1171
15 most expensive space projects and missions
Including construction, ground training and start-up, two-year project "Gaia" cost $ 1 billion, which exceeded initial estimates by 16%. The purpose of the mission was to obtain 3D-card billion stars and cosmic objects that make up 1% of the Milky Way galaxy. To orbit the Earth Observatory brought the Russian spacecraft "Soyuz ST-B."

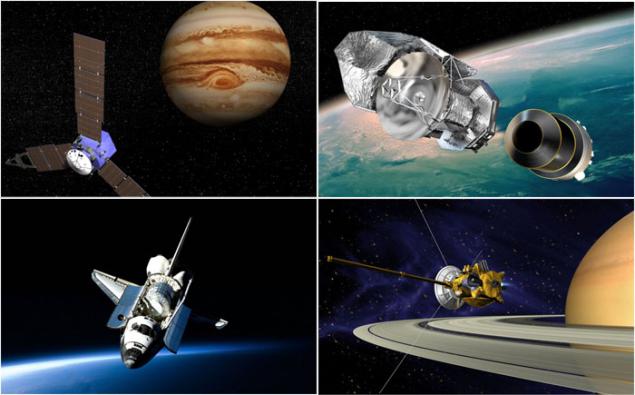
Mother ship Atlants in October 1989 orbited interplanetary station "Galileo", which went to the side of the planet Jupiter and reached its orbit in December 1995. The purpose of the mission was to study the planet and its satellites. It is clear that the study of the solar system is not a cheap exercise. The cost of the mission was 1, 4 billion dollars. By the 2000s a very strong radiation from the planet damaged station, besides almost out of fuel. Flight Director decided to destroy the machine, dropping him to the planet, not to pollute the moons of Jupiter.

Autonomous interplanetary station "Juno" according to preliminary estimates had to do $ 700 million, but in June 2011, the project was worth 1, 1 billion dollars. The station was launched into space in August 2011, it is expected that it will reach Jupiter in October 2016. It will be on the orbit of the planet and collect data on the composition of its atmosphere, gravity, and magnetic fields. The mission will be over when the station circled around Jupiter 33 times. On board are in some sense the strange objects for a serious mission: figures from the designer LEGO (Galileo Galilei, the god Jupiter and his wife Juno). True designer cubes are made of aluminum, as the plastic used is not withstood the test of cosmic cold.

Space observatory "Herschel" the largest in the history of space research infrared telescope, which worked from 2009 to 2013, was built by the European Space Agency. In 2010, the cost of the project amounted to 1, $ 3 billion, which included the launch of scientific apparatus and costs. In May 2009, the Observatory has reached orbit and worked until April 2013, when the exhausted possibilities of cooling agents. Apparatus and so exceeded expectations, as calculations showed that the work will stop at the end of 2012. The contribution of NASA is to supply special technological tools. The telescope, which was named in honor of William Herschel sulfur, studied the planet Uranus.

On board the International Space Station in 2011, it has been found the most expensive equipment for the study of cosmic rays, antimatter and dark matter - Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS-02). Initially, calculations showed that the cost of the project will be limited $ 33 million, but due to a number of difficulties and technical problems the cost had risen to $ 2 billion. In 2012 the equipment already recorded 18 billion cosmic rays.

To carry out research distant from Earth space objects in our solar system, especially the planet Saturn, was drafted with the participation of spacecraft "Cassini-Huygens mission." Autonomous interplanetary complex consisting of two modules (the orbital and atmospheric, landing on Titan), was launched in 1997, and in 2004 he reached the orbit of Saturn. It is not surprising that the study of the second largest planet of the solar system under the auspices of NASA, the European Space Agency, the Italian Space Agency, at a cost of 3, 26 billion dollars.

Laboratory of NASA's Mars Exploration was responsible for landing the rover "Kyuriositi" on the surface of the planet. The cost of this project, which fortunately turned out to be successful, was 2, 5 billion dollars, although intended to be limited $ 650 million. In August 2012 the rover landed on Mars in Gale Crater, and today he is on the planet 687 days - Martian year. Rover transmits various data about the planet: on the forms of life, climatic features, geological features.

Prior to the orbital station "Mir" in 2001, descended from orbit and fell into the Pacific Ocean, it lasts 5 years since 1986. Yuri Koptev, director of the Russian Federal Space Agency, it was noted that for the entire period of the complex, the purpose of which was to study the microgravity, was spent 4, $ 2 billion. In addition to microgravity, the station conducted experiments in various fields of science: physics, biology, meteorology and astronomy. At the station "Mir" were set records for the length of stay of man in space, for example, Valery Polyakov spent 437 days in orbit and 18 hours.

Each state has established space in Earth orbit its positioning system. No exception is Russia, which has its own system of navigation "GLONASS". During the period of its operation from 2001 to 2011 was spent 4, 7 billion dollars, and from 2012 to 2020 on the functioning of the system $ 10 billion. Unlike the US navigation system GPS, Russian station is rarely used, although it is considered a priority Russian space project, which spend huge sums of public funds. The whole system "GLONASS" includes 24 satellites. Development of the navigation system of the USSR began in 1976.

For the implementation of the European project for the withdrawal of the orbit of the Earth navigation system "Galileo", as a response to the American system of GPS, spent 6, $ 3 billion. Today, these two systems overlap one another and are assisted, and in case of failure of one, the other can replace it. European navigation system consisting of 30 satellites, two of which are not displayed on the right orbit until 2019 passes between completion and improvement.

Back in 1996, scientists and experts of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency began to engage in the development of space telescope, which was named in honor of James Webb. In 2013 the cost of the project amounted to 8, $ 8 billion. During this period, there were financial problems, for example, in 2011 it was necessary to find $ 3 billion, and the project was on the verge of closing, when the US Congress has funded further work in the amount of $ 8 billion. The telescope is expected to bring into space in 2018.

As part of a global positioning system are 24 satellites that are able to determine the location of a person anywhere in the world. To display all the satellites into Earth orbit expected to spend $ 12 billion, but did not consider that the system requires constant investments to ensure its functionality, and this $ 750 million. Global Positioning System and the program Googlemaps, which works based on it have become an integral and indispensable part of not only a military complex, but also everyday life. This year, planned to launch an additional satellite, but the project was suspended.

In 1972, the program was developed for reusable spacecraft, which included the implementation of 135 scheduled flights to six aircraft or reusable shuttles, aboard two of them, Columbia and Challenger, killed 14 astronauts at different times. The last flight of space shuttle Atlantis was launched in July 2001, and he returned to Earth in July 2011. To ensure the entire program has been spent 196 billion dollars, although the original budget was planned at 7, 45 billion dollars, adjusted for inflation, 2011 amounted to $ 43 billion.

Not surprisingly, the International Space Station in its scope and importance of the destination is considered not only the most expensive spacecraft, but also the most expensive in the history of mankind. Its cost is estimated at data presented in 2010, 160 billion dollars, and in connection with operating costs amount is constantly increasing. From NASA's development of the project has received $ 59 billion from $ 12 billion in Russia, the European Space Agency and Japan - at $ 5 billion. Costs associated with the delivery of cargo to the station space shuttle on one flight were 1, 4 billion dollars.

In the history of space exploration project "Apollo" was considered not only very important, but one of the most expensive. Upon completion of the development in 1973 it was estimated at 25, 4 billion dollars, adjusted for inflation in 2005. The initial amount that should have been allocated to the project amounted to $ 7 billion. The goal that put the US President John F. Kennedy regarding delivery man on the moon, was carried out in 1969 as a result of the mission "Apollo 11". Then the astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin were able to Take a short walk on the moon.