1376
Road to the Moon or the second generation of spacecraft
first generation of manned spacecraft showed that the space can be up to several days and is quite successful work. Therefore, the next generation went to more complex tasks, the crew of several people, rendezvous and docking, extravehicular activity, a long flight. More interesting to see how these problems are solved development teams on both sides of the ocean.
Introduction h4> It should be understood that the use of the word "generation" is somewhat arbitrary. The fact is that after the "East" in the USSR had to fly "Union", and initially no "Sunrise" was not planned. But the delay in the development of the "Union" on a background of American success led to the creation of a political solution to the ship, which could solve at least some of the new challenges.
Targets US h4> May 25, 1961, when the United States was only one flight into space on a suborbital trajectory length of 15 minutes, President Kennedy had already sent a proposal to Congress with a manned flight to the moon. Actively promote the idea of the president (famous speech «We choose to go to the Moon»). Objective of the mission to the moon to form a clear list of intermediate tasks that previously had to be solved:
- The crew of several people.
- The flight duration of 8-14 days.
- extravehicular activity (EVA).
- docking.
- The exact landing on Earth.
- The selection and training of crews for future lunar missions. The "Gemini" was officially launched December 7, 1961.
The objectives of the USSR h4> In the Soviet Union, unfortunately, occurred uncertainty goals and objectives. Was lunar program, but she did not have the full financial and political support of the government. There was a clear space program, designed for several years. Therefore, as a focus for future flights offered various experiments:
- The crew of several people.
- extravehicular activity (EVA)
- Long flight for two to three weeks.
- Flight completely female crew.
- Flying with creating artificial gravity.
- Flying with medical and biological experiments, such as the operation on the animal.
- EVA astronaut with autonomous means of transportation (without the cable that connects to the ship).
Tools excretion h4> Setting the RN "Sunrise" on the launch pad. Through the farm between the second and third stages of the combustion chamber 4 can be seen the RD-0108 unit "and". Chess coloring third stage is likely to mean that photo with one of the test starts. I>
"Sunrise" introduces a new modification of the R-7, which has already become the main "workhorse" of Soviet space exploration. Booster "Sunrise" has a more powerful third stage - the block "I", which increased its capacity up to ~ 6 tons. A mass of "Sunrise" rose slightly, to 5, 3-5, 6 tons, which means no weight problems for the ship.
To the orbit "Gemini" was used a modification of ICBM "Titan-II». Changes is to increase the reliability and redundancy of some nodes. Carrying capacity of 3, 5 tons of still far behind rockets USSR, which is very limited development of the ship. A specificity of the missile, which is designed as an ICBM, has led to the fact that the excretion was almost uncomfortable landing - on the end part of the second stage of the astronauts are overstretched 8, 5 "same" that is unique to launch manned spacecraft (usually not more than 4 g )
Exterior design elements h4>
Case form h5> and the USSR, and the US continued to follow its traditions - "Sunrise" flew under the fairing and had absolutely neaerodinamicheskie form similar "East". "Gemini" is developing the same firm («McDonnell Aircraft»), and that "Mercury", and both ships were very similar to each other.
The subdivision h5> "Voskhod" recurring pattern "of the East." Spherical lander and conical equipment compartment separated after braking. No longer need to aggregate compartment burned in the atmosphere, and the lander took dense layers of the atmosphere and was landing.
In the ship "Mercury" was the only part of the discharged brake motors. In developing the "Gemini" brake motors have developed into a full compartment, and behind him put equipment compartment. On returning to Earth first reset equipment compartment. Then fires brake motors. After braking already unnecessary compartment TDU also reset. The scheme looks a bit awkward, but has the convenience that you need without propulsion compartment brake less mass remaining ships, which saves weight brake motors.
Thermal protection h5>
The lander "Voskhod-2". Airlock added for clarity, in reality she was discharged before braking. I>
"Sunrise" repeated the idea of the "East" with a spherical descent module automatically occupies the desired position as "Roly-Poly" and the same thermal protection. At the same time, certain issues are mounting the lock chamber, which theoretically could cause a spin machine. To check the security shutter ring, similar to fixing the sluice chamber, was found on one of the satellite reconnaissance "Zenith" with same lander. The satellite successfully returned, the ring did not prevent the passage of the dense layers of the atmosphere, no parachute work.
