1810
Aviation Museum. Vantaa, Finland.
I remember that I promised to go to the tank museum in the password, but instead roll into Park Moomin)) and on the way stopped Aviation Museum in Vantaa (Suomen Ilmailumuseo, Tietotie 3, 01530 Vantaa).
Well, once I stopped, which would not take pictures even though on a bar of soap. And just took off something, so it is possible to share. For quality images please do not kick, I'll know everything. The museum is quite cramped and not very light, exhibits tightly obstruct each other. Because as I could and could)
Photos will be about 70 pieces

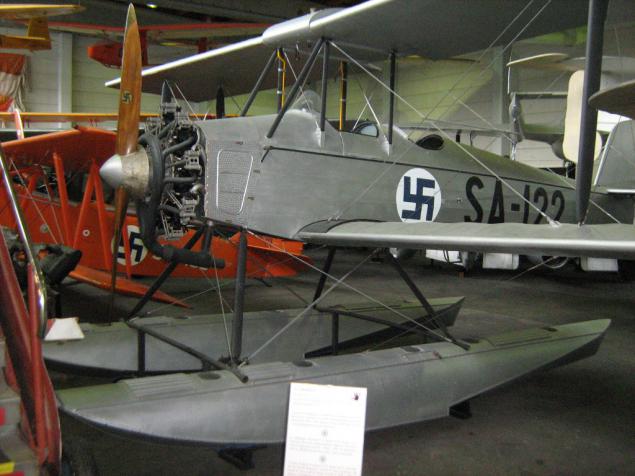
At the entrance to the first room - one of the first-born of Finnish aviation industry - license Frenchman Caudron C.60 local buildings. The development of a successful C.59, the classic single-engine biplane with fabric covering, for its intended purpose - trainer. Thirty cars were built in France at the request of the Finnish Air Force, 34 more are made under license in Finland itself in 1927-28.
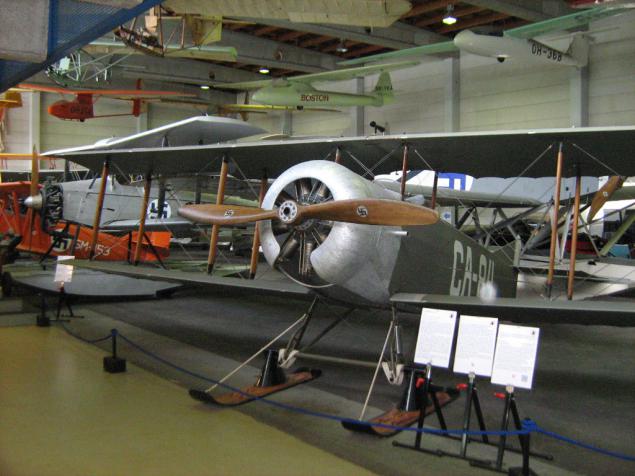

Caudron C.60, France / Finland.
Crew: 2
Length: 7.50m
Wingspan: 10.24m
Wing area: 26.00m²
Empty weight: 505kg
Takeoff weight: 862 kg
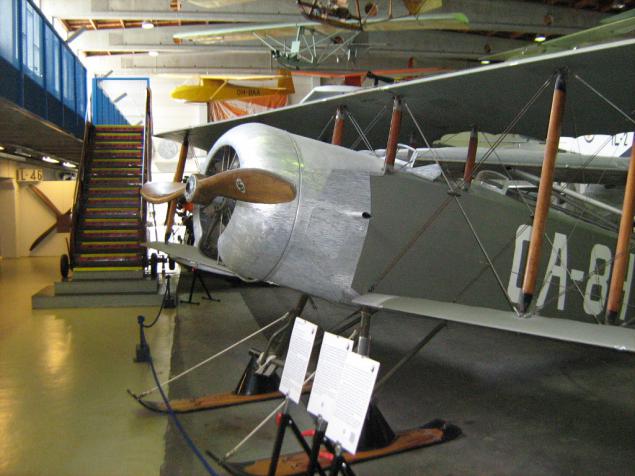

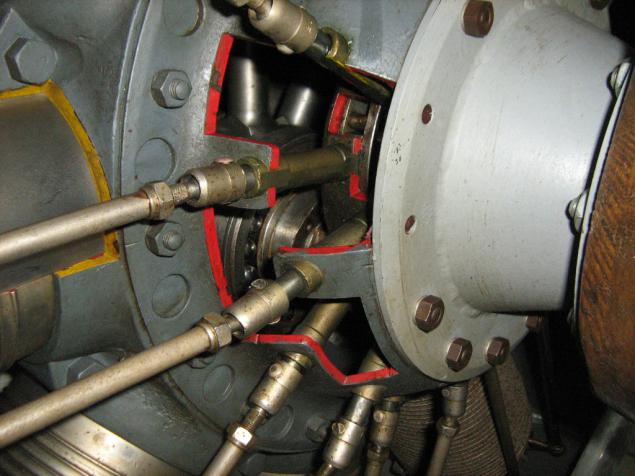
Clerget 9B engine of French origin, produced in France and in England. The star, rotative, nine-, 16.3 liters, 130 hp
In this instance the engine partly in section for clarity:
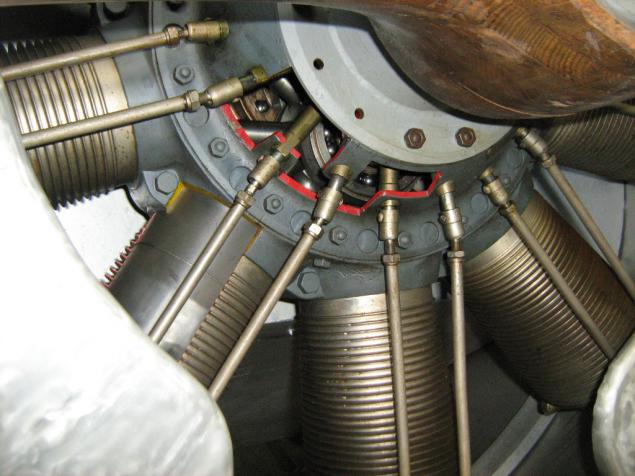

More engine:
And further. Actually, I aircraft engines even more interesting than the actual aircraft, because they will be more than one or two. By the way, the engine is interesting because it is rotative. Quite popular in the early twentieth century, the system - the crankshaft rigidly fastened on the plane, and the entire engine revolves around him.
Do not hold back, moved - naturally rotates)

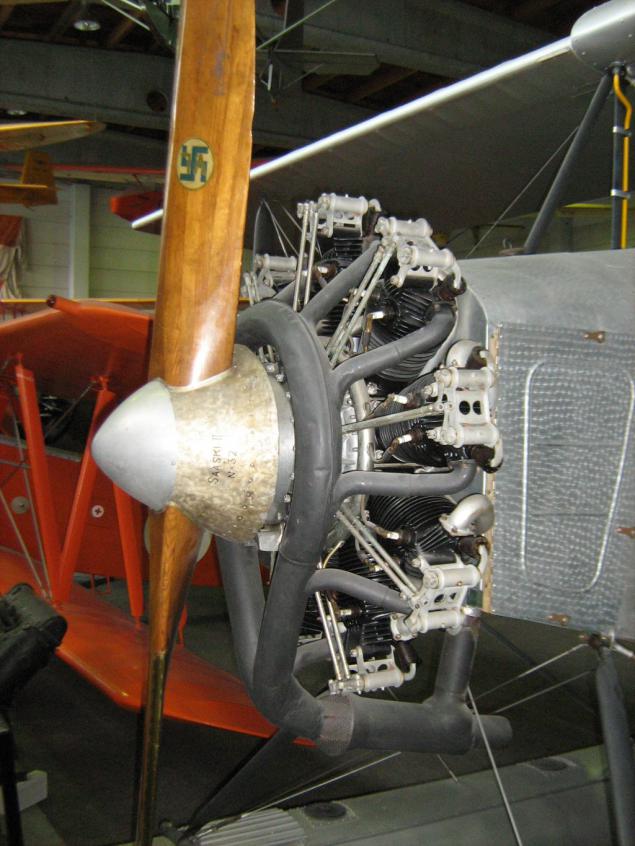
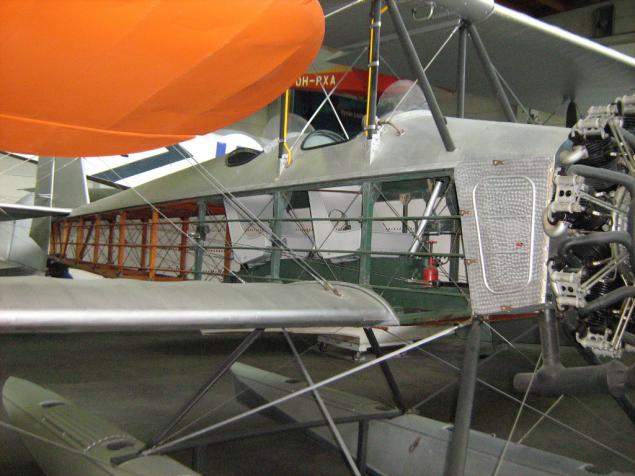
V.L. (Valtion Lentokonetehdas) Sääski II.
«Sääski» in Russian something like midges or gnats like. Popravte if anyone knows.
The first production aircraft of the Finnish private development, a training on the main destination. In 1928 - 32 years made about fifty planes of three series of the second float chassis. Patrol option for the Coast Guard. In principle, the same does not particularly remarkable classic nine-engine biplane with Siemens-Halske Sh 12 110 forces.

