3171
Breitspurbahn - Railway Third Reich
So, my friends, - YaPovtsy. I became interested in one topic about which I have you now and tell. I had vaguely heard about the fact that in the 40 years in Hitler's Germany was being developed broad-gauge railway. And, purely by chance, I came across this topic again in Wikipedia. The topic is interesting enough, so I began to look for the Old and the other resources (which I must say was surprisingly little). I present to you the results of their excavations.
Fasting does not claim to originality and authorship, as I used existing sources, a text compiled into a single whole, something he has added. Figures from the Internet.

Background
The first railway lines were long before the steam-powered engines. In the XVI century in the coal mines of Germany used wooden railway tracks, and in the XVIII century began to replace the wooden rail to rail.
For a long time the railways used only in the mines. The first rail road with regular passenger traffic was English railway, built in 1806, between the fishing village of Swansea and Mumbles. As draft animals used horse-drawn carriages as a really efficient locomotives at a time did not exist.
"Railroad Swansea-Mumbles»

The beginning of mass construction of railways for freight and passenger traffic due to the industrial revolution of the XVIII century. While many engineers were working on the self-propelled steam engine for the crew, but the most successful was the car of George Stephenson. Subsequently, Stephenson was invited to participate in the development of the railway wealthy English industrialist Edward Pease, who was authorized by Parliament to service coal mines in Darlington. Coal was delivered to Stockton, where he loaded on the ships. Stephenson has developed new principles of steam locomotive, perfecting his early achievements and, in 1825, it was opened Stockton-Darlington railway.
"Stockton-Darlington railway»

I must say that in the beginning there was no uniform standards gauge railway track, but most of Europe has adopted a standard railroad George Stephenson (1435 mm), which is standardized by the use of web width cartage with two horses in harness.
The first railway to the crews on the steam-powered in Russia became Tsarskoye Selo railway, built in 1836, it can also be considered the first broad-gauge rail tracks - its width is 1829 mm. However, after 1897 the railway was converted to the 1524 mm gauge and the track has become the standard in Russia until 1970.
The first project for the radical expansion gauge railways in Europe spent Isambard Kingdom Bryunnel - British engineer and one of the major figures of the Industrial Revolution. His project involved the use of track width 2140 mm. Railroads led Brunel built the company «Great Eastern Railway». These roads have proven themselves in operation. But in 1864 began the conversion of these tracks on the track of 1435 mm, the time has become the standard in England already.
Since then, the use of broad-road was forgotten ...
"Railway Brunel»

New German idea of Hitler
After Hitler came to power, he began to hatch plans for the restructuring of large cities in Germany with a new monumental way corresponding to its vision of the future cities of the Third Reich. Land of flooded buildings, and across Germany started to reach the highest quality highways.
Aesthetic ideals, expressed in the first tastes of Hitler himself, it was announced the return to the ancient classics, which at the same time creatively processed minimalist spirit harsh Teutonic traditions. The massive size, chopped rectangular shapes, endless colonnades and arches - even Roman emperors, on the idea of the Fuhrer, had to bow before the power of the Third Reich, expressed in architecture.
In 1932, architect Albert Speer, received the first orders for the restructuring of the objects of the NSDAP. In 1933, by order of Goebbels, Speer rebuilt the building of the Reich Ministry of Public Enlightenment and Propaganda of the Third Reich. In the same year, Speer met with Hitler, who noticed his talent and appointed deputy architect Paul Ludwig Troost and ordered restructuring the Reich Chancellery.
"Facade of the Reich Chancellery»

Speer quickly went into Hitler's private circle, and in 1937, he was appointed Inspector General of the imperial capital for the construction, with the task of reconstruction of Berlin. In 1938-1939, he developed a master plan for the reconstruction of the German capital.
"Part of the project for reconstruction of Berlin's main streets. In the foreground - Palace Hitler »

Everything changed after the outbreak of war with the Soviet Union. Germany was required to develop new plans for the land "lebensraum" in the postwar period. Sea lines of communication and highways could no longer meet the needs of Germany and, in September 1941, Reich Minister of weapons and ammunition Fritz Todt, proposed to build a railway heading to a track of a much wider between Germany and Ukraine. Hitler quite warmed to the idea and said: "Building a wide railroad, maybe bring us difficulties, but we will not allow themselves to be intimidated." As a consequence of this project he called "having strategic importance." I must say that Hitler saw in this project a huge prospect for the implementation of their plans to rebuild Germany. Broad-gauge railway fits perfectly into the monumental architectural projects of the Third Reich and Hitler had already seen trans-European highway, on which of the major industrial cities in Germany with incredible urgency moving troops, weapons and cash are increasingly expanding the territory conquered by them in the course of a victorious war.
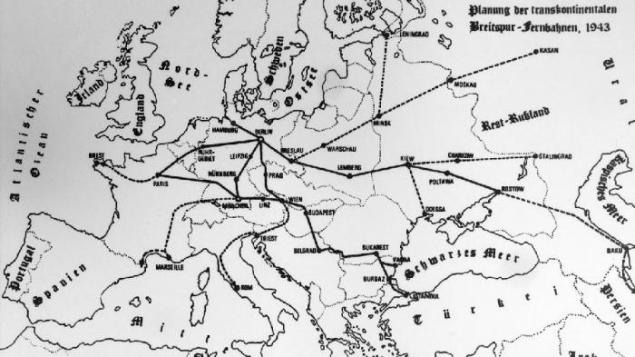
Suggested routes:
East-West: Rostov-on-Don - Donetsk - Poltava - Kyiv - Lviv - Krakow - Katowice - Wroclaw - Cottbus - the world capital of Germany (Berlin)) - Hannover - Bielefeld - Ruhr region - Aachen - Liege - Saint-Quentin - Paris
North-South-East: Hamburg - Wittenberg - the world capital of Germany (Berlin) - Leipzig - Gotha - Bamberg - Nuremberg - Munich - Simbach am Inn - Linz - Vienna - Bratislava - Budapest - Belgrade - Bucharest - Varna / Burgas - Istanbul
North-South-Parallel: The capital of the world, Germany (Berlin) - Dresden - Ústí nad Labem - Prague - Jihlava - Znojmo - Vienna - Trieste - Rome
East-West 2: Munich - Augsburg - Stuttgart - Karlsruhe - Metz - Reims - Paris - Marseille - Spain
"Routes Breitspurbahn»
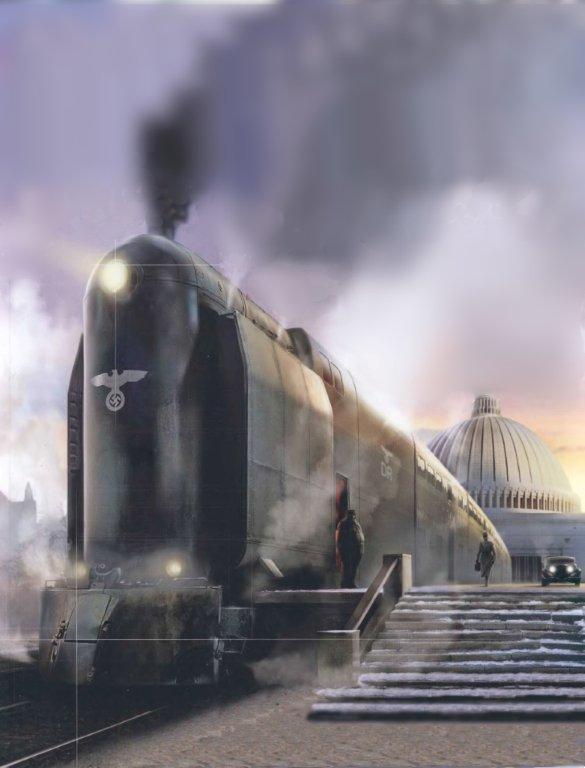
Curator and head of project of construction of the road was broad-appointed Fritz Todt. All the arguments of experts Deutsche Reichsbahn of possible difficulties of this project and of the incompatibility of such a road with a conventional railway technology, which would require the construction of additional infrastructure, rejected. He later recalled: "Questions the need for and feasibility of these huge highways were considered minor and never stood on the first page of the agenda. In essence, it's up to them had never reached. Perhaps not everyone knows that, but the motivation of the project is not to be sought in relation to the ambitions of European railways. This project is of value in itself: a monumental building in Hamburg, Berlin, Nuremberg, Munich meant the corresponding road between the cities ».
"Reich Minister of weapons and ammunition Fritz Todt»