"Gemini" was used already familiar to US heat shield. Pay attention to the unevenness of its erosion - it clearly indicates that the ship performed controlled descent. The center of mass is not located on the axis of the ship, so when running a small lifting force arose:
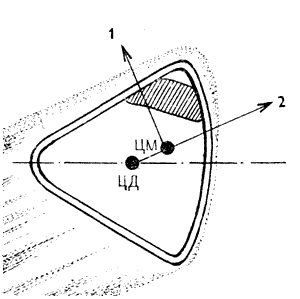
The lift force can be used to control the process of landing and take more accurately than in the case of uncontrolled descent.
Material thermal protection "Gemini" before and after landing i>
Brakes h5> On the "Sunrise" braking system consisted of the main brake fluid engines and spare the solid. From a security perspective, it was better than laminated engine on "East».
On the "Gemini" in the compartment TDU were four solid brake motor (more powerful version of engines for "Mercury"). Four identical engine braking improves reliability (failure of one does not mean a complete failure of inhibition), but just in case, when you first start up a manned "Gemini 3" height was selected so that in the event of failure TDU ship stalled on the atmosphere rather quickly.
Landing System h5> On the "Sunrise" refused bail astronauts landing. First of all, for the catapult was no place in the new cabin for 2-3 people. Secondly, the idea of the bailout failure should look at the background of the experience of "the East." Landing system consisted of two main parachutes, motor soft landing and probe the earth:
Reserve parachute on the ship was not. Security was increased using several dvuhkupolny system (first and last time in space of the USSR). Failure of one dome threatened serious injuries but was not fatal.
Overall, despite the lack of a reserve parachute landing system was progressive than the "Vostok". The combination of a parachute and a soft landing engines provide enough comfortable fit without having to eject from the ship serviceable.
On the "Gemini" was originally proposed to manage the landing on a folding wing Rogallo (by the way, this idea grew the modern hang gliders):
But the wing was developed slowly, and at some point in the NASA decided to go back to the already tested a parachute and landing on water. As a result, the ship set the domed main parachute. If he opens successfully, the astronauts change the mode on the two-point suspension, and the ship was getting into the water obliquely. Reserve parachute was not - in the event of failure of the main parachute astronauts had to eject.
The system of landing abandoned cumbersome and inefficient cushioning bag "Mercury", replacing it with oblique entry unit in water. This idea was great, it was used in the "Apollo" and will be used on vehicles designed to be splashed (eg, Orion).
Emergency Rescue h5> On the "East" rescue system was absent. Up to 27 seconds of crew rescue was impossible. In the event of an accident after 27 seconds the ship was separated from the rocket and emergency use standard landing system. Fortunately, during the time the program crashes on breeding was not.
On the "Gemini" used ejection seats. Since the booster used fuel pair UDMH / AT estimated engineers it should explode slower and explosion would be less than the explosion of oxygen-kerosene rocket. Therefore, according to engineers, ejection seats would have been enough. Ejection seats weigh less than a full recovery system and can operate the emergency rescue vehicle during landing.
Ejection seat "Gemini" had the most powerful engines of aircraft among peers. When you first try to start the "Gemini VIA", which failed because of fallen out of the nest cable, instructions had to eject. But the astronauts did not do, not least because of what happened at the trial: because little i> error timers triggering elements of salvation chair with a dummy knocked not had time to open the hatch. Astronauts feared for his health at ejection and would only catapult completely in extreme cases, may even be later than was necessary.
In terms of design, emergency rescue system better than ejection seats, so in a sense it was a step backward compared with the "Mercury". Fortunately, accidents and "fighting" for the bailout program was not time.
Engines orbital maneuvering and orientation h5> «Sunrise» used engines focus on compressed gas similar "East" and could not perform orbital maneuvers.
"Gemini" had two propulsion systems:
- System orbital orientation and maneuvering (OAMS - Orbit Attitude and Maneuvering System), which was used in normal flight and allows you to focus and to maneuver the ship to change the orbit.
- orientation system (RCS - Reaction Control System), which is nominally used at planting and could only turn the ship without changing its orbit.
The fuel was a couple of UDMH / AT. High boiling fuel with good specific impulse was much better hydrogen peroxide or compressed gas, and in the "Gemini" were besides sufficiently large amounts of fuel.
Overall propulsion system "Gemini" was extremely successful and the ideas and execution.
thermoregulatory system h5> «Sunrise» used the system of thermoregulation with shutters, similar to the "East." The system was simple, reliable and not satisfactory in operation.
