689
NASA: 30% of space debris in orbit - a consequence of a 10 "accident"
10 missions from 5160 generated 30% of the total amount of space debris orbiting the Earth
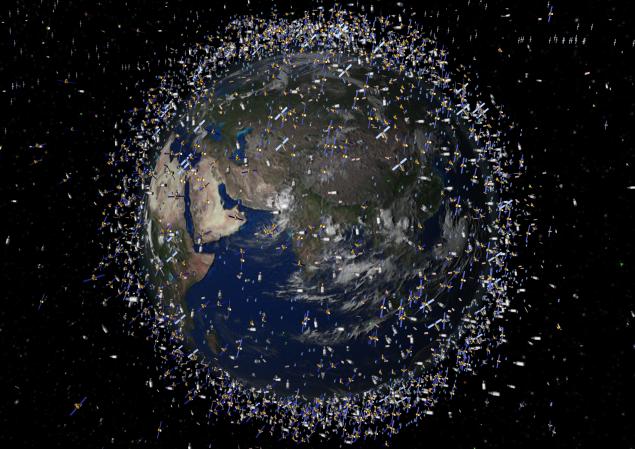

NASA Agency and other space agencies, research organizations track the wreckage of spacecraft in Earth orbit. With each launch missiles, with each incident in orbit of debris is growing, and they represent a danger for future missions.
Clash of the unit cost of many hundreds of millions of dollars with a small fragment is fraught with the loss of this unit for the science / business. In this debris and as much as the collision of objects in space, they are separated by even a greater number of parts which, when confronted with something else, give rise to new objects. And so on and so forth - almost a chain reaction. There are even fears that the debris can be removed to make space for a person. But few people know that a third of all the debris - the result of all 10 accidents in space, which can be called "garbage."
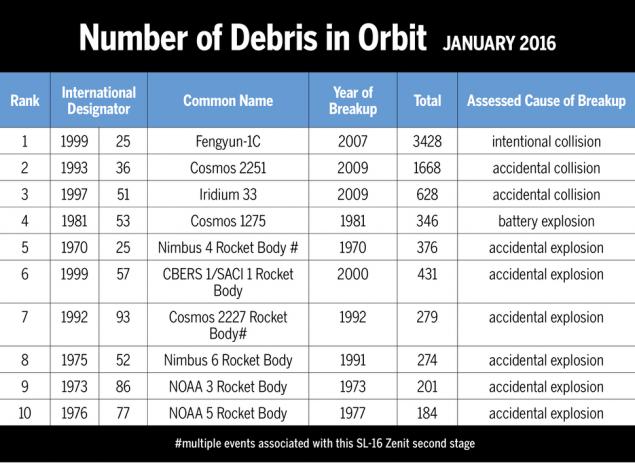
The leader among such missions is to destroy the Chinese Fengyun-1C spacecraft. The Chinese satellite destroyed in a special operation carried out in 2007. China then announced that they were testing, during which tested the very possibility of remote destruction of satellites in Earth orbit. This operation is very complicated life for all TsUPam on Earth, as well as professionals who are responsible for the launch of the spacecraft. Fengyun-1C has become the source of 3428 cataloged debris is 20% of the debris.
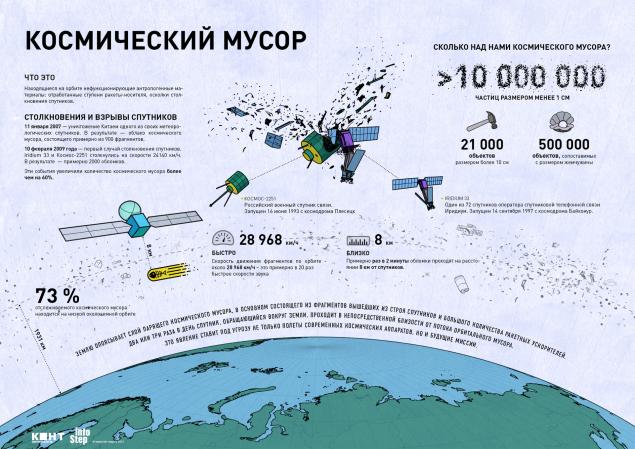
detailed infographics on the situation in orbit
Since 1957, NASA space missions naschitalo 5160, of which only 10 are the source of a third of all debris in Earth orbit vehicles.
A huge amount of debris produced in the course of "Space 2251" collision of satellites and Iridium 33. This is the first orbital "accident" when the two spacecraft collided in orbit. The collision took place February 10, 2009 on the territory of the Russian Federation, at an altitude of 788, 6 kilometers. The rates of both satellites were approximately equal and amounted to about 7470 m / s, the relative velocity is equal to about 11, 7 km / s.
What to do with all this rubbish, no one knows. Various companies, agencies and individuals develop clean projects near-Earth space, but the practical implementation of all this, no one has yet started.
By the way, I recommend SF story Dzh.Uayta "deadly dust". It is interesting told about future missions to eliminate debris and the rules for the new missions.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/274554/

NASA Agency and other space agencies, research organizations track the wreckage of spacecraft in Earth orbit. With each launch missiles, with each incident in orbit of debris is growing, and they represent a danger for future missions.
Clash of the unit cost of many hundreds of millions of dollars with a small fragment is fraught with the loss of this unit for the science / business. In this debris and as much as the collision of objects in space, they are separated by even a greater number of parts which, when confronted with something else, give rise to new objects. And so on and so forth - almost a chain reaction. There are even fears that the debris can be removed to make space for a person. But few people know that a third of all the debris - the result of all 10 accidents in space, which can be called "garbage."
The leader among such missions is to destroy the Chinese Fengyun-1C spacecraft. The Chinese satellite destroyed in a special operation carried out in 2007. China then announced that they were testing, during which tested the very possibility of remote destruction of satellites in Earth orbit. This operation is very complicated life for all TsUPam on Earth, as well as professionals who are responsible for the launch of the spacecraft. Fengyun-1C has become the source of 3428 cataloged debris is 20% of the debris.

detailed infographics on the situation in orbit
Since 1957, NASA space missions naschitalo 5160, of which only 10 are the source of a third of all debris in Earth orbit vehicles.
A huge amount of debris produced in the course of "Space 2251" collision of satellites and Iridium 33. This is the first orbital "accident" when the two spacecraft collided in orbit. The collision took place February 10, 2009 on the territory of the Russian Federation, at an altitude of 788, 6 kilometers. The rates of both satellites were approximately equal and amounted to about 7470 m / s, the relative velocity is equal to about 11, 7 km / s.

What to do with all this rubbish, no one knows. Various companies, agencies and individuals develop clean projects near-Earth space, but the practical implementation of all this, no one has yet started.
By the way, I recommend SF story Dzh.Uayta "deadly dust". It is interesting told about future missions to eliminate debris and the rules for the new missions.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/274554/