After heavy defeats on the eastern front the discussion of building new railways postponed, but May 24, 1942 at the headquarters of the Fuehrer held a meeting, which was attended by Albert Speer, Reichsleiter Martin Bormann and the Minister of Railways Dropmyuller. At the meeting Hitler defined the basic parameters of the new railway. So, in his opinion, the track width should be 4 meters, width of the car 6 meters, and height should be 5 meters. Hitler explained his demands: "It must be roomy, because the whole family will live there for a few days. But we will do one-story restaurant. Six meters wide, long and thirty-five high. Yes, right palace banquet hall, are not you, Minister Speer? ". Residential cars Hitler assumed two-story, with a central corridor on both sides of which offers comfortable bedrooms. Further, Hitler demanded that count Dropmyullera capacity boxcar. By calculation it turned out that the car of this size could take a weight of 100 tons.
Project Manager «Breitspurbahn» was appointed doctor of technical sciences Gunter Vince.
"Doctor of Technical Sciences Gunter Vince»

April 5, 1943 Dr. Gunter Vince made a report, which outlined the technical features of the project. On the basis of the analysis and all sorts of calculations established track width of 3,000 mm. The optimum value of the diameter of the wheel, taking into account the parameters of velocity, rotation angles, axle loads, turned 1250 mm.
Due to promising areas of the Third Reich, the maximum train speed of 300-400 km / h were rejected as having no practical value. And at a speed of 250 km / h in a sleeping car is not a problem to reach any point of the empire from Rome to Berlin - 1627 km, from Bucharest - 1759 km, to Moscow - 1923 km to Istanbul - 2429 km. Therefore, all the calculations were made for a maximum speed of 250 km / h for passenger trains and 100 km / h for freight.
The problem of resistance to air flow is very important when oncoming traffic gigantic trains with a speed of 250 km / h or when following in the tunnels solved special sleek trains. Turning radius of the train was 180 degrees 500 m.
Even with the latest braking systems proposed by Knorrbremse AG, calculated braking distance at a speed of 250 km / h was set in 1600 meters during emergency braking, and 3000 m in the ordinary.
At such speeds and braking distance optical signaling system is ineffective, especially in snow or fog. Therefore, we developed a new system that is somewhat reminiscent of modern electronic: using high-frequency sensors, all information displayed on the operator console and engine room.
The total weight of the composition of trade is estimated at 10 000 tonnes (compared to the mass of the most difficult contemporary compositions - up to 2000 m). If necessary, the three freight trains could be combined into one, with a total mass of 30 000 t. The length of a freight train with a locomotive was 1100-1200 m (maximum length of a modern, but without a locomotive - about 500 m). If the length of only twice the mass increased to five or seven times. Attention was paid to the new systems of heating, ventilation, lighting, trains, because the window, for example, at such speeds can not be opened.
Rate it, even approximately, the cost of construction Dr. Vince difficult, noting that the project must first be created an entire industry.
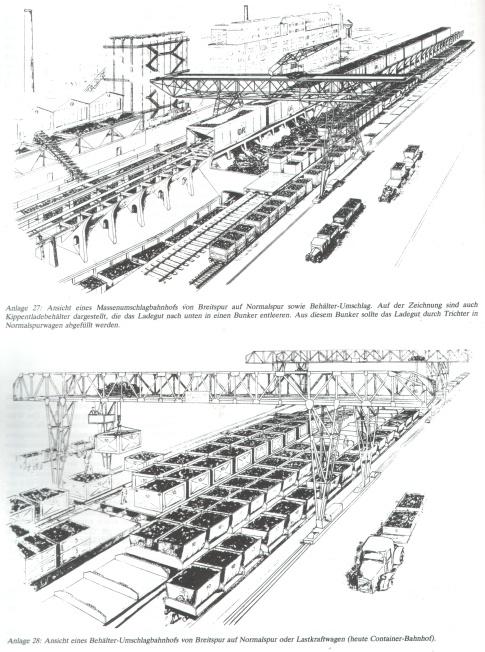
Recommendations related to the laying of tracks contained in the secret work of Dr. Rumlera. Calculations profile rail loadings on sleepers, decking and schemes are ways to strengthen the soil. In other documents we are talking about interchanges, tunnels, office buildings, hangars, bridges. A special case - the railroad tracks in towns and railway stations. On the sketches and models - different architectural solutions for Munich, Nuremberg, Linz, Berlin.
"The wheel trolley for a new type of cars & quot;