VL Saaski IIA
Wingspan: 9.90 m
Length: 7.40 m
Height: 2.40 m
Wing area: 24.00 m²
Empty weight: 609 kg
Takeoff: 913 kg
Engine: Siemens-Halsken Sh 12
Power: 120 hp
Maximum speed at the ground: 145 km / h
Cruising speed: 110 km / h
Flight duration: 3 hours and 30 minutes
Service ceiling: 4500 m
Crew: 2

Starboard sectional plane for clarity:

Eviscerated rotative motor star Le Rhône.
One of the most popular engines of those years, available in versions from semitsilindrovogo to chetyrhryadnogo 28-cylinder. Last terrible to me - is there any load on the crankshaft should be.
It is this - the early nine-9C circa 1916 vosmidesyatisilny.

Another celebrity of those years - Hispano-Suiza 8.
The most massive aircraft engine of the Entente in the First World War - made a total of a little less than fifty thousand copies by the twenty odogo companies in France, Spain, England, the USA and Italy.
The designer, of course, Marc Birkigt.
V8, overhead camshaft, 11.76 liter and from 140 to 235 hp (Later, in the version 8F - 18.47 liters and 300 hp)
This copy - model 8AB sample of 1917, 180 hp at 2100 rev / min.

Another training aircraft, being built in Finland, has a license - Czech Letov Š.218
In 1930-31 the Finns bought ten aircraft of Czech production - in the museum, as I understand it, is one of them, like, the only preserved at all - and then built their own 29 more pieces with a more powerful engine.
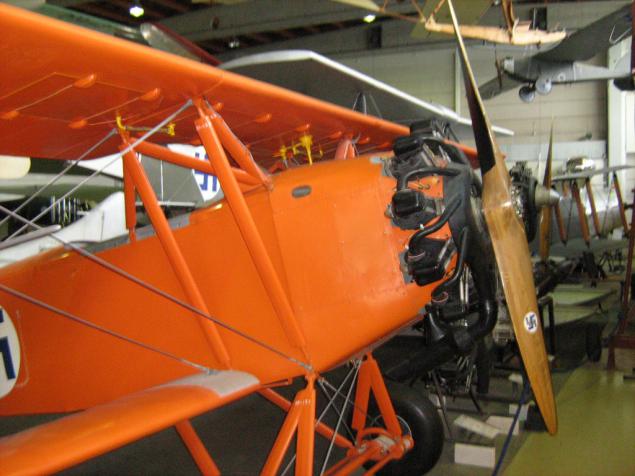

Letov S.218
Wingspan, m: 10.00
Aircraft length, m: 6.90
Wing area, m2: 16.30
Weight, kg
empty aircraft: 510
maximum take-off: 742
Engine: Walter Gemma NZ 120
Power hp: 120
The maximum speed, km / h: 150
Cruising speed, km / h: 120
Practical range, km: 375
Service ceiling, m 4000
Crew: 2
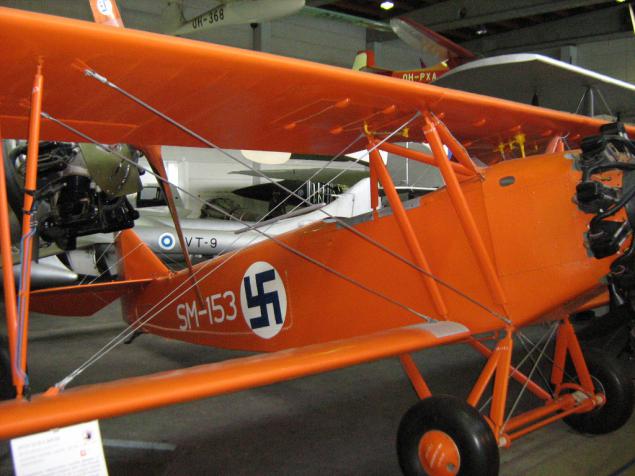

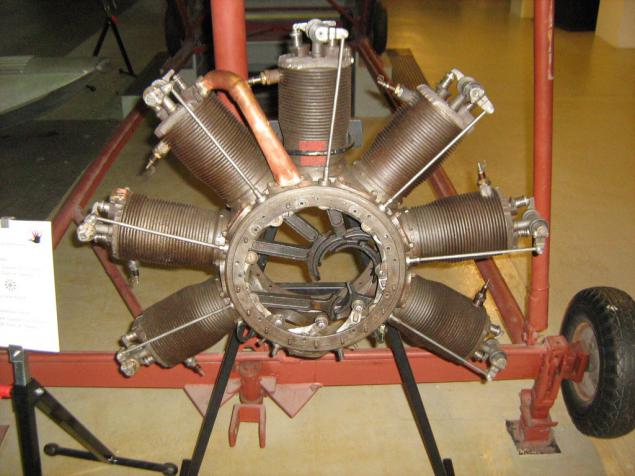
A separate exhibit of another engine Walter Gemma NZ120 - nine-"star" 120 hp, Czech Republic:
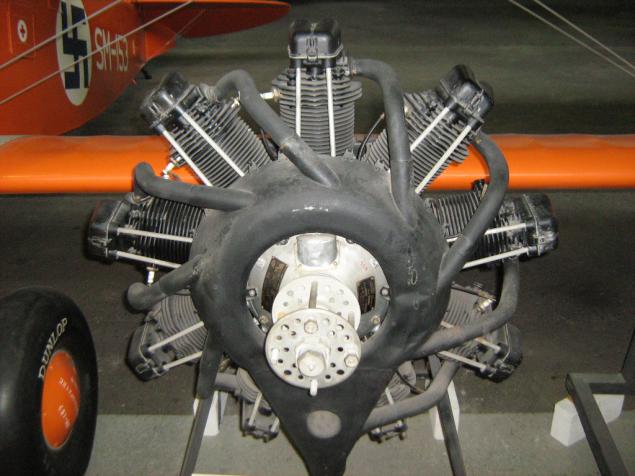

Another classic piece of iron - British air - and not only - engine Napier Lion.
W-shaped (three rows of four cylinders), 12-cylinder engine volume of 23.9 liters developed by Napier in 1918 and was produced in various versions until the mid-1930s. In addition to aviation, there was the ship's Sea Lion, also specially prepared engines used on several record-breaking cars.
This copy - Napier Lion IXa sample 1928 and a capacity of 580 hp (The first 1918 engines developed about 400 hp, and compressor record - up to 1350.)

More Lion full face. It is clearly seen three cylinder.
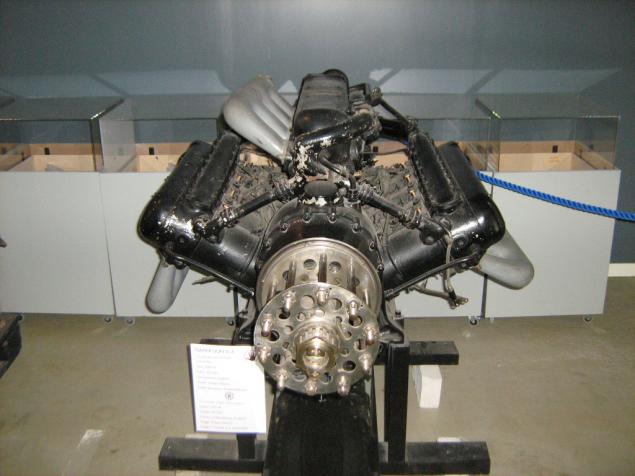