"Gemini" system used liquid thermoregulation. The coolant absorbs heat from the crew and instruments in the cockpit and transfers it to the surface of the adapter (aggregate modules and TDU). The entire surface of the adapter (white) was heat radiator. The idea of such a system has been very progressive (better than the evaporator water on "Mercury"), but it had some problems. Even in the middle of the program (for example, on a mission to "Gemini 7"), she chips trick: the temperature in spacesuits then fell to + 4 ° C, then raised to an uncomfortable level.
System software EVA h5> Since both types of ships envisaged task extravehicular activity, it was necessary to develop appropriate systems to astronaut / cosmonaut get out of the ship and back.
On the "Sunrise" was installed inflatable airlock. When folded, it takes up little space, and after disclosure allowed to leave the ship without dumping it in the atmosphere.
Left - airlock folded to the right - in the open. I>
Scheme of the lock chamber. I>
On the "Gemini" cabin depressurized completely, and for spacewalks to use standard boarding hatch. When first spacewalk revealed that the developers forgot about cold welding of metals in a vacuum - there were problems with the opening of the hatch.
If we compare these two approaches to the implementation of the tasks of extravehicular activity, they both have their pros and cons. Special gateway beneficial for large volumes of ship and atmosphere with great pressure. In this case, depressurization loss smaller. Also, it is advantageous in that the mode is not broken appliances and other contents of the cab. No need to design guaranteed to work in a vacuum ship devices. EVA with depressurization of the ship is beneficial for small ships with an atmosphere with little pressure. Both variants have been used successfully in the future - on the "Apollo" EVA was with depressurization of the ship, and now on the ISS are special compartments with locks - all ISS can not depressurize.
The docking system h5> «Sunrise" had no connecting devices.
The "Gemini" nose used for placement of antennas and docking radar. Also, the nose was used for docking - at target "Agena" has a corresponding recess with the docking locks, electrical connectors, etc. at the end.
The internal design elements h4>
Toolbar h5>
A "Sunrise" recognizable development toolbox "East". The main drawback is that, despite the rotation of the crew seats (they are in the foreground at the bottom, seen from the right side seat) controls were placed in the same way as in the "East", causing discomfort during manual operation. Portholes are small, but are located on different sides.
Control Panel "Gemini" develops aviation approach with a variety of devices. Windows are located on an aircraft that provides an excellent view forward. Side windows was not.
We should also note the appearance of the onboard computer. The system could not pilot the ship on their own (as it did then board computers "Apollo"), but seriously helped astronauts during docking and landing.
Life support system h5> On the "Voskhod-1" flying without spacesuits because of lack of space. On the "Voskhod-2" space suits were due to the need spacewalks. On the "Voskhod" atmosphere was maintained close to the earth.
On the "Gemini" flight occurred in spacesuits, and the atmosphere was similar to "Mercury" - pure oxygen with reduced pressure.
From the standpoint of convenience "Gemini" was very uncomfortable ships. Astronauts were very few places, it was not possible to stand up, stretch out full-length, stretch their legs. The situation is complicated by the smells of unwashed bodies (it was not possible to maintain the purity of the body, there was not a replacement of clothing), and using the toilet. Especially hard for astronauts on long missions - 8 days "Gemini 5" and two weeks "Gemini 7". The crew of the "Gemini 5" called his mission "for eight days in the garbage," and astronauts "Gemini 7", recalling the mission, said that the last few days have been especially heinous, and accuse each other (now, after so many years jokingly) in too frequent toileting.
Electrical h5> «Sunrise" for the supply of used batteries. Despite the shortcomings of batteries for long missions ship with dogs successfully forth to 22 days, ie, could well be used for a long flight of people.
"Gemini" was used to fly the most appropriate duration of 2-3 weeks the system - fuel cells. Hydrogen and oxygen combine to produce electricity, and the resulting water is consumed by the crew. Fuel cells have shown some great (if we disregard the problem in the first flight) and then used to "Apollo" and "Space Shuttle».
Conclusion h4> «Sunrise", being, in fact, hastily modified "East", despite its technological backwardness, will solve important political task. First flight crew of three and the first output of the open space are widely covered by media worldwide.
- The crew of several people.
The market of portable devices has grown by almost 700%
The first step to smart home and remote control home appliances