It was prepared with five volumes of technical documents, which contained detailed descriptions of all types of trains future. Each volume has an application with technical diagrams and drawings.
Tom A. "Locomotives"
Drawings of 33 commodity and high-speed locomotives and multiple shunting developed by Krauss-Maffei, Henschel, Borsig, BBC, Krupp, SSB, RZA Berlin, Schwartzkopff, RZA München, Wien-Floridsdorf etc.
Among them - the steam turbine electrical and mechanical, diesel-hydraulic, steam, diesel, electric, gas turbines, and other engines.
For high-speed locomotives envisaged:
• maximum speed of 200-250 km / h
• for commodity - 100 km / h
Power:
• freight trains - 12 900-40 000 hp,
• passenger - 11 350-33 300 hp
Tom V. "electricity traction"
European plan for the electrification of railways and documentation for three to five trade and high-speed passenger electric locomotives and multiple shunting locomotives.
Approximate parameters of electric commodity:
• Maximum speed - 100 km / h
• capacity - 25 500-28 600 hp
For high-speed electric locomotives:
• Maximum speed - 250 km / h
• capacity - 12 500-21 100 hp
Tom C. "Motor Train"
Passenger train without a locomotive, where the first car - the engine, the number of cars - from 2 to 10, the maximum speed - 250 km / h.
Drawings of various trains, diesel-electric, diesel-hydraulic, "trains" with 5 or 8 cars, seating, sleeping and special.
Option engine train: a restaurant car, 2 intermediate and 2 end car.
The end cars are the same, only the luggage and a post office can be interchanged when moving in one direction or another.
An example of the device end motor car
Ground floor:
• The cab
• lobby
• staff room
• engine room
• luggage compartment
• toilet
• washrooms
• showers
Upper floor:
• overview Hall
• Deck for walking
• Ten of the third class compartments
• two toilets
Total number of beds:
• 80 - in the third grade
• 42 - on the deck for walking
• 26 - in the review room
• Total - 148

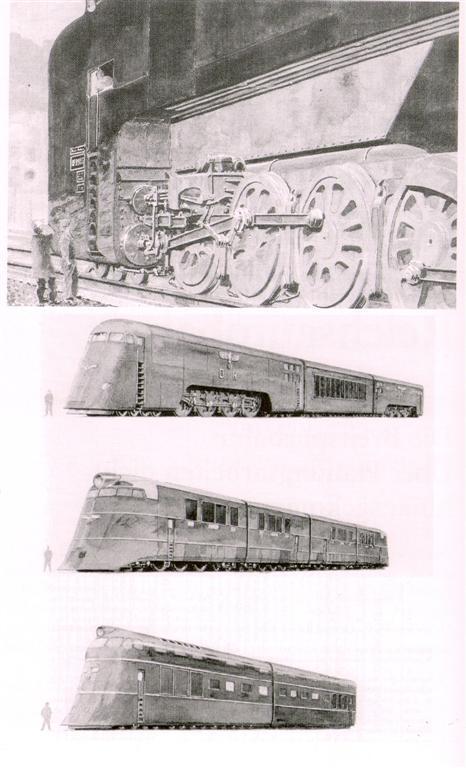
"The appearance of the locomotive Breitspurbahn»
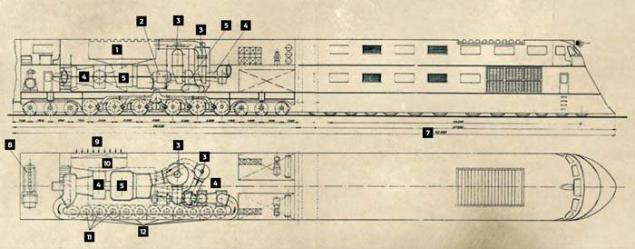
The device locomotive Breitspurbahn
1. Heater Air
2. Start the engine
3. The combustion chamber
4. Air cooling
5. The gas turbine
6. Fuel
7. Total length of the locomotive
8. Diesel-electric starting system
9. Air intake
10. oil cooler
11. Fans
12. Intercooler
Tom D and E. "The cars of passenger and freight trains of all types"
Among the special carriages of passenger trains:
• wagon cinema with 196 seats
• common carriage for 192 seats with a reading room, a cafe, a bar, a conversation, luggage and 12 toilets (eight on the ground floor and 4 on the top)
• comfortable with the car seats / berths for ostarbeiters (Eastern workers) to 480 seats dining room, pantry, 18 toilets, washrooms, where each seating position is much wider and more comfortable than modern trains.

