1262
Cars from the republics of the former USSR
Let us remember the automotive brand that after the collapse of the Soviet Union passed into oblivion.
Thanks to the planned economy of the Soviet car industry something of a lottery. Estonia fell produce racing cars, Armenia - vans and Central Asian republics did not get anything at all: automotive assembly site in Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan emerged only after the collapse of the USSR. We offer top-5 car of former Soviet republics
But seriously, the auto industry had its only a few Soviet republics. Some of the produce on the outskirts of the Soviet car was maybe not very successful technically, but interesting in terms of history.
Source

Ukrainian crossover
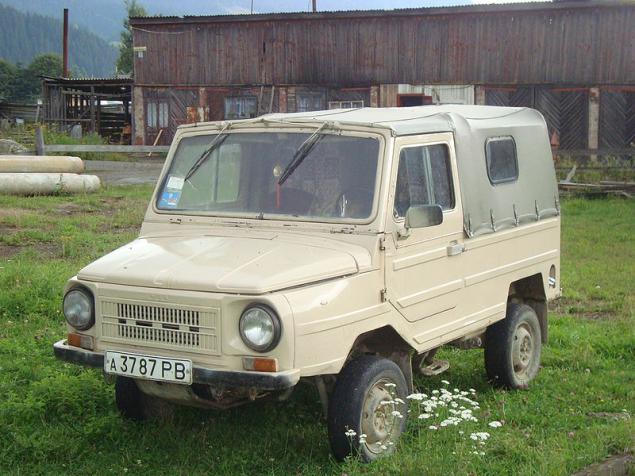
Located in the western Ukrainian city of Lutsk Automobile SUVs produced on the basis of "The Cossacks." Loiseau differed a good cross, a minimum of comfort and disgusting dynamics - for fast driving these cars is not suitable. But in 1990 in Lutsk finally able to develop a new model, which was to break down the old stereotypes.
LuAZ-1302Po compared to its predecessors, the new LuAZ 1302 looked much the same as the look modern crossovers next to a military jeep. Instead of the old "Zaporozhye" LuAZ engines received a 53-horsepower engine from the front-wheel drive "Tavria". The car less suitable for off-road, but learned relatively quickly pick up speed, it has become stockier and easier to manage.
Under the conditions of the Soviet economy LuAZ-1302 could well become a massive car for summer residents and residents of the village, but instead turned into a rarity. In 1302, Russia LuAZ exported small quantities of these machines and now the country is almost gone. In Ukraine Loiseau with "Tauride" motors at each intersection is also not found.

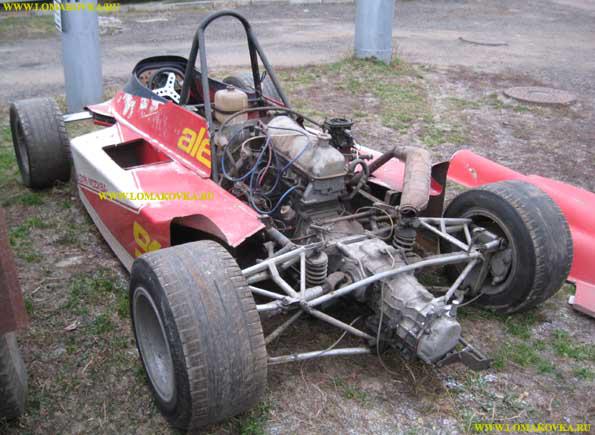
Estonian "formula»
Estonia in the Soviet auto industry has been a special place. Republic specialized in the production of racing cars for the championship of the USSR in the class "Formula East" and the International Friendship Cup - the competition racers from Eastern European socialist countries.
In Tallinn, built almost formulaic real race cars with carefully calculated aerodynamics, adjustable rear wing and the use of some of the technical solutions of the then "Formula 1" such as ground-effect. All these tricks, but were undone disabled by choice of engines. As a rule, the cars "Estonia" staged motors from the "Zhiguli" eleventh or six models. Even after the afterburner these engines were given power not more than 120 liters. p. As for the rate of the Estonian cars, it usually does not exceed 200 km / h. For comparison: the cars "Formula 1" in the 1980s developed the speed above 350 km / h.
The main problem was ideological duality. On the one hand, technical sports, including racing, the Soviet Union maintained and considered beneficial for the youth. But "Formula 1" condemned as not for sports, and commercial and also deadly show. Therefore, the Soviet "formula" to get a compromise - chase was possible, but only very slowly.

Latvian bus
In the early 1980s, the taxis have become popular in many large cities of the USSR. Almost the only car that was used then as the bus was the Latvian RAF-2203 - a minivan that looks vaguely reminiscent mersedesovsky Sprinter.
RAF-2203Po Soviet standards RAF had a good car with a more or less comfortable interior. The engine of the GAZ-24 allows you to keep on a country road cruising speed of 90-100 km / h. In terms of the reliability of the RAF it was more capricious than the "Volga" - apparently because of the higher compared with passenger car loads of vans often broke and required constant maintenance.
Rafa out of use as soon as in Nizhny Novgorod have begun to produce "Gazelle". Latvian minivan proved uncompetitive in Russia, and another market in Riga automobile was not. At the end of the 1990s, Riga Autobus Factory ceased to exist.
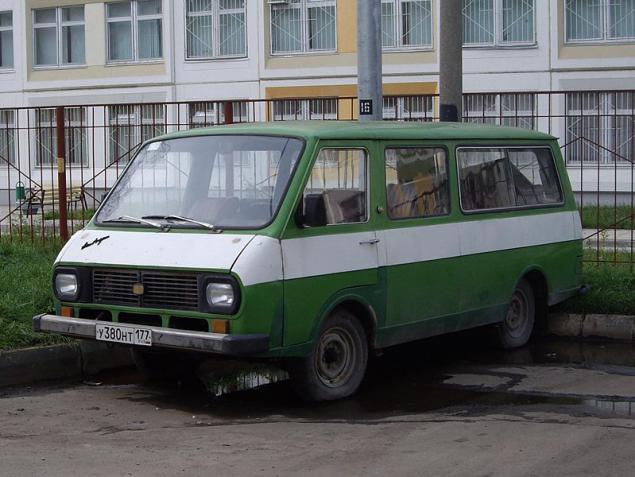

Armenian camper
YerAz 762Erevansky-car factory specialized in the production of small vans, which today would be called commercial vehicles - one class with today's "Sable" or Hyundai Porter. Manufacturing process of the van was not too difficult - the engine of the "twenty-first" "Volga", chassis and driver's cab of an old Latvian minibus RAF-977. The body of the van in Yerevan made independently, sometimes placing it in the refrigerator.
But Yerevan has and in-house development - YerAz-3730, which was scheduled to release in a few modifications. The most original version was camper - car travel. Inside were provided beds, TV, sink and even a compartment for the barbecue.
YerAz-3730 has passed the state tests and was recommended for serial production. But to begin production of the model did not succeed. To upgrade to a new model needed to change the scheme of production and permanently stop the conveyor. Get permission for a long simple guide Automobile failed. Therefore, the new Yeraz produced individually - for international exhibitions or maintenance activities such as the 1980 Moscow Olympics. One of the vehicles was a minivan Superior and is used for receiving VIP guests of the Armenian government.
The last attempt to run YerAz-3730 in a series undertaken in 1995, and a portion of the machine is the Polish diesel engines. In Yerevan the cars were used as minibuses. Their production continued until 2002, when the Yerevan Automobile Plant was declared bankrupt.
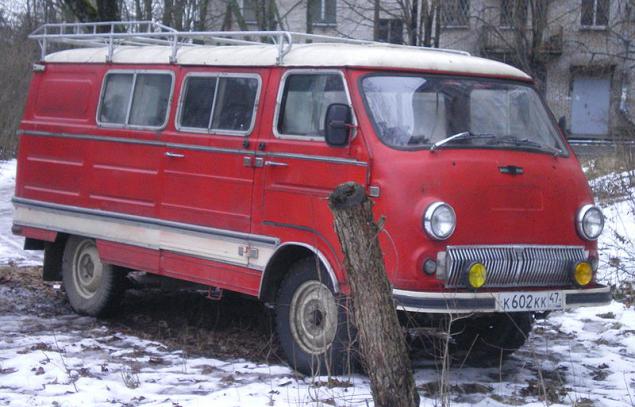