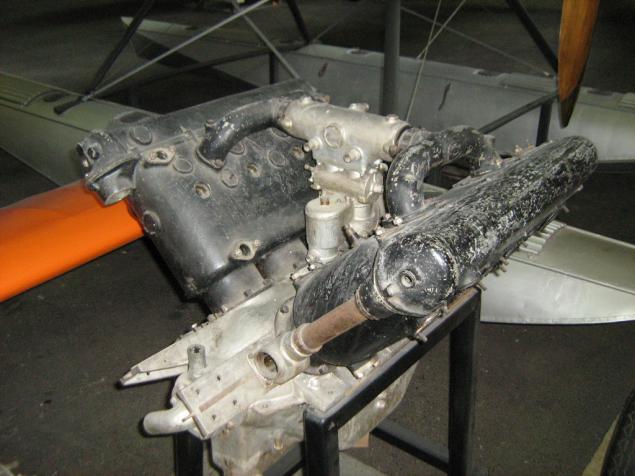
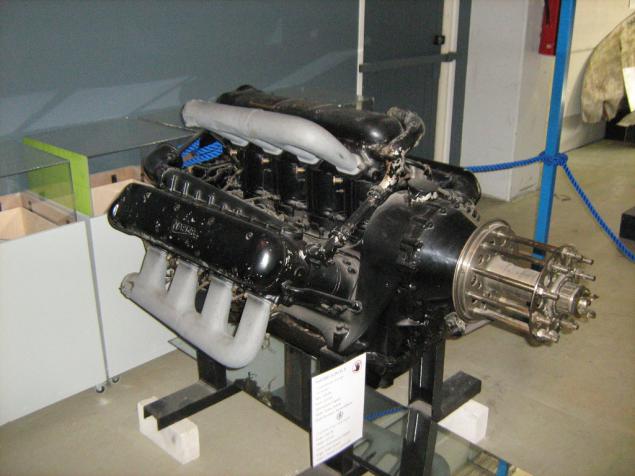
Soviet aircraft engine M-103 design VY Klimov, a modernized M-100.
V12, 36 liters, compressors, 850 hp on the rise.
This sample was mounted on a bomber SB-2 bis, downed the Finnish Air Force June 25, 1941 and raised from the bottom of the lake is not, is not the swamp in 1976.
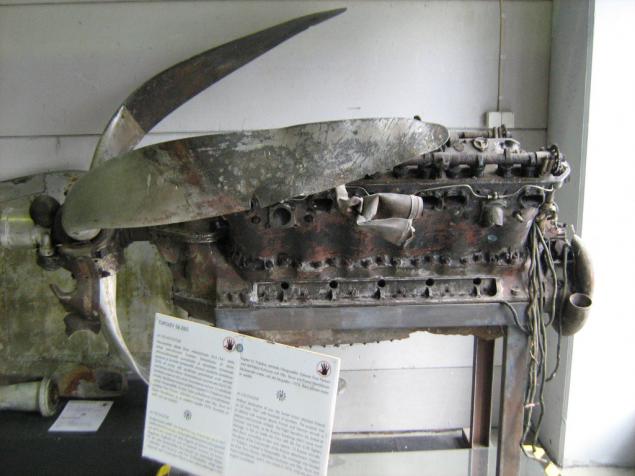
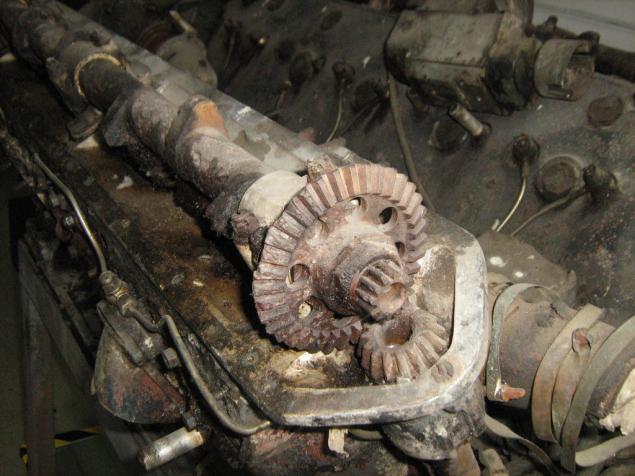
Timing M-103:

And here is another creation of the harsh Finnish genius - the already mentioned office Valtion Lentokonetehdas - VL Pyry - in our opinion, therefore, "snow". In this particular case - Pyry II.
The Finnish Air Force ordered a new training aircraft in 1937, the prototype Pyry I was ready in 1939, and forty-serial Pyry II built in 1941.
American engine, nine-«Star» Wright R-975-E3 Whirlwind 450 hp
The last two aircraft were in operation until 1962, one of them - PY-27 - and is in the museum.
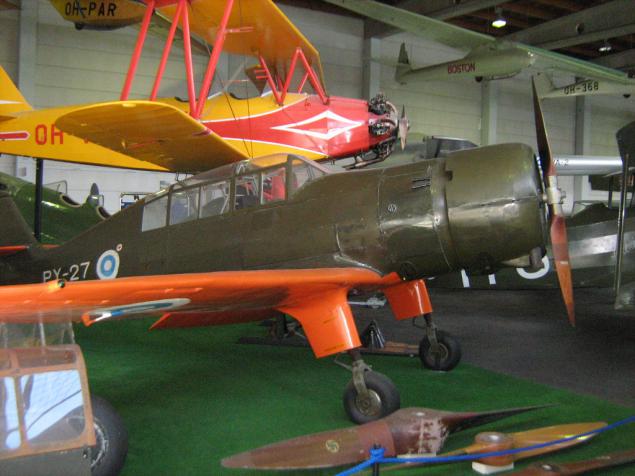

VL Pyry II
Wingspan, m: 9.80
Length, m: 7.70
Height, m: 2.55
Wing area, m2: 12.70
Weight, kg
empty aircraft: 1045
normal takeoff 1535
Engine: Wright R-975-E3 Whirlwind
Horsepower 450 hp .:
Maximum speed at the ground, km / h: 330
Cruising speed, km / h: 286
Practical range, km 1050
Rate of climb, m / min: 300
Service ceiling, m 5600
Crew: 2
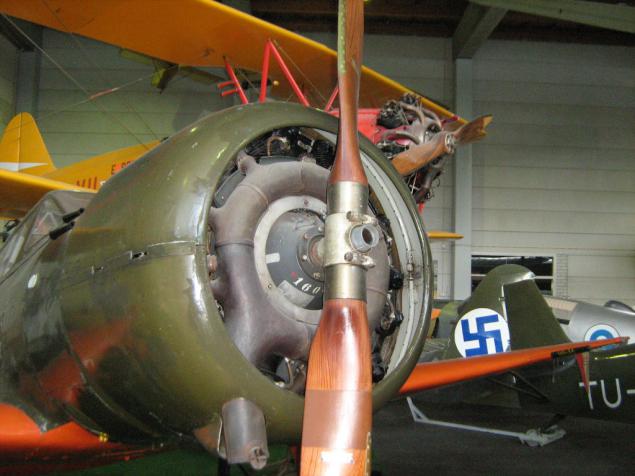

Soviet aircraft engine-survivor AI-62 (previously - M62) design AD Shvetsov. Creative rethinking of the American motor Wright Cyclone R-1820, bought with a license to manufacture the aircraft Douglas DC-3 (in the USSR - Li-2). Zvёzdoobrazny, 9-cylinder, 30 liter 840-1000 bhp and depending on the modification. Designed in 1938, produced somewhere before the end of the eighties - early nineties, it is still used on the aircraft AN-2. In wartime, it was used on the fighters I-153 and I-16.
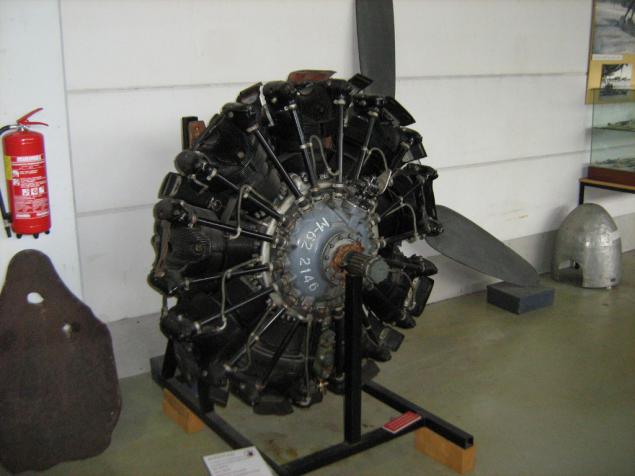

He fragment)

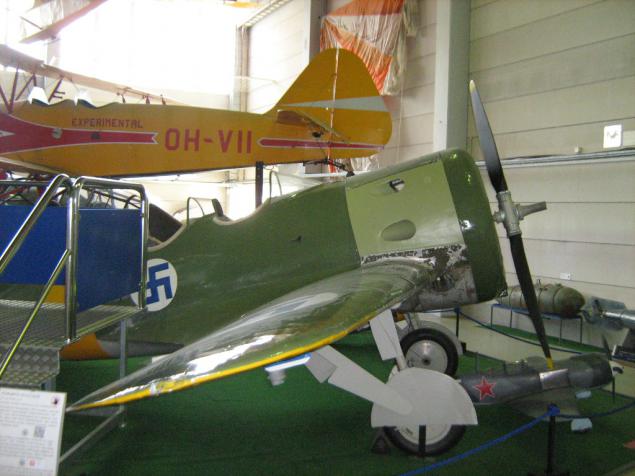
The only surviving copy of the Soviet training fighter UTI-4, part-time - the only surviving of several dozen Finns captured during the war, the Soviet aircraft.
Double training kind of famous I-16 fighter. In 1941-42 it was used by the Finnish Air Force for its intended purpose.