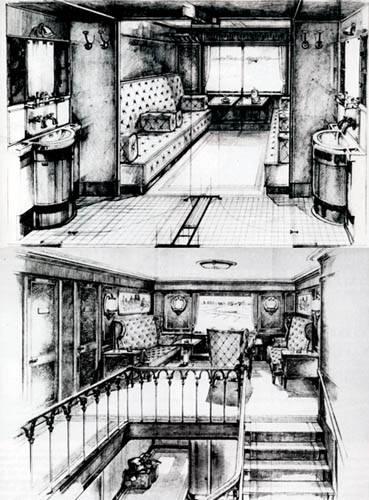
Example devices "bath" car
Ground floor:
• Hair salon for ladies and gentlemen
• 4 bathrooms
• 20 shower
• 2 waiting room
• room for the staff
• Technical compartment
• 2 laundry room
• 4 toilets
Upper floor:
• rooms for smokers and non-smokers (120 seats)
• kitchen for cooking to order
• confectionery
• pantry
• 2 staff rooms
• 3 toilets
Assumes different options formulations
Regular daily train:
• 1st wagon - postal and baggage car
• 2nd - third grade
• 3rd - third class dining room
• 4th - first, second and third classes
• 5th - diner
• 6th - the first and second classes
• 7th - first, second and third classes
Total first-class seats - 96, the second - and third 288 - 1100.
The dining car is a dining room for 130 seats of the first and second class and 176 - the third, as well as a restaurant on 172 seats.
Long-distance trains. Seven wagons where:
• 1st wagon - postal and baggage car
• 4th - "bath"
• rest - passenger
First-class seats - 32, the second - 82, and the third - 624, a restaurant with 200 seats.
Train "suite":
• 1st wagon - postal and baggage car
• then 2 passenger
• 2 dining car
• more passenger car
• and the car-cinema
First-class seats - 144, the second - 432.
Dining room for 260 seats of the first and second classes, a restaurant with 400 seats.
Number of seats in the train for ostarbeiters (also 7 cars) was 2 880.
As for freight wagons, here you can find cars for transportation of coal, grain, cars, machines, non-standard and oversize cargo, mail and refrigerated cars, all kinds of tanks and even the platform for the transport of vehicles.
Work on the railway were to end the war, but has not been completed.
On this I have everything.
Fasting does not claim to originality and authorship, as I used existing sources, a text compiled into a single whole, something he has added. Figures from the Internet.

Background
The first railway lines were long before the steam-powered engines. In the XVI century in the coal mines of Germany used wooden railway tracks, and in the XVIII century began to replace the wooden rail to rail.
For a long time the railways used only in the mines. The first rail road with regular passenger traffic was English railway, built in 1806, between the fishing village of Swansea and Mumbles. As draft animals used horse-drawn carriages as a really efficient locomotives at a time did not exist.
"Railroad Swansea-Mumbles»

The beginning of mass construction of railways for freight and passenger traffic due to the industrial revolution of the XVIII century. While many engineers were working on the self-propelled steam engine for the crew, but the most successful was the car of George Stephenson. Subsequently, Stephenson was invited to participate in the development of the railway wealthy English industrialist Edward Pease, who was authorized by Parliament to service coal mines in Darlington. Coal was delivered to Stockton, where he loaded on the ships. Stephenson has developed new principles of steam locomotive, perfecting his early achievements and, in 1825, it was opened Stockton-Darlington railway.
"Stockton-Darlington railway»

