1324
Flying a single unit for the Apollo missions to the Moon: The Story of a Project

That's look first controlled rover mission Apollo 15. And could have wings of a jet engine. I>
From the beginning, "Lunar Project" at NASA planned several stages of development of the moon man so to speak. The first step - it's just a flight there and back of the spacecraft with a man on board. To test the technical capabilities of this journey.
Then, subject to the successful completion of the first phase, already planned and scientific expeditions, with the landing of man on the moon, and the subsequent examination of the region landing. Needless to say, the legs pass would come out a little, so the use of the vehicle was planned from the very beginning of the project.
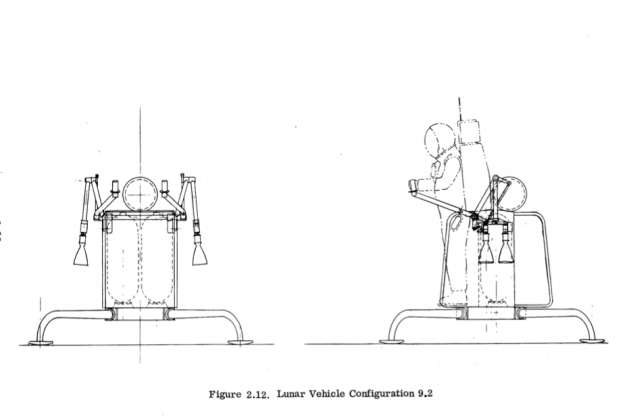
In NASA tried to provide a lot, and therefore parallel to the designed several options rovers. At the same time involved and outside organizations, for example, Bell Aerosystems. This company and created a lunar rover project flying jet engine (of course, not the most powerful, otherwise we could fly away in an unknown direction).