To the charge of UTI-4 ladder, you can look at the cockpit. I think I that never got to be.
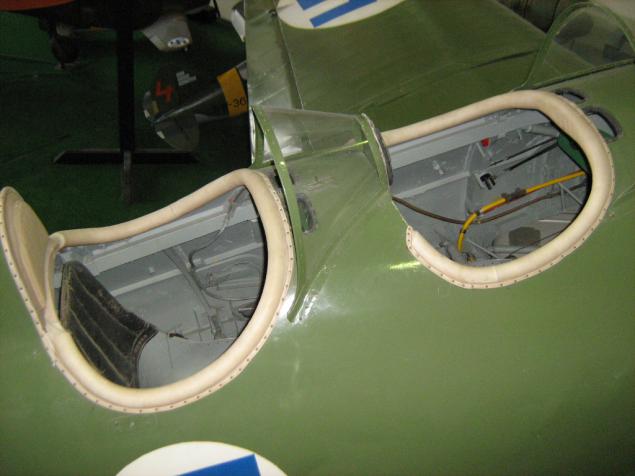

UTI-4
Wingspan, m: 9.00
Length, m: 5.99
Height, m: 3.25
Wing area, m2: 14.45
Weight, kg
empty aircraft 1156
maximum takeoff 1458
Engine: M-25A
Horsepower 730 hp .:
The maximum speed, km / h
at ground level: 398
at an altitude of 450
Practical range, km: 364
Service ceiling, m: 8960
Crew: 2

Exhibit number next - re-training. Now the post-war.
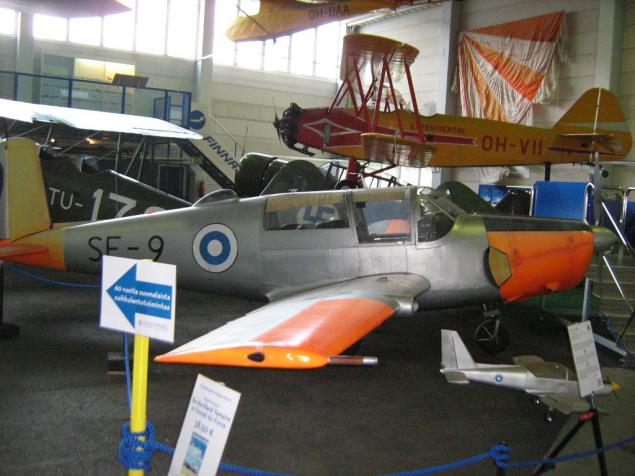
Swedish SAAB 91D Safir - «Sapphire" in our opinion. 91D - the last of the four major modifications.
The engine, again, American. 180-strong Opposite "quartet» Lycoming O-360.
Blue Circle has replaced the swastika as an emblem of the Finnish Air Force in 1944.

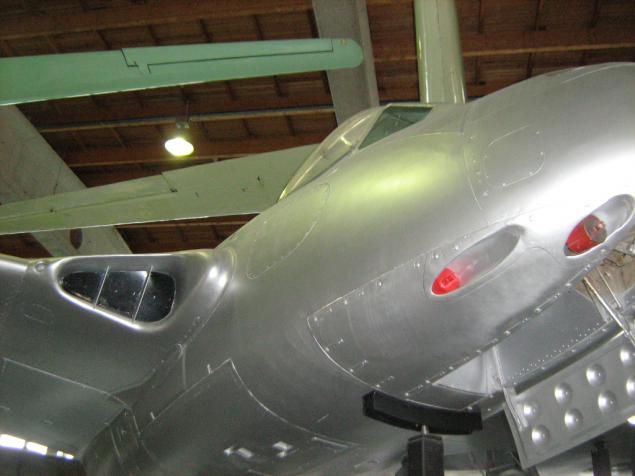
Then just two exhibits - relative. The family of vampires.
First in Finland and one of the world's first mass-produced jet fighters - the British De Havilland DH.100 'Vampire' FB.52 (export version of Vampire Mk.6) and his double training DH.115 option in the export version of the T.55 . Finland purchased DH.100 six in 1953 and nine more DH.115 in 1955, they operated until 1965.
Four 20-mm cannon Hispano and up to 900 kg bomb load. Usually - two bombs and 8 Nursi.

Vampire FB.Mk.5
Wingspan, m: 11.58
Length, m: 9.37
Height, m: 2.69
Wing area, m2: 24.34
Empty weight, kg: 3290
Maximum Takeoff Weight: 5606
Engine: de Havilland Goblin DGN.2 / 2
Link unforced kN: 16.46
Top speed km / h: 861
Service ceiling, m: 12190
Crew: 1
Armament:
Four 20-mm cannon Hispano Mk.5 with 150 rounds per gun in the front underside of the fuselage
The payload of 454 kg at two suspension (under the wings), a typical load - two 227 or 113 kg bombs or eight rockets 27 kg
Modification Vampire T.55
Wingspan, m: 11.58
Length, m: 10.55
Height, m: 1.90
Wing area, m2: 24.30
Weight, kg
empty aircraft: 3,350
maximum take-off: 5960
Engine: de Havilland Goblin 35
Link unforced, kgf 1590
Top speed km / h: 885
Practical range, km 1370
Service ceiling, m: 12200
Crew: 2

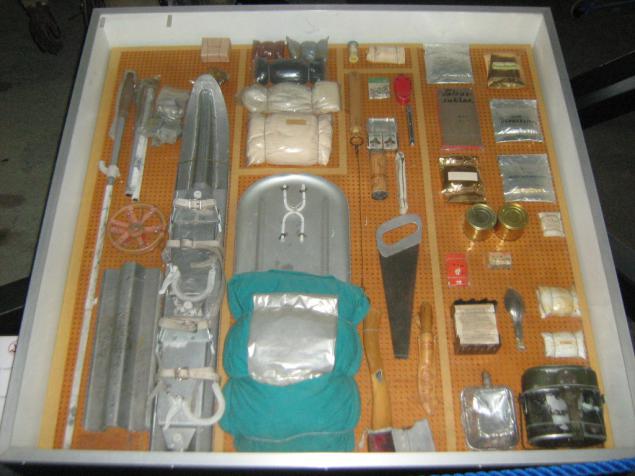
Content set vizhivaniya pilot Vampire:

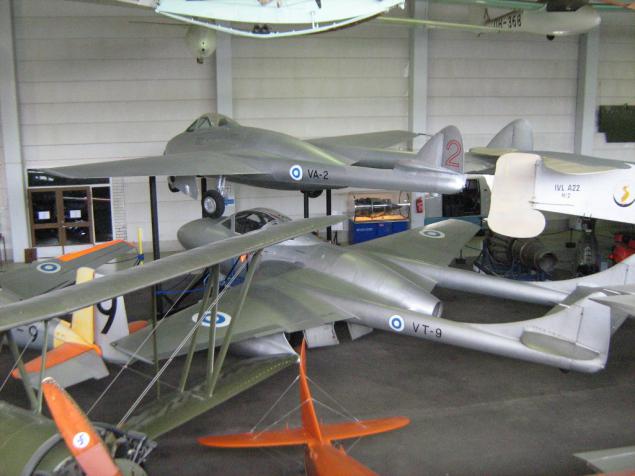
Further, the first-born of Finnish aviation industry, of course, a license.
Marine scout IVL A.22 Hansa, a copy of the German Hansa-Brandenburg W.33 sample 1916.
In the years 1922-25 the Finns built 120 of these aircraft have served until the mid-thirties.
The first room is the largest exhibit - a length of 11.1m, a wingspan of 15.85m - because the whole picture in general does not fit. Engine FIAT A.12bis 300 hp