I must say that in the beginning there was no uniform standards gauge railway track, but most of Europe has adopted a standard railroad George Stephenson (1435 mm), which is standardized by the use of web width cartage with two horses in harness.
The first railway to the crews on the steam-powered in Russia became Tsarskoye Selo railway, built in 1836, it can also be considered the first broad-gauge rail tracks - its width is 1829 mm. However, after 1897 the railway was converted to the 1524 mm gauge and the track has become the standard in Russia until 1970.
The first project for the radical expansion gauge railways in Europe spent Isambard Kingdom Bryunnel - British engineer and one of the major figures of the Industrial Revolution. His project involved the use of track width 2140 mm. Railroads led Brunel built the company «Great Eastern Railway». These roads have proven themselves in operation. But in 1864 began the conversion of these tracks on the track of 1435 mm, the time has become the standard in England already.
Since then, the use of broad-road was forgotten ...
"Railway Brunel»

New German idea of Hitler
After Hitler came to power, he began to hatch plans for the restructuring of large cities in Germany with a new monumental way corresponding to its vision of the future cities of the Third Reich. Land of flooded buildings, and across Germany started to reach the highest quality highways.
Aesthetic ideals, expressed in the first tastes of Hitler himself, it was announced the return to the ancient classics, which at the same time creatively processed minimalist spirit harsh Teutonic traditions. The massive size, chopped rectangular shapes, endless colonnades and arches - even Roman emperors, on the idea of the Fuhrer, had to bow before the power of the Third Reich, expressed in architecture.
In 1932, architect Albert Speer, received the first orders for the restructuring of the objects of the NSDAP. In 1933, by order of Goebbels, Speer rebuilt the building of the Reich Ministry of Public Enlightenment and Propaganda of the Third Reich. In the same year, Speer met with Hitler, who noticed his talent and appointed deputy architect Paul Ludwig Troost and ordered restructuring the Reich Chancellery.
"Facade of the Reich Chancellery»

Speer quickly went into Hitler's private circle, and in 1937, he was appointed Inspector General of the imperial capital for the construction, with the task of reconstruction of Berlin. In 1938-1939, he developed a master plan for the reconstruction of the German capital.
"Part of the project for reconstruction of Berlin's main streets. In the foreground - Palace Hitler »

Everything changed after the outbreak of war with the Soviet Union. Germany was required to develop new plans for the land "lebensraum" in the postwar period. Sea lines of communication and highways could no longer meet the needs of Germany and, in September 1941, Reich Minister of weapons and ammunition Fritz Todt, proposed to build a railway heading to a track of a much wider between Germany and Ukraine. Hitler quite warmed to the idea and said: "Building a wide railroad, maybe bring us difficulties, but we will not allow themselves to be intimidated." As a consequence of this project he called "having strategic importance." I must say that Hitler saw in this project a huge prospect for the implementation of their plans to rebuild Germany. Broad-gauge railway fits perfectly into the monumental architectural projects of the Third Reich and Hitler had already seen trans-European highway, on which of the major industrial cities in Germany with incredible urgency moving troops, weapons and cash are increasingly expanding the territory conquered by them in the course of a victorious war.
Suggested routes:
East-West: Rostov-on-Don - Donetsk - Poltava - Kyiv - Lviv - Krakow - Katowice - Wroclaw - Cottbus - the world capital of Germany (Berlin)) - Hannover - Bielefeld - Ruhr region - Aachen - Liege - Saint-Quentin - Paris
North-South-East: Hamburg - Wittenberg - the world capital of Germany (Berlin) - Leipzig - Gotha - Bamberg - Nuremberg - Munich - Simbach am Inn - Linz - Vienna - Bratislava - Budapest - Belgrade - Bucharest - Varna / Burgas - Istanbul
North-South-Parallel: The capital of the world, Germany (Berlin) - Dresden - Ústí nad Labem - Prague - Jihlava - Znojmo - Vienna - Trieste - Rome
East-West 2: Munich - Augsburg - Stuttgart - Karlsruhe - Metz - Reims - Paris - Marseille - Spain
"Routes Breitspurbahn»

Curator and head of project of construction of the road was broad-appointed Fritz Todt. All the arguments of experts Deutsche Reichsbahn of possible difficulties of this project and of the incompatibility of such a road with a conventional railway technology, which would require the construction of additional infrastructure, rejected. He later recalled: "Questions the need for and feasibility of these huge highways were considered minor and never stood on the first page of the agenda. In essence, it's up to them had never reached. Perhaps not everyone knows that, but the motivation of the project is not to be sought in relation to the ambitions of European railways. This project is of value in itself: a monumental building in Hamburg, Berlin, Nuremberg, Munich meant the corresponding road between the cities ».
"Reich Minister of weapons and ammunition Fritz Todt»

After heavy defeats on the eastern front the discussion of building new railways postponed, but May 24, 1942 at the headquarters of the Fuehrer held a meeting, which was attended by Albert Speer, Reichsleiter Martin Bormann and the Minister of Railways Dropmyuller. At the meeting Hitler defined the basic parameters of the new railway. So, in his opinion, the track width should be 4 meters, width of the car 6 meters, and height should be 5 meters. Hitler explained his demands: "It must be roomy, because the whole family will live there for a few days. But we will do one-story restaurant. Six meters wide, long and thirty-five high. Yes, right palace banquet hall, are not you, Minister Speer? ". Residential cars Hitler assumed two-story, with a central corridor on both sides of which offers comfortable bedrooms. Further, Hitler demanded that count Dropmyullera capacity boxcar. By calculation it turned out that the car of this size could take a weight of 100 tons.

Project Manager «Breitspurbahn» was appointed doctor of technical sciences Gunter Vince.
"Doctor of Technical Sciences Gunter Vince»

April 5, 1943 Dr. Gunter Vince made a report, which outlined the technical features of the project. On the basis of the analysis and all sorts of calculations established track width of 3,000 mm. The optimum value of the diameter of the wheel, taking into account the parameters of velocity, rotation angles, axle loads, turned 1250 mm.
Due to promising areas of the Third Reich, the maximum train speed of 300-400 km / h were rejected as having no practical value. And at a speed of 250 km / h in a sleeping car is not a problem to reach any point of the empire from Rome to Berlin - 1627 km, from Bucharest - 1759 km, to Moscow - 1923 km to Istanbul - 2429 km. Therefore, all the calculations were made for a maximum speed of 250 km / h for passenger trains and 100 km / h for freight.
The problem of resistance to air flow is very important when oncoming traffic gigantic trains with a speed of 250 km / h or when following in the tunnels solved special sleek trains. Turning radius of the train was 180 degrees 500 m.
Even with the latest braking systems proposed by Knorrbremse AG, calculated braking distance at a speed of 250 km / h was set in 1600 meters during emergency braking, and 3000 m in the ordinary.
At such speeds and braking distance optical signaling system is ineffective, especially in snow or fog. Therefore, we developed a new system that is somewhat reminiscent of modern electronic: using high-frequency sensors, all information displayed on the operator console and engine room.
The total weight of the composition of trade is estimated at 10 000 tonnes (compared to the mass of the most difficult contemporary compositions - up to 2000 m). If necessary, the three freight trains could be combined into one, with a total mass of 30 000 t. The length of a freight train with a locomotive was 1100-1200 m (maximum length of a modern, but without a locomotive - about 500 m). If the length of only twice the mass increased to five or seven times. Attention was paid to the new systems of heating, ventilation, lighting, trains, because the window, for example, at such speeds can not be opened.
Rate it, even approximately, the cost of construction Dr. Vince difficult, noting that the project must first be created an entire industry.
Recommendations related to the laying of tracks contained in the secret work of Dr. Rumlera. Calculations profile rail loadings on sleepers, decking and schemes are ways to strengthen the soil. In other documents we are talking about interchanges, tunnels, office buildings, hangars, bridges. A special case - the railroad tracks in towns and railway stations. On the sketches and models - different architectural solutions for Munich, Nuremberg, Linz, Berlin.
"The wheel trolley for a new type of cars & quot;

