456
Zasrat fully
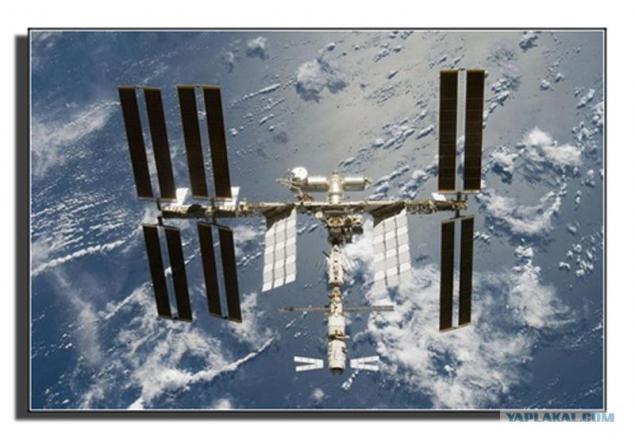
The crew of the ISS on Tuesday was forced to evacuate to the "Soyuz" from the wreckage debris flown dangerously close to the station. It is reported by "Interfax". Currently, all members of the crew returned to the station.
The distance from the ISS to the wreckage was about 250 meters. Debris was discovered too late to perform the avoidance maneuver. Roscosmos cosmonauts Alexander Samokutyaev and Andrei Borisenko and NASA astronaut Ronald Garan took refuge in the "Soyuz TMA-21", and Russian Sergei Volkov and Japanese Satoshi Furukawa and American Michael Fossum - in the "Soyuz TMA-02M." Dangerous proximity to fragment occurred about 16 pm Moscow time.
Space debris is not the first time causes the evacuation of the crew station or an alert. The latter measure is used in the case where the fragments are in the so-called "red zone" - that is, less than a kilometer from the station. Since the debris and fragments of the ISS and moving at a high speed collision, even with a relatively small fragment could be dangerous.
In recent years, the amount of debris in orbit grows out of the fact that space is constantly launching new satellites. In 2009, the US Agency published a map of space debris.

Source:
The distance from the ISS to the wreckage was about 250 meters. Debris was discovered too late to perform the avoidance maneuver. Roscosmos cosmonauts Alexander Samokutyaev and Andrei Borisenko and NASA astronaut Ronald Garan took refuge in the "Soyuz TMA-21", and Russian Sergei Volkov and Japanese Satoshi Furukawa and American Michael Fossum - in the "Soyuz TMA-02M." Dangerous proximity to fragment occurred about 16 pm Moscow time.
Space debris is not the first time causes the evacuation of the crew station or an alert. The latter measure is used in the case where the fragments are in the so-called "red zone" - that is, less than a kilometer from the station. Since the debris and fragments of the ISS and moving at a high speed collision, even with a relatively small fragment could be dangerous.
In recent years, the amount of debris in orbit grows out of the fact that space is constantly launching new satellites. In 2009, the US Agency published a map of space debris.

Source: