1162
As NASA Virtual Reality helps not float away into space
33,406,768
The launch of SpaceX CRS-7 was lost almost 2, 5 tons of equipment < / a>. Among the ship's cargo capsule - points HoloLens. In the framework of the project Sidekick Microsoft has provided NASA's augmented reality glasses. The product has not been put on the market, but only demonstrated at the presentation of Windows 10 and the game conference E3.
It may seem that NASA is doing only the first tentative steps towards the use of virtual reality. In fact, the American space agency with BP has been running since the nineties.
In addition to moving at high speed microscopic objects, loss of consciousness and a failure of the suit at work in the open space there is a danger accidentally detach and float away from the station. Thanks to the numerous training the risk is minimal, but it provides. For example, even during the passage of astronauts gateway test their harnesses tethers, including a 26-meter of braided steel. Astronauts cling to each other. One of the astronauts fixes itself to the station. Then when you exit the Gateway leader first touches the end of his rope to a certain point in the outer parts of the station. At this point, both as an astronaut secured to the interior of the station and to the outside. Only then leader otstegnёt binding astronauts rope and secure to the outside of the second point. The second astronaut might get out of the gateway. 26-meter tethers are clipped, you need to make sure that they are not confused. If necessary, additional cables are taken.
97,323,695
Clay Anderson performs the first spacewalk, НАСА
Let the mounting risk of losing the station is very small, but the danger remains. In this case, the person can start slowly away from the station. It would be too difficult to catch using a spaceship - and undocking maneuvers may take a long time. To avoid this, the astronauts used jetpacks Simplified Aid for EVA Rescue ( SAFER , simplified device for salvation when spacewalk) . Unlike his older brother MMU (Δv ≈ 25 m / s), SAFER (Δv ≈ 3 m / s) - this no means of transportation, and the last salvation. Real SAFER was never used for its intended purpose, take place only if it tests the safety connection. This is where virtual reality comes in.
It started in the nineties. Telescope "Hubble» was launched into orbit in 1990 and from the beginning of the flights provided for maintenance and repair. The first took place already in 1993. Working with such sophisticated equipment as a telescope in space, space suits - this is a very complex operation. By the telescope need to fly up, it must capture and bring to the shuttle, and only then start repairing. A few days in space, and the clock in the suit - it is years of training on Earth. Astronauts studied with the equipment, as well as in the pool to simulate the conditions of outer space. Combining like was difficult. NASA started thinking how to improve the process of preparation. It was during those periods in the Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center in Houston began to develop a virtual reality laboratory (VR Lab).
85,063,574
Laboratory of virtual reality, NASA em>
What began as an experiment is now part of the training program. Today it operates 4-6 engineers of various kinds. Training to work in the open space, and training SAFER - are just two of the four goals of the laboratory. VR Lab is preparing to work with ISS robomanipulyatorom and physical adaptations to the treatment of goods and tools in microgravity. The latter is necessary because the station does not have the weight of the items, but still retain the mass, center of gravity and inertia. For training loads are suspended in a complex system of ropes stretched. So it is possible to simulate the mass of the object to 227 kg (500 pounds).
All equipment is made in the laboratory of NASA. The latest version of head-mounted display shows no visible delays. It has a resolution of 1200 × 800 and a viewing angle of 120 °. Input tools is not only a helmet and special gloves, which detect movements of the arms and flexing his fingers. Tracking input from other means, including the controller SAFER. For training manual knapsack performed many attempts with increasing difficulty as long as the astronaut learns quickly push the controller and perform a maneuver to return to the station. With the example of the work VR Lab and equipment can be found in several recently published videos.
For the process of training was set up detailed model of the ISS with all the important elements. This creates for the first time in out-of-lock a feeling that he was here - the similarity of the astronauts speak. NASA uses the package Dynamic Onboard Ubiquitous Graphics (DOUG), known for its publicly available version of EDGE .
Increasingly, virtual reality is used not only in the training center, but also in orbit. Scott Kelly will live on the ISS for nearly a year, during which time you can forget a lot of studied. Run the station a huge mass of electronics too expensive. To replace the helmet and sophisticated equipment used laptop screen. This solution has the disadvantage of a large mass, which increases the load on the neck with movement. This is the stage at NASA thought about using consumer helmet.
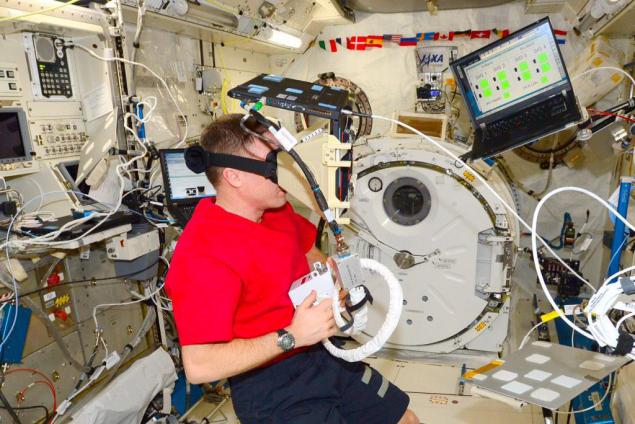

Terry Vёrts station trains use SAFER, picture of microblog astronaut em>
Perhaps in the future, astronauts will use virtual reality for entertainment and stress relief in the long flight to Mars. But while BP NASA - a working tool.
Based on materials статьи TechRepublic , response Clayton Anderson on Quora and страницы Virtual Reality Laboratory, NASA .
Source: geektimes.ru/post/253118/
The launch of SpaceX CRS-7 was lost almost 2, 5 tons of equipment < / a>. Among the ship's cargo capsule - points HoloLens. In the framework of the project Sidekick Microsoft has provided NASA's augmented reality glasses. The product has not been put on the market, but only demonstrated at the presentation of Windows 10 and the game conference E3.
It may seem that NASA is doing only the first tentative steps towards the use of virtual reality. In fact, the American space agency with BP has been running since the nineties.
In addition to moving at high speed microscopic objects, loss of consciousness and a failure of the suit at work in the open space there is a danger accidentally detach and float away from the station. Thanks to the numerous training the risk is minimal, but it provides. For example, even during the passage of astronauts gateway test their harnesses tethers, including a 26-meter of braided steel. Astronauts cling to each other. One of the astronauts fixes itself to the station. Then when you exit the Gateway leader first touches the end of his rope to a certain point in the outer parts of the station. At this point, both as an astronaut secured to the interior of the station and to the outside. Only then leader otstegnёt binding astronauts rope and secure to the outside of the second point. The second astronaut might get out of the gateway. 26-meter tethers are clipped, you need to make sure that they are not confused. If necessary, additional cables are taken.
97,323,695
Clay Anderson performs the first spacewalk, НАСА
Let the mounting risk of losing the station is very small, but the danger remains. In this case, the person can start slowly away from the station. It would be too difficult to catch using a spaceship - and undocking maneuvers may take a long time. To avoid this, the astronauts used jetpacks Simplified Aid for EVA Rescue ( SAFER , simplified device for salvation when spacewalk) . Unlike his older brother MMU (Δv ≈ 25 m / s), SAFER (Δv ≈ 3 m / s) - this no means of transportation, and the last salvation. Real SAFER was never used for its intended purpose, take place only if it tests the safety connection. This is where virtual reality comes in.
It started in the nineties. Telescope "Hubble» was launched into orbit in 1990 and from the beginning of the flights provided for maintenance and repair. The first took place already in 1993. Working with such sophisticated equipment as a telescope in space, space suits - this is a very complex operation. By the telescope need to fly up, it must capture and bring to the shuttle, and only then start repairing. A few days in space, and the clock in the suit - it is years of training on Earth. Astronauts studied with the equipment, as well as in the pool to simulate the conditions of outer space. Combining like was difficult. NASA started thinking how to improve the process of preparation. It was during those periods in the Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center in Houston began to develop a virtual reality laboratory (VR Lab).
85,063,574
Laboratory of virtual reality, NASA em>
What began as an experiment is now part of the training program. Today it operates 4-6 engineers of various kinds. Training to work in the open space, and training SAFER - are just two of the four goals of the laboratory. VR Lab is preparing to work with ISS robomanipulyatorom and physical adaptations to the treatment of goods and tools in microgravity. The latter is necessary because the station does not have the weight of the items, but still retain the mass, center of gravity and inertia. For training loads are suspended in a complex system of ropes stretched. So it is possible to simulate the mass of the object to 227 kg (500 pounds).
All equipment is made in the laboratory of NASA. The latest version of head-mounted display shows no visible delays. It has a resolution of 1200 × 800 and a viewing angle of 120 °. Input tools is not only a helmet and special gloves, which detect movements of the arms and flexing his fingers. Tracking input from other means, including the controller SAFER. For training manual knapsack performed many attempts with increasing difficulty as long as the astronaut learns quickly push the controller and perform a maneuver to return to the station. With the example of the work VR Lab and equipment can be found in several recently published videos.
For the process of training was set up detailed model of the ISS with all the important elements. This creates for the first time in out-of-lock a feeling that he was here - the similarity of the astronauts speak. NASA uses the package Dynamic Onboard Ubiquitous Graphics (DOUG), known for its publicly available version of EDGE .
Increasingly, virtual reality is used not only in the training center, but also in orbit. Scott Kelly will live on the ISS for nearly a year, during which time you can forget a lot of studied. Run the station a huge mass of electronics too expensive. To replace the helmet and sophisticated equipment used laptop screen. This solution has the disadvantage of a large mass, which increases the load on the neck with movement. This is the stage at NASA thought about using consumer helmet.

Terry Vёrts station trains use SAFER, picture of microblog astronaut em>
Perhaps in the future, astronauts will use virtual reality for entertainment and stress relief in the long flight to Mars. But while BP NASA - a working tool.
Based on materials статьи TechRepublic , response Clayton Anderson on Quora and страницы Virtual Reality Laboratory, NASA .
Source: geektimes.ru/post/253118/
Videobloger earned $ 4 million in 2014 and gave more than a million to charity
India has launched a test train, which uses solar energy