It was prepared with five volumes of technical documents, which contained detailed descriptions of all types of trains future. Each volume has an application with technical diagrams and drawings.
Tom A. "Locomotives"
Drawings of 33 commodity and high-speed locomotives and multiple shunting developed by Krauss-Maffei, Henschel, Borsig, BBC, Krupp, SSB, RZA Berlin, Schwartzkopff, RZA München, Wien-Floridsdorf etc.
Among them - the steam turbine electrical and mechanical, diesel-hydraulic, steam, diesel, electric, gas turbines, and other engines.
For high-speed locomotives envisaged:
• maximum speed of 200-250 km / h
• for commodity - 100 km / h
Power:
• freight trains - 12 900-40 000 hp,
• passenger - 11 350-33 300 hp
Tom V. "electricity traction"
European plan for the electrification of railways and documentation for three to five trade and high-speed passenger electric locomotives and multiple shunting locomotives.
Approximate parameters of electric commodity:
• Maximum speed - 100 km / h
• capacity - 25 500-28 600 hp
For high-speed electric locomotives:
• Maximum speed - 250 km / h
• capacity - 12 500-21 100 hp
Tom C. "Motor Train"
Passenger train without a locomotive, where the first car - the engine, the number of cars - from 2 to 10, the maximum speed - 250 km / h.
Drawings of various trains, diesel-electric, diesel-hydraulic, "trains" with 5 or 8 cars, seating, sleeping and special.
Option engine train: a restaurant car, 2 intermediate and 2 end car.
The end cars are the same, only the luggage and a post office can be interchanged when moving in one direction or another.
An example of the device end motor car
Ground floor:
• The cab
• lobby
• staff room
• engine room
• luggage compartment
• toilet
• washrooms
• showers
Upper floor:
• overview Hall
• Deck for walking
• Ten of the third class compartments
• two toilets
Total number of beds:
• 80 - in the third grade
• 42 - on the deck for walking
• 26 - in the review room
• Total - 148

"The appearance of the locomotive Breitspurbahn»

The device locomotive Breitspurbahn
1. Heater Air
2. Start the engine
3. The combustion chamber
4. Air cooling
5. The gas turbine
6. Fuel
7. Total length of the locomotive
8. Diesel-electric starting system
9. Air intake
10. oil cooler
11. Fans
12. Intercooler

Tom D and E. "The cars of passenger and freight trains of all types"
Among the special carriages of passenger trains:
• wagon cinema with 196 seats
• common carriage for 192 seats with a reading room, a cafe, a bar, a conversation, luggage and 12 toilets (eight on the ground floor and 4 on the top)
• comfortable with the car seats / berths for ostarbeiters (Eastern workers) to 480 seats dining room, pantry, 18 toilets, washrooms, where each seating position is much wider and more comfortable than modern trains.

Example devices "bath" car
Ground floor:
• Hair salon for ladies and gentlemen
• 4 bathrooms
• 20 shower
• 2 waiting room
• room for the staff
• Technical compartment
• 2 laundry room
• 4 toilets
Upper floor:
• rooms for smokers and non-smokers (120 seats)
• kitchen for cooking to order
• confectionery
• pantry
• 2 staff rooms
• 3 toilets

Assumes different options formulations
Regular daily train:
• 1st wagon - postal and baggage car
• 2nd - third grade
• 3rd - third class dining room
• 4th - first, second and third classes
• 5th - diner
• 6th - the first and second classes
• 7th - first, second and third classes
Total first-class seats - 96, the second - and third 288 - 1100.
The dining car is a dining room for 130 seats of the first and second class and 176 - the third, as well as a restaurant on 172 seats.
Long-distance trains. Seven wagons where:
• 1st wagon - postal and baggage car
• 4th - "bath"
• rest - passenger
First-class seats - 32, the second - 82, and the third - 624, a restaurant with 200 seats.
Train "suite":
• 1st wagon - postal and baggage car
• then 2 passenger
• 2 dining car
• more passenger car
• and the car-cinema
First-class seats - 144, the second - 432.
Dining room for 260 seats of the first and second classes, a restaurant with 400 seats.
Number of seats in the train for ostarbeiters (also 7 cars) was 2 880.
As for freight wagons, here you can find cars for transportation of coal, grain, cars, machines, non-standard and oversize cargo, mail and refrigerated cars, all kinds of tanks and even the platform for the transport of vehicles.
Work on the railway were to end the war, but has not been completed.
On this I have everything.