Georgian truck
KAZ-608
However, the largest automaker in the Soviet Transcaucasia was still not Yerevan and Kutaisi Automobile Plant. In the late '70s, the company has released several versions of trucks KAZ-608. The machine features the name "Colchis" and angular cab, for which the Georgian truck was nicknamed "servant».
On the roads of the USSR occasionally come across "Colchis" dump trucks, fuel trucks and flatbed trucks. But the main specialization of the company was the release of Kutaisi tractors, about the shortcomings of which drivers composing legends. At KAZ-608 put the same engine as on the ZIL-130, but the pulling power of these machines was different. Loaded trailer ZIL easily drove up the hill, but for "Colchis" with the same motor task to overcome the 10-degree rise is often complex.
Paradoxical KAZov reluctance to take steep slopes, apparently, explains the features of weight distribution of the car. On "Colchis" motor located directly under the driver's seat, while at Zilahi engine was put forward. Center of gravity did not seem to match the Zilovskoye. The motor is initially been imprisoned just under ZIL.
As a result, the most successful project was the creation of Kutaisi autoenterprise the sponsored football team "Torpedo", a few years played in the major league of the Soviet championship. As for the trucks, they stopped in Kutaisi to produce shortly after the declaration of independence of Georgia.
Posted in [mergetime] 1401884677 [/ mergetime]
That's all.

Thanks to the planned economy of the Soviet car industry something of a lottery. Estonia fell produce racing cars, Armenia - vans and Central Asian republics did not get anything at all: automotive assembly site in Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan emerged only after the collapse of the USSR. We offer top-5 car of former Soviet republics
But seriously, the auto industry had its only a few Soviet republics. Some of the produce on the outskirts of the Soviet car was maybe not very successful technically, but interesting in terms of history.
Source

Ukrainian crossover
Located in the western Ukrainian city of Lutsk Automobile SUVs produced on the basis of "The Cossacks." Loiseau differed a good cross, a minimum of comfort and disgusting dynamics - for fast driving these cars is not suitable. But in 1990 in Lutsk finally able to develop a new model, which was to break down the old stereotypes.
LuAZ-1302Po compared to its predecessors, the new LuAZ 1302 looked much the same as the look modern crossovers next to a military jeep. Instead of the old "Zaporozhye" LuAZ engines received a 53-horsepower engine from the front-wheel drive "Tavria". The car less suitable for off-road, but learned relatively quickly pick up speed, it has become stockier and easier to manage.
Under the conditions of the Soviet economy LuAZ-1302 could well become a massive car for summer residents and residents of the village, but instead turned into a rarity. In 1302, Russia LuAZ exported small quantities of these machines and now the country is almost gone. In Ukraine Loiseau with "Tauride" motors at each intersection is also not found.

Estonian "formula»
Estonia in the Soviet auto industry has been a special place. Republic specialized in the production of racing cars for the championship of the USSR in the class "Formula East" and the International Friendship Cup - the competition racers from Eastern European socialist countries.
In Tallinn, built almost formulaic real race cars with carefully calculated aerodynamics, adjustable rear wing and the use of some of the technical solutions of the then "Formula 1" such as ground-effect. All these tricks, but were undone disabled by choice of engines. As a rule, the cars "Estonia" staged motors from the "Zhiguli" eleventh or six models. Even after the afterburner these engines were given power not more than 120 liters. p. As for the rate of the Estonian cars, it usually does not exceed 200 km / h. For comparison: the cars "Formula 1" in the 1980s developed the speed above 350 km / h.
The main problem was ideological duality. On the one hand, technical sports, including racing, the Soviet Union maintained and considered beneficial for the youth. But "Formula 1" condemned as not for sports, and commercial and also deadly show. Therefore, the Soviet "formula" to get a compromise - chase was possible, but only very slowly.

Latvian bus
In the early 1980s, the taxis have become popular in many large cities of the USSR. Almost the only car that was used then as the bus was the Latvian RAF-2203 - a minivan that looks vaguely reminiscent mersedesovsky Sprinter.
RAF-2203Po Soviet standards RAF had a good car with a more or less comfortable interior. The engine of the GAZ-24 allows you to keep on a country road cruising speed of 90-100 km / h. In terms of the reliability of the RAF it was more capricious than the "Volga" - apparently because of the higher compared with passenger car loads of vans often broke and required constant maintenance.
Rafa out of use as soon as in Nizhny Novgorod have begun to produce "Gazelle". Latvian minivan proved uncompetitive in Russia, and another market in Riga automobile was not. At the end of the 1990s, Riga Autobus Factory ceased to exist.

Armenian camper
YerAz 762Erevansky-car factory specialized in the production of small vans, which today would be called commercial vehicles - one class with today's "Sable" or Hyundai Porter. Manufacturing process of the van was not too difficult - the engine of the "twenty-first" "Volga", chassis and driver's cab of an old Latvian minibus RAF-977. The body of the van in Yerevan made independently, sometimes placing it in the refrigerator.
But Yerevan has and in-house development - YerAz-3730, which was scheduled to release in a few modifications. The most original version was camper - car travel. Inside were provided beds, TV, sink and even a compartment for the barbecue.
YerAz-3730 has passed the state tests and was recommended for serial production. But to begin production of the model did not succeed. To upgrade to a new model needed to change the scheme of production and permanently stop the conveyor. Get permission for a long simple guide Automobile failed. Therefore, the new Yeraz produced individually - for international exhibitions or maintenance activities such as the 1980 Moscow Olympics. One of the vehicles was a minivan Superior and is used for receiving VIP guests of the Armenian government.
The last attempt to run YerAz-3730 in a series undertaken in 1995, and a portion of the machine is the Polish diesel engines. In Yerevan the cars were used as minibuses. Their production continued until 2002, when the Yerevan Automobile Plant was declared bankrupt.

Georgian truck
KAZ-608
However, the largest automaker in the Soviet Transcaucasia was still not Yerevan and Kutaisi Automobile Plant. In the late '70s, the company has released several versions of trucks KAZ-608. The machine features the name "Colchis" and angular cab, for which the Georgian truck was nicknamed "servant».
On the roads of the USSR occasionally come across "Colchis" dump trucks, fuel trucks and flatbed trucks. But the main specialization of the company was the release of Kutaisi tractors, about the shortcomings of which drivers composing legends. At KAZ-608 put the same engine as on the ZIL-130, but the pulling power of these machines was different. Loaded trailer ZIL easily drove up the hill, but for "Colchis" with the same motor task to overcome the 10-degree rise is often complex.
Paradoxical KAZov reluctance to take steep slopes, apparently, explains the features of weight distribution of the car. On "Colchis" motor located directly under the driver's seat, while at Zilahi engine was put forward. Center of gravity did not seem to match the Zilovskoye. The motor is initially been imprisoned just under ZIL.
As a result, the most successful project was the creation of Kutaisi autoenterprise the sponsored football team "Torpedo", a few years played in the major league of the Soviet championship. As for the trucks, they stopped in Kutaisi to produce shortly after the declaration of independence of Georgia.
Posted in [mergetime] 1401884677 [/ mergetime]
That's all.