Why, why, our Protons do not fly

Puzzled why accidents occur precisely with the Russian satellites, I decided to explore this theme.
Version number one - hand curves h5> The first thought that comes to mind is prosrali polymers modern Russian engineers have lost the skills and work organization, compared to the Soviet period.
However, turning to Wikipedia (ссылка1 and ссылка2), You can find that in our time, the failure rate is not very different from the Soviet (in both cases, the percentage of successful start-ups is 89%). A respected darkalexey already quite a while even made a more detailed post about it. Yes, in the beginning of the flight Proton accidents was significantly more, but "as a whole the hospital "observed parity.
So I think there is no difference at what social \ economic lifestyle initial start-up.
Version number two - and can have other so well? H5> The second thought, maybe 89% of the successful launches of this not so little? And what about our friends competitors?
The first competitor - European launcher Ариан-5.

Reliability launches Ariane 5 is an impressive 97%. But at the same time start up cost twice as high - about $ 220 million. In the year carried 5-6 starts.
The second competitor - Зенит-3SL (Sea Launch) .

Reliability - analogous proton 89-91%. Cost is also comparable to about $ 80 a year mln.V carried 4-5 starts.
Competitors from the United States - Delta IV and Atlas V .
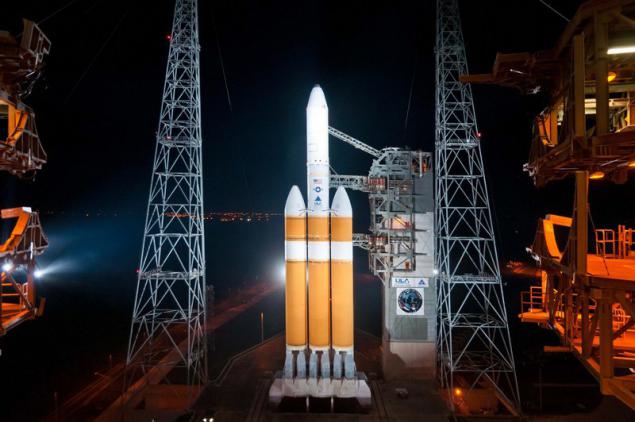
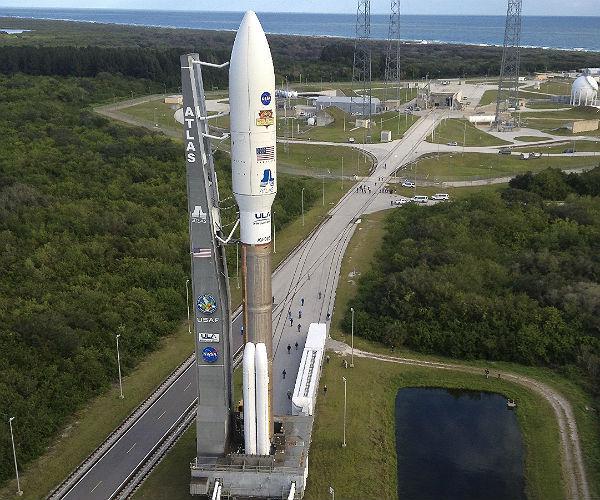