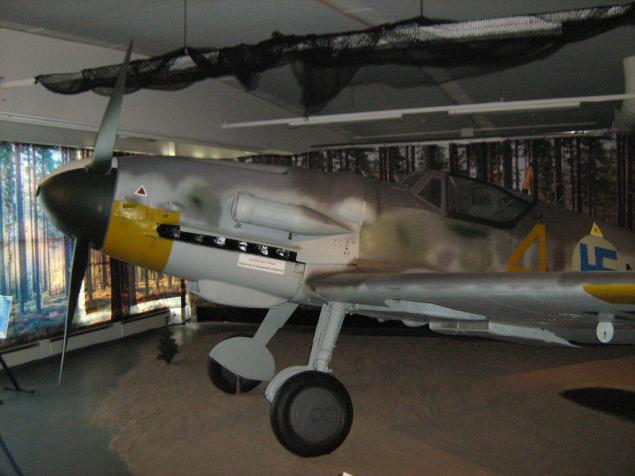
In a small and dark room between the rooms is here such Bf.109

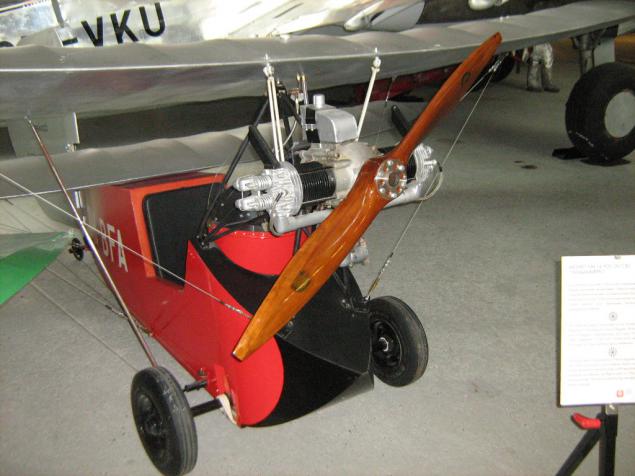
Flying Flea.
Small and lightweight single airplane extremely simple construction. Because of this, it could be built by anyone in the presence of a more or less straight arms, a garage and a minimum set of ninstrumentov ready drawings. For this purpose, and was designed by Frenchman Henri Mignet in 1931-33 years. Officially called Mignet HM.14 'Pou du Ciel'. The engine to be used any suitable available amateur aircraft builders. As a rule, used motorcycle engines air cooling moschnostb 15-25 hp, but also in England was popular motor car Austin 7. In the thirties all over the world have been built several thousand of these devices, including some pieces in Finland. This particular instance - a modern replica of the original drawings.
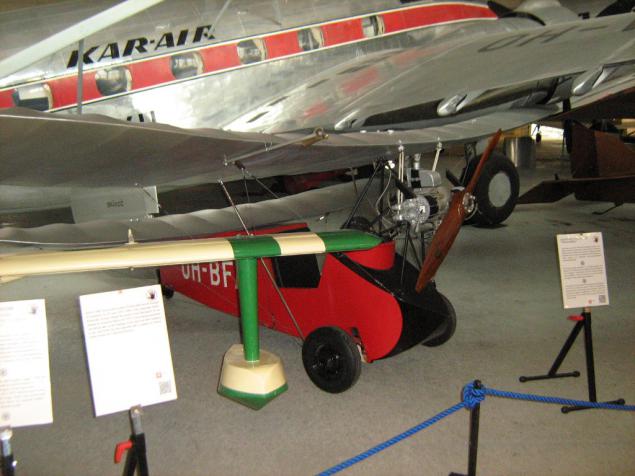

She:

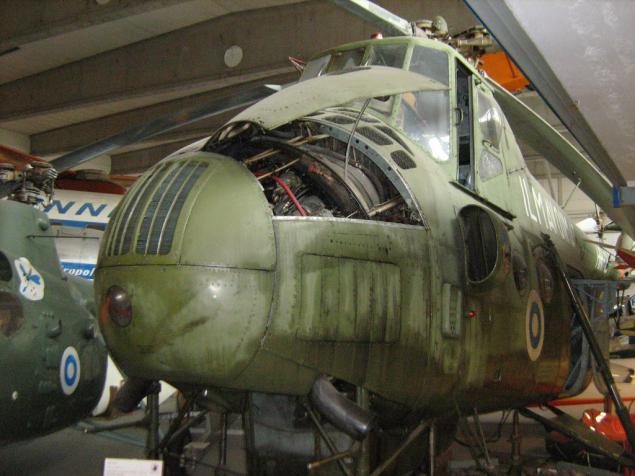
Neutral Soviet Mi-4:

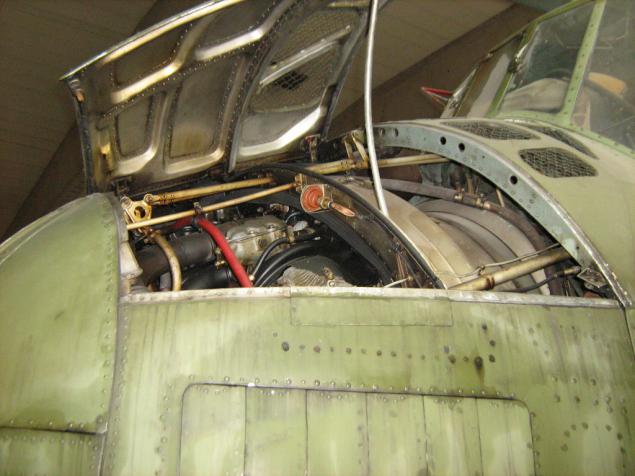
... And its engine. Well, a bit.

Polish helicopter PZL SM-1. A licensed copy of the Soviet Mi-1, produced in Poland since 1957. In Finland, it operated two copies.
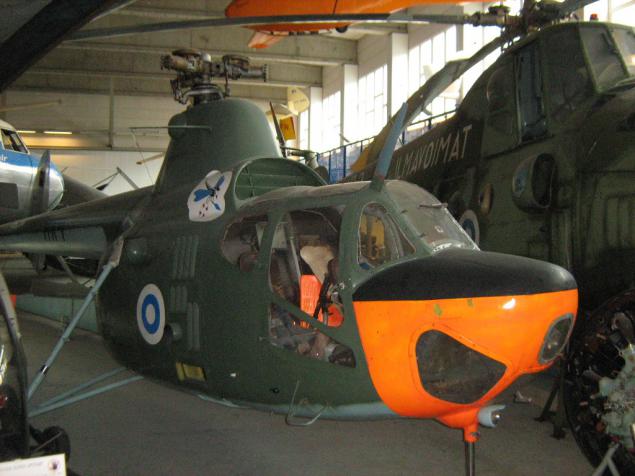

PZL SM-1
The diameter of the rotor, m: 14.35
Tail rotor diameter, m: 2.50
Length, m: 12.09
Height, m: 3.30
Weight, kg
empty 1796
normal take-off: 2230
maximum takeoff 2300
Engine: Progress AI-26B
Power hp: 580
The maximum speed, km / h: 175
Cruising speed, km / h: 130
Practical range, km: 380
Service ceiling, m 3500
Static ceiling, m 2700
Crew: 1
Payload: 2 passengers and / or 255 kg of cargo
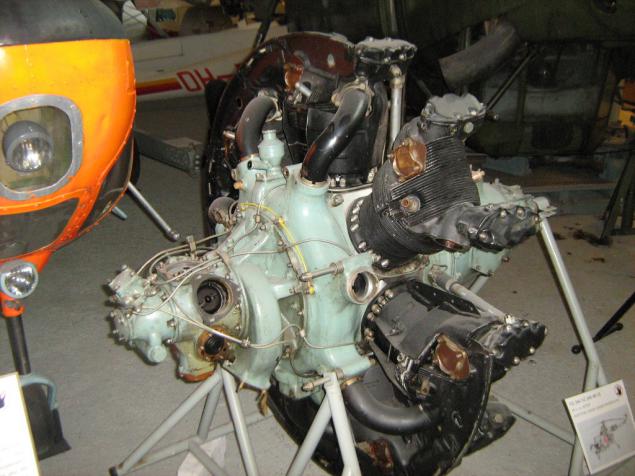

