1160
European Centre for Nuclear Research
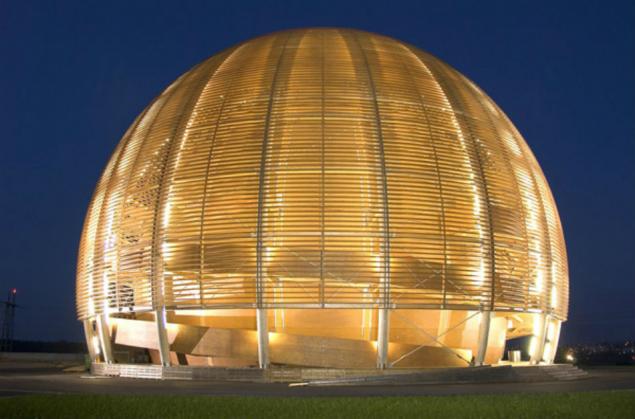

Few visitors to the Geneva suspect that life in this city is in full swing (or rather, a fountain, which became his trademark) is not only the city, but deep underground. There, at a depth of hundreds of meters, many kilometers of tunnels to rush the speed of light beams of elementary particles, protons, trying to shed light on the mysteries of the origin of our universe. CERN - a place that changed the life of all mankind. It is here that there was a "World Wide Web" Internet, it is from this institution all been waiting for doomsday during start Hadron Collider, here is the world's largest laboratory for High Energy Physics.
History h3>
After the success of the international organizations in the settlement of post-war problems, the leading European physicists believed that such an organization is necessary for the physical and experimental studies. These pioneers were Raul Daughtry, Pierre Auger and Leo Kowarski in France, Edoardo Amaldi in Italy and Niels Bohr in Denmark. In addition to combining European scientists similar organization was intended to divide the rising cost of natural experiments in high-energy physics among the participating States. Louis de Broglie formally proposed to create a European laboratory for the European Cultural Conference (Lausanne, Switzerland, 1949).
The next push was made by the American Nobel laureate Isidor Rabi in June 1950 at the Fifth General Conference of UNESCO in Florence (Italy), where he offered "to help and support the establishment of regional research laboratories to increase international cooperation." An intergovernmental meeting of UNESCO in Paris in December 1951, it was decided to create a European Council for Nuclear Research. Two months later, 11 countries signed an agreement on the establishment of the Interim Board, and then there was the name of the CERN
At the third session of the Interim Council in October 1952 Geneva (Switzerland) has been chosen to host a future lab. In June 1953, in the Canton of Geneva passed a referendum in which 2/3 of the voters agreed to the placement of a scientific center. The Convention was signed by the Council gradually 12 participating countries. September 29, 1954 an agreement was signed by France and Germany, was born the European Organization for Nuclear Research, the Council broke up, but the French acronym CERN preserved. At the opening of the organization includes 12 countries that are working today at CERN representatives for 20 powers, including China, Japan, the US and Russia. It employs 7 thousand. People of 80 nationalities in 500 research centers.
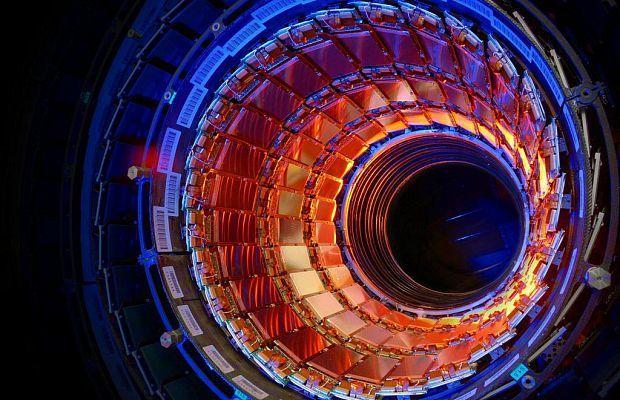

A fantastic machine that discovered the Higgs boson i>
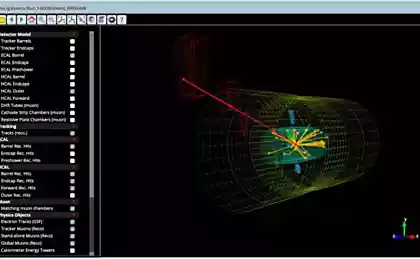
At a time when CERN was created purely physical studies have focused on understanding the components of the atom, so the title of the notion of "nuclear research." The objectives of CERN also includes the study of applied problems of different spheres of science - medicine, pharmaceuticals, energy, research in the field of high technology, and much more. In recent years in the laboratories of the scientific center it was made many high-profile discoveries, one of which - the detection of a structureless particle - the Higgs boson. This discovery can turn all the modern understanding of the matter and to undermine the status of the Standard Model of elementary particles - the popular quantum theory of the interaction of particles.
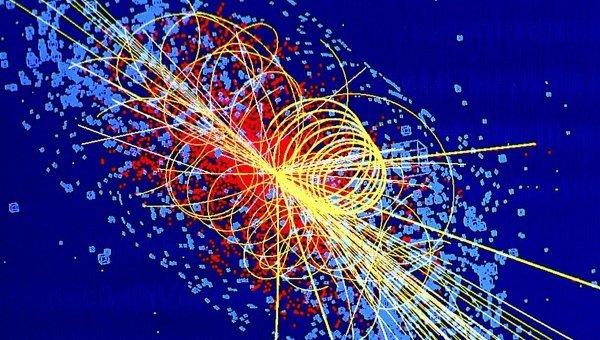
Computer modeling events Higgs boson i>
Overview h3>
Home ground at CERN, in the foreground - Switzerland, in the background - France.

View inside the building where the offices are many scientists working in the CMS collaboration and ATLAS.
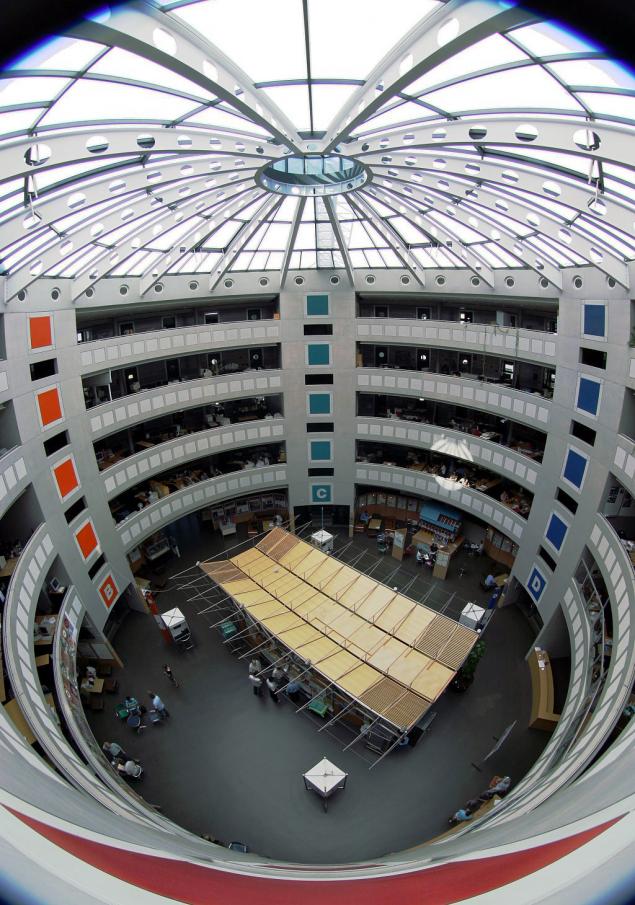

CERN is on the border of Switzerland and France near Geneva. CERN territory consists of two main areas, and several smaller ones. A large complex of buildings includes the operating rooms, laboratories, production facilities, warehouses, conference rooms, living rooms, dining rooms. The accelerator complex is located on the surface (the old accelerator Linac, PS), and under the earth at great depths up to 100 meters (more modern SPS, LHC).
The main area is the area near the Swiss town of Meyrin (Meyrin), t. N. site Meyrin. Another key area is the area near the French commune prévessin-moëns - site Prévessin. Smaller sites are scattered in the immediate vicinity along underground ring, which was built for the accelerator LEP.
The agreement on the formation of CERN was signed in Paris on June 29 - July 1, 1953 the representatives of 12 European countries. The organization was founded September 29, 1954. Currently, the number of member countries increased to 20. In addition, some countries and international organizations have observer status. At CERN constantly employs about 2,500 people, still about 8,000 physicists and engineers from 580 universities and institutes from 85 countries are participating in international experiments at CERN and work there temporarily.
Annual contributions of the Member States of CERN in 2008 is 1075, 863 million Swiss francs (about 990 million US dollars).
In 2013, CERN was awarded the Gold Medal of the Niels Bohr - Award of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) - as an example of international collaboration of scientists from many countries of the world.
Computer technology at CERN h3>
In addition to discoveries in physics, CERN became famous for its walls has been proposed hypertext project of the World Wide Web. English scientist Tim Berners-Lee and the Belgian scientist Robert Cailliau, working independently, have proposed in 1989 a draft binding documents through hypertext links to facilitate the exchange of information between the research groups involved in carrying out more experiments on a large electron-positron collider (LEP). Initially the project was used only on the internal network at CERN. In 1991, Berners-Lee created the world's first web server, website and browser. However, the World Wide Web is becoming truly global only when they were written and published specification URI, HTTP and HTML. April 30, 1993 CERN announced that the World Wide Web will be free for all users.
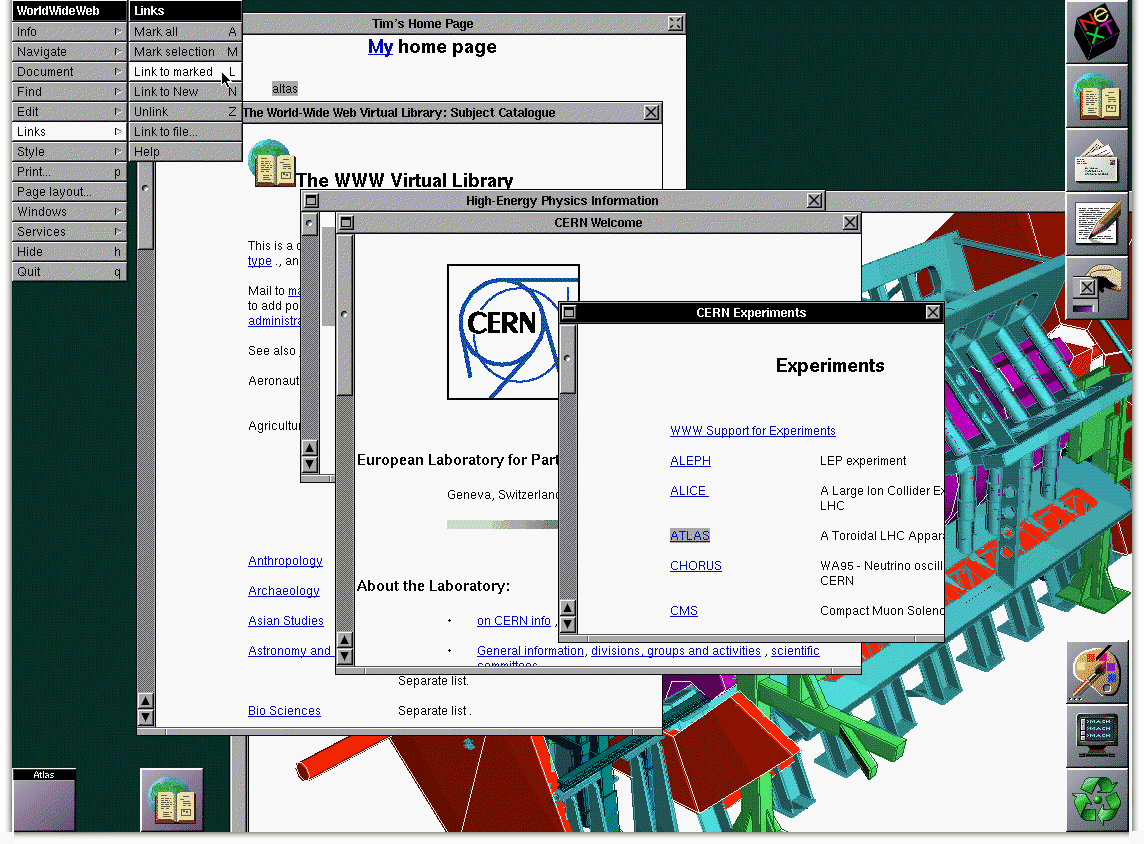
The first site in the world i>
Even before the creation of the World Wide Web in the early 1980s, CERN has been a pioneer in the use of Internet technology in Europe.
At the end of the 1990s, CERN has become one of the centers of a new computer network technology grid. CERN is welcome to join the network GRID, deciding that such a system will help to maintain and promptly handle the huge flow of data that will appear after the launch of the Large Hadron Collider (LHC). Led by CERN, was invited as partners the European Space Agency and national scientific organizations in Europe, created the largest segment of the network system - DataGRID.
At present, a large part of the CERN grid project Enabling Grids for E-sciencE (EGEE), and also develops its own grid services. This deals with a special section related to Collider - LHC Computing Grid.

CERN is also one of the two points of Internet exchange in Switzerland CINP (CERN Internet Exchange Point). It is collected and used its own distribution operating system Linux - Scientific Linux.
CERN staff Jason Stockman, Andy Yen and Wei Song created a popular web-based email service with encryption ProtonMail.
Achievements CERN h3>
By dostizhenieyam CERN include:
the first synchrocyclotron SC with an energy of 600 MeV (opened in 1957, closed in 1990); Proton Synchrotron PS, 28 GeV (1959); proportional chamber ( 1968); the world's first proton-proton collider ISR (Intersecting Storage Rings), 62 GeV (opened in 1971, closed in 1984); proton supercollider SPS, 300 GeV, later - 400 GeV (1976); opening of W-boson and Z-bosons (1983); collider LEP, ring length of 27 km, the energy of 45 GeV (launched in 1989, It stopped in 2000 for alterations in the LHC).

The exhibition "Universe of particles» i>
European Center for Nuclear Research, also known as the training center of scientific personnel. At its base to create a school in which students and young students can improve their knowledge in the study of particle physics, accelerator physics and computer science. For students, graduate students, school teachers and university professors are available internships, educational programs and courses are conducted in the native language of the listener, as well as summer school.
After CERN "lit up" in the book by Dan Brown's "Angels and Demons", the organization has become a place of pilgrimage masses of tourists. Management Center could not refuse hospitality and allowed to conduct tours. Guests are invited to visit the permanent exhibition "Universe of particles", as well as look into the research laboratory «ATLAS», which held one of the most high-profile experiments century - find hypothetical particle - the Higgs boson from, called "God particle" to the elements that make up dark matter. The flow of those wishing to see the LHC so big that it is better to book a tour for a few months.
Source: geektimes.ru/company/ua-hosting/blog/266828/
Western Digital began shipping 10-TB hard drives filled with helium
Amazing pictures of mountains in Pakistan with drone