192
Interesting facts about space disease
Surely you have ever been sick of a long drive in a car or you felt how your stomach compresses, riding a “chamomile”. If this is the case, then you should roughly imagine what astronauts experience when they go into space.
Approximately 60-80% of astronauts experience space sickness (similar to seasickness) in the first few days after launch. Its symptoms are similar to those that appear during a long ride on Earth, and include headaches, dizziness, nausea and in some cases bouts of vomiting.
For most members of the space program, these symptoms disappear after three days in space, but I can return at any time during a mission, often without warning. Perhaps even more interesting is how unpredictable space sickness can be. Even with careful analysis and pre-launch training, no one can tell for sure whether they will get sick or not. Some astronauts with sensitive stomachs may feel pretty good, while others who have never suffered from similar illnesses in their lives may experience severe headaches and nausea while adjusting to life beyond Earth’s atmosphere.
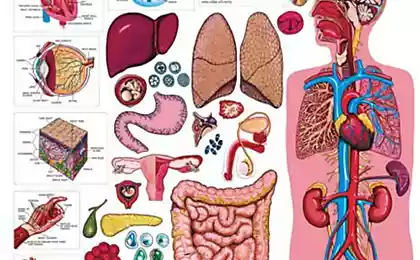
Although scientists have not yet decided what exactly causes space sickness, it is most likely caused by an imbalance in the inner ear that causes motion sickness here on Earth. If you are sitting in a car or in a spaceship, there will be a certain discrepancy between what your eyes can see and how your body senses what is happening.
That discrepancy alone is enough to get you sick, but astronauts in space are even worse off. The displacement of sensations is aggravated by the effects of weightlessness on the proprioceptive sensory system of the body. On Earth, this system uses neural signals to give you an accurate sense of the position of your limbs and the orientation of your body. When you swim above the atmosphere, this system doesn’t work, and you’re surprised that your hands and feet aren’t where you thought they were. Worse, you may not know where the top and bottom are.
All this confusion exacerbates the symptoms of space sickness, which can affect the ability of astronauts to do their jobs - don't forget that they work there a lot. To study the causes and effects of space sickness, as well as other effects of space travel on the human body, NASA opened the National Space Institute for Biomedical Research in 1997. Some studies of this institute have shown that it is possible to get rid of space sickness by manipulating the inner ear and vestibular system before direct departure. For example, you can train astronauts to move through an obstacle course in dark glasses.
P.S. And remember, just by changing your consciousness – together we change the world!
Source: hi-news.ru/space/sushhestvuet-li-kosmicheskaya-bolezn.html
Approximately 60-80% of astronauts experience space sickness (similar to seasickness) in the first few days after launch. Its symptoms are similar to those that appear during a long ride on Earth, and include headaches, dizziness, nausea and in some cases bouts of vomiting.
For most members of the space program, these symptoms disappear after three days in space, but I can return at any time during a mission, often without warning. Perhaps even more interesting is how unpredictable space sickness can be. Even with careful analysis and pre-launch training, no one can tell for sure whether they will get sick or not. Some astronauts with sensitive stomachs may feel pretty good, while others who have never suffered from similar illnesses in their lives may experience severe headaches and nausea while adjusting to life beyond Earth’s atmosphere.
Although scientists have not yet decided what exactly causes space sickness, it is most likely caused by an imbalance in the inner ear that causes motion sickness here on Earth. If you are sitting in a car or in a spaceship, there will be a certain discrepancy between what your eyes can see and how your body senses what is happening.
That discrepancy alone is enough to get you sick, but astronauts in space are even worse off. The displacement of sensations is aggravated by the effects of weightlessness on the proprioceptive sensory system of the body. On Earth, this system uses neural signals to give you an accurate sense of the position of your limbs and the orientation of your body. When you swim above the atmosphere, this system doesn’t work, and you’re surprised that your hands and feet aren’t where you thought they were. Worse, you may not know where the top and bottom are.
All this confusion exacerbates the symptoms of space sickness, which can affect the ability of astronauts to do their jobs - don't forget that they work there a lot. To study the causes and effects of space sickness, as well as other effects of space travel on the human body, NASA opened the National Space Institute for Biomedical Research in 1997. Some studies of this institute have shown that it is possible to get rid of space sickness by manipulating the inner ear and vestibular system before direct departure. For example, you can train astronauts to move through an obstacle course in dark glasses.
P.S. And remember, just by changing your consciousness – together we change the world!
Source: hi-news.ru/space/sushhestvuet-li-kosmicheskaya-bolezn.html
The island of Crete — the sun 340 days a year
Cars Google Street View will create a map of air quality