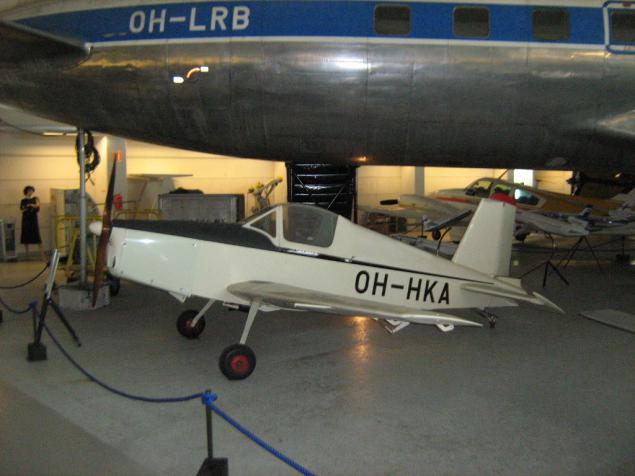
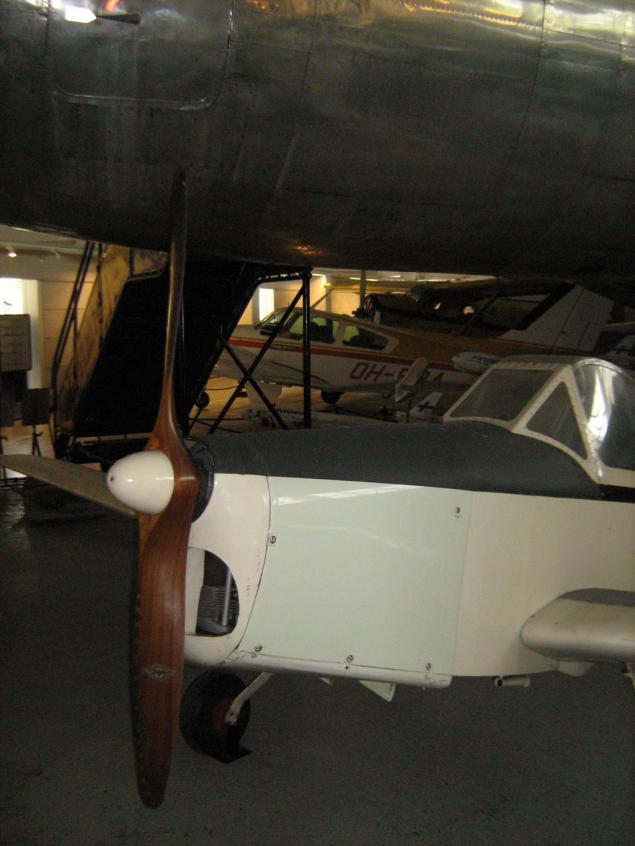
The only Finnish aircraft, which set a world record. Heinonen HK-1 'Keltiäinen' Juhani Heinonen. July 10, 1957 on it was committed nonstop flight from Madrid to Turku, 2844 km in 17 hours, 1 minute, which until 1974 was a world record for a single-engine aircraft weighing less than 500kg vzlёtnym.

Engine - survivor, produced so far in 1938 Czech Walter Mikron III. Inverted row "quartet", and 65 hp 2.4l
Excuse me, I will now pause for ten minutes.

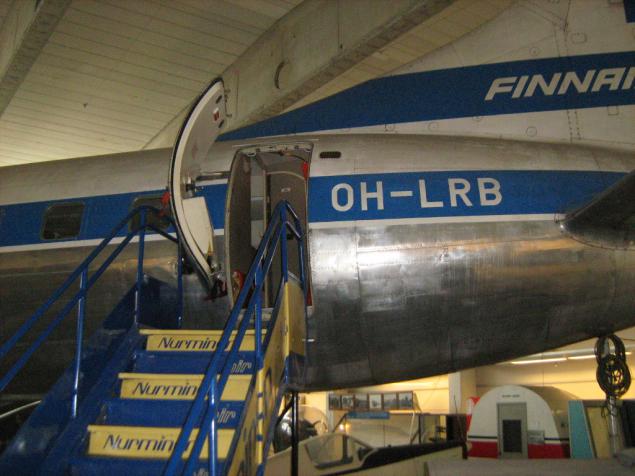
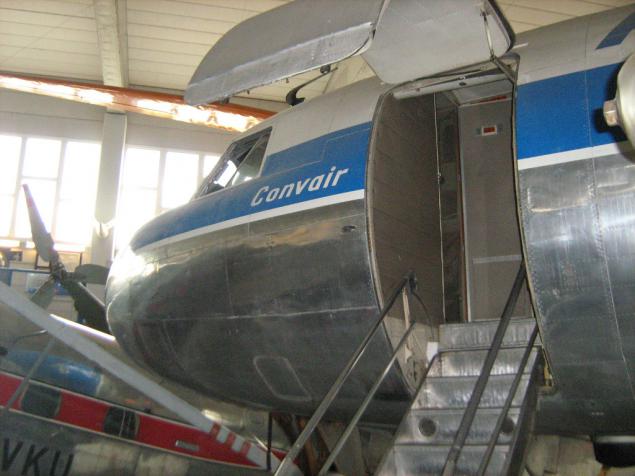
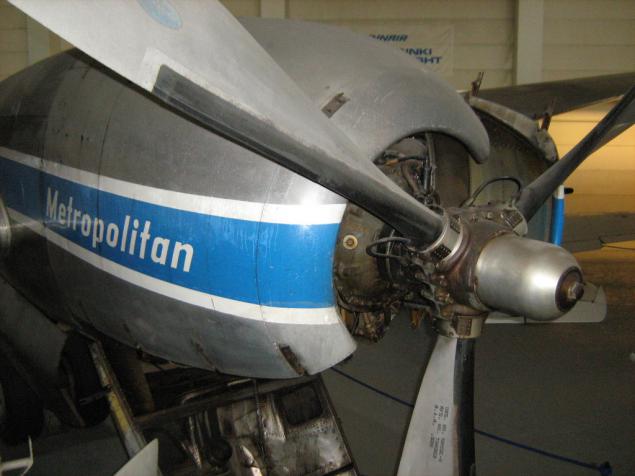
And this exhibit - the largest in the second hall. American Convair 340 Metropolitan. This particular instance - the plane with the greatest life in the Finnish Civil Aviation Authority. The first flight was made May 18, 1953, the last - April 30, 1980, after which he was sent to the museum.
It is not at all in a single frame does not fit:

But you can climb the stairs inside:

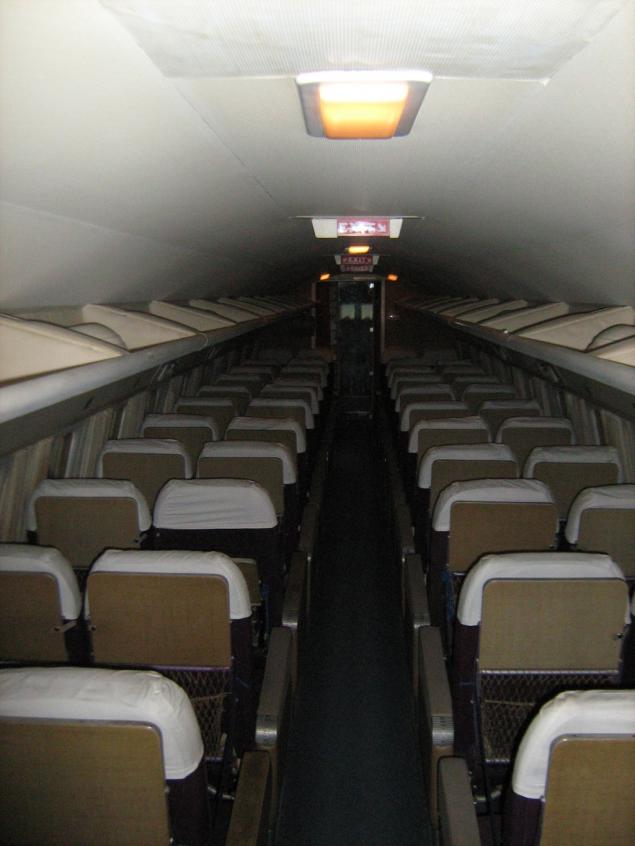
Forty-four seats, the ceiling even with me height:

The chair could barely fit:

In front of the salon here are chairs:

Convair CV-340
Wingspan, m: 32.12
Aircraft length, m: 24.13
Height, m: 8.58
Wing area, m2: 85.50
Weight, kg
empty aircraft: 13375
Maximum take-off: 21320
Engines: Pratt Whitney R2800CB16 Double Wasp
Power, HP .: 2 x 2400
The maximum speed, km / h: 521
Cruising speed, km / h: 457
Ferry range, km: 2940
Practical range, km: 935
Service ceiling, m: 7340
Crew: 2-3
Payload: 44 passengers or 6075 kg payload to

Well, here, from the far wall to frame it like this breaks:

A nacelle is open "to serve»:

Double Wasp close-up:
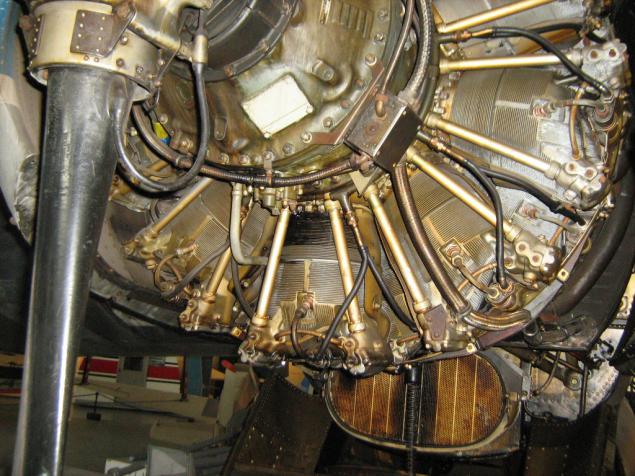

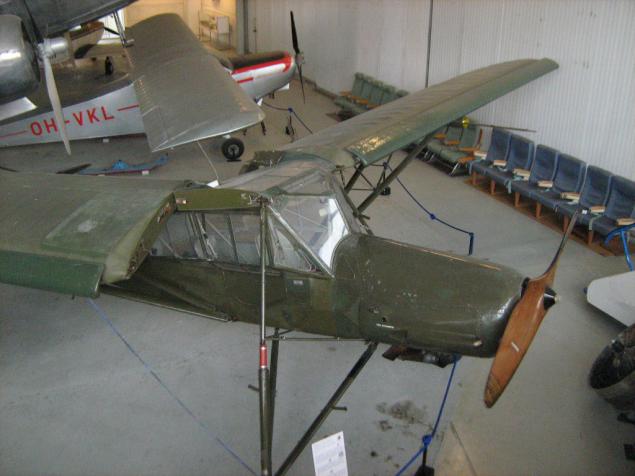
Fieseler Fi 156 Storch, in our Stork.
German light aircraft, in wartime to use. as a reconnaissance, communication and health.
It features extremely low running start - enough to take off the band no longer than 60m.
Designed in 1936, produced in Germany until 1949, and in France until 1965.
In 1940, the Soviet Union planned to start producing copies Shtorha. Under the direction of DC Antonova, then leading engineer Yakovlev Design Bureau and at the direct orders of IV Stalin was built several prototypes OKA-38 "Stork", differed from the prototype primarily Soviet engine CF-6 instead of the German "Argus", but June 22, 1941 all the prototypes were destroyed along with the factory, and the work on the aircraft were not resumed.
Visible folding back for storage and transportation of wings:

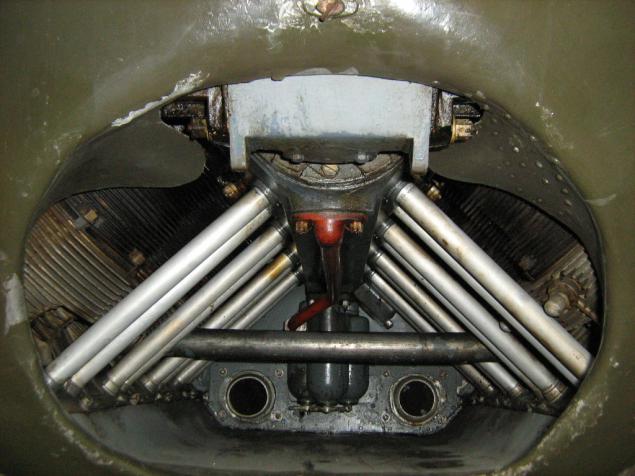
240-hp Argus AS 10C - inverted air-cooled V8.

In general, a meaningful selection this can be considered complete, for other photos or awkwardness or haphazard and fragmented. So I, of course, povykladyvayu something else, but if you suddenly want to discuss-- it is already possible)))
And yet the angle pairs Vampire:

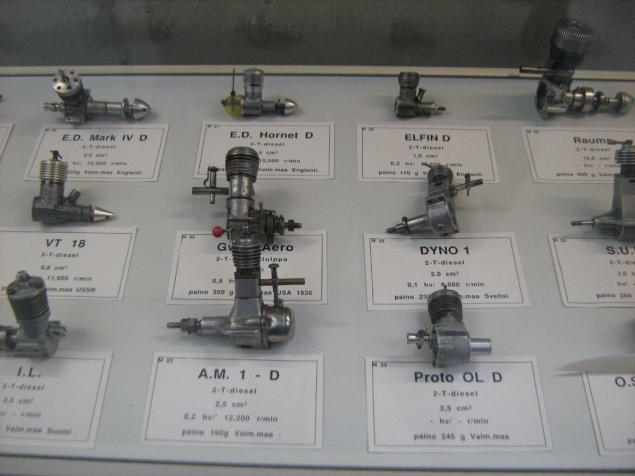
An entire collection of a motor model aircraft. They were there for a few of these windows:
Source:
Well, once I stopped, which would not take pictures even though on a bar of soap. And just took off something, so it is possible to share. For quality images please do not kick, I'll know everything. The museum is quite cramped and not very light, exhibits tightly obstruct each other. Because as I could and could)
Photos will be about 70 pieces

At the entrance to the first room - one of the first-born of Finnish aviation industry - license Frenchman Caudron C.60 local buildings. The development of a successful C.59, the classic single-engine biplane with fabric covering, for its intended purpose - trainer. Thirty cars were built in France at the request of the Finnish Air Force, 34 more are made under license in Finland itself in 1927-28.

Caudron C.60, France / Finland.
Crew: 2
Length: 7.50m
Wingspan: 10.24m
Wing area: 26.00m²
Empty weight: 505kg
Takeoff weight: 862 kg

Clerget 9B engine of French origin, produced in France and in England. The star, rotative, nine-, 16.3 liters, 130 hp
In this instance the engine partly in section for clarity:

More engine:

And further. Actually, I aircraft engines even more interesting than the actual aircraft, because they will be more than one or two. By the way, the engine is interesting because it is rotative. Quite popular in the early twentieth century, the system - the crankshaft rigidly fastened on the plane, and the entire engine revolves around him.
Do not hold back, moved - naturally rotates)

V.L. (Valtion Lentokonetehdas) Sääski II.
«Sääski» in Russian something like midges or gnats like. Popravte if anyone knows.
The first production aircraft of the Finnish private development, a training on the main destination. In 1928 - 32 years made about fifty planes of three series of the second float chassis. Patrol option for the Coast Guard. In principle, the same does not particularly remarkable classic nine-engine biplane with Siemens-Halske Sh 12 110 forces.

VL Saaski IIA
Wingspan: 9.90 m
Length: 7.40 m
Height: 2.40 m
Wing area: 24.00 m²
Empty weight: 609 kg
Takeoff: 913 kg
Engine: Siemens-Halsken Sh 12
Power: 120 hp
Maximum speed at the ground: 145 km / h
Cruising speed: 110 km / h
Flight duration: 3 hours and 30 minutes
Service ceiling: 4500 m
Crew: 2

Starboard sectional plane for clarity:

Eviscerated rotative motor star Le Rhône.
One of the most popular engines of those years, available in versions from semitsilindrovogo to chetyrhryadnogo 28-cylinder. Last terrible to me - is there any load on the crankshaft should be.
It is this - the early nine-9C circa 1916 vosmidesyatisilny.

Another celebrity of those years - Hispano-Suiza 8.
The most massive aircraft engine of the Entente in the First World War - made a total of a little less than fifty thousand copies by the twenty odogo companies in France, Spain, England, the USA and Italy.
The designer, of course, Marc Birkigt.
V8, overhead camshaft, 11.76 liter and from 140 to 235 hp (Later, in the version 8F - 18.47 liters and 300 hp)
This copy - model 8AB sample of 1917, 180 hp at 2100 rev / min.

Another training aircraft, being built in Finland, has a license - Czech Letov Š.218
In 1930-31 the Finns bought ten aircraft of Czech production - in the museum, as I understand it, is one of them, like, the only preserved at all - and then built their own 29 more pieces with a more powerful engine.

Letov S.218
Wingspan, m: 10.00
Aircraft length, m: 6.90
Wing area, m2: 16.30
Weight, kg
empty aircraft: 510
maximum take-off: 742
Engine: Walter Gemma NZ 120
Power hp: 120
The maximum speed, km / h: 150
Cruising speed, km / h: 120
Practical range, km: 375
Service ceiling, m 4000
Crew: 2

A separate exhibit of another engine Walter Gemma NZ120 - nine-"star" 120 hp, Czech Republic:

Another classic piece of iron - British air - and not only - engine Napier Lion.
W-shaped (three rows of four cylinders), 12-cylinder engine volume of 23.9 liters developed by Napier in 1918 and was produced in various versions until the mid-1930s. In addition to aviation, there was the ship's Sea Lion, also specially prepared engines used on several record-breaking cars.
This copy - Napier Lion IXa sample 1928 and a capacity of 580 hp (The first 1918 engines developed about 400 hp, and compressor record - up to 1350.)

More Lion full face. It is clearly seen three cylinder.

