the Atlantic Union Dr. Banning Garrett investigated the problem of the world, manipulated by algorithms, and the risks associated with it. He notes that progress in the field of algorithms has attracted much less public attention than the increase in microprocessor performance (and the speed of the development of algorithms substantially beyond Moore's law). The speed of processors has accelerated 1000 times, but during the same period, between 1988 and 2003, the work algorithms had improved as much as 43 thousands of times.
Algorithms and the Internet of things, which is increasingly called the Internet of everything — a match made in heaven, making a substantial contribution in science, health, resource efficiency and smart cities. However, big data and algorithms can lead to a massive attack on personal information. Moreover, there is a huge potential for abuse prediction algorithms. "Already today, insurance companies and the Commission on early conditional release use predictive algorithms to calculate risks; in the United States more and more places where the police work is based on the prediction, after processing data out of the street, groups or individuals who become objects of greater attention," said Garrett. As explained by Garrett, the main limiting factor for the analysis of algorithms is that results are based on correlations, not causal dependence. In his book on big data Viktor Mayer-Schoenberg and Kenneth Cukier explain that correlation is good, if you can detect "much faster and cheaper than causal dependence". However, about correlation can lead to erroneous assessment with all the consequences: for example, harassment by law enforcement of innocent citizens on the basis of a predicted propensity to commit crimes.
The labour market Even in developing countries, robots can replace the local workforce in areas such as electronics, which will adversely affect the level of local salaries. Foxconn — the Chinese manufacturer of Apple products — as you know, plans to replace 80% of the staff robots. The company is worried about rising labour costs and difficulties in finding reliable employees for little money. The retention percentage of employees began to decline as soon as began to appear numerous opportunities in other areas and increased salary demands of the Chinese workers.
The use of robots is not confined to the workplace or everyday life. Autonomous motor vehicles, including the iconic unmanned vehicle from Google may have in the next 10 years to fill our freeways. Long-term consequence of the introduction of unmanned vehicles and other Autonomous vehicles can become a radical change in the ways of car use, which will affect transportation infrastructure and use of urban areas. Unmanned vehicles would encourage the reorganization of cities and changes in urban lifestyle. Robotic vehicles, especially if together with their appearance, change the schema of possession and use, would have devastating consequences for the global economy primarily the automotive industry. Some producers could benefit from the situation (or there would be a new manufacturers), but can completely change the very idea of what a car is, if people will start to appreciate it for convenience, not status.
A greater threat to the promise of breakthroughs in software, the emergence of programs that can do the work of highly skilled workers faster and more accurately. Incredible features of search engines such as Google Search or Microsoft Bing, based on powerful ranking algorithms significantly surpass human: the search engines can sift through billions of data points in search of an answer to the request. Other powerful algorithms replace lawyers with eDiscovery, scanning millions of legal documents with great speed, incredible accuracy and lower material costs than men. X-rays computers are described much more accurately than radiologists. Constantly improving the quality of online translator Google Translate by analyzing huge amounts of data and advanced algorithms. In short, a profession or even areas of activity will be completely eliminated with the advent of revolutionary software.
This brings us to an important question: will this create more jobs than it destroyed. In fact, no one with certainty can not say, but concerns voiced, even those economists whose theories predict the emergence from the ashes of the destroyed jobs of these new professions, which we can't imagine. A recent OECD report has opened our eyes to some startling facts: according to studies, a new technology was 80% to blame for what happened over the last 20 years a 4% decrease in the share of global GDP attributable to the working class. But those few who have the skills and talent in those areas, where they began to apply new technologies — as well as the management and owners of corporations — reinvested his fortune. I here's optimistic and believe that there will be a new professional direction.published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: theoryandpractice.ru