Safety factor of 95-97%. Start up cost is between $ 160 million impressive for the Atlas V 521 to $ 265 million upomrachitelnyh for Delta IV Heavy. In the year that Americans run only 5-6 ships of both species.
Thus, it can be a banal conclusion that reliable starting is directly correlated with their cost.
Wikipedia has a wonderful табличка Proton on competitors. I took the liberty to edit it a bit:
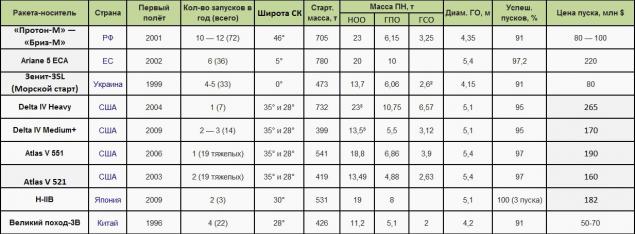
Altogether Atlas IV - 45 successful launches, but half of them are in the start-up light options 401 and 501. By eliminating them, we get a figure of 19 starts for general heavy modifications. A similar situation with the Delta IV, from 25 starts overall share of heavy and medium had 21.
Let us return to the long-suffering h5> The basis of the question on accidents with protons is the fact that a lot of accidents related to the launch of various Russian high-tech satellite communication and navigation. Which, in theory, can compete with foreign satellites. Here is a short list of failed launches lately:
May 6, 2014 Ekspress AM4R (Satellites)
July 2, 2013 Glonass-M (satellite navigation)
August 6, 2012 Express MD2 (Satellites)
August 18, 2011 Express AM4 (Satellite Communications)
December 5, 2010 Glonass-M (satellite navigation)
It would seem that one could argue that insidious saboteurs crept into the center of Russian space exploration and sabotage it launches Russian units.
But "not so simple." I liked here is an opinion , which, by the way, I met a distinguished Learn Zelenyikot :
The essential role when you start playing the pricing policy of the state.
THE WEST: The State always pays more than the commercial buyer. That is, for a reason - for Public Procurement price is higher. This risk are explained. In the US, for example, when buying state services associated with the risk - do not buy commercial insurance (anti-corruption law). Therefore, the state customer "himself of fear" by buying additional services - checking, testing, etc.
Example: Price-Falcon run for commercial customers 9 = 56 million. $ Fixed and it - does not depend on the type of satellite, or the final orbit. But - already booked a two-run government satellites Folkonami and they will cost 87 million and 95 million. (In fact, more and kom.zakazchiki buy insurance - 15-25 million, depending on the price of the satellite. But all the same, the difference is significant) . The state pays more.
IN RUSSIA: all naoborot.U state here "Boyarsky approach" to Khrunichev - say, we allow you to trade with the infidels - for this makes us a discount. And bargains start almost at cost. The result is quite obvious - the quality suffers.
Miser pays twice. And crying - also twice. Blockquote>
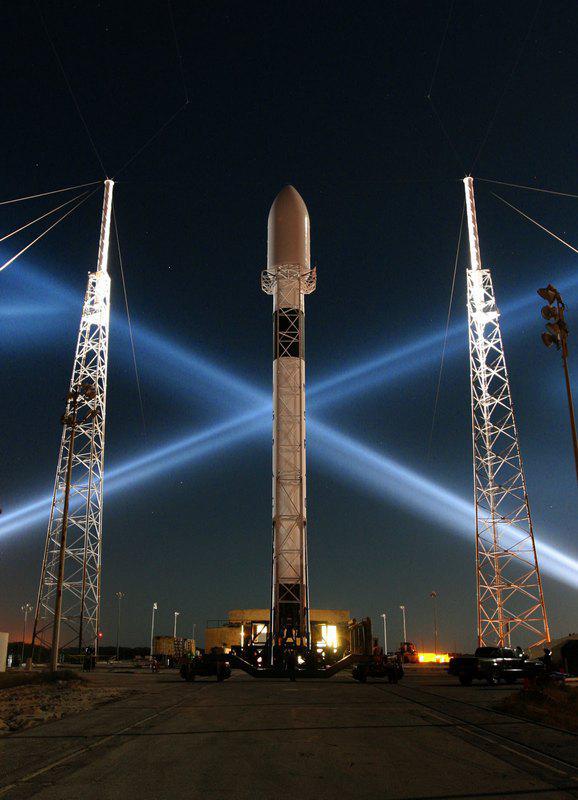

Protons on the heels of advanced development of private US corporation «SpaceX» Falcon 9. Since 2010, there were only nine starts, including 1 partially unsuccessful. Start up cost estimate $ 49, 9 million to $ 56 million depending on the load. But it is very load is 13 tons for Low Earth orbit (23t against the proton), and 4, 8 tons (vs. 6, 15t for protons) to geosynchronous transfer orbit. Heavy version of the Falcon 9 has not even flown.
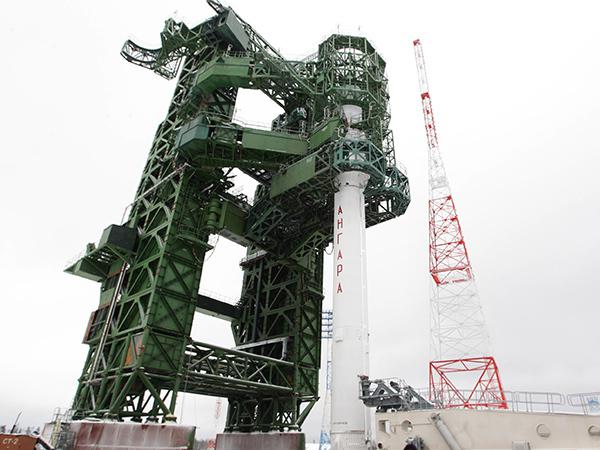

Proton itself is "outgoing" carrier rocket. To replace him is Angara. Angara rocket is modular, ie depending on the required load exists modifications pH 8 with output weights from 2 to 50 tons for Low Earth orbit. In this case, allegedly complex will be fully designed and manufactured cooperation of Russian companies in the territory of Russia. The main point of the launch will be a fully-Russian cosmodrome "Plesetsk". The first launch of LV "Angara" was planned from the cosmodrome "Plesetsk" for 2005. But then he was repeatedly postponed: in 2011, 2012, 2013, and now in 2014. At the moment it is - the ninth transfer of the first launch rocket. Dmitry Rogozin reported to back in 2013 following the launch date of the light missile - May 2014, heavy - the end of November 2014. Let's see, start or not. It is believed that a certain amount of parts for the Angara is still made in Ukraine. In this case, we will see the start of the Angara is not soon.
Conclusion h5> Thus, we can say that the quality of flights to a large extent influenced by chronic underfunding of Russian launches than mythical saboteurs. Especially because recently Proton was successfully launched specific Russian military communications satellite.

Predict anything I will not, because I do not belong to the sphere of professional space. I hope that too after this accident will be taken really true "financial" measures and not "frame-punitive." Also I will be glad to any additions \ refinements to the article.
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/223461/