Soviet aircraft engine M-103 design VY Klimov, a modernized M-100.
V12, 36 liters, compressors, 850 hp on the rise.
This sample was mounted on a bomber SB-2 bis, downed the Finnish Air Force June 25, 1941 and raised from the bottom of the lake is not, is not the swamp in 1976.

Timing M-103:

And here is another creation of the harsh Finnish genius - the already mentioned office Valtion Lentokonetehdas - VL Pyry - in our opinion, therefore, "snow". In this particular case - Pyry II.
The Finnish Air Force ordered a new training aircraft in 1937, the prototype Pyry I was ready in 1939, and forty-serial Pyry II built in 1941.
American engine, nine-«Star» Wright R-975-E3 Whirlwind 450 hp
The last two aircraft were in operation until 1962, one of them - PY-27 - and is in the museum.

VL Pyry II
Wingspan, m: 9.80
Length, m: 7.70
Height, m: 2.55
Wing area, m2: 12.70
Weight, kg
empty aircraft: 1045
normal takeoff 1535
Engine: Wright R-975-E3 Whirlwind
Horsepower 450 hp .:
Maximum speed at the ground, km / h: 330
Cruising speed, km / h: 286
Practical range, km 1050
Rate of climb, m / min: 300
Service ceiling, m 5600
Crew: 2

Soviet aircraft engine-survivor AI-62 (previously - M62) design AD Shvetsov. Creative rethinking of the American motor Wright Cyclone R-1820, bought with a license to manufacture the aircraft Douglas DC-3 (in the USSR - Li-2). Zvёzdoobrazny, 9-cylinder, 30 liter 840-1000 bhp and depending on the modification. Designed in 1938, produced somewhere before the end of the eighties - early nineties, it is still used on the aircraft AN-2. In wartime, it was used on the fighters I-153 and I-16.

He fragment)

The only surviving copy of the Soviet training fighter UTI-4, part-time - the only surviving of several dozen Finns captured during the war, the Soviet aircraft.
Double training kind of famous I-16 fighter. In 1941-42 it was used by the Finnish Air Force for its intended purpose.

To the charge of UTI-4 ladder, you can look at the cockpit. I think I that never got to be.

UTI-4
Wingspan, m: 9.00
Length, m: 5.99
Height, m: 3.25
Wing area, m2: 14.45
Weight, kg
empty aircraft 1156
maximum takeoff 1458
Engine: M-25A
Horsepower 730 hp .:
The maximum speed, km / h
at ground level: 398
at an altitude of 450
Practical range, km: 364
Service ceiling, m: 8960
Crew: 2

Exhibit number next - re-training. Now the post-war.
Swedish SAAB 91D Safir - «Sapphire" in our opinion. 91D - the last of the four major modifications.
The engine, again, American. 180-strong Opposite "quartet» Lycoming O-360.
Blue Circle has replaced the swastika as an emblem of the Finnish Air Force in 1944.

Then just two exhibits - relative. The family of vampires.
First in Finland and one of the world's first mass-produced jet fighters - the British De Havilland DH.100 'Vampire' FB.52 (export version of Vampire Mk.6) and his double training DH.115 option in the export version of the T.55 . Finland purchased DH.100 six in 1953 and nine more DH.115 in 1955, they operated until 1965.
Four 20-mm cannon Hispano and up to 900 kg bomb load. Usually - two bombs and 8 Nursi.

Vampire FB.Mk.5
Wingspan, m: 11.58
Length, m: 9.37
Height, m: 2.69
Wing area, m2: 24.34
Empty weight, kg: 3290
Maximum Takeoff Weight: 5606
Engine: de Havilland Goblin DGN.2 / 2
Link unforced kN: 16.46
Top speed km / h: 861
Service ceiling, m: 12190
Crew: 1
Armament:
Four 20-mm cannon Hispano Mk.5 with 150 rounds per gun in the front underside of the fuselage
The payload of 454 kg at two suspension (under the wings), a typical load - two 227 or 113 kg bombs or eight rockets 27 kg
Modification Vampire T.55
Wingspan, m: 11.58
Length, m: 10.55
Height, m: 1.90
Wing area, m2: 24.30
Weight, kg
empty aircraft: 3,350
maximum take-off: 5960
Engine: de Havilland Goblin 35
Link unforced, kgf 1590
Top speed km / h: 885
Practical range, km 1370
Service ceiling, m: 12200
Crew: 2

Content set vizhivaniya pilot Vampire:

Further, the first-born of Finnish aviation industry, of course, a license.
Marine scout IVL A.22 Hansa, a copy of the German Hansa-Brandenburg W.33 sample 1916.
In the years 1922-25 the Finns built 120 of these aircraft have served until the mid-thirties.
The first room is the largest exhibit - a length of 11.1m, a wingspan of 15.85m - because the whole picture in general does not fit. Engine FIAT A.12bis 300 hp

In a small and dark room between the rooms is here such Bf.109

Flying Flea.
Small and lightweight single airplane extremely simple construction. Because of this, it could be built by anyone in the presence of a more or less straight arms, a garage and a minimum set of ninstrumentov ready drawings. For this purpose, and was designed by Frenchman Henri Mignet in 1931-33 years. Officially called Mignet HM.14 'Pou du Ciel'. The engine to be used any suitable available amateur aircraft builders. As a rule, used motorcycle engines air cooling moschnostb 15-25 hp, but also in England was popular motor car Austin 7. In the thirties all over the world have been built several thousand of these devices, including some pieces in Finland. This particular instance - a modern replica of the original drawings.

She:

Neutral Soviet Mi-4:

... And its engine. Well, a bit.

Polish helicopter PZL SM-1. A licensed copy of the Soviet Mi-1, produced in Poland since 1957. In Finland, it operated two copies.

PZL SM-1
The diameter of the rotor, m: 14.35
Tail rotor diameter, m: 2.50
Length, m: 12.09
Height, m: 3.30
Weight, kg
empty 1796
normal take-off: 2230
maximum takeoff 2300
Engine: Progress AI-26B
Power hp: 580
The maximum speed, km / h: 175
Cruising speed, km / h: 130
Practical range, km: 380
Service ceiling, m 3500
Static ceiling, m 2700
Crew: 1
Payload: 2 passengers and / or 255 kg of cargo

The only Finnish aircraft, which set a world record. Heinonen HK-1 'Keltiäinen' Juhani Heinonen. July 10, 1957 on it was committed nonstop flight from Madrid to Turku, 2844 km in 17 hours, 1 minute, which until 1974 was a world record for a single-engine aircraft weighing less than 500kg vzlёtnym.

Engine - survivor, produced so far in 1938 Czech Walter Mikron III. Inverted row "quartet", and 65 hp 2.4l
Excuse me, I will now pause for ten minutes.

And this exhibit - the largest in the second hall. American Convair 340 Metropolitan. This particular instance - the plane with the greatest life in the Finnish Civil Aviation Authority. The first flight was made May 18, 1953, the last - April 30, 1980, after which he was sent to the museum.
It is not at all in a single frame does not fit:

But you can climb the stairs inside:

Forty-four seats, the ceiling even with me height:

The chair could barely fit:

In front of the salon here are chairs:

Convair CV-340
Wingspan, m: 32.12
Aircraft length, m: 24.13
Height, m: 8.58
Wing area, m2: 85.50
Weight, kg
empty aircraft: 13375
Maximum take-off: 21320
Engines: Pratt Whitney R2800CB16 Double Wasp
Power, HP .: 2 x 2400
The maximum speed, km / h: 521
Cruising speed, km / h: 457
Ferry range, km: 2940
Practical range, km: 935
Service ceiling, m: 7340
Crew: 2-3
Payload: 44 passengers or 6075 kg payload to

Well, here, from the far wall to frame it like this breaks:

A nacelle is open "to serve»:

Double Wasp close-up:

Fieseler Fi 156 Storch, in our Stork.
German light aircraft, in wartime to use. as a reconnaissance, communication and health.
It features extremely low running start - enough to take off the band no longer than 60m.
Designed in 1936, produced in Germany until 1949, and in France until 1965.
In 1940, the Soviet Union planned to start producing copies Shtorha. Under the direction of DC Antonova, then leading engineer Yakovlev Design Bureau and at the direct orders of IV Stalin was built several prototypes OKA-38 "Stork", differed from the prototype primarily Soviet engine CF-6 instead of the German "Argus", but June 22, 1941 all the prototypes were destroyed along with the factory, and the work on the aircraft were not resumed.
Visible folding back for storage and transportation of wings:

240-hp Argus AS 10C - inverted air-cooled V8.

In general, a meaningful selection this can be considered complete, for other photos or awkwardness or haphazard and fragmented. So I, of course, povykladyvayu something else, but if you suddenly want to discuss-- it is already possible)))
And yet the angle pairs Vampire:

An entire collection of a motor model aircraft. They were there for a few of these windows:

Source: